Amazon EC2 vs Atlex Cloud VDC: Performance Comparison
Everyone heard about AWS. We can say that the Amazon cloud has managed to become a kind of industry standard. We are no exception. And so they decided to check how a virtual machine in our cloud based on OpenStack looks compared to an AWS machine that is similar in functionality.

Details under the cut.
Cloud "instansy" differ from traditional VPS by the absence of the need to pay a monthly fee immediately after a month. Such a virtual machine works just like a taxi - the counter ticks as it travels. You will have to pay some amount for simple, because even the machine that is turned off uses storage capacities. It is much cheaper and more convenient to pay for actually consumed computing resources if there is no constant need for them. Developers and testers can save a lot of money, and even the owners of the corporate IT infrastructure can shut down unnecessary servers, say, during non-working hours or upon completion of a project. In the cloud, you can quickly increase resources (add a processor or another, increase the amount of RAM), if the load has increased, or discard excess when the need for them disappears. Solid benefits: it does not need to buy hardware and licenses for the operating system. The server goes up in a couple of minutes via the web interface and is paid for what is called on-demand.
')
Amazon has become a pioneer in this market with its Amazon Web Services (AWS). Then came the Microsoft Corporation with the Azure platform and the Google Cloud Platform already appeared - this trio grabbed a significant part of the market, but Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) has long been synonymous with scalable computing resources in the cloud. In addition to the three giants, a lot of domestic and foreign companies have similar offers. Therefore, it was a natural desire for us to compare our four-processor configuration with the EC2 proposal.
It should be noted that the Russian services have several undeniable advantages. Their prices are not tied to hard currency, you will not lose access to your data in the event of another round of sanctions war, and most importantly, our companies use a prepaid payment plan, although legal entities can also pay monthly bills. Major Western providers, even with individuals, work on a postpaid basis and require a bank card to be linked to an account. If any villain hijacks your account, serious debts may arise, such precedents have already been .
The registration process itself, for example, in AWS is also quite complicated - the practice of collecting debt from individuals in Russia does not work well in practice, so your account will most likely be immediately blocked, ostensibly due to problems with the payment method (this does not interfere with $ 1 ). Then you will have to contact support and send a bunch of additional information to the provider (paid utility bills, etc.).
To allocate quotas for resources in each data center, Amazon will also have to create a support request and wait about a day. If your support is paid, the speed of the request may increase, but we did not check this point. Basic free plan allows you only to request limits and solve billing related issues:

Virtual machine configurations:
Atlex (Czech Republic, Prague):
Amazon EC2 (instance type: t2.xlarge; data center: US East (Ohio), us-east-2b):
The configurations are not completely identical, but in Amazon EC2, instances can only be created from ready-made templates, and we could not find closer options with four vCPUs. Since we did not use 8 GB of RAM in the testing process, the difference in the amount of RAM did not affect the result. Amazon has data centers in Europe, but since we mainly check the computing power and performance of the disk subsystem, the location of the virtual server is also not critical.
First, we check the availability of both virtual machines from the Russian-speaking segment of the global network - for the purity of the experiment, we will check from another virtual server running in external to both experimental St. Petersburg data centers. With the help of the ping utility, we will look at the response time of hosts at a message size of 64 bytes and 1 kilobyte (we send 100 packets). The response time of the Atlex virtual machine was 48.328 milliseconds and 48.436 milliseconds, respectively; no packets were harmed during transmission (0% loss). For the machine Amazon EC2 in the data center of Ohio - 126,748 and 126,846. For the purity of the experiment, we created another machine in the Amazon data center in Frankfurt, and there the response time was 46.005 and 46.1 milliseconds. That is, we have almost the same indicators in the Czech Republic and in AWS in Germany.
The popular package conducts more than two dozen tests, divided into several categories: Cryptography, Integer, Floating Point, Memory. Compression operations, work with JPEG, parsing HTML, SQLite are used. This is one of the most comprehensive tests for Windows, although it does not cover the disk subsystem (for this, we used CristalDiskMark). There were no surprises with our virtual machine, the test showed the expected performance:
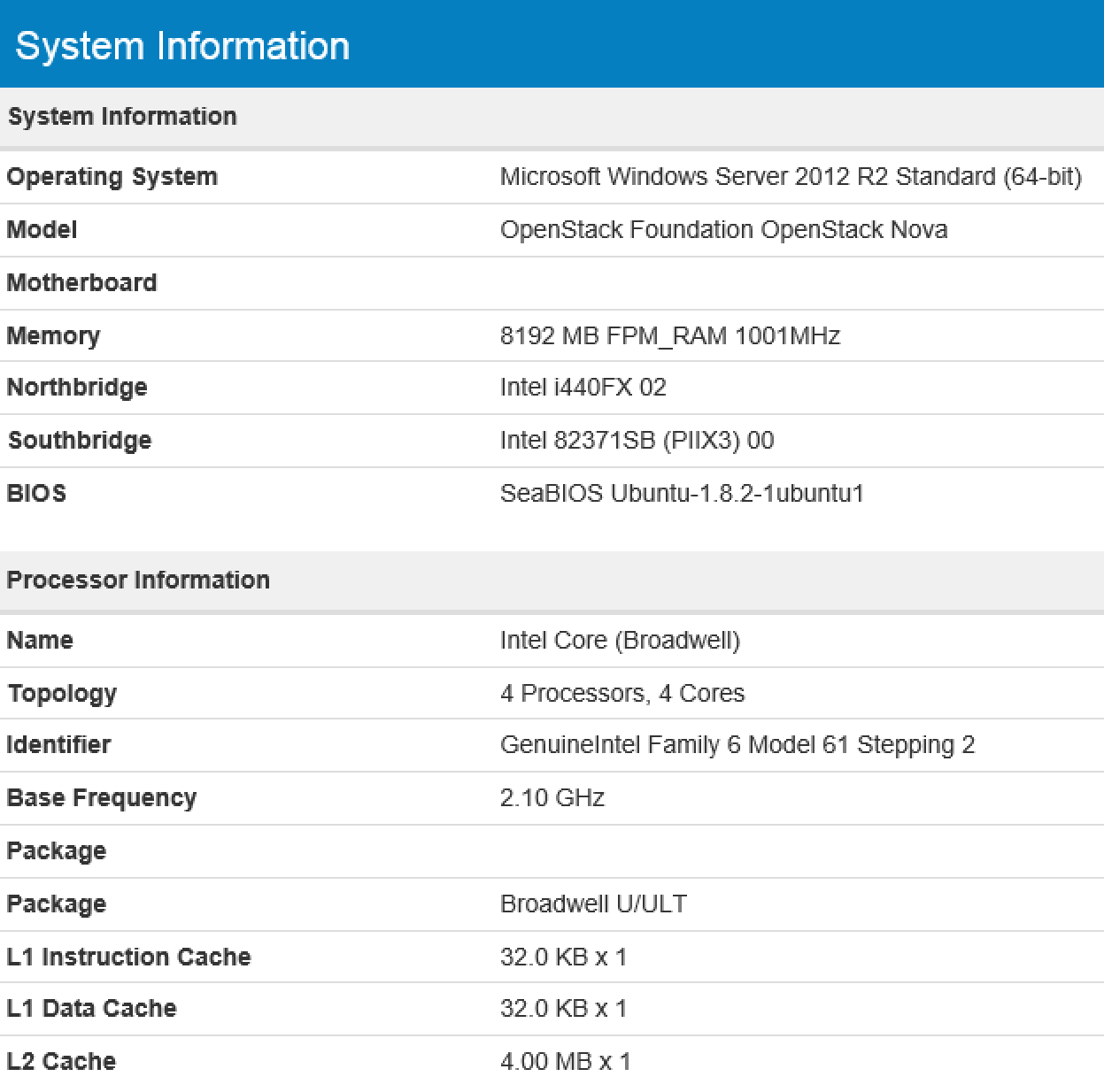

