Inventory (business *) processes through updating job descriptions in the interests of information security
Hello, habrazhitel!
I offer to your attention an article that unites things, at first glance, having nothing in common with each other: official duties of employees, inventory (business - *) processes and information security.
The following topics will be covered:
- Instead of intro
- About job descriptions
- Pro processes and approaches
- About information security
- Pro all together
- Automation example
- Ways of development of ideas reflected in the article
- Instead of conclusion
Welcome under the cut!
Hello again under the cut :)
Before continuing to read, the author would like to point out some features of the narration and special blocks in which important, in his opinion, information and / or clarifications are placed in them that will help the reader to better understand the thought he wanted to share:
Important!
Important text
OR
Important!Important text
If we turn to English-speaking sources, we will not find any business process, there is only a “business process” - which would be correctly translated as a “business process”.
The word "business" is used only to separate processes that are directly related to the creation of economic value from all other processes: chemical, physical, mathematical, etc.
This article will present a vision of how the information security division, while carrying out its work, helps the Human Resources Department to update / form a set of documents - job descriptions / job families description, and for the business - to compile a catalog of competences and inventory processes in the Company. With examples.
Activity goals :
- Formation of job descriptions;
- Identification of competencies;
- Definition of job responsibilities;
- Description of the functions;
- Combining functions into processes;
- Formation of services;
- Maintaining the main processes that bring profit to the Company.
Let's start with the formation of a common conceptual series.
Information - information (messages, data) regardless of the form of their presentation (149-FZ);
Information security - preservation of confidentiality, integrity and possibility of application (availability) of information. Often, the provision of other properties, such as authenticity, controllability, irrefutable authorship and reliability, is referred to as information security.
(ISO / IEC 27000: 2014);
Competence - availability of knowledge and experience necessary for effective activity in a given subject area;
Activity - active interaction of the subject with the world, during which the subject satisfies any of his needs;
A process is a purposeful, manageable, stable set of interrelated activities carried out by resources, which, according to a certain technology, transforms inputs into outputs that are of value to the consumer;
A business process is a process in which the value created (satisfied need) is paid (directly or indirectly) by a consumer external to the Company;
Function - a set of actions (or one action), which is aimed at the implementation of instructions for creating a product;
A project is a targeted, temporary activity designed to create unique products>, services, or results (a managed activity aimed at uniquely changing a particular system and carried out by resources under constrained conditions);
Management - actions of a particular subject, aimed at changing and manipulating objects and subjects to achieve predetermined goals.
In connection with the focus of the article on the broad masses of readers, mostly not related to information technology and information security, the author would like to propose "simplified" concepts.
Data - the initial, not yet processed set of evidence or facts collected as a result of observation or research;
Information is the result of data processing for the purpose of ordering;
Information - the result (result) of the application of the competence (technology) of the contractor (system) to information.
Example including all 3
Q. Why do mathematicians confuse Halloween and Christmas?
A. Because 31 Oct = 25 Dec.
Important!
the author's personal whim to call employees of private companies employees, not employees. The meaning of the statements does not affect.
Instead of intro
Today, most Companies remain built in a functional way and are a mechanism with a set of functions. These functions are distributed among divisions where they are performed by executing employees. In carrying out their highly specialized tasks, workers no longer see the end results of the work of the entire enterprise and become aware of their place in the common chain. They are no longer focused on the Company's target tasks, since their vision of what is happening most often does not go beyond the framework of their own divisions in which they work. The monopoly position of each service within the Company leads to the fact that the employees of these services consider themselves indispensable, which is why interaction between functional departments and services often becomes destructive for them. By and large, this situation is not good, but not bad; it is none.
About job descriptions
Important!
Unfortunately, in the modern world (especially in the Russian Federation) job descriptions are not at all regarded as a powerful tool contributing to a positive effect on increasing the efficiency of workers' activities. The situation is stalemate initially: the law never stipulates the requirement for a job description, HR specialists do not have time / effort / desire to write (choose 2 out of 3), line managers set aside for later, subordinates are not at all interested in them, because . The courts in most cases make decisions in favor of the employee if they do not exist (based on the judicial practice of the city of Moscow).
The attitude to the question of the presence or absence of job descriptions in general can be expressed in 4 groups:
- Instructions should be . Such an approach is rare, but some managers and employees of HR services are convinced that the Companies need instructions developed for each position, since Without them, it is extremely difficult to organize the effective work of the staff. However, many do not fully understand what their presence can give, but they strive to make them as high-quality as possible. Up to 15% of Companies.
- No instructions are needed . There are many more people who believe that the instructions play no role in the management of human resources. Therefore, there is no job description in such Companies, especially since the law does not require it. This approach can be found in about 30% of Companies.
- Instructions are needed, but their quality does not matter. With this approach, the job description has nothing to do with the actual activities of the Company's employees. You can safely give more than 50% of the total.
- Instructions - this is a management tool - the most effective approach, but it is used by only a very small number of Companies, up to 5% of the total. It lies in the fact that relevant instructions are not only created, but also regularly reviewed and updated, and are actively used in practice.
In general, we can talk about two approaches to the creation of job descriptions: the Western and the Russian. The western approach is to write very short instructions, where the description of the functional takes literally a few lines. At the same time, a separate regulation is created for each of the functions, where it is described in more detail.
The Russian approach is expressed in the fact that the instruction describes the functionality as fully as possible, without additional references to the regulations.
Regardless of the approach to creation, the goals of the job descriptions can be formulated as follows:
- Clear regulation of the obligations of the parties to the employment contract (transparency of labor relations), both at the stage of recruitment and in the process of employment.
- Determination of the employee’s specific work functions, detalization of the procedure for his actions, limitation of his area of responsibility and limits of authority.
- To be a guide to action, as well as a basis for resolving disputes in the event of disagreement (between an employee and an employer, between employees within a structural unit, between structural divisions, in court).
- Become a tool for evaluating personnel and, of course, corporate business process management.
Job descriptions are a necessary and effective tool for improving business performance. Their presence allows:
- create a management system that makes the business more transparent and manageable;
- clearly regulate the main obligations that are taken by the employer and the employee applying for a job, which greatly simplifies the relations of both parties;
- streamline the work of each structural unit in particular, and the enterprise as a whole;
- to formulate the labor functions of employees, their areas of responsibility, powers and restrictions in decision making, qualification requirements for the position, functional responsibilities of the person occupying it, the algorithm of actions in standard situations;
- avoid duplication of functions when performing certain types of work and uneven distribution of load;
- ensure effective interaction of employees holding different positions in solving production and management tasks;
- to select high-quality staff: a recruiter, having read the instructions, will be able to competently organize work with the candidates, and the applicant will be able to know in advance what will be required of him in this position;
- create comfortable conditions for the adaptation of a new employee: if the instructions clearly state what the newcomer should do and within what limits, and who his immediate supervisor is, this will make it easier for him the first days of work;
- to attract negligent employees to disciplinary responsibility for non-fulfillment of their job duties.
Like any other toolkit, job description with proper formation and maintenance can be:
Business Performance Tool
The formal approach to the development of job descriptions, when they are drawn up according to templates, do not correspond to the business objectives, does not reflect the main tasks of the employee in this position, does not aim at achieving the main goal of the Company, leads to the result that useless, inoperative documents are obtained. In this matter, the attitude to the job descriptions of the employer plays a big role. If he views them as an effective tool for personnel management, most likely it will be so. But if the instructions are developed by employees who are far from understanding the real functionality of specialists, their creation will be of no use to anyone.
