How EdTech Leaders Earn
Freemium is automatically issued in conjunction with the concepts of "monetization model" and "MOOCs". Historically, the first EdTech platforms offered educational content for free, earning from the sale of certificates. But in 6 years, much has changed.

The evolution of monetization approaches
“In many new online markets, companies initially did not have well-developed monetization models and simply worked for rapid expansion, capturing an audience. Investors did not attach importance to whether startups receive income. It was important for them to see an aggressive growth plan and a proactive team with a serious background, ”explains this historical fact, Sergei Oparin, one of the founders of SOLventures .
MOOCs leaders - Coursera and edX achieved results by capturing huge audiences and securing popularity. However, the freemium model did not allow them to attract enough funds not only for development, but also to maintain status.
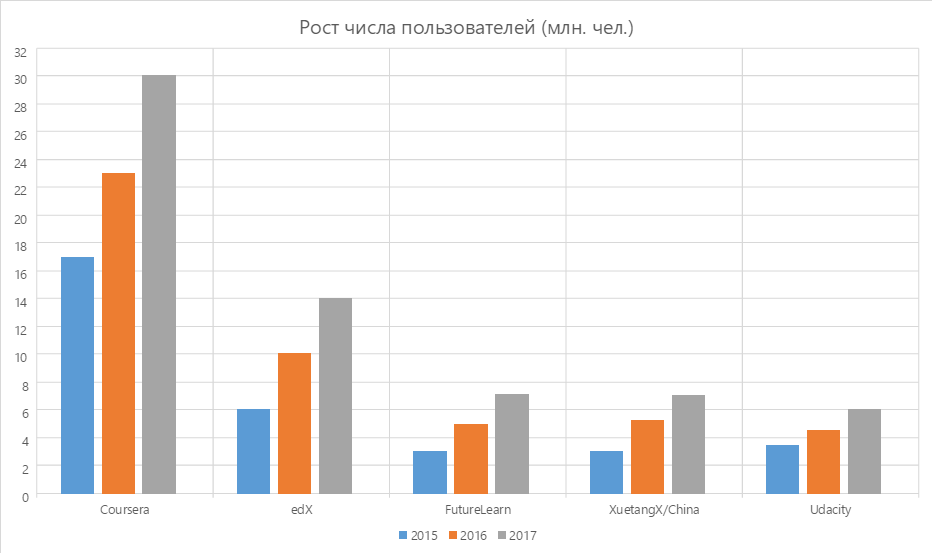
By 2014, many new players appeared on the market, including local players (for example, the Chinese XuetangX). The competition for the user has grown.
The edX creators were the first to understand this in 2014 and, while maintaining free access to training materials for short-term courses, they switched to selling paid programs (MicroMasters, Professional Certificate, XSeries). And also began to actively attract donations (crowdfunding) and grants. As a result, edX began to step on the heels of the leader.
Coursera to support development in 4 rounds attracted $ 210.3 million of investment, but this was not enough for sustainable development. The platform was not limited to attracting additional funding.
In 2015, Coursera launched a paid product - the first online MBA program. Thus, both leaders introduced direct sales of the product to end users, complementing the freemium model, and attracted funding for the funds.
They also noticed the interest of corporations and government organizations that had ripened by 2016. In response to demand, Coursera offered annual subscriptions in B2B and B2G segments, and edX offered a flexible package of educational programs for the B2B market and a paid additional recruitment service for successful online students.
