Work with problem * .dwg-files in the environment of nanoCAD

Format * .dwg - the most popular format for storing electronic drawings. Often, * .dwg-files are stored for years, stored in different systems, used by different users, and because of this can accumulate various errors. To protect yourself and your documents, before starting work with files in nanoCAD, it is recommended to perform a series of actions for checking, cleaning and optimizing them. Below we will look at the main tools and methods for working with * .dwg files.
How to find out the version of * .dwg-file?
Open the * .dwg file through a text editor - for example, Notepad . The first characters will point to the version, the rest of the file will be displayed in encrypted form.
It may take extra time to open large files in Notepad.

')
You can find out the version of dwg in which the file is saved from the list:
AC1015 - dwg 2000
AC1018 - dwg 2004
AC1021 - dwg 2007
AC1024 - dwg 2010
AC1027 - dwg 2013
AC1032 - dwg 2018
* .dwg file does not open
If for some reason the file does not open, do not panic. Let's try to restore it using utilities. When you open this type of drawing, you will most likely see a message:
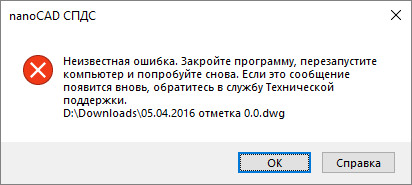
Restart the nanoCAD program and use the Document Recovery utility.
- Menu: File> Utilities> Document Recovery ...
- Command Line: RECOVER
This command allows you to recover damaged documents that do not open in nanoCAD , as well as to check their errors and correct individual errors. Upon completion of the recovery, the program will provide a report on the corrected errors on the command line.
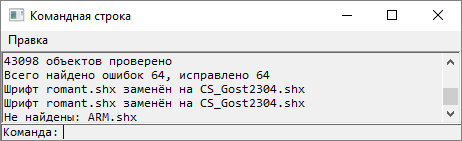
If the file still cannot be opened, send it to technical support specialists with a detailed description of the problem.
How to clean * .dwg file?
Before you start working with cleaning utilities, be sure to unblock, turn on and defrost all layers of your document, otherwise you will not be able to correct all file defects.

1. Document Verification
- Menu: File> Utilities> Document Verification
- Command Line: CHECK (AUDIT)
The command is designed to identify and correct problem objects in the drawing that are out of range. There are two modes:
- Check_Z_coordinates - checking the coordinates along the Z axis of all objects in the drawing;
- Check_Striches - verifies the correctness of displaying hatchings within the boundaries of contours.
Broken Z-coordinates, in my opinion, is one of the most common ailments of the * .dwg format. They can be in the drawing for years, remaining undetected, as most often users work in the plane. To identify this problem, you need to look at the drawing from a different view. Hold down the Shift key and use the mouse wheel to rotate the drawing in 3D space. If your drawing is flat, everything is fine; if not, it's time to fix it. You can return to the top view by clicking Top View in the <View> Views and Projections> Top menu .

