New technology accelerates WAN networks up to 40 Gbps
As cloud technologies evolve, there is a growing need for effective data and server management. An important condition is to simplify infrastructure maintenance by transferring business-generated data to cloud environments. Fulfillment of new technical requirements entails a multiple increase in the amount of data transferred between cloud environments via WAN channels. Of paramount importance is the creation and introduction of new technologies to accelerate data transfer in WAN-networks. About one of these technologies, developed by Fujitsu, we will discuss in this article.
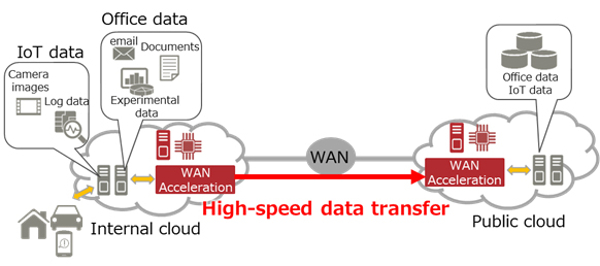
Using WAN Acceleration Technology in the Cloud
Today, data most often in WANs is transmitted between cloud environments with speeds from 1 to 10 Gbit / s. However, for the proper functioning of modern IT solutions, including the Internet of things and artificial intelligence, an even higher data transfer rate is required. Existing technologies for accelerating WAN networks increase the effective transmission rate by reducing the amount of data transmitted by compression or deduplication.
However, in 10-gigabit WAN networks, the total amount of information already reaches maximum values. Existing acceleration technologies in cloud servers can not seriously increase the speed of data transfer, which becomes the "bottleneck" of the entire cloud infrastructure. In order to bring the speed of cloud services to a new level, you must either use processors with a higher clock frequency, or use WAN acceleration technology, which uses different algorithms.
')
Fujitsu has developed WAN network acceleration technology that will provide data transfer in cloud environments (in real time) at speeds up to 40 Gbps. This speed is achieved with the simultaneous use of several 10-gigabit channels. In this case, the Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) matrices installed on the server act as accelerators. The technology is designed to help transfer large amounts of data between cloud environments. The implementation of the new development was made possible by the allocation of a special computational node for processing compression operations. It provides highly parallel operation of the main computational nodes, transmitting data at exactly the specified time, based on the predicted completion of each stage of the calculations.
Below are the features of technology.
1. FPGA Matrix Parallelization Technology uses dedicated compute nodes
Fujitsu has developed a technology for parallelizing FPGA arrays that can significantly reduce the processing time required for their compression and deduplication. The result is achieved by deploying dedicated compute nodes and ensuring a high degree of parallelization of computations.

Accelerating WAN networks with servers equipped with FPGA arrays
2. Optimizing the flow of data processing between the CPU and FPGA arrays
Previously, to compress data without loss using duplication, it was necessary to read them twice - before and after determining the data duplication. As a result, resource consumption increased, and the speed of the systems decreased. The new technology optimizes the use of computing resources by transferring the computational load to the FPGAs.
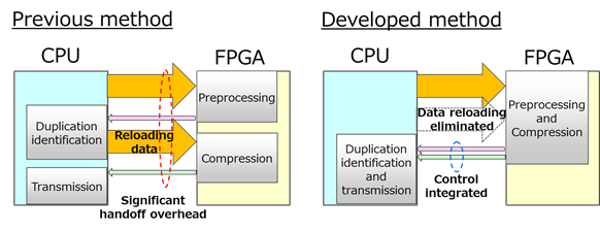
Method for reducing resource consumption between CPUs and FPGAs
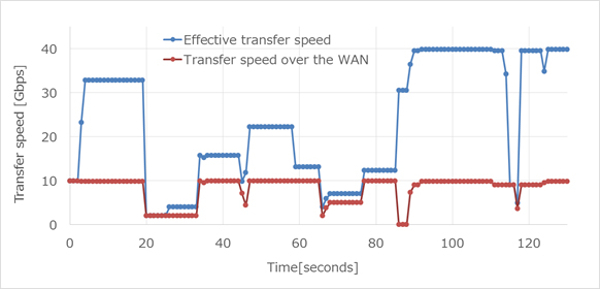
Fujitsu experts have estimated the speed of transferring large amounts of business-generated data. In a test environment, FPGA matrix servers were interconnected using 10 Gigabit channels. In the test simulating data backup, the transfer rate was fixed at 40 Gbit / s. This is a new industry record. As a result, the speed of the system has increased by about 30 times compared with a system equipped only with a processor. The new technology will provide an opportunity to create a new generation of cloud services that share large amounts of data from several companies from several geographically dispersed data centers.
Fujitsu plans to implement this technology in the form of an application loaded on servers with FPGA matrices. In the first place it can be used in cloud environments. The company's lab will continue to test new development. The commencement of commercial use of technology is scheduled for mid-2018.

Using WAN Acceleration Technology in the Cloud
Today, data most often in WANs is transmitted between cloud environments with speeds from 1 to 10 Gbit / s. However, for the proper functioning of modern IT solutions, including the Internet of things and artificial intelligence, an even higher data transfer rate is required. Existing technologies for accelerating WAN networks increase the effective transmission rate by reducing the amount of data transmitted by compression or deduplication.
However, in 10-gigabit WAN networks, the total amount of information already reaches maximum values. Existing acceleration technologies in cloud servers can not seriously increase the speed of data transfer, which becomes the "bottleneck" of the entire cloud infrastructure. In order to bring the speed of cloud services to a new level, you must either use processors with a higher clock frequency, or use WAN acceleration technology, which uses different algorithms.
')
How does the new technology work?
Fujitsu has developed WAN network acceleration technology that will provide data transfer in cloud environments (in real time) at speeds up to 40 Gbps. This speed is achieved with the simultaneous use of several 10-gigabit channels. In this case, the Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) matrices installed on the server act as accelerators. The technology is designed to help transfer large amounts of data between cloud environments. The implementation of the new development was made possible by the allocation of a special computational node for processing compression operations. It provides highly parallel operation of the main computational nodes, transmitting data at exactly the specified time, based on the predicted completion of each stage of the calculations.
Below are the features of technology.
1. FPGA Matrix Parallelization Technology uses dedicated compute nodes
Fujitsu has developed a technology for parallelizing FPGA arrays that can significantly reduce the processing time required for their compression and deduplication. The result is achieved by deploying dedicated compute nodes and ensuring a high degree of parallelization of computations.

Accelerating WAN networks with servers equipped with FPGA arrays
2. Optimizing the flow of data processing between the CPU and FPGA arrays
Previously, to compress data without loss using duplication, it was necessary to read them twice - before and after determining the data duplication. As a result, resource consumption increased, and the speed of the systems decreased. The new technology optimizes the use of computing resources by transferring the computational load to the FPGAs.

Method for reducing resource consumption between CPUs and FPGAs
results

Fujitsu experts have estimated the speed of transferring large amounts of business-generated data. In a test environment, FPGA matrix servers were interconnected using 10 Gigabit channels. In the test simulating data backup, the transfer rate was fixed at 40 Gbit / s. This is a new industry record. As a result, the speed of the system has increased by about 30 times compared with a system equipped only with a processor. The new technology will provide an opportunity to create a new generation of cloud services that share large amounts of data from several companies from several geographically dispersed data centers.
Fujitsu plans to implement this technology in the form of an application loaded on servers with FPGA matrices. In the first place it can be used in cloud environments. The company's lab will continue to test new development. The commencement of commercial use of technology is scheduled for mid-2018.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/346730/
All Articles