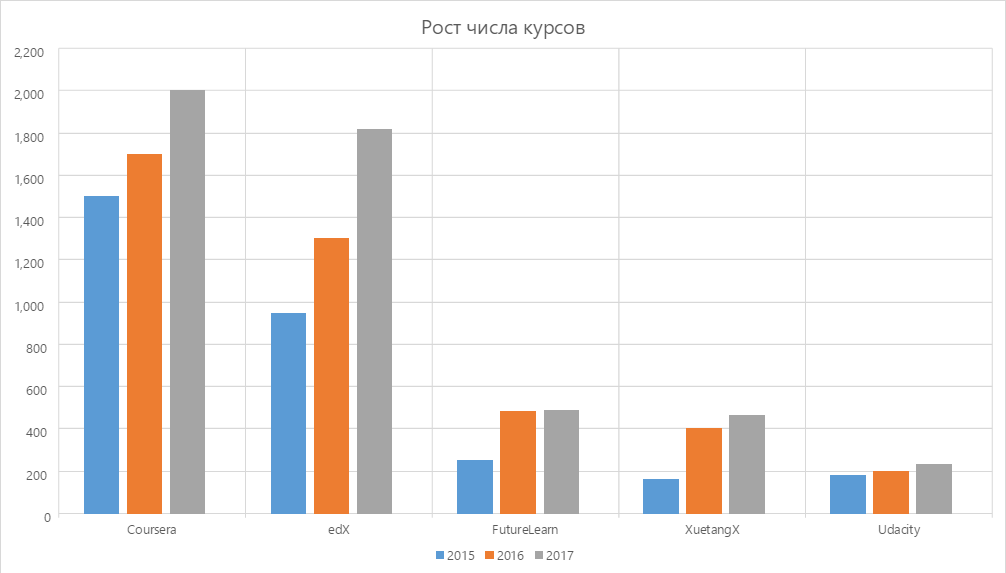
In 2017, their example was followed by the FutureLearn platform - the third in the MOOCs leaderboard. FutureLearn, by analogy with its predecessors, supplemented freemium with direct sales: it restricted free access to course content and exams, began to actively develop paid FutureLearn-programs and launched an online MBA.
Among the leaders, only Chinese XuetangX retained freemium in its pure form - today it is in 4th position among global MOOCs. The platform has several advantages compared with market players, as it is affiliated with the state.
Udacity today ranks 5th on the list of global MOOCs. The platform, like other leaders, retaining free courses, introduced paid programs Nanodegrees. In 2016, Nanodegrees were supplemented with paid services. New employment services for a loyal audience appeared on the resource - freelcing-platform for graduates. In partnership with Georgia Tech, Udacity launched a low-cost program - completely online Masters in Computer Science. Today, Udacity uses a hybrid monetization model that combines online and offline learning. Udacity offers paid courses with accompaniment, feedback, assignment testing and subsequent graduation.
Key Trends
- MOOCs market is young and just being formed. The main trend is constant change. The speed of reaction to changes is important.
- New strong local players appear, the old global ones are losing ground. So, for example, Udacity in 2016 was among the top three, and today it takes the 5th position. Chinese XuetangX has sharpened the competition in the group of leaders.
- An obvious trend is the increase in paid content on MOOCs.
- In the arsenal of MOOCs, there are different monetization models: freemium and free trial, direct sales of courses and additional paid services for all market segments, crowdfunding and grants, sponsoring corporations and state financial support. We did not mention the advertising model because we did not find it in the arsenal of MOOCs leaders and believe that it has many potential negative effects for EdTech projects: distraction from educational content, loss of audience loyalty due to the sale of personal data.
- Leaders are constantly evolving, improving monetization models. Today it is already clear that the most effective solution is an integrated approach and a combination of several models of attracting funding.
We offer you a detailed description of the evolution of leaders' approaches to monetization in case studies.
Cases
Coursera
Coursera, the world leader in MOOCs in terms of the number of courses and the number of registered users, started in January 2012. The platform was founded by two professors from Stanford. Today Coursera partners are more than 150 universities from 29 countries.
On the B2C market Coursera offers Courses (2000 short-term programs, duration 1-1.5 months), Specializations (180 medium-term programs, duration 4-6 months) and four full online MBA (1-3 years).
Coursera is active in the B2B and B2B markets, offering complex products to companies and government organizations.
