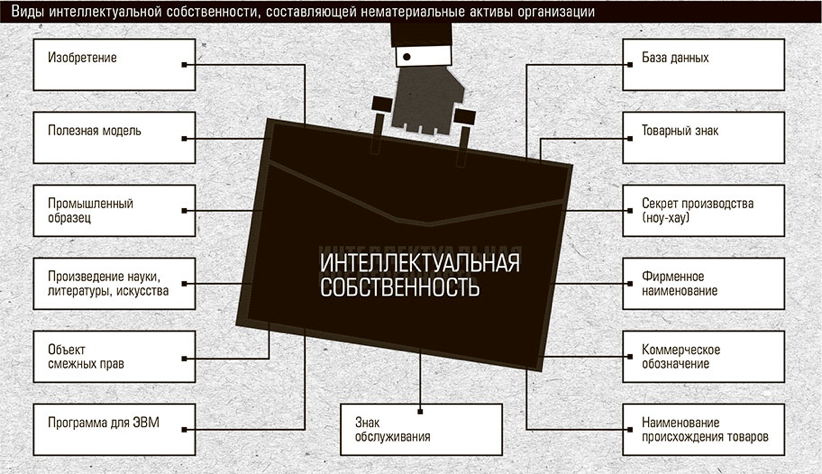
Intellectual property - intangible asset

Due to the obvious progress in the field of information technology and the general growth of the service sector, intangible assets acquire much greater value than it was years before. Enterprises are increasingly striving to efficiently use their intangible assets, which implies the need for their legal protection. Against this background, there is an increase in the commercialization of intellectual property (IP) and the investment attractiveness of IP rights, the use of exclusive rights in the fight against competitors. It is known that IP can be more than 80 percent of the value of the whole company. For example, Coca-Cola Corporation accounts for 96% of intangible assets.
')
The development of IP institutions is closely related to information security, which is a necessary condition for the development of innovations. The innovation process, as a result of which inventions are successfully introduced onto the market, is the main driving force behind the development of companies, competitiveness and economic growth in general.
Intellectual property threats
In the digital age, it became much easier to violate intellectual property rights (IP), to steal and copy IP. Cyber-theft becomes the main method of realizing such threats. At the time, as the theft of credit card data, the media speak with enviable constancy, the theft of IP objects mentioned very little. However, this does not mean that such situations are minor. In fact, the losses of the American economy due to the international theft of IP were estimated at $ 300 billion per year (according to the report of the commission on the theft of American intellectual property from 2013).
Three categories of IP theft are divided: counterfeit and pirated goods, pirated software and theft of trade secrets. Due to the division into categories, the IP Commission was able to more accurately assess the scale and cost of IP theft in the United States compared with 2013 (update of the report from 2017). For example, in 2015, fake and pirated goods imported to the United States are estimated at $ 58– $ 118 billion, while exported = $ 85 billion (updating the report of the commission on the theft of American intellectual property). But pirated software, although estimated at lower amounts, is a much bigger problem due to the ease of downloading and the presence of malicious elements.
According to US IP Coordinator Danny Marty , "advances in technology, increased mobility, rapid globalization, and the anonymous nature of the Internet are creating new challenges in protecting trade secrets." Offenders can carry out theft from anywhere in the organization and beyond, while maintaining anonymity and expanding the range of suspects. Malicious can be both former and current employees of the company, competitors, criminal and frivolous hacker groups, as well as subjects of foreign states and so on. At the same time, insider threats are one of the most frequent causes of violations. Although such threats often arise in the face of negligence and ignorance, insider threats in general are becoming an increasingly urgent problem of cyber security. Threats from competitors are caused by the assumption that the theft or purchase of stolen IP can be much faster and cheaper than developing innovation from scratch.
The remaining risks of cyber threats to IP rights include the following types of violations: unauthorized interference with databases, the creation and use of computer software tools for changing and blocking information, the dissemination of false information about the company on the network, and the illegal use of means of individualization (including trademarks).
Cost of IP Infringement
As you know, there are two types of damages from the violation of IP rights: direct costs and lost profits. In the practice of the United States there is also the term reduction of business value.
