Nemesida WAF: intellectual protection against brute-force attacks

The classic brute-force protection tools are utilities of the fail2ban type, which work on the principle: many requests - one source. This may not always help block the offender, and may also lead to false (positive-positive blocking). In this article I will write about the pros and cons of classic remedies and the possibilities of intellectual blocking attacks.
Brute-force
The “brute-force” attack is based on the mathematical method of the same name (“brute force”), in which the correct solution — a finite number or symbolic combination — is found by iterating through various options. In fact, each value from a given set of potential answers (solutions) is checked for correctness.
A “brute-force” attack or a “dictionary search” attack is a type of attack on a web application in which an attacker searches through account values, passwords, session data, etc. trying to access a web application or data.
')
The main disadvantages of classic remedies
I do not in any way want to play down fail2ban, but in my opinion such solutions have a number of significant drawbacks.
1. One source of attack - many requests. Such a policy will prevent the "attack in the forehead", but at the same time, it will allow distributed brute-force from multiple IP addresses (for example, using proxy lists). Also, such a policy can block an unnecessarily "zealous" search bot, etc.
2. The context of the request is not taken into account: the usual protection systems do not take into account the request direction - multiple requests GET requests / somefile, POST requests to the authorization form, or parsing the product catalog - blocking will occur when the set requests are exceeded for a period of time from one source, more likely to result in false-positive locks.
Intelligent Attack Detection
In order to minimize the number of false positives and identify real brute-force attacks, two mechanisms were implemented: the first allows detecting the web application's input fields to identify exact areas subject to brute-force attacks (this allows you to more accurately configure the protection of the web application) . The second module reveals the similarity of requests sent to the web application.
For example, a brute-force attack using the burp suite with the dictionary 10k_most_common.txt (10.000 most popular passwords) will show 88% query similarity and will be blocked:
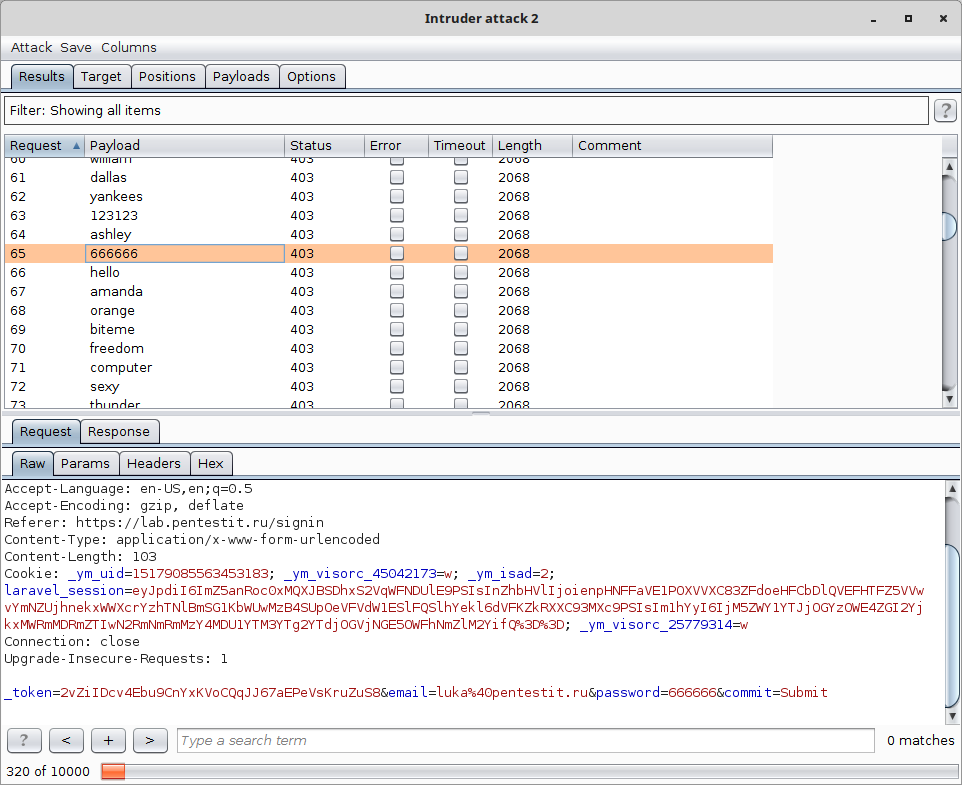
The approach to detecting brute-force attacks is based on calculating the mutual distance between requests received by the web application (via Nemesida WAF), and also takes into account sources and zones. The Levenshtein distance was chosen as the metric for calculating the proximity measure. Adjust the observation interval, the minimum required number of requests and the threshold value of the measure of proximity of these requests.

The Levenshtein distance (also the editorial distance or editing distance) between two lines in information theory and computational linguistics is the minimum number of operations to insert one character, delete one character, and replace one character with another, necessary to turn one line into another.
The consolidation of the classical principles of blocking using the principles of intelligent detection of attacks will make it possible to protect the web application from attacks using automated systems (as the most effective in brute-force attacks). Protection from "manual" brute force, which is subject to a large proportion of entropy such means can not be provided, in this case, you need to configure the web application, given the number of incorrectly entered passwords for a reasonable time unit.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/348402/
All Articles