Many Companies, having developed job descriptions once, no longer correct them, although business processes periodically undergo certain changes, which should be reflected in the instructions. In the conditions of strict requirements of modern business, it makes no sense to use job descriptions that do not reveal the specifics of the Company and do not contain strictly fixed tasks, functional responsibilities of staff, a description of the desired result of work and transfer of those responsible for its effectiveness.
Motivation management tool
In the face of fierce competition, more and more managers began to realize that the main resource that allows them to achieve strategic goals is personnel who need to be given due attention, primarily stimulated, both materially and non-materially. One of the most effective HR-tools that can help the Company to solve these problems is the system of grades / bands, in the development of which an important role is played by a verified and transparent organizational structure and well-described job descriptions / competencies that avoid many problems and reduce the cost of this procedure .
Employee Performance Assessment Tool
At any stage of the Company's development, errors and deviations from planned business results are possible. To minimize such risks, clear planning and control are needed. The presence in the Company of such an effective management tool that performs an organizational, regulatory and regulatory role, as a job description, simplifies control over employee performance.
Carried out with the help of job descriptions control over the activity is part of the personnel management system. The data contained in job descriptions make it possible to quickly assess what an employee needs to do in order to achieve the goals he has set, what measures should be taken to improve the efficiency of his activities. Detailed job descriptions set the standards and technologies for performing the tasks, which can be supported by both the employee and his manager. With their help, it is possible to assess how much an employee corresponds to his position, and to apply certain measures of influence to him.
Training needs assessment tool
Instructions are a great career planning tool if they include a clause on the required knowledge and qualifications. Using the information from this point, it is very easy to understand what skills one or another employee needs in order to take one or another position.
Pro processes and approaches
Thanks for the sectionThe author wants to thank Orphan V.E. for assistance in preparing the section
The author does not seek to impose a process approach, as the only true one. However, it wants to remind that each functional division of the Company optimizes the activities in its area of responsibility, which, ultimately, may lead to the substitution of the strategic goal of the Company with the target functions of a separate division, which, in turn, leads to inhibition of development of both a separate division and and Companies.
Before proceeding you should classify the processes. In general, it makes sense to classify something only when the groups identified in the classification will be used in the future, and their presence will “simplify” life. While it is always necessary to remember that any objects can be classified in different ways, but always retain their common characteristics.
By classification we mean the grouping of objects of study in accordance with their common features, called the basis of classification.
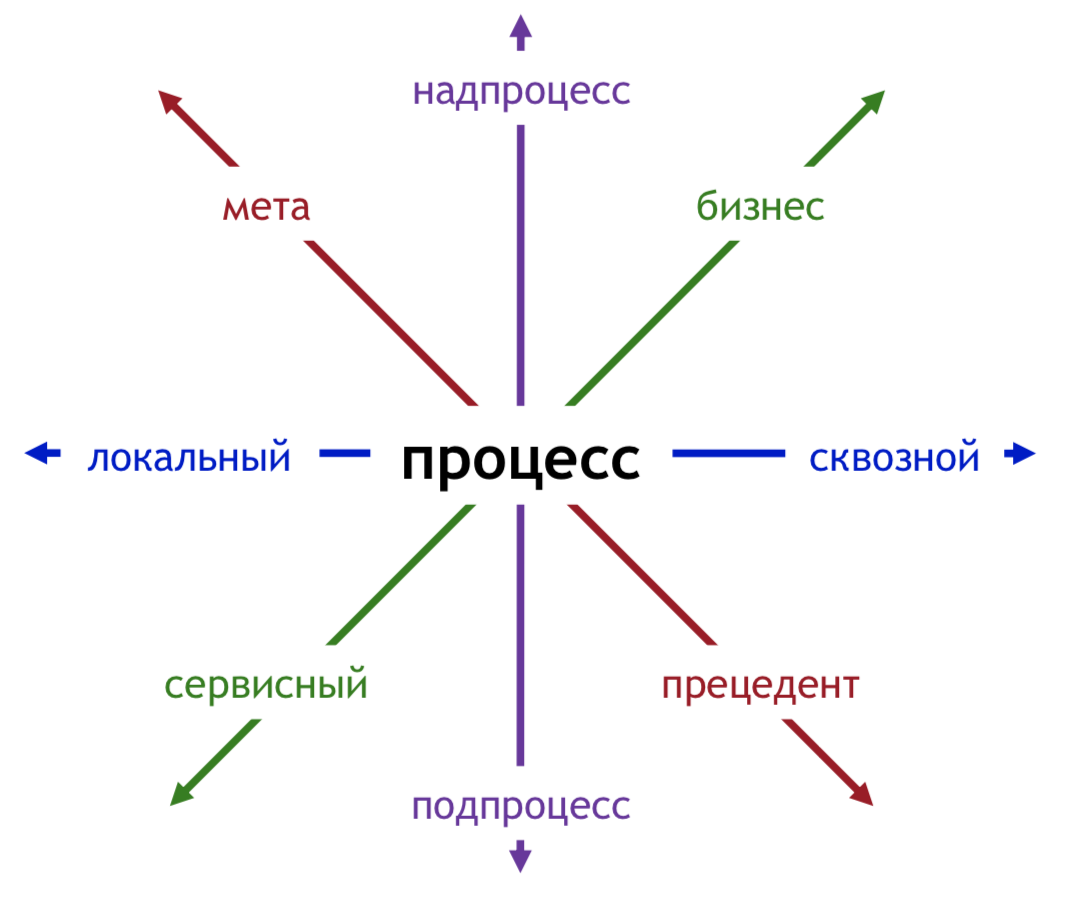
Reasons for classifying processes:
- Business is a process in which the value created (satisfied need) is paid (directly or indirectly) by a consumer external to the Company.
- Service - a process that is carried out in the interests of the consumer, internal to the Company.
- The overprocess is a stable, purposeful system of processes at a lower level (subprocesses in relation to the current one), which generally meets all the requirements for the process.
- A subprocess is an activity element that meets all the requirements for a process and is part of a higher level process (overprocess relative to the current one).
- Meta-process - a class of processes of a certain type, obtained as a result of abstraction from an object on which an action is taken and aimed at satisfying a group of needs.
- Process use case is an instance of a process.
- A local process is a process that exists entirely within the framework of the division in whose interests it is operating, i.e. all participants in the process are employees of the same department.
- The cross-functional (cross-functional) process is a process that is carried out within several divisions, i.e. some of his tasks (functions, subprocesses) are solved within one division, and some within another.
A continuous process that is carried out in the interests of the internal consumer, affecting all the units acting in the interests of specific individuals, at a particular point in time relative to a specific object, and which is part of a higher level process.
Here is a comparison of the characteristics of the Function / Process / Project:
| Characteristic | Function | Process | Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Why is carried out? | Produce result | Satisfy consumer need | Achieve the goals of the project participants |
| How is it done? | According to the standard algorithm | According to a certain technology | Every time is different |
| Who performs? | Same performer | A group of the same performers | A team of unique specialists |
| What is the result? | The same product that meets certain specifications. | Non-unique product that meets the needs of the consumer | A unique product that allows you to achieve project goals |
| Where is it managed? | Outside | Inside | Inside |
| Does it repeat often? | Often | Often | Rarely or never |
Management - actions of a particular subject, aimed at changing and manipulating objects and subjects to achieve predetermined goals.
