How users perceive different authentication methods
The most common method of online authentication at the moment is the password. There are other equally popular methods of online authentication, such as: two-factor authentication (or 2FA), social network logins.
Modern users have about 25 different online service accounts, while only 6.5 are on average to protect them. This statistic makes it clear that users have real problems with remembering passwords and repeatedly using the same passwords on different sites.
A number of authentication methods were proposed to solve the memory problem, some of which were already implemented, although they were not widely used. The most common ones are:
Passphrase authentication. This method involves the use of phrases instead of passwords, such phrases may be regular sentences. The passphrase is usually longer than the password and includes spaces, but is more easily remembered. The main advantage of this method is that it allows you to increase password retentivity while maintaining the length of the key phrase needed to ensure a reliable level of security.
')
Two-factor authentication enters the security enhancement process, that is, another authentication step, in addition to the password. This step may include one of the following solutions:
Another authentication method is single sign-on (SSO). This method allows users to use one of their accounts in one service to log in to another service. This makes it possible to reduce the amount of data that the user needs to remember. The SSO architecture assumes two roles, one of which stores user information (for example, VK, Google, Facebook, Twitter) and authenticates them, the second role on behalf of the trusting party (for example, CNN, Sears, Groupon) relies on authenticated identity cards for making decisions about permission. The most popular example of such a solution is called Social login, where social networks (for example, Facebook, Twitter, etc.) act as a relying party.
There are solutions for PCs, such as: 1password (https://1password.com/), Dashlane (https://www.dashlane.com/), LastPass (https://www.lastpass.com), etc. . They allow you to store a large number of passwords for different services, and these solutions are synchronized with mobile devices.
Since there is a wide range of authentication methods, it is important to determine which users would prefer to use most often, so that developers can take this information into account when choosing authentication for their online services.
To identify preferences, which authentication method is more convenient and more commonly used, a survey was conducted among users of online services.
This survey was conducted among students SPBGTI (TU).
The first question: "Is it convenient for you to use a password to log into online services?". According to the survey results, 71% of respondents consider a password as a convenient authentication method, when 29% are considered inconvenient.

