SOLID principles in action: from Slack to Twilio

It seems that nowadays the RESTful API exists absolutely for everything. From payments to booking tables, from simple notifications to deploying virtual machines - almost everything is available through a simple HTTP interaction.
If you develop your own service, you often want to make it work simultaneously on several platforms. The time-tested principles of OOD (object-oriented design) will make your code more fault-tolerant and simplify extensibility.
')
In this article we will explore one specific design approach called SOLID (this is an acronym). We use it in practice in writing a service with Slack integration, and then expand it for use with Twilio .
This service will send you a random Magic the Gathering card. If you want to check it in action right now, then send the word magic to the number 1-929-236-9306 (only USA and Canada - you will receive an image via MMS, so the tariffs of your operator may apply). You can also join my Slack organization by clicking here . After logging in, type: / magic .
SOLID for "Magic"
If you are not familiar with SOLID , this is a set of object-oriented design (OOD) principles that Uncle Bob Martin popularized. SOLID is an acronym for:
- S - SRP - Single Responsibility Principle
- O - OCP - Open Closed Principle
- L - LSP - The Substitution Principle of Barbara Liskov
- I - ISP - Interface Segregation Principle
- D - DIP - Dependency Inversion Principle
If you follow this set of principles, you will make the code more fault tolerant and simplify extensibility. Further in the article we will talk more about each of these principles.
There are many good examples of SOLID in a variety of languages. Instead of repeating the well-known example of
Shape , Circle , Rectangle , Area I would like to show the advantages of SOLID in a full-featured real-world application.I recently played with the Slack API . It’s really really easy to build your teams with a slash. I'm also a big fan of Magic the Gathering , so I got the idea to make a Slack slash command that produces an image of the random Magic the Gathering card.
I quickly realized my plan with the help of Spring Boot . As you will see, Spring Boot observes a couple of SOLID principles right out of the box.
Twilio has a great API for voice and text messaging. I thought it would be interesting to see how easy it is to take my Slack example and integrate it with Twilio. The idea is that you send a text message with the team to a known phone number - and get a random image of Magic the Gathering.
The following is an analysis of the SOLID principles (not in order) in action during this programming exercise.
All code can be found here . Later we will see how to apply this code on your own Slack and / or Twilio account if you wish.
First Pass: "Magic" with Slack
Just the fact of using Spring Boot to create a Magic application immediately provides two of the five SOLID principles without any special effort on your part. However, you are still responsible for the proper architecture of the application.
Since in the process of writing the code, we will study different principles, you can look at the sample code at any time by checking the corresponding tags in the GitHub project (you will find them in the “Releases” section). The full code for this chapter is displayed by the
slack-first-pass tag.Look at the
SlackController code (all Java sources are here: magic-app / src / main / java / com / afitnerd / magic), which presents an example of the principles D and I in SOLID: @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class SlackController { @Autowired MagicCardService magicCardService; @Autowired SlackResponseService slackResponseService; @RequestMapping( value = "/slack", method = RequestMethod.POST, consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED_VALUE, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE ) public @ResponseBody Map<String, Object> slack(@RequestBody SlackSlashCommand slackSlashCommand) throws IOException { return slackResponseService.getInChannelResponseWithImage(magicCardService.getRandomMagicCardImage()); } } DIP: dependency inversion principle
The principle of DIP says:
A. The modules of the upper levels should not depend on the modules of the lower levels. Both types of modules must depend on abstractions.
B. Abstractions should not depend on details. Details must depend on abstractions.
Java and Spring Boot extremely simplify the implementation of this principle.
SlackController * has * MagicCardService . This is * an abstraction * because it is a Java interface. And since this is an interface, there are no details.The implementation of
MagicCardService not specifically dependent on SlackController . Later we will see how to provide such a separation between the interface and its implementation by breaking the application into modules. Additionally, consider other modern ways to implement dependencies in Spring Boot.ISP: interface separation principle
The ISP principle states:
Many separate client interfaces are better than one universal interface.