- Functional control is the establishment (determination) of parameters for the execution of functions, including establishing the execution plan, the input and output requirements (result), the definition of the algorithm for converting the input to the output, and the requirements for the resources performing the function.
- Process management is a technology based on the recognition and application of the fact that the perception and management of the Company's activities, as interrelated processes, contributes to the enhancement of its (Company) performance and efficiency.
- Project management - the application of knowledge, skills, tools and technologies in project activities to meet the requirements and achieve the expectations of project participants.
Example:
| An approach | Example |
|---|---|
| Functional | The manager responsible for the function: " Sidewalk cleaning : sidewalks must be clean " - bring snow onto the road; The manager responsible for the function: “ Road cleaning : the roads should be clean ” - put snow on the sidewalks; |
| Process | The manager responsible for the process: " Cleaning the streets of the city : from the moment of snow falling until the time of cleaning the streets " - we collect the snow and dispose of it. |
| Project | The manager responsible for the project: “ Providing access : from a snowdrift to the end of the street ” - first we clean the one who pays. |
If at your enterprise you hear the phrases: “the ball is on their side”, then you have no process approach. Most likely you have a problem in performing the function and the participants are trying to choose the culprit, because the result has not yet been presented.
The functional approach answers the question “What to do?”.
The functional model is based on the universal principle of division of labor between services, departments, workshops, teams with assignment to them of certain functions (operations).
Main features Functions :
- Context Independence. Inputs (outputs) are part of the function and their composition and characteristics do not directly depend on their source (receiver), but are set by the control.
- External management. The function is controlled “from the outside” by setting rules and plans for the work of resources and setting requirements for the result (output). Decisions on each case are made by the person in charge of management.
Behavioral patterns:
Management:
• “I gave instructions - let them carry out”;
• “If something goes wrong - I will refer to the next unit”;
• “While it is important that we do our work, we will do as much of our work as possible”;
Performers:
• “I don’t care - I do what they say”;
• “My boss is my consumer: he is satisfied - there is a salary”;
• "Solutions? This is not a question of my salary! ”;
The process approach answers the question “How to do?”.
The process approach in its essence leads to the transition to the so-called “lean production” or “lean” resource-saving organizational structure (Lean production). The main features of such an organizational structure are:
wide delegation of powers and responsibilities to performers;
- reducing the number of decision levels;
- the combination of the principle of target management with the group organization of labor;
- increased attention to ensuring the quality of products or services, as well as the work of the enterprise as a whole.
The main features of the process :
- Focus. The purpose of the activity is to satisfy the consumer's need, and there are clear criteria for assessing the achievement of a goal (performance) and the cost of it (efficiency).
- Constant needs and manufacturability. The satisfied need is neither one-time nor unique, therefore the process is carried out by performing certain steps (technology).
- The need can change only after trying to satisfy it, and not during time.
- Integrity of activity and responsibility. The process is carried out from the moment of identifying the consumer's need to the moment of its satisfaction, and the one who makes the decision is responsible for the “from and to” activity.
- Manageability "from the inside." Since there is a responsibility for effectiveness and efficiency, the process implies (requires) management decisions by the process participants themselves. Moreover, all participants in the process are motivated for its effectiveness and efficiency.
Behavioral patterns:
• No goal - no resources!
• As patted - and burst!
The project approach is used for project-oriented companies, for example, research, consulting, construction, etc. It can be applied to any company when creating innovative products within these projects.
Main features of the project :
- Time constraints. Time constraints mean that any project has a clear start and a clear conclusion. Completion occurs when project goals are achieved; or realized that the objectives of the project will not or cannot be achieved; or the need for the project has disappeared, and it stops.
- The uniqueness of the product. , , .
:
:
• I !
• , !
• .
:
• !
• , ;
• – !
About information security
At the very beginning of the article, the author gave a list of terms and definitions, in which the definition of information security was given. We give it again:
Information security - preservation of confidentiality, integrity and possibility of application (availability) of information.
Often, other properties, such as authenticity, controllability, irrefutable authorship and reliability, belong to information security.
ISO / IEC 27000: 2014
The employee, following his official duties, enshrined in job descriptions, performs the Functions that lead either to the implementation of the Project or are included in the Processes, uses in its activities information stored in different information systems and resources.
, , .
.
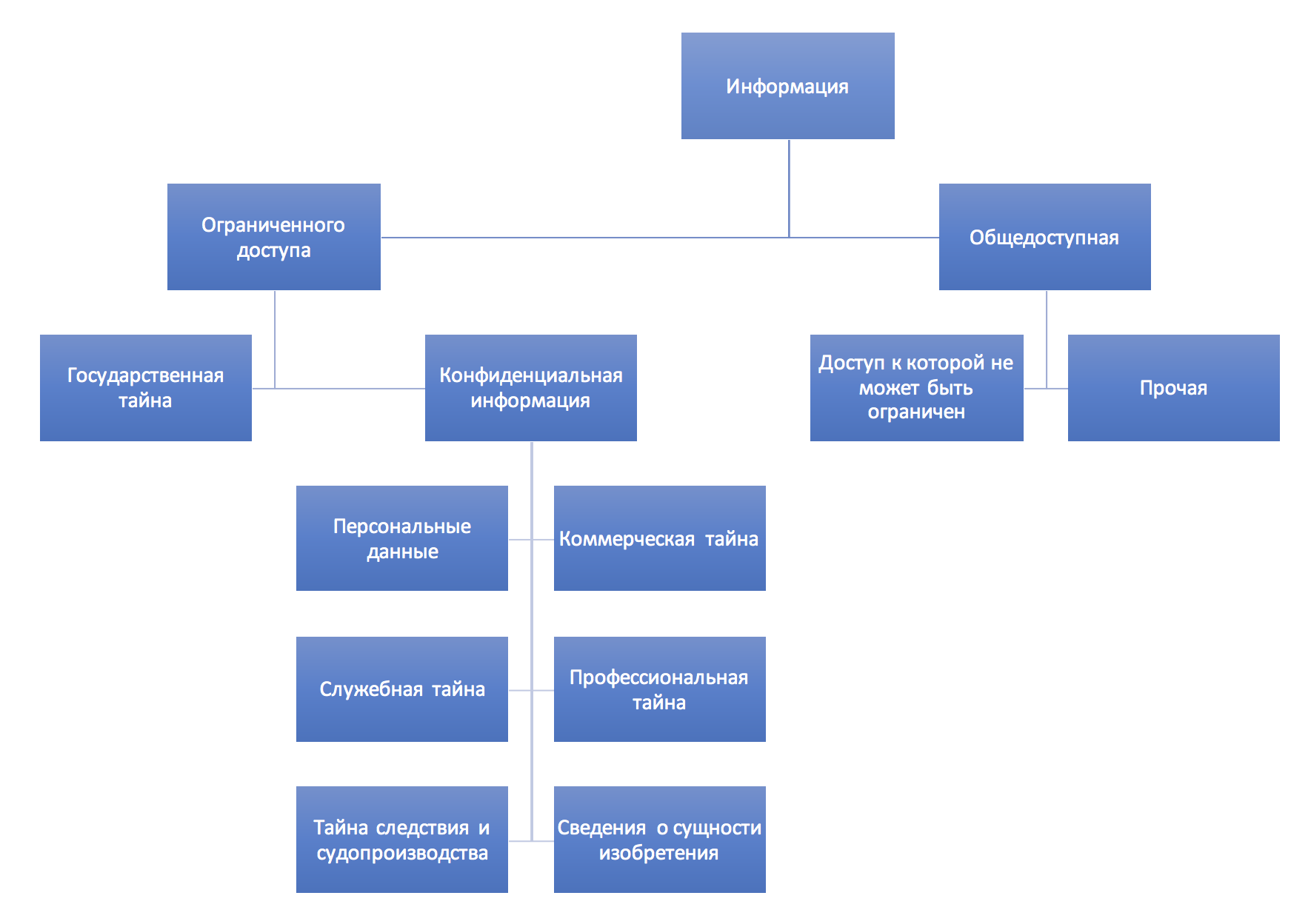
, ( ) — , , , "" ( — ) ( / ), "" ( , ).