One of the common arguments in favor of passwords was that survey participants memorized them well. Most respondents who answered “No” stated that the inconvenience of entering a password is associated with a variety of requirements for its creation, such as the use of symbols, lowercase / capital letters, and others.
Further, participants were asked to indicate their preferences by choosing the methods they would prefer to use. Respondents were asked: "What method of authentication would you prefer over others?"
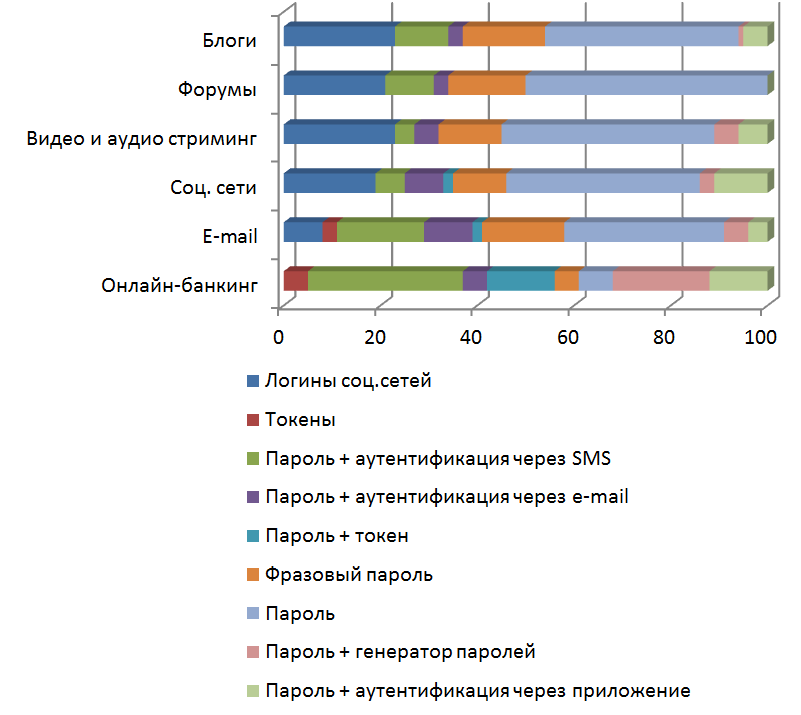
The results showed that most people (about 60%) who participated in the survey would still prefer to use a password for most online services other than online banking. At the same time, alternatives such as two-factor authentication methods were often chosen: the most popular of them was “password + authentication via SMS” (11 out of 34 respondents chose it).
Token and two-step authentication using a token were the least popular choice for all classes of online services, one of the typical reasons for this was that, at present, this method has not gained much popularity.
In general, user preferences can be explained by the fact that participants usually give priority to different types of services, which is based on the level of importance.
In the next question, participants were asked to choose one of three possible alternatives to a password, which they would prefer to use regardless of the online service. These 3 alternatives were social login, code phrase and token.
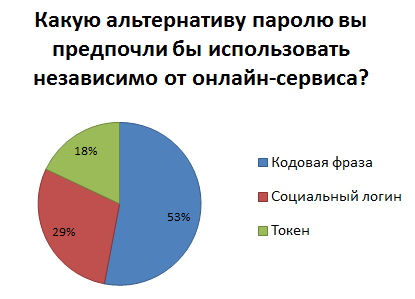
As a result of the survey, it was found that the most preferred alternative is a passphrase, this method was chosen by 53% of respondents, while the social login and token were selected respectively 29% and 18% of the participants.
The last question concerned preferences in two-step authentication: “What would you prefer as a second step, two-factor authentication for the login procedure? ".
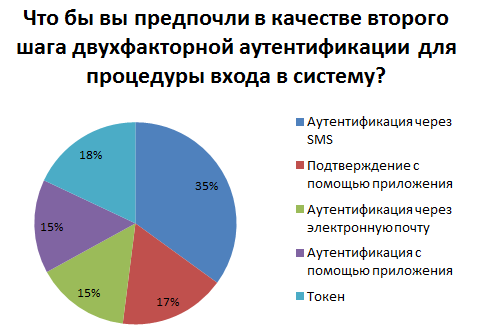
The method chosen by 35% of participants was “authentication via SMS”, the two less popular were “token” and “confirmation using application”, they accounted for 18% and 17% of respondents' answers. The remaining options: "authentication via email" and "authentication using the application" are distributed by 15%.
The results of the survey showed that users have strong preferences regarding online authentication and the motives for these choices are usually clear and understandable.
Regarding the second question about authentication methods that users prefer, users usually give priority to services where 2FA is possible. The first and foremost factor is the participation of any financial assets. If they are involved, users prefer to maximize the security of their account and, therefore, choose advanced methods of identification. The second factor is the involvement of any personal information, such data require additional protection.
From this it follows that users are ready to use secure passwords, instead of the usual and convenient sake of security.
The problem raised by this study was that it is sometimes difficult for some services to determine which authentication method is the most appropriate. In this case, it may be a good idea to give the user a choice of several alternatives that will allow him to choose the method that suits him.
The results of the study expanded the understanding of how users perceive different authentication methods in connection with various types of services. Such an understanding may be useful for developers of online services who may use the most appropriate authentication methods in the future.
Modern users have about 25 different online service accounts, while only 6.5 are on average to protect them. This statistic makes it clear that users have real problems with remembering passwords and repeatedly using the same passwords on different sites.
Alternative authentication methods
A number of authentication methods were proposed to solve the memory problem, some of which were already implemented, although they were not widely used. The most common ones are:
Passphrase authentication. This method involves the use of phrases instead of passwords, such phrases may be regular sentences. The passphrase is usually longer than the password and includes spaces, but is more easily remembered. The main advantage of this method is that it allows you to increase password retentivity while maintaining the length of the key phrase needed to ensure a reliable level of security.
')
Two-factor authentication enters the security enhancement process, that is, another authentication step, in addition to the password. This step may include one of the following solutions:
- SMS verification. The one-time code is sent to the user's mobile phone and must be entered to complete the authentication process.
- Confirmation by email. In this case, the one-time code is sent to the user account.
- Checking the application code. Codes are generated by a special application installed on the user's phone (for example, Google authenticator, Yandex key).
- Confirmation using the app. To confirm the login attempt, the user must open the corresponding application on his mobile phone and confirm the login.
- Touch ID, Face ID. Fingerprint authentication, facial recognition.
- Check token. For this method to complete authentication, the user must insert a small USB device and press a button on it, or depending on the device, you may need to enter the displayed code on the device screen.
Another authentication method is single sign-on (SSO). This method allows users to use one of their accounts in one service to log in to another service. This makes it possible to reduce the amount of data that the user needs to remember. The SSO architecture assumes two roles, one of which stores user information (for example, VK, Google, Facebook, Twitter) and authenticates them, the second role on behalf of the trusting party (for example, CNN, Sears, Groupon) relies on authenticated identity cards for making decisions about permission. The most popular example of such a solution is called Social login, where social networks (for example, Facebook, Twitter, etc.) act as a relying party.
There are solutions for PCs, such as: 1password (https://1password.com/), Dashlane (https://www.dashlane.com/), LastPass (https://www.lastpass.com), etc. . They allow you to store a large number of passwords for different services, and these solutions are synchronized with mobile devices.
Since there is a wide range of authentication methods, it is important to determine which users would prefer to use most often, so that developers can take this information into account when choosing authentication for their online services.
User preferences
To identify preferences, which authentication method is more convenient and more commonly used, a survey was conducted among users of online services.
This survey was conducted among students SPBGTI (TU).
The first question: "Is it convenient for you to use a password to log into online services?". According to the survey results, 71% of respondents consider a password as a convenient authentication method, when 29% are considered inconvenient.