The symptomatology of this problem is different. Bindings do not work properly, some objects are not displayed, the cursor disappears in the model, or the drawing is slowly working. The problem is very relevant when working with large files: master plans, substrates, etc.Starting with version 7, the nanoCAD platform checks the Z-coordinates automatically when launching * .dwg files, and if a problem is found in your file, you will see the following window:
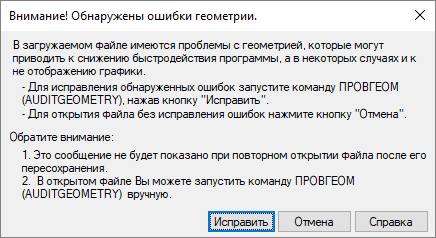
Just click Fix , and the utility will transfer all objects that have flown away. It is important to note that this function does not make your drawing completely flat, but simply brings objects with the flown away Z coordinate closer to the zero value. If you have three-dimensional objects, they will not be destroyed. After checking the geometry, inspect your drawing in 3D - if there are any defects left, it is recommended to use the Conversion to 2D function .
3. Conversion to 2D
- Menu: File> Utilities> Convert to 2D
- Command Line: CONV2D (FLATTEN)
This feature allows you to make all drawing objects completely flat. Therefore, if you are working with 3D polylines, it should be used with extreme caution. Here are a couple of ways that I use when working with such files:
Method number 1
In this case, you must select all the objects lying outside the zero plane. For this we need:
- Turn on the side view and select all objects that are above or below zero.
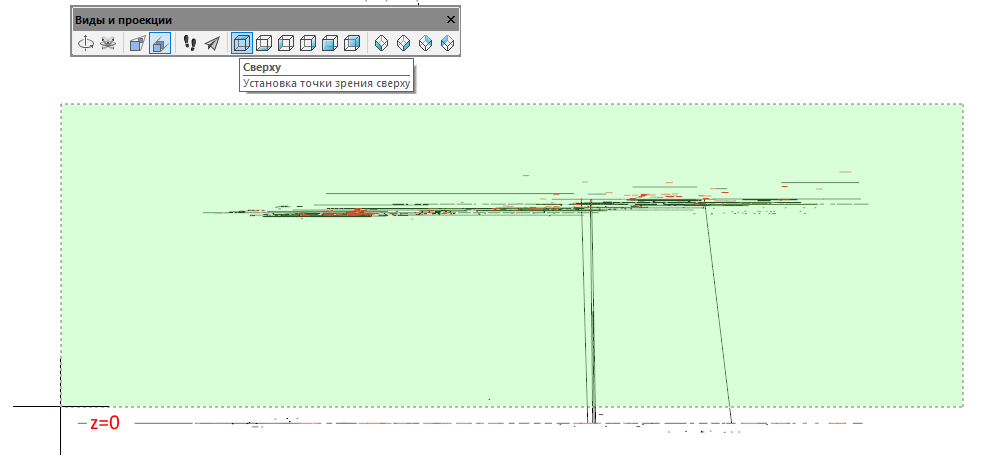
- After selecting all the objects that are outside the zero plane, we switch to the top view (this is important, otherwise the function flattens us the drawing on the wrong plane) and, without removing the selection of objects, we call the Conversion function in 2D.