:
- — "", , — ;
- — .
- "" / , — , , — .
, 5 () :
- — ;
- — / - . ( , );
- — , — PCI DSS;
- (/ ) ;
- , ( ///).
, 3 :
- — , , — , - .
– – , .. , . - — , , . . - , , ..
– , ;
, , ,
. - .
— .
, -30, ( ) : 100 ; , .
: " ?". " ?". " ?" - " - "?
, , !
-?
— . .
(, , ) , , . , , «-» — . , , . .
, . , , . , . «-» .
" ".
( ) , — () () ().
. , ( ), ( ), .

.
. .
, :
- ?
- ?
- ?
. , -. , , , . — .
, , « » . , , . . .
:
- - ;
- , , , ;
- , , , - ();
- - ;
- , .
, :
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ( ).
. (- ) ( ).
, , . .
– -. , - ( 146%) , - .
. . , .
, . , «» , .
:
- — ;
- , (-). , , ( );
- , : , , , , .
, :
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ( ).
— . , .
– , . , , – , «».
, , , . .
: , .
– . , , , , . – , , ..
! , , .
. ( ) , . – .
.
( / ) 2 : .
| [ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
"", "" "" , , . .. .
*
Important!
— , , .
, - — , , . , , , / / / .
, , ( ), .
.
, :
| [ | Experience | / | Other | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , , + . | . | , , . | - , | |||||
Important!
(, , 2 ), . . — , : .
, , , / / .
( ), .
? -, ; . -, . -, . -, .
, .
:
(KPI) — , ;
— , , ( — , — ).
Important!
, .
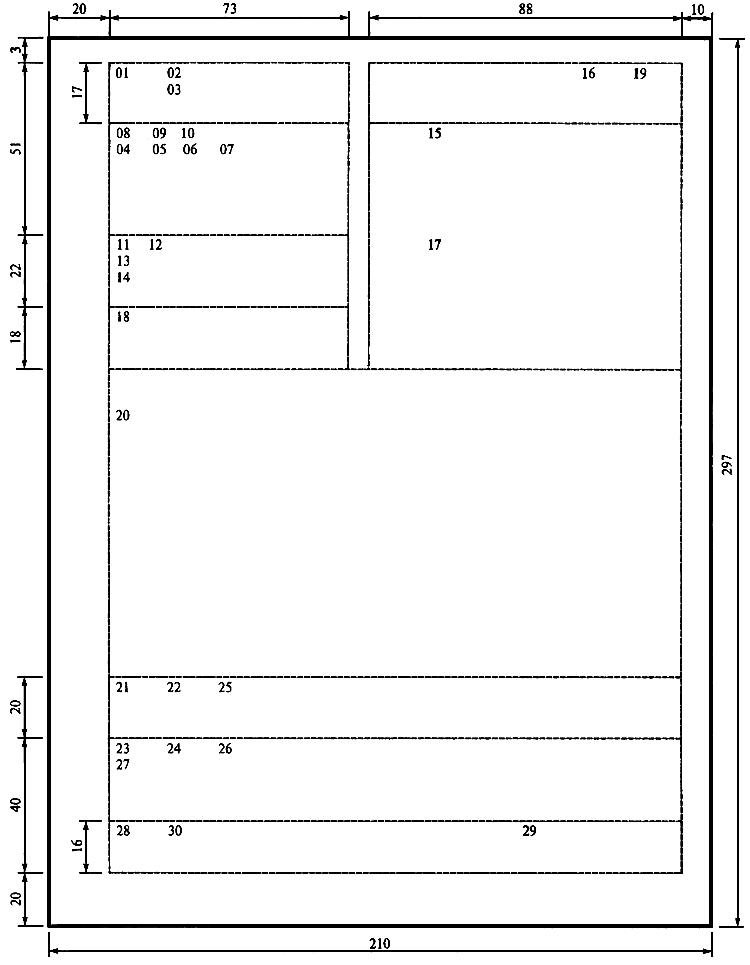
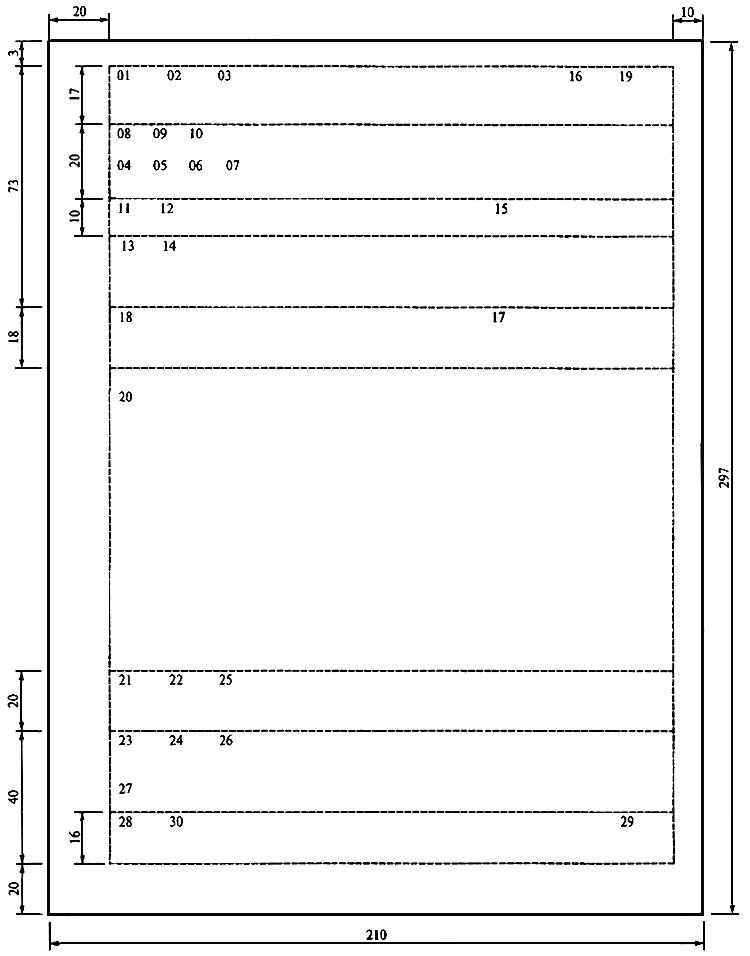
- 08 - the name of the organization - The name of the organization that is the author of the document should correspond to the name enshrined in its constituent documents. The abbreviated name of the organization is given in cases where it is enshrined in the constituent documents of the organization;
- 10 - name of the type of document - The name of the type of document compiled or published by the organization must be determined by the charter (organization regulation) and must correspond to the types of documents stipulated by the OKUD;
- 11 - document date - The date of the document is the date of its signing or approval;
- 12 - the registration number of the document - the number assigned to it according to the rules of registration of documents in the organization. The registration number of the job description may include an index of the case (as part of which it is supposed to store a control copy of the job description) according to the organization’s nomenclature of affairs, the letter designation of the name of the document type (for example, “d / i”), information about the document executor, etc .;
- 14 - the place of compilation or publication of the document - The place of compilation or publication of the document is indicated if its definition is difficult by the details of “Name of the organization” and “Reference data about the organization”. The place of compilation or publication is indicated taking into account the accepted administrative-territorial division, it includes only generally accepted abbreviations .;
- 16 - the stamp of approval of the document - props, giving the regulatory or legal nature of its content. In general, the stamp of approval of the job description includes the word “approve” (in capital letters, without quotation marks), the position of the person authorized to approve the job description, signature and decryption of the signature (initials, last name, and date of approval, verbal digitally) ;
- 18 - heading to the text - The heading to the text includes a summary of the document;
- 20 - text of the document - Texts of documents are drawn up in the form of a questionnaire, a table, a coherent text or in the form of a combination of these structures;
- 21 - mark on the presence of the application - mark on the presence of an annex to the document;
- 22 - signature - The Signature requisite includes: the title of the person who signed the document (full, if the document was not drawn up on the form of the document, and abbreviated form - on the document drawn up on the form); personal signature; Signature transcript (initials, surname);
- 23 - document approval stamp — a requisite expressing the consent of an organization that is not the author (developer) of a document with the content of the latter. This requisite is applied only in cases where the draft job description is subject to external agreement with interested parties;
- 24 - document approval visas - Document approval is drawn up with a document approval visa (hereinafter referred to as a visa), which includes the signature and position of the document endorsing the document, the decryption of the signature (initials, last name) and the date of signature;
- 26 - mark of the certification of the copy - When certifying the compliance of the copy of the document with the original below the "Signature" requisite, they affix a witness inscription: "True"; the position of the person who certified the copy; personal signature; Signature transcript (initials, surname); certification date;
- 27 - mark on the performer - Mark on the performer includes the initials and surname of the performer of the document and its phone number. A mark about the artist is placed on the front or back side of the last sheet of the document in the lower left corner;
- 30 - document electronic copy identifier - The identifier of the electronic copy of the document is a mark (footer) affixed in the lower left corner of each page of the document and contains the name of the file on the machine carrier, the date and other search data set in the organization.
Location of details and boundaries of zones on the A4 format
Location of details and border areas on the A4 format of the angular form
Location of details and border areas on the A4 format longitudinal form
In his activities, the author met with a situation when it was necessary to update the job descriptions of all employees of the Company.