In
SlackController we implemented two separate interfaces: MagicCardService and SlackResponseService . One of them interacts with the Magic the Gathering site. The other interacts with Slack. Creating a single interface to perform these two separate functions would violate the ISP principle.Next: “Magic” with Twilio
To track the code in this chapter, see the
twilio-breaks-srp tag.Let's look at the TwilioController code:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class TwilioController { private MagicCardService magicCardService; static final String MAGIC_COMMAND = "magic"; static final String MAGIC_PROXY_PATH = "/magic_proxy"; ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TwilioController.class); public TwilioController(MagicCardService magicCardService) { this.magicCardService = magicCardService; } @RequestMapping(value = "/twilio", method = RequestMethod.POST, headers = "Accept=application/xml", produces=MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE) public TwilioResponse twilio(@ModelAttribute TwilioRequest command, HttpServletRequest req) throws IOException { log.debug(mapper.writeValueAsString(command)); TwilioResponse response = new TwilioResponse(); String body = (command.getBody() != null) ? command.getBody().trim().toLowerCase() : ""; if (!MAGIC_COMMAND.equals(body)) { response .getMessage() .setBody("Send\n\n" + MAGIC_COMMAND + "\n\nto get a random Magic the Gathering card sent to you."); return response; } StringBuffer requestUrl = req.getRequestURL(); String imageProxyUrl = requestUrl.substring(0, requestUrl.lastIndexOf("/")) + MAGIC_PROXY_PATH + "/" + magicCardService.getRandomMagicCardImageId(); response.getMessage().setMedia(imageProxyUrl); return response; } @RequestMapping(value = MAGIC_PROXY_PATH + "/{card_id}", produces = MediaType.IMAGE_JPEG_VALUE) public byte[] magicProxy(@PathVariable("card_id") String cardId) throws IOException { return magicCardService.getRandomMagicCardBytes(cardId); } } As mentioned earlier, a more modern approach to dependency injection is applied (best practices). As you can see, we did this using the Spring Boot Constructor Injection. This is just a beautiful way to say that in the latest version of Spring Boot, dependency injection is implemented as follows:
1. Install one or more hidden fields in your class, for example:
private MagicCardService magicCardService; 2. Define the constructor for the installed hidden fields:
public TwilioController(MagicCardService magicCardService) { this.magicCardService = magicCardService; } Spring Boot will automatically handle object injection at runtime. The advantage is that here it is possible to run error checking and validation on the embedded object inside the constructor.
The controller contains two parts:
/twilio and /magic_proxy/{card_id} . The magic_proxy path requires a little explanation, so we first analyze it before talking about violation of the SRP principle.TwiML Fun
TwiML is the Twilio Markup Language markup language. This is the basis of all Twilio answers, because TwiML is a Twilio manual. This is also XML. Usually this is not a problem. However, the URLs returned by Magic the Gathering site present a problem for inclusion in TwiML documents.
The URL where the Magic the Gathering card image is retrieved looks like this:
http://gatherer.wizards.com/Handlers/Image.ashx?multiverseid=144276&type=card Notice the ampersand (&) in the URL. There are only two valid ways to embed an ampersand in XML documents:
1. Escape characters
<Response> <Message> <Body/> <Media>http://gatherer.wizards.com/Handlers/Image.ashx?multiverseid=144276&type=card</Media> </Message> </Response> Here, instead of an ampersand, the element
& .2. Fragment of CDATA (character data)
<Response> <Message> <Body/> <Media> <![CDATA[http://gatherer.wizards.com/Handlers/Image.ashx?multiverseid=144276&type=card]]> </Media> </Message> </Response> Any of these options are easy to implement in Java with the Jackson Dataformat XML extension in the Jackson JSON processor built into Spring Boot.
The problem is that the first version leads to an error when retrieving an image from the Wizards of the Coast website (the Magic maintainers of the game Magic the Gathering), and the second version is not supported in Twilio (hey Twilio: maybe implement CDATA support in TwiML?)