Method number 2
The method is more time consuming, but also safer.
The point is that converting to 2D destroys the objects of the SPDS design (callouts, axes, level marks, etc.), so before starting the conversion we need to exclude these objects from the selection.
- Select all drawing objects (Ctrl + A). Go to the functional Properties panel, select design objects from the drop-down list and exclude them from the selection. Repeat this operation until the selection will not be objects design SPDS.
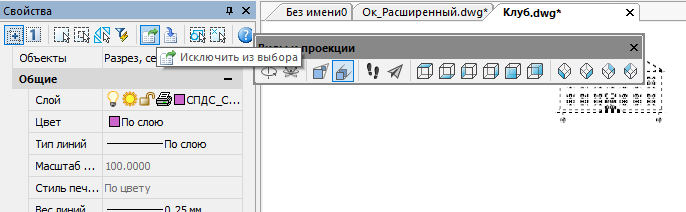
- Without discarding the selection from objects, we call the function Conversion in 2D . Then the file can be checked again for errors. After verification, save the file under a different name - for example, And architecture_audit_flatten.dwg . I use versioning when saving, so that in case of any error I return to the previous version of the file and do not do all the cleaning operations from scratch.
4. Purge the document
- Menu: File> Utilities> Document Cleanup ...
- Command Line: CLEAN, PAN, REMOVE (PURGE, PU)
After launching, the command brings up the Cleanup document a dialog box, which contains a list of items available for deletion and a list of items that cannot be removed from the document. Select from the list the items to be deleted, or click Delete All.
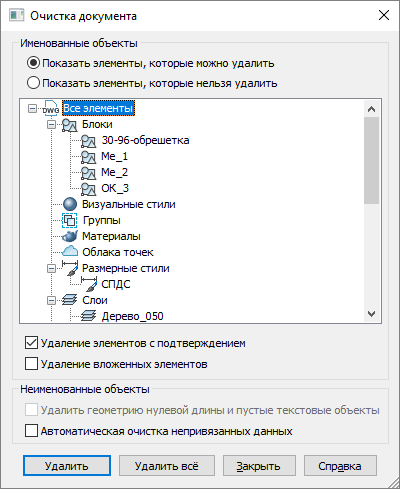
- Remove Nested Items — Enables the delete mode for all unused named objects contained within other unused named objects.
- Automatic cleaning of unbound data - deletes outdated DGN format vector data styles.
Files with DGN-styles weigh more than usual, although they contain little graphics. Such files may work slowly and cause a hang when saving.
- Delete zero-length geometry and empty text objects — enable the mode of deleting graphic garbage. The check box is not available if there is no corresponding geometry in the document.
Such objects are hard to find in the model. Texts are visually displayed only after selection, as they have no content.
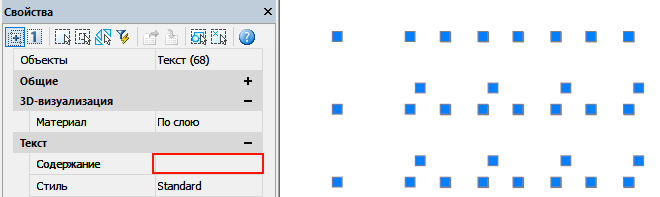
It is convenient to detect them through the Drawing Manager ( Tools> Drawing Manager ). In this functional panel, empty single-line and multi-line texts will be displayed as “NULL TEXT”.

After performing the cleanup, save the file with a different name. I save the drawings with the postfix of the utility that I checked it with. Therefore, the name of our file will now look like this: Architecture_audit_flatten_purge.dwg.
5. Recoding text
- Menu: File> Utilities> Text Transcoding
- Command Line: DECOD (TEXTDECODER)
Probably, any Russian user at least once faced with problems of encoding, when, for example, the names of files in Explorer or the text in the browser are displayed as incomprehensible icons. This problem is familiar to users of CAD systems.

Text conversion utility is presented as a separate drop-down box. The first thing we need to choose is the type of objects that we will transcode. Such objects can be layers, styles, texts, etc.
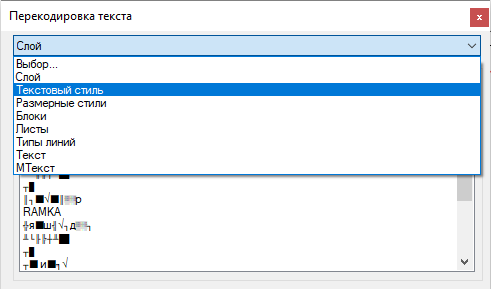
There are two decoding modes: manual and auto matching . The first one is the most accurate and very laborious, the second one is fast, but associated with the risk of errors. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Manually
Select the text from the list and assign the final encoding to it. Then click on Decode and see the result in the Decoding result window. If you have not guessed with the encoding, select another and re-encode.

AutoFit
In this mode, the program selects the final encoding independently. Select the item from the list with the problematic encoding, set the decoding mode to AutoSub, and click the Decode button. The program is not always able to correctly determine the final encoding, so the user is provided with a list of results with different encoding. From the drop-down list, select the correct representation.
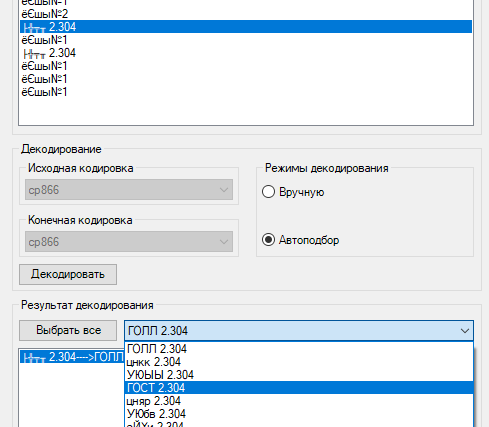
Recoding all objects
You can recode the entire data array. To do this, we click the Select All button, set the decoding mode to Auto Fit, and click on the Recoding button.