Important!
The author knows how the audience Habra likes to automate everything and apply the latest technology! However, the audience of this material can be not only technically savvy specialists, but also people with “You” equipment. Therefore, there will be no databases, fashionable frameworks and other things that will certainly make life easier, but it will be a simple Microsoft Office, in a function accessible to all.
For automation, we need 3 files.
2 Microsoft Excel files and
1 Microsoft Word file.
The first Microsoft Excel file we need to fill it. The second Microsoft Excel file for "transport". As mentioned earlier, the solution is as simplified as possible for the masses. The Microsoft Word file will contain a template and fields for auto-filling from the "transport" document.
| Field | Value | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|
| Family | Department / Office / Division | By family, we mean a group of roles of performers who are organizationally united. As a rule, for the formation of services. |
| Family mission | Brief description of the purpose of the association | "Providing information security services ..." |
| Family situation | The level of office in the family (head of the family -3) | This value is needed not only to predict the cost of the role (compliance with the grade / band), but also to create a catalog competence of the participants in the process (service) |
| Purpose of the post | Description of the objectives of the role (taken from the process description) | The description is needed to highlight competencies for new processes. The description should contain the words "Ensuring ...", "Management ...", "Formation ...", "Execution ...". |
| Activity result | ||
| Key performance indicators | ||
| Position | Name of position | |
| Subordination | Job title direct manager | Together with the item "Position in the family" allows you to automatically create an organizational structure. |
| Number of subordinates | The numerical value of the number of direct subordinates | Value only for direct subordinates without project / contract. |
| Direct duties | The list of tasks, actions and processes that are performed by the employee and are within the scope of personal responsibility (without the constant participation of colleagues / supervisor / subordinates). | |
| Shared responsibilities * | The list of tasks, actions and processes that are performed by the employee together with colleagues + external interaction. | |
| Autonomy level * | The level of self-organization of labor. (freedom to act). | |
| What documents are guided by | List of documents | The list includes documents from general: TK, GK, to local - SLA and so on. |
| What documents creates in activities * | List of documents | Different roles, depending on the set of competencies, may be involved in different processes. |
| Internal interaction | Value | Level (list) of groups of structural units that are necessary to perform direct duties. |
| External interaction | Value | Level (list) of groups of structural units that are necessary to perform joint duties. |
| Budget | Sign of | Sign of having your own budget without specifying amounts. |
| Planning Horizon * | Value | Could and if so, for how long the worker should plan their work. |
| Education | The level and scope of education. Example: in information security, in some cases it is necessary to have a specialized education and a specialty with the code 090000 in order to fulfill their duties. | |
| Experience* | Sign of | Needed when forming a request for a new job in the family. |
| Knowledge / Skills * | Role Specific Requirements | |
| Foreign language skills | ||
| Software knowledge and proficiency | Knowledge of software (standard and / or specialized) necessary to perform direct duties. | |
| Degree of mobility | Willingness to travel / travel (having a passport / visa / exit) | |
| Other * | Requirements that do not fall into the other groups |
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Family | Office of Information Technology |
| Family mission | Providing SAP Accessibility Services |
| Family situation | CIO - 3 |
| Purpose of the post | Ensuring SAP Business Continuity |
| Activity result | 1. Processing user requests. 2. ... 3. ... |
| Key performance indicators | Performing SLA |
| Position | Leading Specialist |
| Subordination | Director of Information Technology |
| Number of subordinates | 0 |
| Direct duties | 1. Making changes ... 2. ... 3. ... |
| Shared responsibilities * | 1. The solution is not typical problems. 2. ... 3. ... |
| Autonomy level * | 0 - not autonomous |
| What documents are guided by | TK, GK, DI ... |
| What documents creates in activities * | Not involved |
| Internal interaction | 0 - Local |
| External interaction | 0 - specialists of contractors |
| Budget | There is no independent budget |
| Planning Horizon * | 0 - month |
| Education | Higher professional education |
| Experience* | Work experience in engineering and technical positions in the field of IT for at least 3 years |
| Knowledge / Skills * | Ability to administer SAP IP |
| Foreign language skills | English |
| Software knowledge and proficiency | SAP |
| Degree of mobility | Willingness to travel |
| Other * | Lack of "watchman" syndrome |
The second Microsoft Excel file is nothing more than a transposed table. This is a natural limitation, because The data to be used in the Microsoft Word file must be in plain text format. At the same time, it is inconvenient to fill in the initially transposed table - it becomes unreadable, especially if there are more than 7 participants in the family.