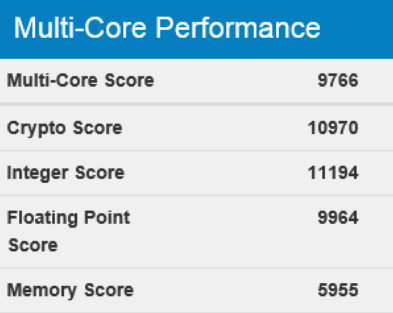
With the Amazon EC2 virtual machine, everything turned out to be much more interesting. The properties of this type of instances indicate a Broadwell processor, but GeekBench persistently showed us Haswell:
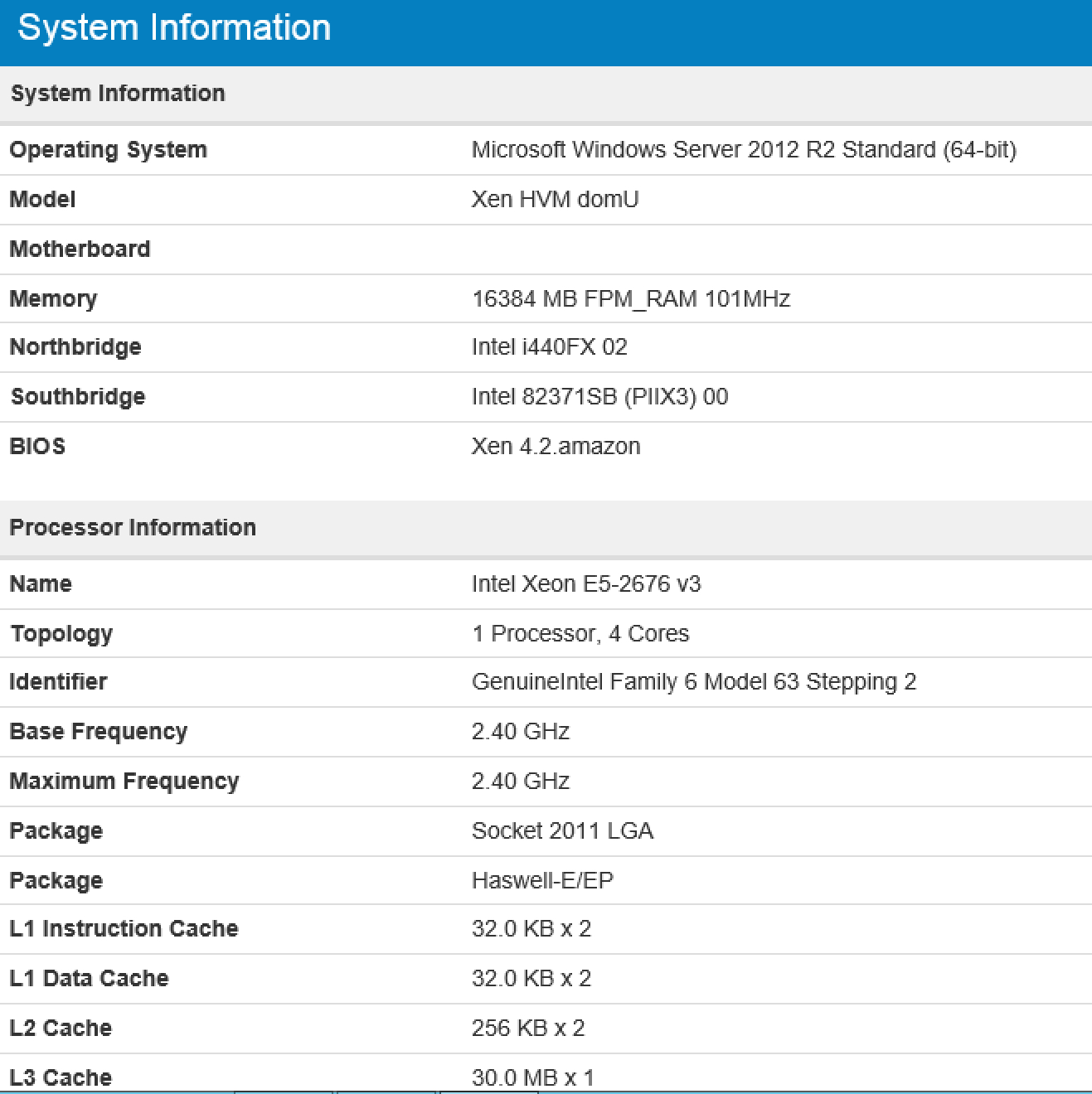
They differ only in technical process. Therefore, for us, as third-party customers, the difference in the end is not fundamental.

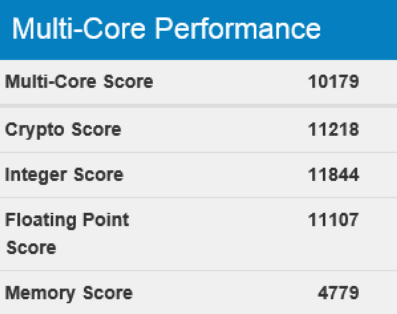
Unfortunately, we did not manage to pick up a complete analog among the four-processor configurations of the Amazon EC2 instances, but the machines turned out to be quite close. Including the results.
This popular benchmark performs sequential and random write / read tests with a queue depth of 1, 8, and 32. The screenshots speak for themselves — despite the use of solid-state drives in the storage of both configurations, the disk subsystem of our virtual machine is much faster. In fact, the threshold is even higher, and the test program could not reach it, while there is load balancing - different clients will not interfere with each other:
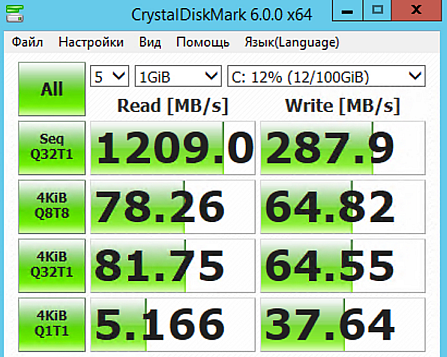
General Purpose SSD from Amazon EC2 showed at times more modest results:

To assess the performance of Microsoft SQL Server 2017, we used the TPC-H test , which is considered one of the industry standards - it is actively used by the DBMS developers themselves. The test is a set of business-oriented flexible queries and data modification performed in parallel. It illustrates the work of decision support systems that analyze large amounts of data, fulfill queries of a high degree of complexity, and provide answers to critical business questions. We didn’t observe all the TPC-H specifications completely, because it’s too complicated - there are more than one and a half hundred pages of fine text in pdf. To simplify the testing process, we downloaded the free version of the Benchmark Factory for Databases program. TPC-H assumes the generation of eight tables using a given scale factor. In our case, it is equal to 1, and the base volume was 1.54 GB (1.18 GB occupied the tables and 364.96 MB — indices).
The test consists of 22 SQL queries of varying degrees of complexity that perform four virtual users three times in a circle (a total of 264 SQL queries). A pleasant surprise in the latest version of Benchmark Factory for Databases was the ability to generate test data and load them into the database. Previously, you had to download the dbgen utility source files from the TPC and build them under Windows in Visual Studio. In this test, too, everything went without surprises.
Atlex cloud server:
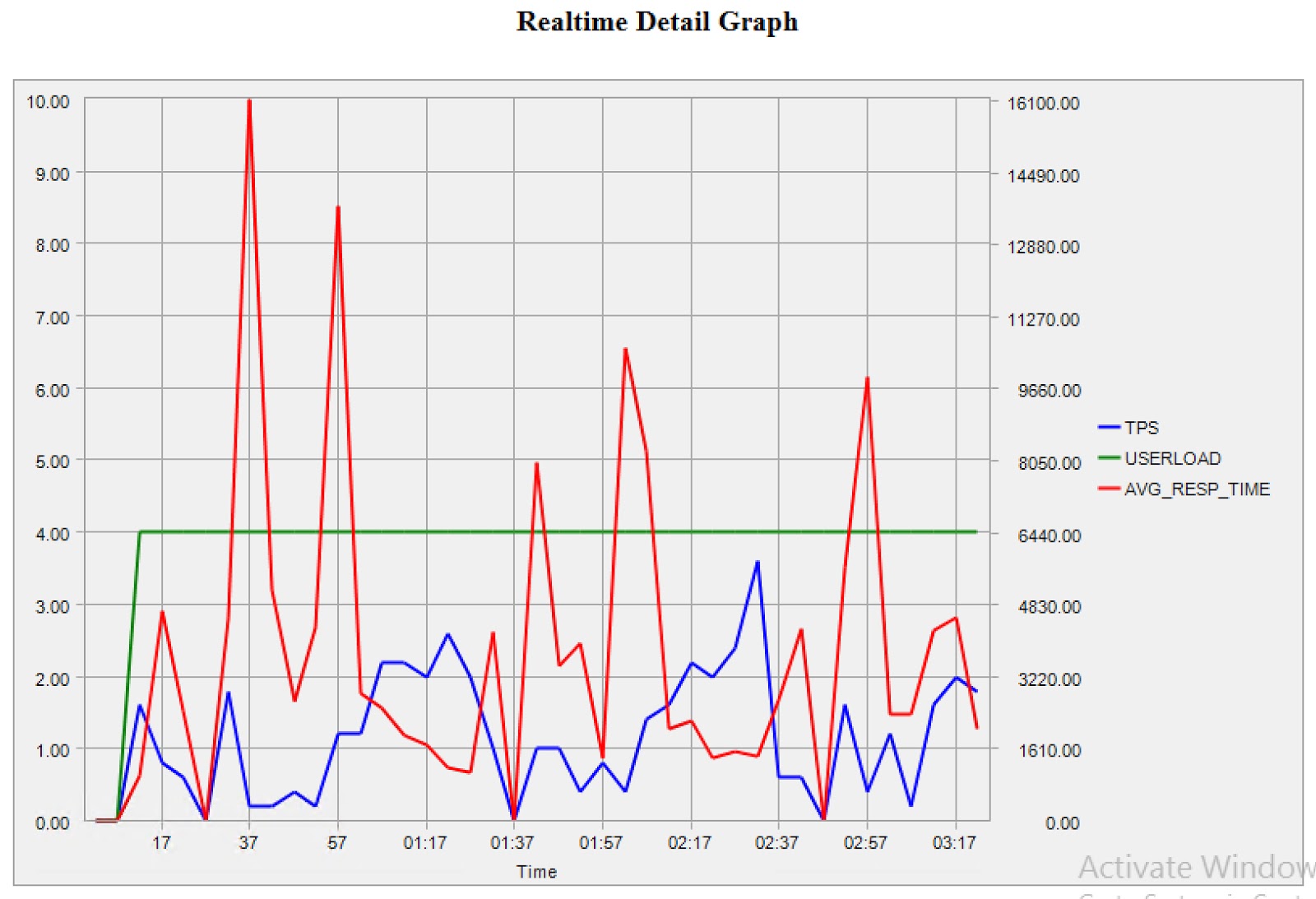
Amazon EC2 Cloud Server:
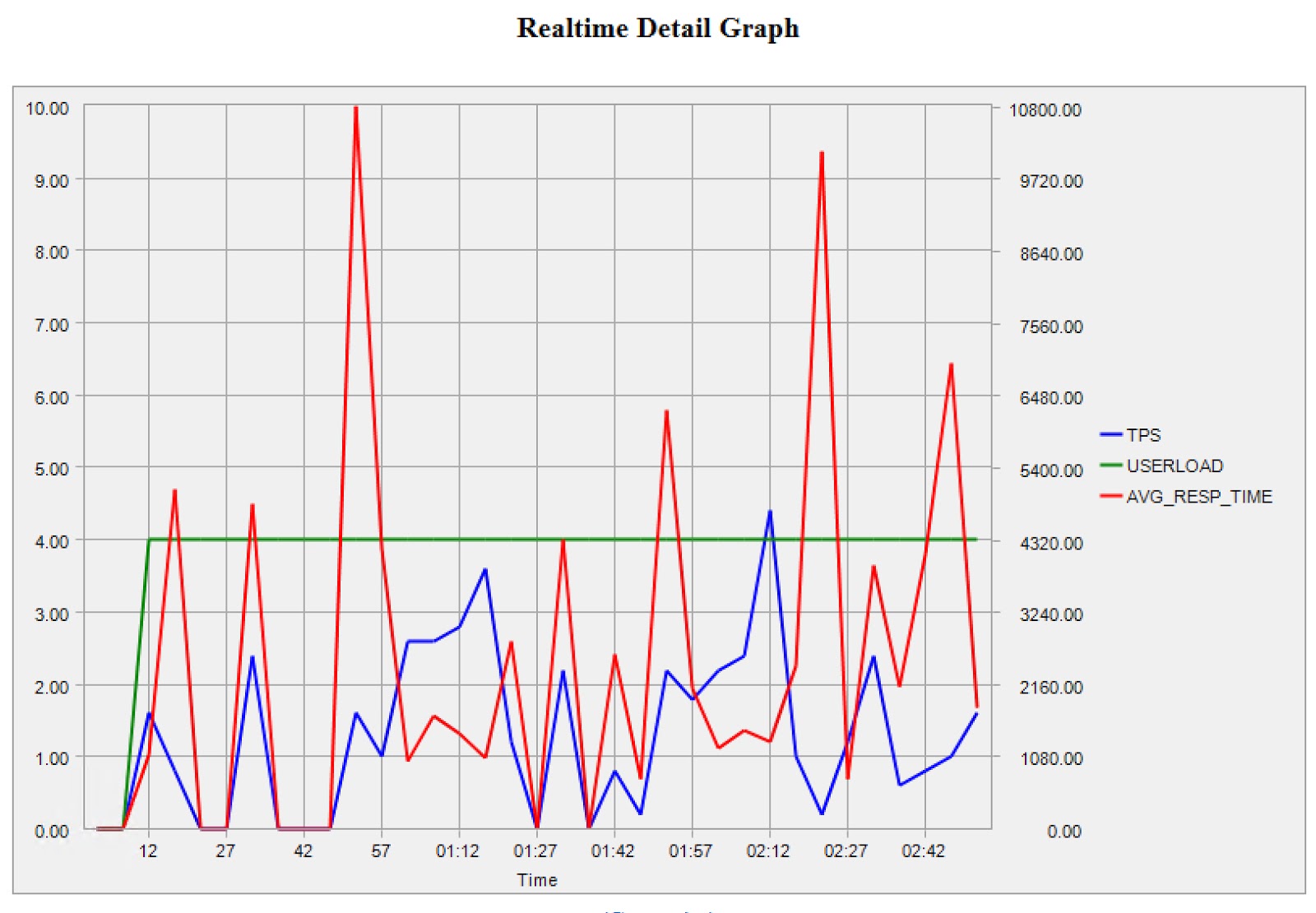
Do not be surprised at the discrepancy between the total test run time and the average response time multiplied by the number of requests: four users execute requests at the same time, so this is quite natural.