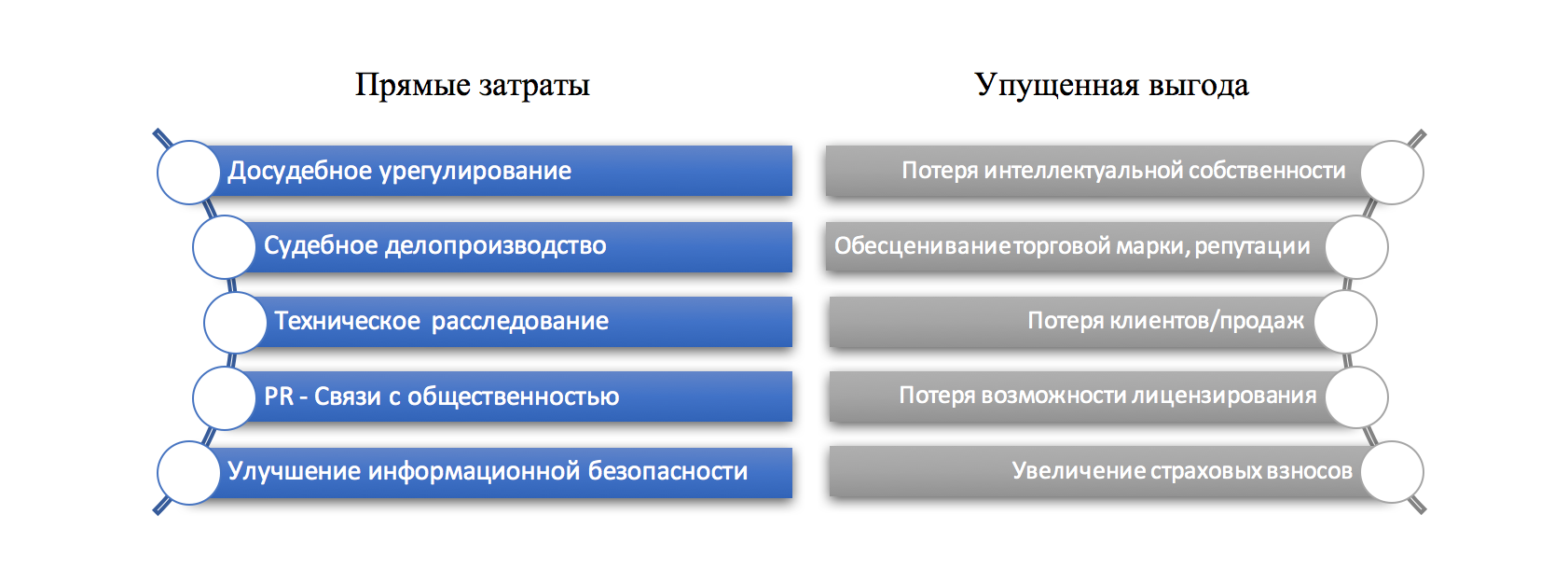
Since many of the costs are hidden and indirect, it is extremely difficult to calculate the full cost of a potential IP violation. After all, the assessment requires consideration of: a decrease in consumer confidence in goods and services with a registered trademark; reduction of market share at the disposal of the copyright holder; loss of income by the right holder due to the replacement of products with counterfeit products; loss of income from imperfect commercial agreements with potential licensees, etc.
When filing a lawsuit in court, the main complaint is that the offender’s sales could have been sold by the right holder. The claim concerns the profit that the claimant would have received if the sale were made by him, and not by the violator. The claimant may claim both damages and compensation without specifying the cost of the losses incurred.
Various sources describe the three main methods for calculating economic damage and loss of profits resulting from a violation of IP rights: the “before and after” value method of violation; the “if not violation” method and the method of actual costs and missed opportunities. Each of the methods has its limitations and features, for example, it is not always possible to measure costs and profits simultaneously before and after the violation, it is also not known when exactly the violation will be eliminated and there is no assessment of the residual effect of the event and so on. Under the method of costs and missed opportunities, real or necessary expenses are determined to restore the violated right, the cost of lost property rights to IP due to the violation, as well as income not received by the right holder due to the violation (or income received by the infringer).

The losses incurred by Apple and software developers for the iPhone and iPod as a result of piracy, in total, exceeded $ 450 million. According to IDC estimates, Russian companies will spend on eliminating the consequences of technical risks from using pirated software - detecting problems and recovering data - about $ 5 billion a year. Do not be piracy, in 2015, software manufacturers could earn in Russia an additional $ 1.34 billion. In 2013 - $ 2.6 billion (according to BSA).
Conclusion
Do not forget about other types of damage caused by counterfeit products on the market. In addition to the economic damage appear social and political. Consumption of falsified products and drugs can lead to irreparable consequences, which causes social protest. A country in which counterfeit goods are produced and sold almost uncontrollably loses a positive image in the eyes of the global community. Political leaders of such countries are accused of weakness and inability to cope with fakes.
In modern conditions, intellectual property (IP) is of particular value not only for business, but also for the entire state and international economy. Ensuring the protection of information, trademarks, copyrights and other IP objects contributes to the successful development and generation of stable incomes.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/344432/
All Articles