File 1, page 1 - Filled fields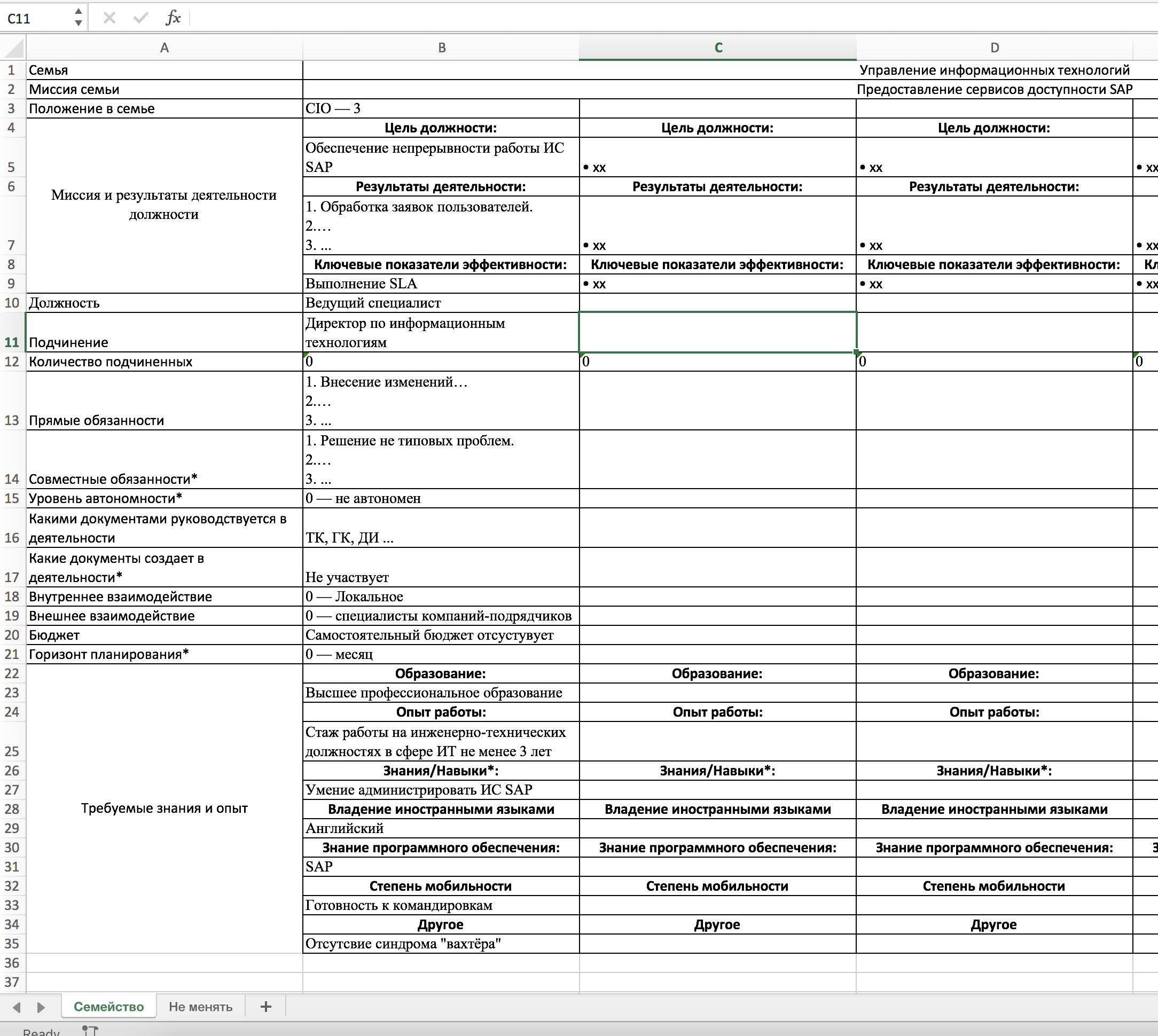
File 1, sheet 2 - transposed table, in the reference field you can see the link to the cell of the first sheet: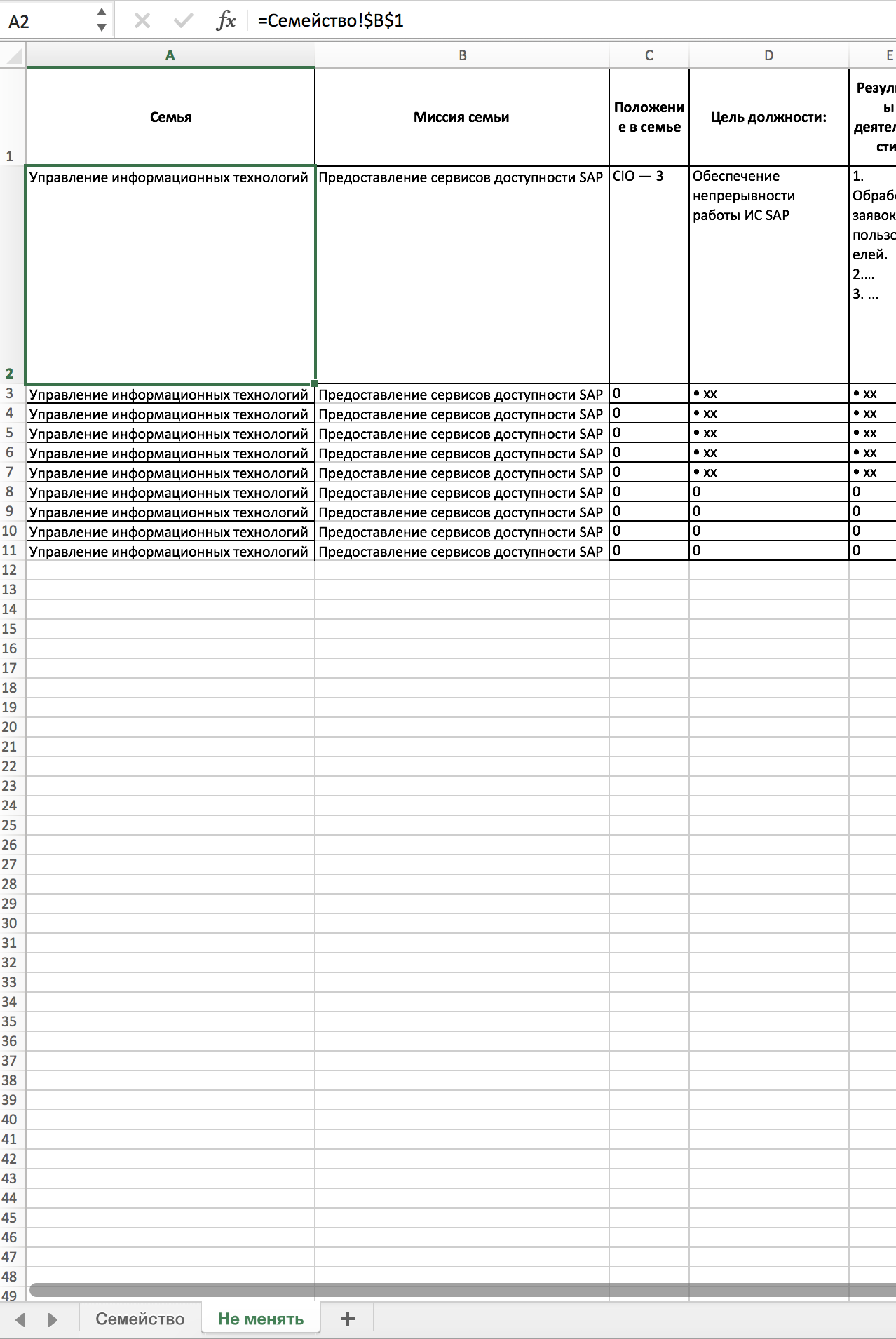
File 2, sheet 1 - plain text, without formatting.