How does Coursera earn? Freemium model and paid programs
Freemium model: subscription development
By 2016, new players entered the market, competition for users and investors' money became tougher. Coursera had to explore new markets, experiment and develop subscription terms for Courses and Specializations. Until 2016, users had free access to all Course materials and had to pay for grading and a certificate. In June 2016, Coursera began testing a new course subscription format. The essence of innovation is paid access to all course materials, including video. To date, only a few courses have become fully paid. In October 2016, Courser significantly reduced the cost of a subscription to Specializations (from several thousand dollars per month for subscribing to one Specialization to 39-79 dollars per month depending on the Specialization - for access to grading and obtaining a certificate).
As a result of experiments with the terms of a subscription to Courses and Specializations, not only restrictions on access to study materials and exams (freemium model) appeared, but also time limits (free trial model).
In 2016, Coursera began working in the B2B and B2G markets, realizing a one-year subscription to Courses and Specializations. oursera works with more than 50 corporate clients, incl. BCG, BNY Mellon, L'Oreal, Paypal, and Air France KLM. In the B2G market Coursera cooperates with the government organizations of the USA, Pakistan, Egypt, Malaysia, Singapore, Kazakhstan.
Paid programs
In 2015, Coursera began to develop a new segment - an online MBA, opening the first two programs. Today Coursera offers 4 fully accredited online MBA programs. Tuition per student from 19,000 to 30,000 dollars (University of Illinois) and 20,000 euros (HEC).
Coursera develops the platform’s traditional subscription monetization model and introduces new paid products. However, for the effective development of self-earned funds is not enough, therefore Coursera actively attracts investment.
In total, over 6 years in 4 rounds, Coursera raised $ 210.3 million, of which $ 64 million in 2017. The platform has traditionally been supported by GSV Asset Management, New Enterprise Associates (NEA), Kleiner Perkins Caufield Byers (KPCB) and Learn Capital. The new investment partner in 2017 was the Lampert Foundation.
edX
edX is a non-profit organization founded in 2012 by Harvard and Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It occupies the 2nd place among the global players in the MOOCs market and cooperates with 109 partners.
On the B2C market, edX offers Courses (1,819 short courses in selected disciplines, duration 1-2 months) and Programs (43 MicroMasters, 35 Professional Certificate, 32 XSeries). The training materials of most Courses are available free of charge, paying from 49 to 150 dollars for a Certificate.
Since 2014, edX was the first to switch to the implementation of paid programs. Some programs are available on credit. MicroMasters (750-1500 dollars, duration 10-12 months) are developed mainly with leading universities and allow students to continue their studies at the MBA of a university developer. Professional Certificate developed by leading corporations (Microsoft, Linux, GE and others). Cost from 300 to 800 dollars, duration - 2-8 months. XSeries - developed by well-known, recognized in their field experts, provide a deep understanding of the relevant subject areas. The cost of 300 dollars, the duration of 6-18 months.
edX is active in the B2B market, offering companies a comprehensive product for employee development.
How does edX earn?
According to the official version, edX uses 2 models:
Self Serve Model
edX receive the first $ 50,000 from the sale of the course, or $ 10,000 for each repeated course. A partner — a company or a university — gets 50 percent of all profits that exceed this threshold.
Supported Model
edX charges $ 250,000 for each new course, and also receives $ 50,000 each time a course is posted for a new period. The partner receives 70 percent of the revenue generated from the sale of the course.
Additionally, edX uses several more monetization models.
On the company's website you can find the Donate section - “Donate”. Users are invited to make a target donation from 25 to 250 dollars. Probably, this source brings a small income, but the section is valuable as a tool for obtaining feedback from students.
Grants are another edX revenue item. For example, in October 2016, the Lumina Foundation gave edX a grant of $ 900,000 for the development of 30 MicroMasters. A related service training service is the recruitment of employees from among the successfully completed specialized courses for a partner company. Companies are actively using edX for Business to train and recruit employees.
FutureLearn
FutureLearn ranks 3rd among global MOOCs in terms of the number of registered users and the number of courses. The platform was founded by Open University in 2013. FutureLearn collaborates with 139 partners, including more than 70 European universities.