One of the common arguments in favor of passwords was that survey participants memorized them well. Most respondents who answered “No” stated that the inconvenience of entering a password is associated with a variety of requirements for its creation, such as the use of symbols, lowercase / capital letters, and others.
Further, participants were asked to indicate their preferences by choosing the methods they would prefer to use. Respondents were asked: "What method of authentication would you prefer over others?"

The results showed that most people (about 60%) who participated in the survey would still prefer to use a password for most online services other than online banking. At the same time, alternatives such as two-factor authentication methods were often chosen: the most popular of them was “password + authentication via SMS” (11 out of 34 respondents chose it).
Token and two-step authentication using a token were the least popular choice for all classes of online services, one of the typical reasons for this was that, at present, this method has not gained much popularity.
In general, user preferences can be explained by the fact that participants usually give priority to different types of services, which is based on the level of importance.
In the next question, participants were asked to choose one of three possible alternatives to a password, which they would prefer to use regardless of the online service. These 3 alternatives were social login, code phrase and token.

As a result of the survey, it was found that the most preferred alternative is a passphrase, this method was chosen by 53% of respondents, while the social login and token were selected respectively 29% and 18% of the participants.
The last question concerned preferences in two-step authentication: “What would you prefer as a second step, two-factor authentication for the login procedure? ".

The method chosen by 35% of participants was “authentication via SMS”, the two less popular were “token” and “confirmation using application”, they accounted for 18% and 17% of respondents' answers. The remaining options: "authentication via email" and "authentication using the application" are distributed by 15%.
results
The results of the survey showed that users have strong preferences regarding online authentication and the motives for these choices are usually clear and understandable.
Regarding the second question about authentication methods that users prefer, users usually give priority to services where 2FA is possible. The first and foremost factor is the participation of any financial assets. If they are involved, users prefer to maximize the security of their account and, therefore, choose advanced methods of identification. The second factor is the involvement of any personal information, such data require additional protection.
From this it follows that users are ready to use secure passwords, instead of the usual and convenient sake of security.
The problem raised by this study was that it is sometimes difficult for some services to determine which authentication method is the most appropriate. In this case, it may be a good idea to give the user a choice of several alternatives that will allow him to choose the method that suits him.
The results of the study expanded the understanding of how users perceive different authentication methods in connection with various types of services. Such an understanding may be useful for developers of online services who may use the most appropriate authentication methods in the future.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/344406/
All Articles