I circumvented this restriction using a proxy for requests. In this case, this TwiML code is generated:
<Response> <Message> <Body/> <Media> http://<my magic host>/api/v1/magic_proxy/144276 </Media> </Message> </Response> When such a code is received, Twilio refers to the endpoint
/magic_proxy , and already behind the scenes, the proxy receives a picture from the Magic the Gathering site and issues it.Now let's continue studying the principles of SOLID.
SRP: sole responsibility principle
The SRP principle states:
A class must have only one function.
The above controller works as it is, but violates the SRP, because it is also responsible for returning the TwiML response, and for the proxy for the pictures.
In this example, this is not a big problem, but it is easy to imagine how the situation quickly gets out of control.
If you go through the
twilio-fixes-srp tag, you will see a new controller called MagicCardProxyController : @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class MagicCardProxyController { private MagicCardService magicCardService; public MagicCardProxyController(MagicCardService magicCardService) { this.magicCardService = magicCardService; } @RequestMapping(value = MAGIC_PROXY_PATH + "/{card_id}", produces = MediaType.IMAGE_JPEG_VALUE) public byte[] magicProxy(@PathVariable("card_id") String cardId) throws IOException { return magicCardService.getRandomMagicCardBytes(cardId); } } His only task is to return the bytes of the image received on the proxy from the Magic the Gathering website.
Now the only
TwilioController function is to issue TwiML code.DIP implementation modules
Maven makes it easy to split a project into modules. They may have different areas (scopes), but they are the same: compilation (by default), execution and test.
Regions take control when modules are involved in a given area. The
runtime field checks that the classes for a particular module are * not * available at compile time. They are available only at run time. This helps to realize the principle of DIP.Simply show an example. See the code for the
modules-ftw tag. You can see that the project organization has radically changed (as seen in IntelliJ):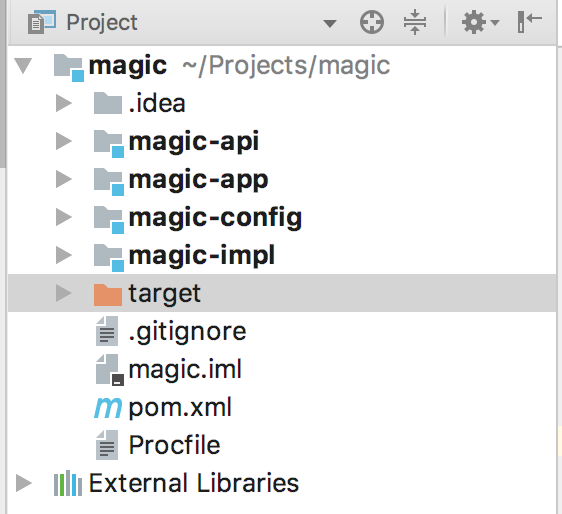
Now there are four modules. If you look at the
magic-app module, then from pom.xml can see how it relies on other modules: <dependencies> ... <dependency> <groupId>com.afitnerd</groupId> <artifactId>magic-config</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.afitnerd</groupId> <artifactId>magic-api</artifactId> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.afitnerd</groupId> <artifactId>magic-impl</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> Note that
magic-impl is in the runtime , and magic-api is in the compile .In
TwilioController we automatically bind to TwilioResponseService: @RestController @RequestMapping(API_PATH) public class TwilioController { private TwilioResponseService twilioResponseService; … } And now look what happens if we try to automatically bind the implemented class like this:
@RestController @RequestMapping(API_PATH) public class TwilioController { private TwilioResponseServiceImpl twilioResponseService; … } 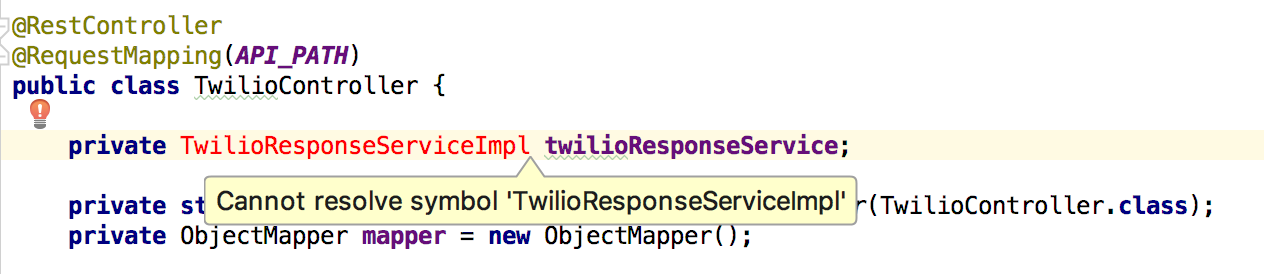
IntelliJ cannot find the TwilioResponseServiceImpl class because its * no * is in the
compile .As a joke, you can try to delete the
runtime line from pom.xml - and you will see that then IntelliJ will happily find the TwilioResponseServiceImpl class.As we have seen, maven modules in combination with scopes helps to realize the principle of DIP.
