The system bus PC transmits music in the middle frequencies
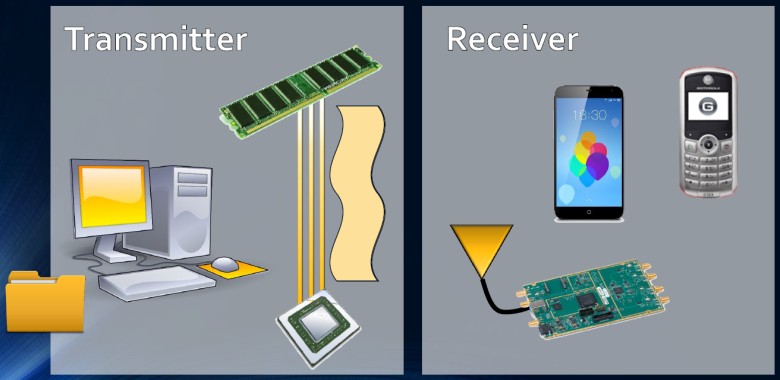
A bus between the processor and the memory is used as the antenna of the radio transmitter.
In information security, there is the concept of "physical isolation" (air gap), when a secure computer network is physically isolated from unsafe networks: the Internet and local networks with a low level of security. These are military systems, command centers, NPP control systems, medical equipment, and so on.
But if someone infected a physically isolated computer, and then he badly needed to remove the information - what to do? Here we have to invent various clever and non-standard ways. For example, to turn an ordinary PC into a radio signal generator - and catch this signal with a radio receiver. This is the task that the System Bus Radio utility performs, which was once mentioned on the GT. Although to be honest, hardly anyone will use it for espionage - this is just a curious program for entertainment. It uses the system bus of a PC or laptop as a radio transmitter to broadcast any sounds at a set radio frequency.
')
During the time that has passed since the beginning of development, users have collected extensive statistics on which model radio and at what frequency the signal is caught. In addition, an online modulator was created where you can compose music without leaving the browser - and generate a radio signal at a frequency of 1560 Hz with the press of a single Play Tune button.

Online modulator format :
400 2673
400 2349
400 2093
400 2349
400 2673
400 0
400 2673
400 0
790 2673
400 2349
400 2349
400 0
790 2349
400 2673
400 3136
400 0Here, the first digit indicates the time the note is sounding in milliseconds, and the second digit indicates the frequency of that note in hertz.
In Chrome, there may be errors when opening a file locally (
file:// ), so it is recommended to use a command like php -S localhost:8000 for a fast web server.The program generates radiation using the
_mm_stream_si128 instruction, the result of which is written to a specific address in the RAM (you can use x++ instead of _mm_stream_si128 ). This concept, called GSMem, was presented in a report by experts from Ben-Gurion University (Israel) at the USENIX Security 15 conference (see pages 849-864 in the conference report collection or in a separate pdf ). In their report, the authors mention other works in the related field, when information from a physically isolated computer is transmitted in non-standard ways:- on FM radio frequencies by registering radiation from a monitor cable ( AirHopper ), frequency 78-108 MHz, distance 7 meters, speed 104-480 bps
- via audio speakers ( Ultrasonic ), 19.7 m, 20 bps
- by reading CPU radiation with special sensors ( SAVAT ), 80 kHz, distance 1 m
- by reading the heat dissipation of the CPU / GPU heat sensors ( BitWhisper ), 0.4 m, 8 bits / hour
The scientific work provides such an algorithm for modulating an audio signal with digital information:
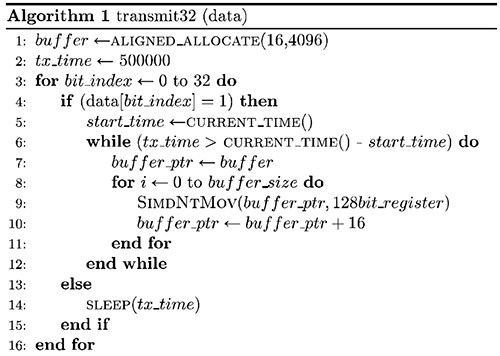
Sending one bit of information is a variant of B-ASK (Binary amplitude shift keying) binary amplitude modulation. In this case, for the transmission of “0” we do nothing for T seconds, and for the transmission of “1” we increase the amplitude of the signal by T seconds. Framing is used to determine if the receiver is transmitting and synchronizing, where every 12 bits of useful information is preceded by the standard 1010 sequence.
From the point of view of information security, this method is convenient for an attacker, because the generator program takes only 4 kilobytes in memory, does not use any APIs, and does not require root rights on the victim’s computer to work. At the same time, it will work fine on machines with any processors (Intel, AMD ...) and under any operating system (Windows, Linux, macOS and others).
Here is an algorithm for receiving (decoding) a signal from a physically isolated computer:

Theoretically, even a mobile phone can act as a receiver, since many modern phones have antennas for receiving radio signals at mid frequencies with AM modulation. You only need to modify the firmware of the baseband chip in the phone. There is the OsmocomBB project, where hundreds of enthusiasts have for several years been working on modifying GSM phone firmware. This project was described in detail in Habré ( introduction , hardware , software ).
Experiments have shown that a good receiver Sony STR-K670P with a drain antenna receives the signal at a distance of up to 2 meters (1 meter through the wall).
Signal generation has already been tested on MacBook Air laptops, HP ENVY 15-j142na, Asus X201E, Mac mini, MacBookPro Retina, Lenovo X1 Carbon, Dell Inspiron 17 7000, Acer Aspire E1-572-6 BR691, on a desktop computer with Athlon II X2 240 and Gigabyte GA-MA785GM-US2H motherboard. Signal found in all cases. But the Raspberry Pi does not seem to generate waves of sufficient amplitude to be caught. In general, the amount of interference and the maximum distance to the transmitter seem to depend on the computer model. Some generate a more powerful signal, while others are weaker or do not generate at all. Although the quality of the reception depends on many other factors that have not yet been formalized.

The authors of the research using a high-quality antenna and software-defined radio system (SDR) registered a steady reception from a distance of 30-40 meters.
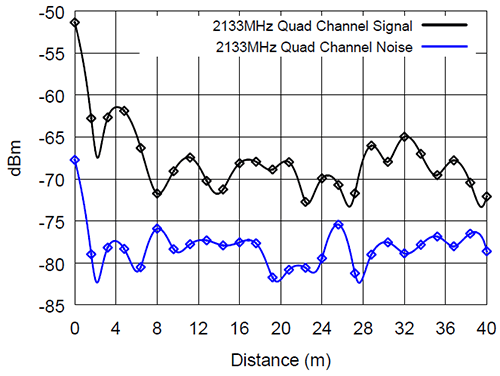
In their opinion, the maximum distance is even greater. That is, such a system can receive a signal from the street that radiates a physically isolated computer inside a building.
Radio signal modulation from the system bus can be used not only for espionage. For example, one craftsman in this way debugged his Apple Newton computer , which did not want to turn on, but there it was possible to fill in a new firmware. Actually, the hacker did just that: he uploaded a new firmware with small cycles that performed different tasks on the bus and sounded differently on AM waves, while being associated with different boot paths. After an hour of listening to the radio, he still determined where the problem was.
PROMOTION GLOBALSIGN: Wildcard SSL + 1 YEAR AS A GIFT
Protect all subdomains with one certificate!
Save up to 30 thousand rubles when you buy Wildcard SSL certificate for 2 years!
Promotional Code: WC001HRFR
The promotion is valid for subscribers of the blog GlobalSign until June 15, 2018.
For more information, please contact GlobalSign managers by phone: +7 (499) 678 2210 or by filling out a form on the website indicating the promotional code.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/348416/
All Articles