Amazon EC2 price list can be found here . Pricing can be quite different depending on the type of cloud virtual server - for short-term testing, we used on-demand instances , but there are other options if you are ready, for example, to reserve resources for a year right away or to dispose of free computing resources on Amazon EC2. A virtual cloud server t2.xlarge with Windows will cost the user $ 0.2266 per hour of work + tax (all prices in the price list do not include taxes and fees). If the machine is working for a month (~ 720 hours), the user will pay about $ 163.15 without tax - the exact amount can not be calculated, because in months a different number of days. The usage fee for EC2 instances is charged in one second increments, and the minimum usage period is 60 seconds. Similarly, charges for dedicated storage for EBS SSD (gp2) volumes will be charged on a per-second basis with a minimum usage period of 60 seconds. 1 GB of storage in a data center in Ohio costs $ 0.10 per month ($ 10 without tax per 100 GB), but there is also a payment scheme with dedicated IOPS.
Our virtual server will cost the customer 4208 rubles per month of work, or approximately 5.56 rubles (around $ 0.1) per hour. The tests were based on the standard Intel Xeon E5-2620v4 processor, but we recently added new processors with higher performance (3.8 GHz clock speed) for databases.
Both cars showed very close results. Despite the fact that the Amazon EC2 instance has the results of computational tests, it was formally slightly better, we go around them several times in disk operations. The main conclusion is obvious: although our service cannot with the world's largest cloud providers in terms of the number of services offered to customers, it is quite competitive in quality in its narrow niche. Well, for the price we go around them more than doubled.