Finish line: Slack refactoring
When I wrote this application for the first time, I did not think about SOLID. I just wanted to hack the Slack application to play around with the functionality of slash commands.
In the first version, all Slack-related services and controllers simply gave out
Map<String, Object> . This is a good trick for Spring Boot applications — to output any JSON response without worrying about the formal Java models that represent the structure of the response.As the application developed, the desire arose to create more formal models for readable and reliable code.
See the source code for the
slack-violates-lsp .Let's look at the
SlackResponse class in the magic-api module: public abstract class SlackResponse { private List<Attachment> attachments = new ArrayList<>(); @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY) public List<Attachment> getAttachments() { return attachments; } @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL) public abstract String getText(); @JsonProperty("response_type") public abstract String getResponseType(); ... } Here we see that in the
SlackResponse class SlackResponse is an Attachments array, a text string and a response_type string.SlackResponse declared the type abstract , and the implementation functions of the getText and getResponseType methods fall on the child classes.Now, take a look at one of the child classes of
SlackInChannelImageResponse : public class SlackInChannelImageResponse extends SlackResponse { public SlackInChannelImageResponse(String imageUrl) { getAttachments().add(new Attachment(imageUrl)); } @Override public String getText() { return null; } @Override public String getResponseType() { return "in_channel"; } } The
getText() method returns null . With this answer, the answer will contain * only * image. Text is returned only in the case of an error message. Here * clearly * smells like LSP.LSP: Barbara Liskov substitution principle
The principle of the LSP says:
Objects in the program should be able to be replaced by their subtypes without changing the accuracy of the program.
When you are dealing with the inheritance hierarchy and the child class * always * returns null, this is a clear sign of a violation of the LSP principle. Because the child class does not need this method, but it has to implement it because of the interface described in the parent class.
Look at the
master branch in a project on github. It refactored the SlackResponse hierarchy to match the LSP. public abstract class SlackResponse { @JsonProperty("response_type") public abstract String getResponseType(); } Now the only thing common to all child classes that they have to implement is the
getResponseType() method.In the
SlackInChannelImageResponse class SlackInChannelImageResponse is everything you need for the correct answer with a picture: public class SlackInChannelImageResponse extends SlackResponse { private List<Attachment> attachments = new ArrayList<>(); public SlackInChannelImageResponse(String imageUrl) { attachments.add(new Attachment(imageUrl)); } public List<Attachment> getAttachments() { return attachments; } @Override public String getResponseType() { return "in_channel"; } … } No more returning to
null .There is another minor improvement: we used to have some JSON annotations in the
SlackResponse class: @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY) and @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL) .They were needed to ensure that an empty array of attachments or a text field with a zero value does not fall into JSON. Although these are powerful annotations, because of them the objects of our model become fragile, and it may not be clear to other developers what is happening.
OCP: the principle of openness / closeness
The last principle we’ll look at in our SOLID journey is OCP.
The principle of OCP says:
Software entities ... must be open for expansion, but closed for modification.
The idea is that if you change the terms of reference, your code will more effectively cope with any new requirements if you expand the classes and not add the code to existing classes. This helps to keep the code from spreading.