The platform offers adult users 462 courses (2-6 weeks, cost from $ 44 to $ 100), 4 courses for schoolchildren and 23 FutureLearn Programs (3-14 months, $ 450-1500, analogue of CourseX Specializations or XSeries from edX). Some programs provide for an assessment at the end of their knowledge, and students who successfully complete the assessment will receive an “Award”. Some of the programs allow students to get a university loan, others offer to continue their studies on accredited Continuing Professional Development (CPD) programs.
Since 2017, FutureLearn has introduced a new pricing model that restricts access to content and exams. Prior to this, the fee was charged only for the certificate, and study materials and exams were completely free. In 2017, FutureLearn launched 8 full online master programs (full post-graduate degrees). 1 MBA program in partnership with Coventry University and 7 programs in partnership with Australian Deakin University Master's degree is about 20,000 Australian dollars, certificate of completion of the program or diploma costs about 9,000 Australian dollars. For some master programs there is a possibility of free testing for 2-3 weeks.
FutureLearn works only on the B2C market, offering short, medium and long term training programs. FutureLearn Programs and post-graduate are fully paid, course materials (short-term programs) are available for free. In 2017, FutureLearn was the last of the leaders to follow a general trend in the development of approaches to monetization: it refused to completely free access to content and expanded the line of paid products by introducing online long-term full masters programs.
XuetangX / China
XuetangX - the first and largest MOOC platform in China - ranks 4th among global leaders in terms of the number of courses and the number of registered users.
The platform was founded in October 2013 by Tsinghua University under the supervision of the Chinese Ministry of Education (China Ministry of Education Research). Tsinghua Holdings Co., Ltd. invested in MOOC-CN Information Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd., which manages XuetangX.
XuetangX is one of the fastest growing platforms: more than 460 courses. 133 unique courses designed for XuetangX. About 30 courses obtained under license from edX, the rest - courses of partner universities. In 2017, 63 courses were released. XuetangX partner universities recognize courses hosted on the platform. Among all courses, 42 are considered by universities as programmatic and are recommended to students as elective courses. University students track student progress through an individual ID, which a student enters when entering a resource.
XuetangX plans to develop the MicroDegree Program, which integrates university courses, industry courses developed by leading companies, and project work. At the end of the program, successfully completed students receive a certificate and recommendations to well-known companies. XuetangX is active in all markets: B2C, B2B and B2G. All courses and programs on the platform are free.
Udacity
Udacity today ranks 5th on the list of global MOOCs. The resource is based on Stanford instructors Peter Norvig and Sebastian Trun. Today, Udacity works with more than 100 partners from 60 countries of the world.
On the platform, free-of-charge training materials are available for 213 courses (lasting 1-3 months), but Udacity has not remained fully committed to the freemium model. Offering Nanodegrees (duration 6-12 months), the project specializes in preparing students for some specialties - professions of the future.
In 2016, 6 new ones appeared and by the end of the year there were 12 Nanodegrees (the platform as a result of the audit closed several programs), now the platform offers 22 Nanodegrees. Innovation has become paid services. New employment services for a loyal audience appeared on the resource - freelcing-platform for graduates.
In partnership with Georgia Tech, Udacity launched a low-cost program - completely online Masters in Computer Science ($ 6,600).
Udacity works in the B2B segment, offering corporate clients 2 virtual training, as well as corporate development programs and the ability to attract new employees from among the Udacity students.
Udacity is supported by such corporate partners as: IBM Watson, Mercedes Benz, BMW, McLaren, Google, Bosch and others. Udacity recently introduced a hybrid model that combines online and offline training. The platform offers paid courses with accompaniment, feedback, verification of tasks and the subsequent receipt of diplomas. These courses are created on the money of companies interested in highly qualified personnel.
For those who want to pump English!
We invite readers of the blog to participate in our New Year campaign: a gift from our partners is attached to any product - subscriptions to WIKIUM, MEGOGO, HTML-academy! Choose yourself and your loved ones New Year's gifts .
Materials
In preparing the article used materials sites and blogs Corsera, edX, FutureLearn, XuetangX, Udacity. As well as Forbes , Class Central , Medium , Edsurge .
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/345550/
All Articles