Details under the cut.
Cloud "instansy" differ from traditional VPS by the absence of the need to pay a monthly fee immediately after a month. Such a virtual machine works just like a taxi - the counter ticks as it travels. You will have to pay some amount for simple, because even the machine that is turned off uses storage capacities. It is much cheaper and more convenient to pay for actually consumed computing resources if there is no constant need for them. Developers and testers can save a lot of money, and even the owners of the corporate IT infrastructure can shut down unnecessary servers, say, during non-working hours or upon completion of a project. In the cloud, you can quickly increase resources (add a processor or another, increase the amount of RAM), if the load has increased, or discard excess when the need for them disappears. Solid benefits: it does not need to buy hardware and licenses for the operating system. The server goes up in a couple of minutes via the web interface and is paid for what is called on-demand.
')
General issues
Amazon has become a pioneer in this market with its Amazon Web Services (AWS). Then came the Microsoft Corporation with the Azure platform and the Google Cloud Platform already appeared - this trio grabbed a significant part of the market, but Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) has long been synonymous with scalable computing resources in the cloud. In addition to the three giants, a lot of domestic and foreign companies have similar offers. Therefore, it was a natural desire for us to compare our four-processor configuration with the EC2 proposal.
It should be noted that the Russian services have several undeniable advantages. Their prices are not tied to hard currency, you will not lose access to your data in the event of another round of sanctions war, and most importantly, our companies use a prepaid payment plan, although legal entities can also pay monthly bills. Major Western providers, even with individuals, work on a postpaid basis and require a bank card to be linked to an account. If any villain hijacks your account, serious debts may arise, such precedents have already been .
The registration process itself, for example, in AWS is also quite complicated - the practice of collecting debt from individuals in Russia does not work well in practice, so your account will most likely be immediately blocked, ostensibly due to problems with the payment method (this does not interfere with $ 1 ). Then you will have to contact support and send a bunch of additional information to the provider (paid utility bills, etc.).

