Creating a blockchain application for an insurance company using IBM's Hyperledger Fabric
Due to the distributed registry, smart contracts and the impossibility of refutation, blockchain technology revolutionizes the way financial institutions operate, and the insurance industry is no exception. IBM has developed a pattern that allows you to create blockchain applications to simplify insurance processing and processing claims for insurance payments.
Most of us found ourselves in such a situation: a minor accident occurred, we are already terrified of how much time and effort we now have to spend on the proceedings with the insurance company, the police and another participating driver. Even if the case is moving fast enough, all the same, all this greatly violates your plans.
And what if you, as a developer, could turn everything around and completely change the insurance industry? What if you can improve not only personal experience, but also the experience of millions of other people around the world who are facing the same inconveniences, delays and violation of plans?
Blockchain provides the most extensive opportunities for the insurance industry. It gives a chance to update the process of data exchange, processing claims for insurance payment and protection against fraudulent activities. Blockchain can bring together developers from technology companies, regulators and insurance companies to co-create a new valuable asset of insurance management.
')
Due to its distributed registry, smart contracts and the impossibility of refutation, which work as a common infrastructure, the blockchain can transform all types of insurance processes. Currently, many insurance processes are performed manually, are not immune to errors, and take a lot of time. Often the same data in multiple registration systems have different versions, which leads to additional costs and lengthy disputes.
With the help of the blockchain, manual processes are automated by distributing information about the program participants, the conditions for receiving payments and the data specified in the applications for receiving insurance payments. Smart contracts are computer coded in accordance with the rules for registering and checking the credentials of participants. The commonality of data and the computerization of smart contracts reduce the number of subsequent disputes. Checking the size of insurance payments is based on data from several sources that are clearly available to all service providers.
The main point is that the blockchain technology provides the insurance industry with a chance to increase the efficiency of its operations, reduce transaction processing costs, improve customer service, improve data quality and increase trust between the parties.
Attached - four participants or a feast:
The Insurer's Feast is a company that insures a product (for example, a car) and is responsible for processing the claim for insurance payment. The Police Feast is responsible for verifying the allegations of an accident or theft. The auto repair shop is responsible for the product repair. Pir Store sells the product to the consumer.
How does the application actually work? Imagine that Suzy, who is actively involved in sports, decides that she wants to buy a new bike. She goes to the bike shop and finds there an amazing discount on a road bike. In the process of buying, she is offered to conclude an insurance contract, and she agrees that such an agreement is relevant for her. She signs it, specifying her personal data and the dates of commencement and expiration of the contract. The daily rate is calculated by the formula in the chatcode when processing the contract. When all the paperwork is finished, Suzy will give out the user's details, and she can register at any time when she needs to apply for an insurance payment. At this time, a block of transaction is recorded in the blockchain.
And as if on purpose, ten days later, Susie’s bike was stolen. After informing the police about the theft, she opens the self-service panel in the application, registers, describes the theft and registers her appeal to the insurance company. When she submits an application, it is recorded in a blockchain chain as a separate transaction. First, the application is processed by the police, which must either confirm or not confirm the fact of theft. In the event that the theft is confirmed, the police attach the appropriate number of the theft case, and another block is recorded in the chain. (Similarly, if Suzy registered a statement about an accident involving a bicycle, as a result of which the bicycle was damaged, instead of the police, an auto repair shop would deal with the application). The insurance company monitors all active claims for insurance payments on the blockchain, so that when the police give their confirmation, the company receives such confirmation and pays compensation for the appeal. In the same way as in the case of previous transactions, the payment of compensation is recorded in the blockchain. Suzy is happy to see that the insurance company has paid her a refund - although not as much as she would have been happy if she had her bike returned!
Please note that the insurance company has the ability to block and unlock certain contracts. This does not mean that contracts already signed by customers are no longer valid; locking simply does not allow entering into new contracts of this type. In addition, the insurance company can create new model contracts with different conditions and terms or with different price structures.