File 3 is a Microsoft Word document template with auto-fill fields. The source of data for filling is file 2, sheet 1. Auto-completion is implemented using the distribution mechanism.
File 3, page 1
File 3, page 2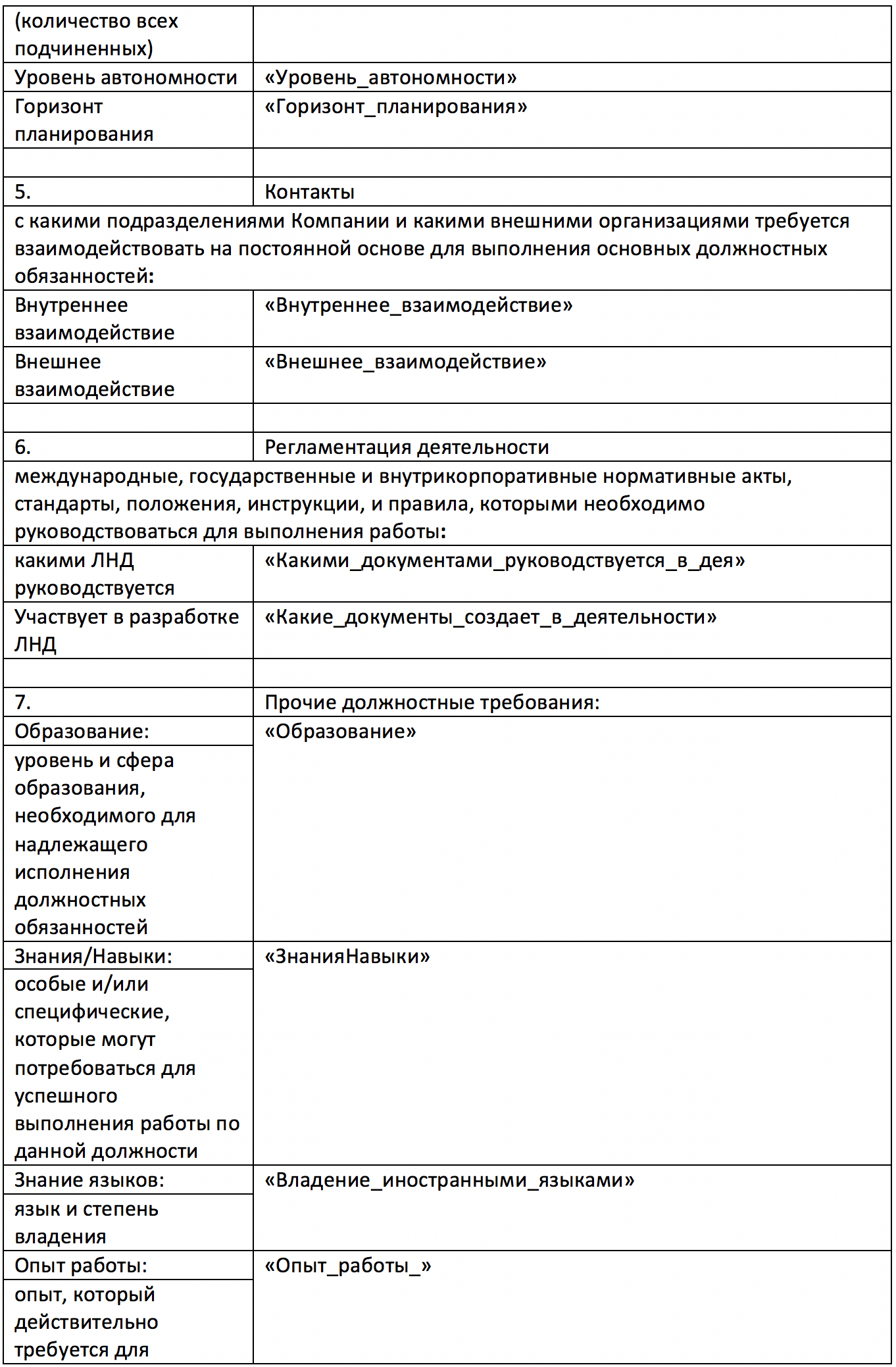
File 3, page 3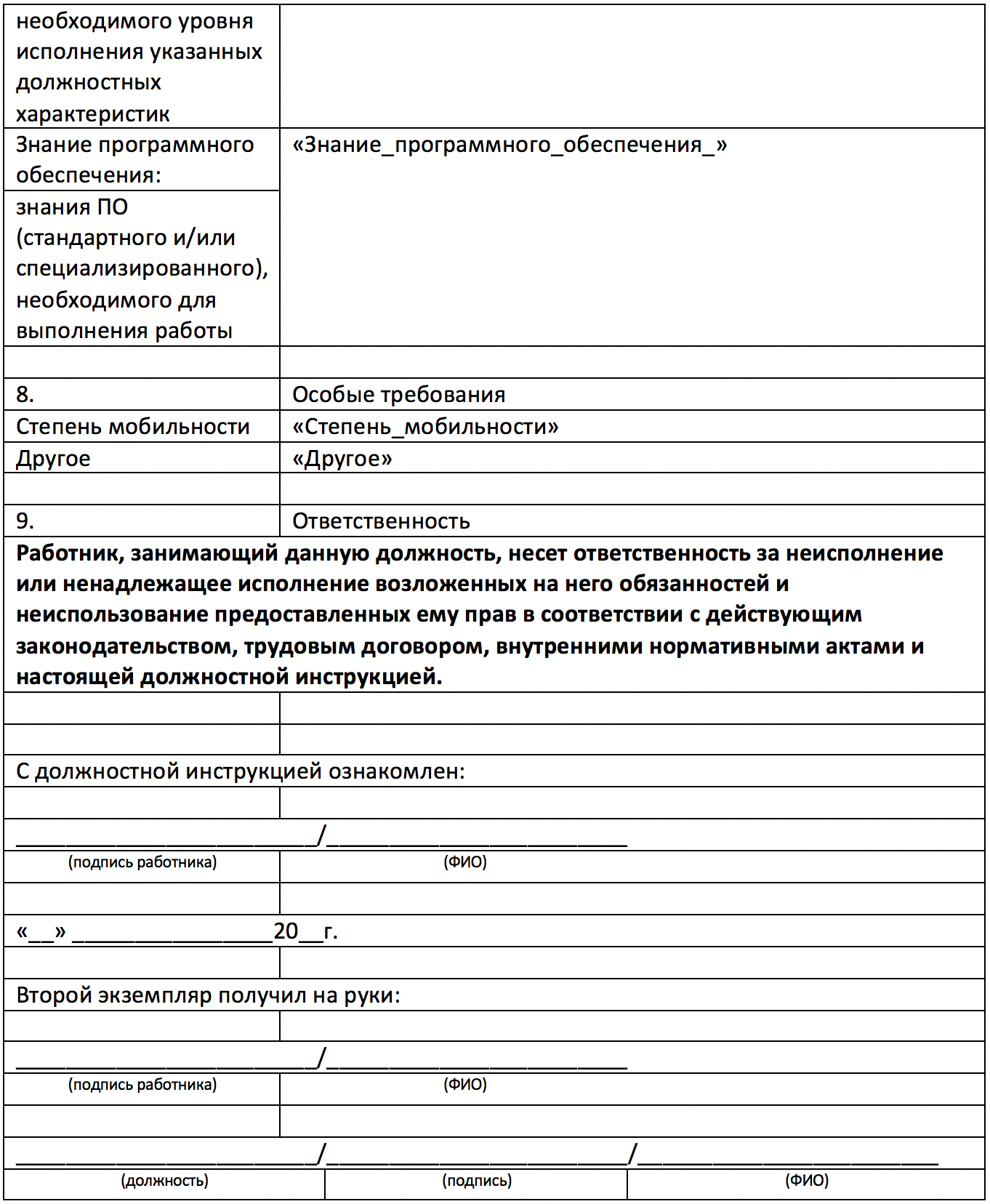
Filled template: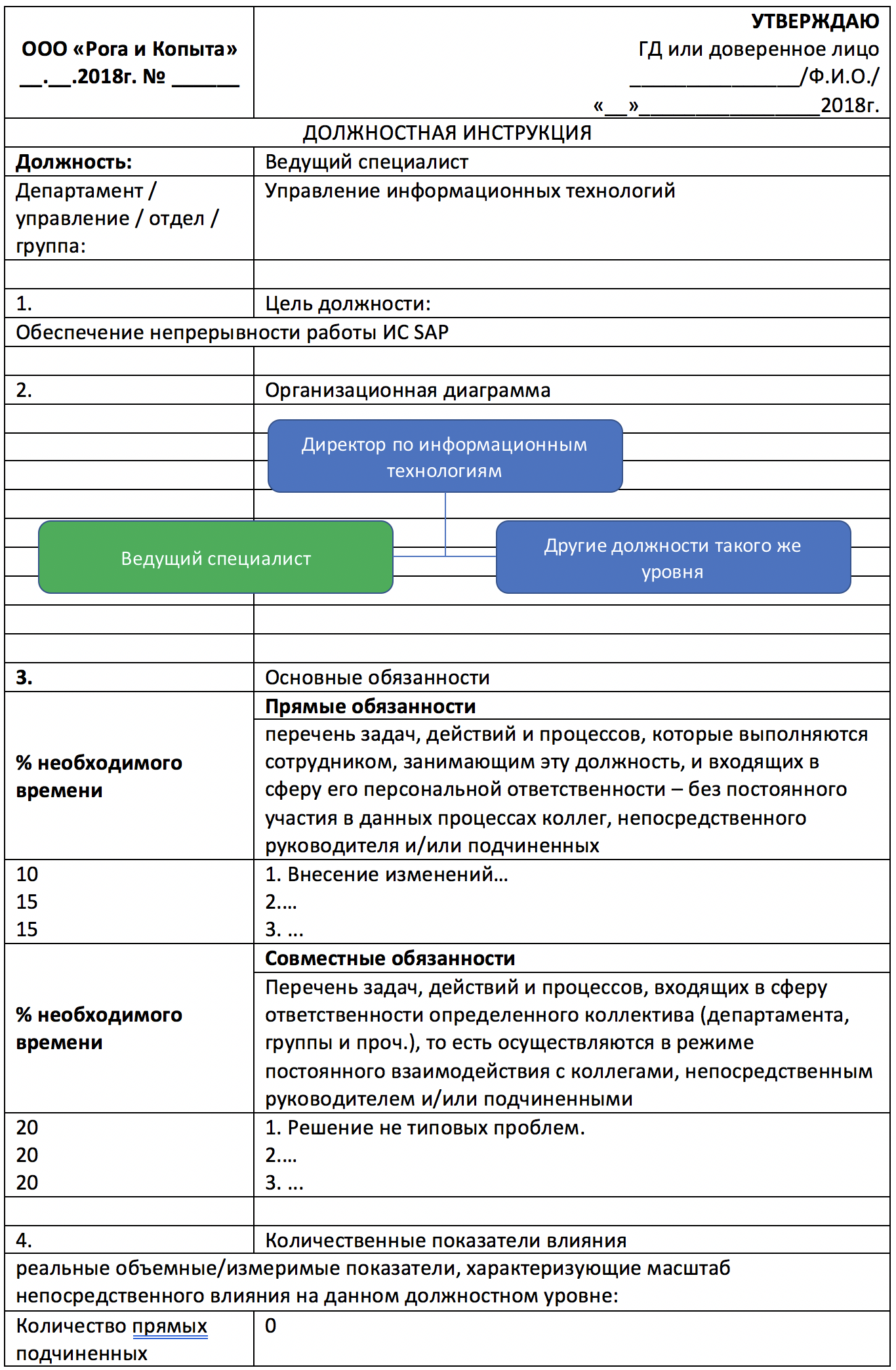

Ways of development of ideas reflected in the article
The approach described in the article aims to meet the needs of the following interest groups:
Human Resources Department - the formation of a family of positions for the rapid formation of requirements for candidates, depending on the needs of the processes;
Project / process office - formation of a set of competencies available for the implementation of new projects / processes;
Information security - the formation of a role model formed around a role in the process, and, therefore, around the level of confidentiality of information;
Information technologies - formation of configuration sets (server / user / AWS), licensing and budget expenditure management during the implementation of process automation;
The decision maker is the generation of relevant data for making management / strategic decisions.
- Families combine the roles and competencies on which the Company's processes are based. Understanding the place of the role in the process, you can determine the level of confidentiality of information to which the role will have access - based on the competence of the role and the ability to effectively apply the information;
- Easily implement a listing of processes - roles - competencies. With the help of task tracking systems and their execution - it is easy to determine the value of each role and the comparison of the value of this role and its value;
- based on the task tracking and execution, you can get an idea of the number of process instance launches, the need for the superprocess to start the process multiple times, the number of process launches leading to payment by the Consumer, and, consequently, profit;
- Key performance indicators of roles / performers (function indicators) are directly related to process performance indicators (business indicators - level of profitability, profitability, capitalization) in which the role / performer is involved;