To allocate quotas for resources in each data center, Amazon will also have to create a support request and wait about a day. If your support is paid, the speed of the request may increase, but we did not check this point. Basic free plan allows you only to request limits and solve billing related issues:

Tests
Virtual machine configurations:
Atlex (Czech Republic, Prague):
- 4 Intel Xeon E5-2620v4 vCPUs (Broadwell U / ULT) with a clock frequency of 2.1 GHz;
- 8 GB of RAM;
- 100 GB SSD drive;
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard;
- OpenStack (KVM).
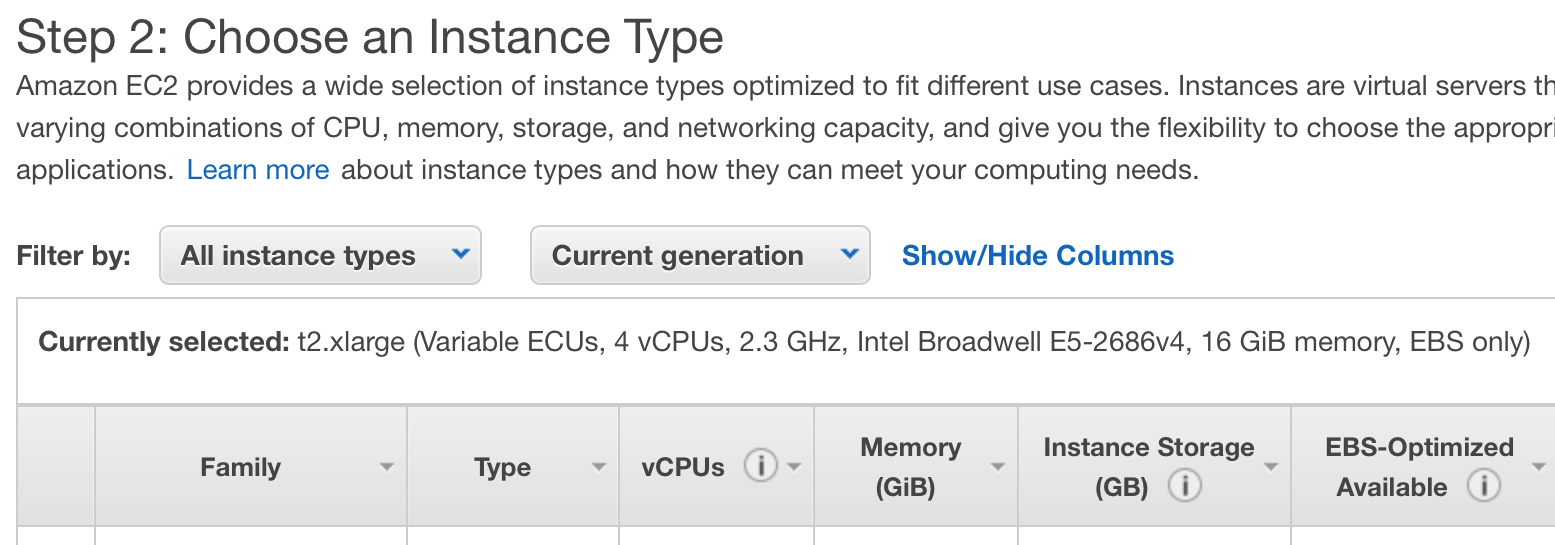
Amazon EC2 (instance type: t2.xlarge; data center: US East (Ohio), us-east-2b):
- 4 Intel Broadwell E5-2686v4 vCPUs with a clock frequency of 2.3 GHz
- 16 GB of RAM;
- 100 GB SSD drive;
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standart;
- Xen HVM DomU.
The configurations are not completely identical, but in Amazon EC2, instances can only be created from ready-made templates, and we could not find closer options with four vCPUs. Since we did not use 8 GB of RAM in the testing process, the difference in the amount of RAM did not affect the result. Amazon has data centers in Europe, but since we mainly check the computing power and performance of the disk subsystem, the location of the virtual server is also not critical.
Ping
First, we check the availability of both virtual machines from the Russian-speaking segment of the global network - for the purity of the experiment, we will check from another virtual server running in external to both experimental St. Petersburg data centers. With the help of the ping utility, we will look at the response time of hosts at a message size of 64 bytes and 1 kilobyte (we send 100 packets). The response time of the Atlex virtual machine was 48.328 milliseconds and 48.436 milliseconds, respectively; no packets were harmed during transmission (0% loss). For the machine Amazon EC2 in the data center of Ohio - 126,748 and 126,846. For the purity of the experiment, we created another machine in the Amazon data center in Frankfurt, and there the response time was 46.005 and 46.1 milliseconds. That is, we have almost the same indicators in the Czech Republic and in AWS in Germany.
Geekbench 4
The popular package conducts more than two dozen tests, divided into several categories: Cryptography, Integer, Floating Point, Memory. Compression operations, work with JPEG, parsing HTML, SQLite are used. This is one of the most comprehensive tests for Windows, although it does not cover the disk subsystem (for this, we used CristalDiskMark). There were no surprises with our virtual machine, the test showed the expected performance:



With the Amazon EC2 virtual machine, everything turned out to be much more interesting. The properties of this type of instances indicate a Broadwell processor, but GeekBench persistently showed us Haswell:


They differ only in technical process. Therefore, for us, as third-party customers, the difference in the end is not fundamental.