The figure shows an example of a blockchain application using IBM's Hyperledger Fabric technology.
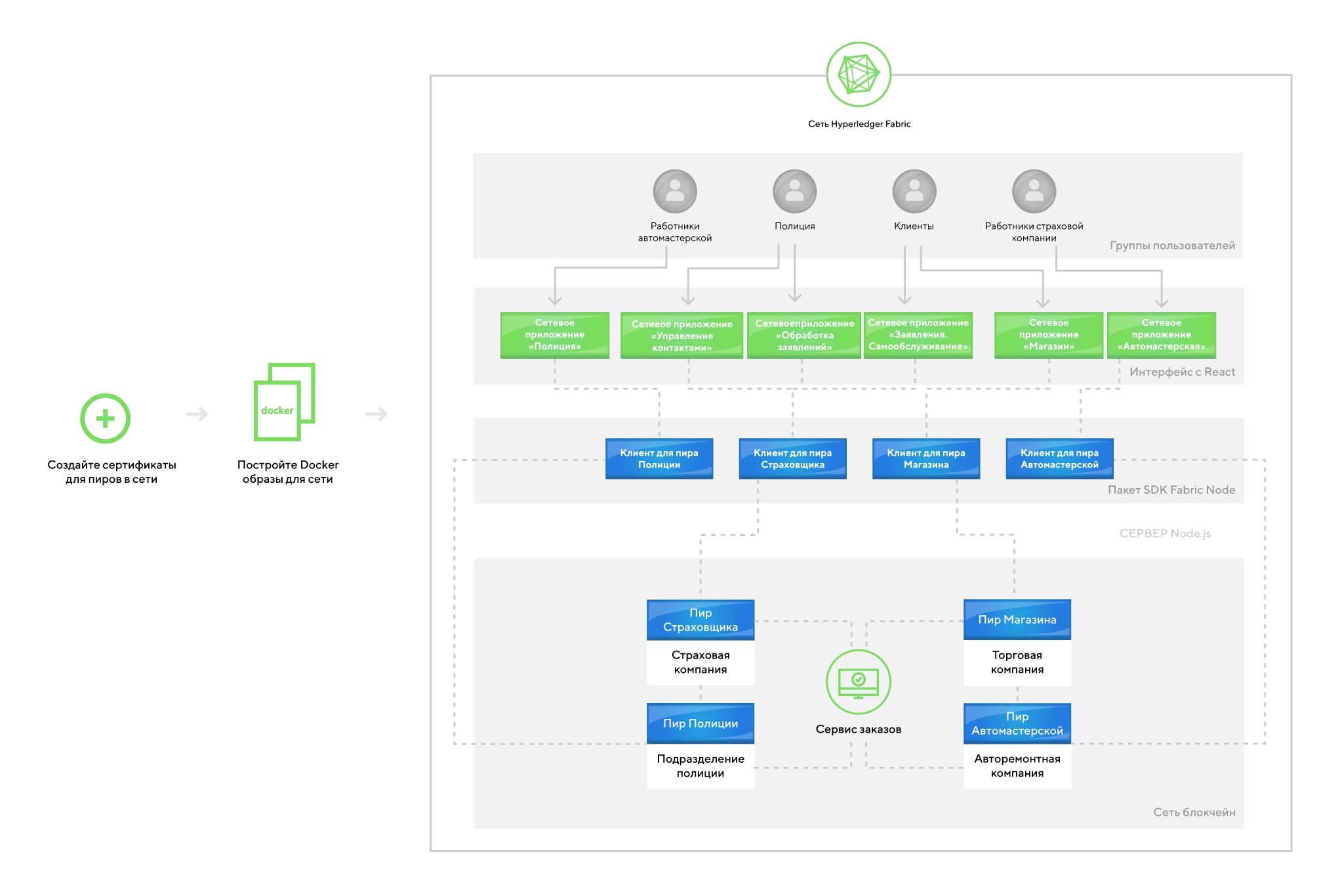
A source
Most of us found ourselves in such a situation: a minor accident occurred, we are already terrified of how much time and effort we now have to spend on the proceedings with the insurance company, the police and another participating driver. Even if the case is moving fast enough, all the same, all this greatly violates your plans.