If you have to transcode a large array of objects, try to exclude from them those that are displayed correctly. This can be done by clicking on the list item with the left mouse button while holding the Ctrl key (Ctrl + LMB).

After correcting the encoding, save the file under a different name - for example, Architecture_audit_flatten_purge_decod.dwg
6. Insert drawing to new file
There is another good method that allows you to fix even the nastiest files. Users of CAD-systems use this method for a long time, I just want to remind about it again.
It is worth resorting to this method if cleaning and checking do not help to correct this or that defect. Attention! In the drawing will disappear all the decorated sheets.
Create a new file in nanoCAD ( File> New menu). Next, you need to insert the problem drawing into this open file as a block ( Insert menu > Block ). In the Insert block window, uncheck the Check box on the screen to insert the drawing immediately to zero coordinates. You also need to check the box next to Split so that the inserted drawing does not have to be broken after insertion.
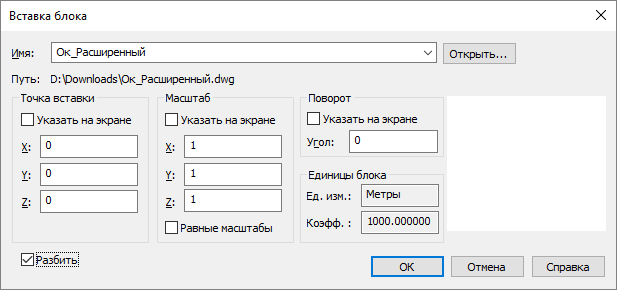
After inserting the drawing in this way, the entire database of the * .dwg file will be regenerated. This way you can fix a number of errors that were in your old files. When inserting, you will also lose all proxy objects of your drawing, so be careful when using this method. After inserting the drawing, save the file under a different name, for example, Architecture_insert.dwg.
7. Breakdown and deletion of proxies
- Menu: Edit> Advanced Tools> Remove Proxy Objects
- Menu: Edit> Advanced Tools> Proxy Breakdown
* .dwg files may contain third-party objects created in other applications. All unidentified objects are called proxy objects (they may or may not have a graphical representation). Proxy objects create specialized applications under various CAD-platforms. Probably every designer came across such objects. They can not be edited, they do not have "pens".
Proxy is a transit storage technology. Speaking in simple human language, it allows an application to save its object and protect it from destruction, even if you open it in another CAD system that does not have this application. Therefore, before breaking and deleting a proxy, think about it: suddenly a third-party application object will still come in handy and you should not hurry with its splitting into primitives.
Some developers of specialized applications protect their objects by not allowing them to be split with the EXPLODE command. For such cases, special utilities for splitting and deleting proxies are implemented in nanoCAD. They work quite simply, you only need to select the proxy objects and call the necessary command (breakdown and delete). These commands are available in the context menu of the Drawing Manager , a special tool showing the entire structure of the * .dwg file.

Conclusion
After working with all the utilities carefully read the final file. Sometimes complex files may require 2-3 utilities. If all the necessary project data are intact and you are completely satisfied with the current result, delete the intermediate files and leave the original file architecture.dw g, and give the final name architecture_rec.dwg.
Using this marking, you will know which files you have already processed and which ones should be checked. Always work in files marked with _rec.I hope this information will help you clean up your files, simplify and speed up your work in the * .dwg environment, and also avoid critical errors and data loss.
Have a good design!
Sergey Spirin, mahbak
ZAO Nanosoft
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/347022/
All Articles