Unfortunately, we did not manage to pick up a complete analog among the four-processor configurations of the Amazon EC2 instances, but the machines turned out to be quite close. Including the results.
CrystalDiskMark 6
This popular benchmark performs sequential and random write / read tests with a queue depth of 1, 8, and 32. The screenshots speak for themselves — despite the use of solid-state drives in the storage of both configurations, the disk subsystem of our virtual machine is much faster. In fact, the threshold is even higher, and the test program could not reach it, while there is load balancing - different clients will not interfere with each other:

General Purpose SSD from Amazon EC2 showed at times more modest results:

Tests with Microsoft SQL
To assess the performance of Microsoft SQL Server 2017, we used the TPC-H test , which is considered one of the industry standards - it is actively used by the DBMS developers themselves. The test is a set of business-oriented flexible queries and data modification performed in parallel. It illustrates the work of decision support systems that analyze large amounts of data, fulfill queries of a high degree of complexity, and provide answers to critical business questions. We didn’t observe all the TPC-H specifications completely, because it’s too complicated - there are more than one and a half hundred pages of fine text in pdf. To simplify the testing process, we downloaded the free version of the Benchmark Factory for Databases program. TPC-H assumes the generation of eight tables using a given scale factor. In our case, it is equal to 1, and the base volume was 1.54 GB (1.18 GB occupied the tables and 364.96 MB — indices).
The test consists of 22 SQL queries of varying degrees of complexity that perform four virtual users three times in a circle (a total of 264 SQL queries). A pleasant surprise in the latest version of Benchmark Factory for Databases was the ability to generate test data and load them into the database. Previously, you had to download the dbgen utility source files from the TPC and build them under Windows in Visual Studio. In this test, too, everything went without surprises.
Atlex cloud server:
| Transactions per second | Average response time (s) | Average Transaction Time | Number of transactions | Test run time | Total rows |
| 1,313 | 3,030 | 3.040 | 264 | 3 minutes 27 seconds | 11616 |

Amazon EC2 Cloud Server:
| Transactions per second | Average response time (s) | Average Transaction Time | Number of transactions | Test run time | Total rows |
| 1,542 | 2,586 | 2,591 | 264 | 2 minutes 57 seconds | 11532 |

Do not be surprised at the discrepancy between the total test run time and the average response time multiplied by the number of requests: four users execute requests at the same time, so this is quite natural.
Price tag
Amazon EC2 price list can be found here . Pricing can be quite different depending on the type of cloud virtual server - for short-term testing, we used on-demand instances , but there are other options if you are ready, for example, to reserve resources for a year right away or to dispose of free computing resources on Amazon EC2. A virtual cloud server t2.xlarge with Windows will cost the user $ 0.2266 per hour of work + tax (all prices in the price list do not include taxes and fees). If the machine is working for a month (~ 720 hours), the user will pay about $ 163.15 without tax - the exact amount can not be calculated, because in months a different number of days. The usage fee for EC2 instances is charged in one second increments, and the minimum usage period is 60 seconds. Similarly, charges for dedicated storage for EBS SSD (gp2) volumes will be charged on a per-second basis with a minimum usage period of 60 seconds. 1 GB of storage in a data center in Ohio costs $ 0.10 per month ($ 10 without tax per 100 GB), but there is also a payment scheme with dedicated IOPS.
Our virtual server will cost the customer 4208 rubles per month of work, or approximately 5.56 rubles (around $ 0.1) per hour. The tests were based on the standard Intel Xeon E5-2620v4 processor, but we recently added new processors with higher performance (3.8 GHz clock speed) for databases.
Results and conclusions
Both cars showed very close results. Despite the fact that the Amazon EC2 instance has the results of computational tests, it was formally slightly better, we go around them several times in disk operations. The main conclusion is obvious: although our service cannot with the world's largest cloud providers in terms of the number of services offered to customers, it is quite competitive in quality in its narrow niche. Well, for the price we go around them more than doubled.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/345704/
All Articles