And what if you, as a developer, could turn everything around and completely change the insurance industry? What if you can improve not only personal experience, but also the experience of millions of other people around the world who are facing the same inconveniences, delays and violation of plans?
How blockchain application changes the insurance industry
Blockchain provides the most extensive opportunities for the insurance industry. It gives a chance to update the process of data exchange, processing claims for insurance payment and protection against fraudulent activities. Blockchain can bring together developers from technology companies, regulators and insurance companies to co-create a new valuable asset of insurance management.
')
Due to its distributed registry, smart contracts and the impossibility of refutation, which work as a common infrastructure, the blockchain can transform all types of insurance processes. Currently, many insurance processes are performed manually, are not immune to errors, and take a lot of time. Often the same data in multiple registration systems have different versions, which leads to additional costs and lengthy disputes.
With the help of the blockchain, manual processes are automated by distributing information about the program participants, the conditions for receiving payments and the data specified in the applications for receiving insurance payments. Smart contracts are computer coded in accordance with the rules for registering and checking the credentials of participants. The commonality of data and the computerization of smart contracts reduce the number of subsequent disputes. Checking the size of insurance payments is based on data from several sources that are clearly available to all service providers.
The main point is that the blockchain technology provides the insurance industry with a chance to increase the efficiency of its operations, reduce transaction processing costs, improve customer service, improve data quality and increase trust between the parties.
An example of building a functional insurance application based on blockchain technology
Attached - four participants or a feast:
- Insurer
- Police
- Car repair shop
- Score
The Insurer's Feast is a company that insures a product (for example, a car) and is responsible for processing the claim for insurance payment. The Police Feast is responsible for verifying the allegations of an accident or theft. The auto repair shop is responsible for the product repair. Pir Store sells the product to the consumer.
How it works?
How does the application actually work? Imagine that Suzy, who is actively involved in sports, decides that she wants to buy a new bike. She goes to the bike shop and finds there an amazing discount on a road bike. In the process of buying, she is offered to conclude an insurance contract, and she agrees that such an agreement is relevant for her. She signs it, specifying her personal data and the dates of commencement and expiration of the contract. The daily rate is calculated by the formula in the chatcode when processing the contract. When all the paperwork is finished, Suzy will give out the user's details, and she can register at any time when she needs to apply for an insurance payment. At this time, a block of transaction is recorded in the blockchain.
And as if on purpose, ten days later, Susie’s bike was stolen. After informing the police about the theft, she opens the self-service panel in the application, registers, describes the theft and registers her appeal to the insurance company. When she submits an application, it is recorded in a blockchain chain as a separate transaction. First, the application is processed by the police, which must either confirm or not confirm the fact of theft. In the event that the theft is confirmed, the police attach the appropriate number of the theft case, and another block is recorded in the chain. (Similarly, if Suzy registered a statement about an accident involving a bicycle, as a result of which the bicycle was damaged, instead of the police, an auto repair shop would deal with the application). The insurance company monitors all active claims for insurance payments on the blockchain, so that when the police give their confirmation, the company receives such confirmation and pays compensation for the appeal. In the same way as in the case of previous transactions, the payment of compensation is recorded in the blockchain. Suzy is happy to see that the insurance company has paid her a refund - although not as much as she would have been happy if she had her bike returned!
Please note that the insurance company has the ability to block and unlock certain contracts. This does not mean that contracts already signed by customers are no longer valid; locking simply does not allow entering into new contracts of this type. In addition, the insurance company can create new model contracts with different conditions and terms or with different price structures.
The figure shows an example of a blockchain application using IBM's Hyperledger Fabric technology.

A source
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/345150/
All Articles