- Determine the level of confidentiality of information involved in the (business) process, and therefore in information systems / information resources, which directly affects the composition and cost of IS / IR, role-based access model, users' AWP and workplace configuration.
Instead of conclusion

Structured and documented processes in the Company, job descriptions described and maintained, ensuring information security are all factors that indicate the Company's maturity. Following the picture above - level 0 is overcome and left far behind.
From three different sides - processes, organizational management, ensuring information security - only one driver becomes - achieving customer satisfaction, which in turn is characterized by repeatability of functions, the desire to achieve results not only in time (with the motivation “who is faster?”), But also with a given quality (with the motivation "who is better?").
Inventory of (business) processes through updating job descriptions in the interests of information security is an attempt to describe one of the options in which a change in the provision of information security may require routine work, which in turn may affect the overall level of the Company. thus, indirectly, but achieved, the integration of measures to ensure information security in the processes of the Company.
Bibliography
- Process approach to management. Business process modeling / V.V. Repin
V.G. Eliferov; "Mann, Ivanov and Ferber", M.2012- Business Process Models / LAP Lambert Academic
Publishing ", 2012- Business processes. Basic concepts. Theory. Methods / AB. Scheer; "News-
MetaTechnology ", M. 1999- Modern business process reengineering / M.V. Firsov; "Palmarium Academic
Publishing ", M. 2014- Management Encyclopedia / PF. Dryuker; Williams, M. 2006
- 149- "On Information, Information Technologies and Protection of Information"
- ISO / IEC 27001: 2013 "Information technology - Security techniques - Information
security management systems - Requirements »- ISO 9001: 2015 Quality management systems - Requirements
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (Regulation (EU) 2016/679)
- COBIT 5 for Information Security
Thank you for your time.
I am happy to answer comments.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/346954/
All Articles