In the example above, there is no additional reason to change the
SlackResponse class. If we want to add support for other types of Slack responses to the application, we can easily describe these specifics in subclasses.Here again is the power of Spring Boot. Take a look at the
SlackResponseServiceImpl class in the magic-impl . @Service public class SlackResponseServiceImpl implements SlackResponseService { MagicCardService magicCardService; public SlackResponseServiceImpl(MagicCardService magicCardService) { this.magicCardService = magicCardService; } @Override public SlackResponse getInChannelResponseWithImage() throws IOException { return new SlackInChannelImageResponse(magicCardService.getRandomMagicCardImageUrl()); } @Override public SlackResponse getErrorResponse() { return new SlackErrorResponse(); } } According to the interface conditions, the
getInChannelResponseWithImage and getErrorResponse return a SlackResponse object.Inside these methods, various
SlackResponse child objects are SlackResponse . Spring Boot and its built-in jackson mapper for JSON are smart enough to produce the correct JSON for the particular object that is featured inside.If you want to provide integration for your own organization in Slack or to implement support for your Twilio account (or both), then read on! Otherwise, you can go to the summary at the end of the article.
Deploying the application
If you want to use this application to its fullest, then you need to properly configure Slack and Twilio after deploying the application to Heroku.
Alternatively, you can install either Slack or Twilio. In any case, the first thing you need to deploy the application on Heroku. Fortunately, it is simple.
Deploying to Heroku
The easiest way to deploy the application on Heroku is to press the friendly purple button in the README section of the GitHub project . You will need to specify two details:
BASE_URL and SLACK_TOKENS .BASE_URL is the full path and name of your Heroku application. For example, my application is installed here: https://random-magic-card.herokuapp.com . Stick to the same format when choosing an application name: https://<app name>.herokuapp.com .There is a peculiar chicken and egg problem, because the Heroku application needs some information from Slack, and for Slack integration, some information about the Heroku application is needed. At first, you can leave the default value in the
SLACK_TOKENS field — we will return later and update this value with this Slack API token.You can check the installation by going to
https://<app name>.herokuapp.com . You should see the random Magic the Gathering card in your browser. If an error occurs, look at the error log in the Heroku web interface. Here is an example of a web interface in action .Slack setup
Go to https://api.slack.com/apps and click the
Create New App button to get started:
Enter the name
App Name and select the Workspace workspace where you will add the application:
Next, click on the link with
Slash Commands slash commands on the left, and then there is a button to create a new Create New Command :
Fill in the values for the command (for example:
/magic ), Request URL (for example: https://<your app name>.herokuapp.com/api/v1/slack ) and a short description. Then click Save .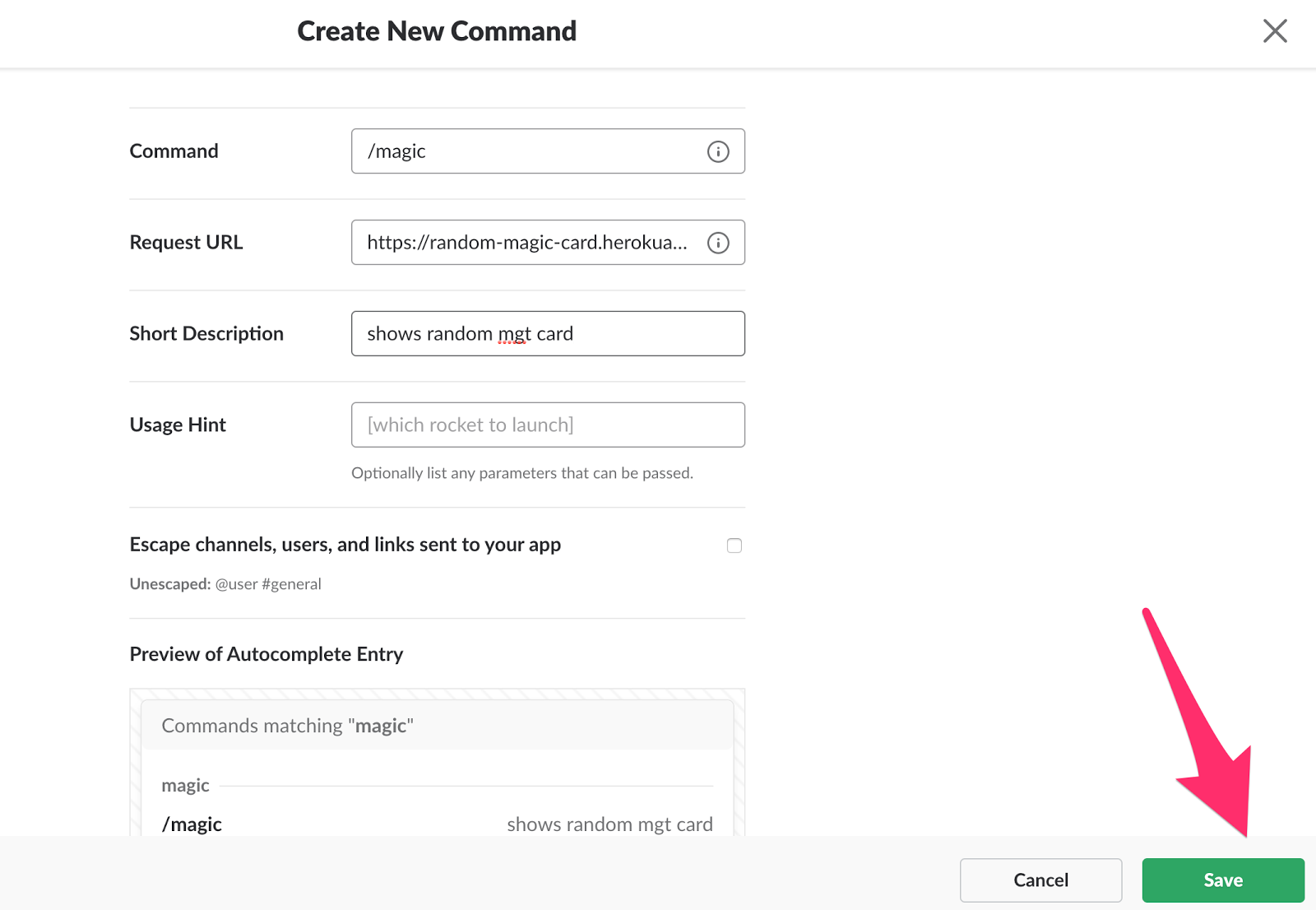
Now your Slack slash command is fully configured:
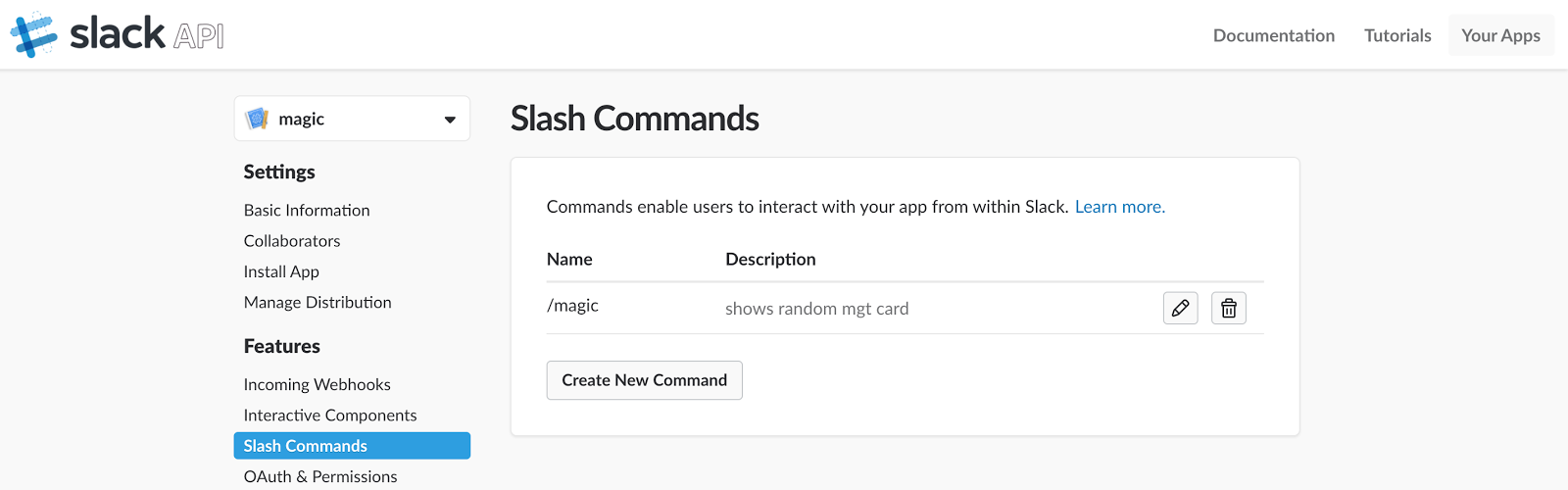
Go to the
Basic Information section in the left pane and expand the Install app to your workspace section on the screen. Click the Install app to Workspace button.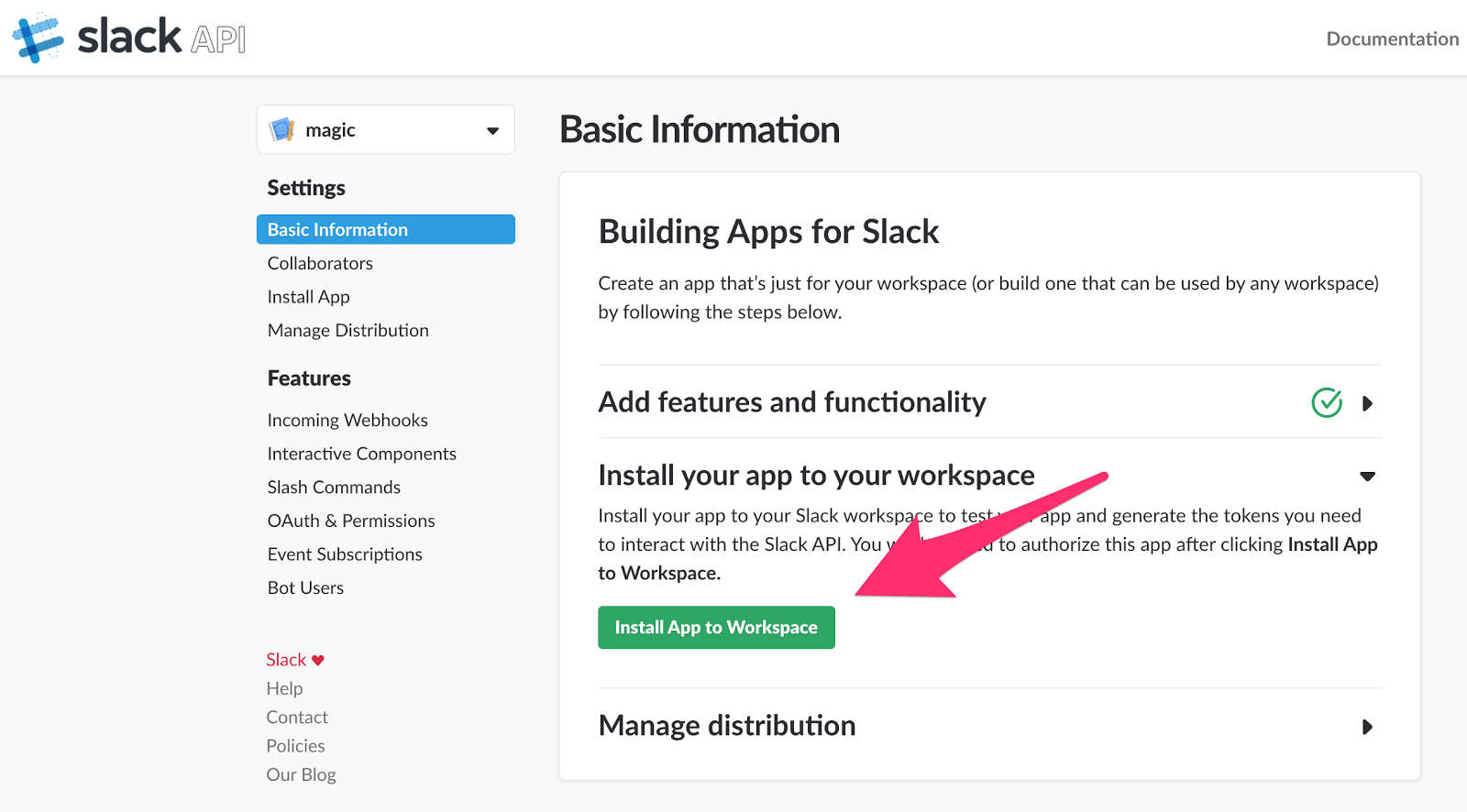
Then the button for authorization:
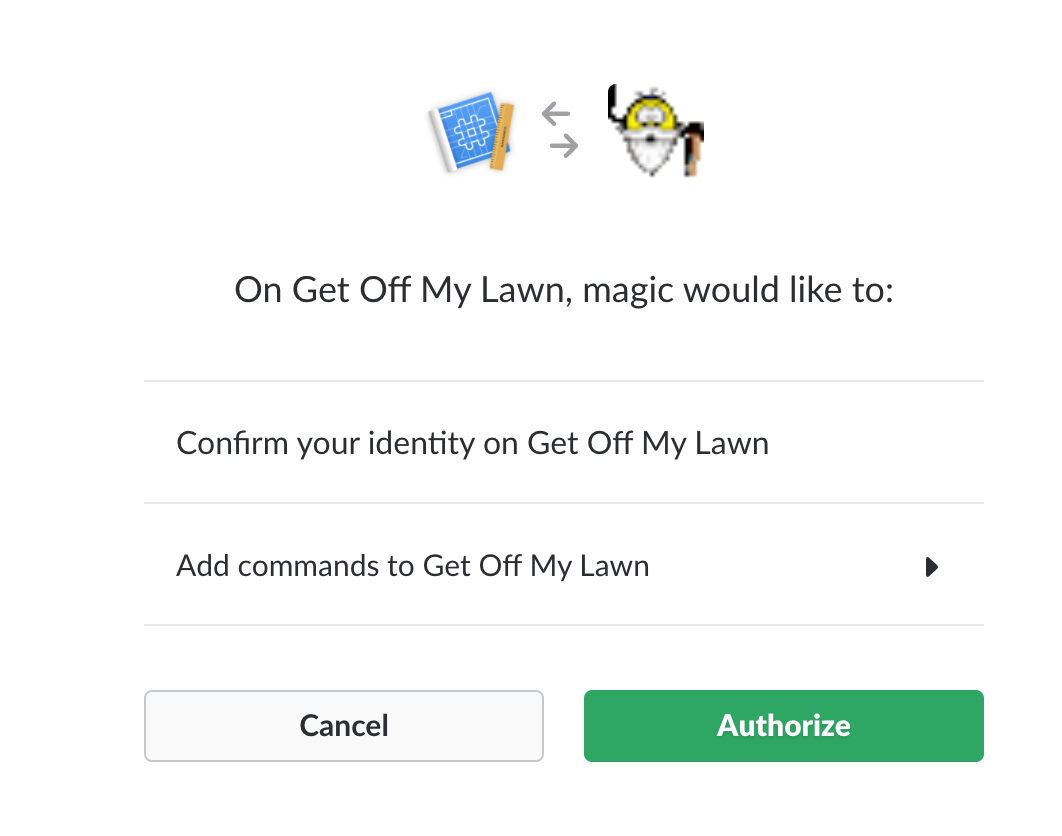
Scroll to the
Basic Information screen where you returned, and record the verification token.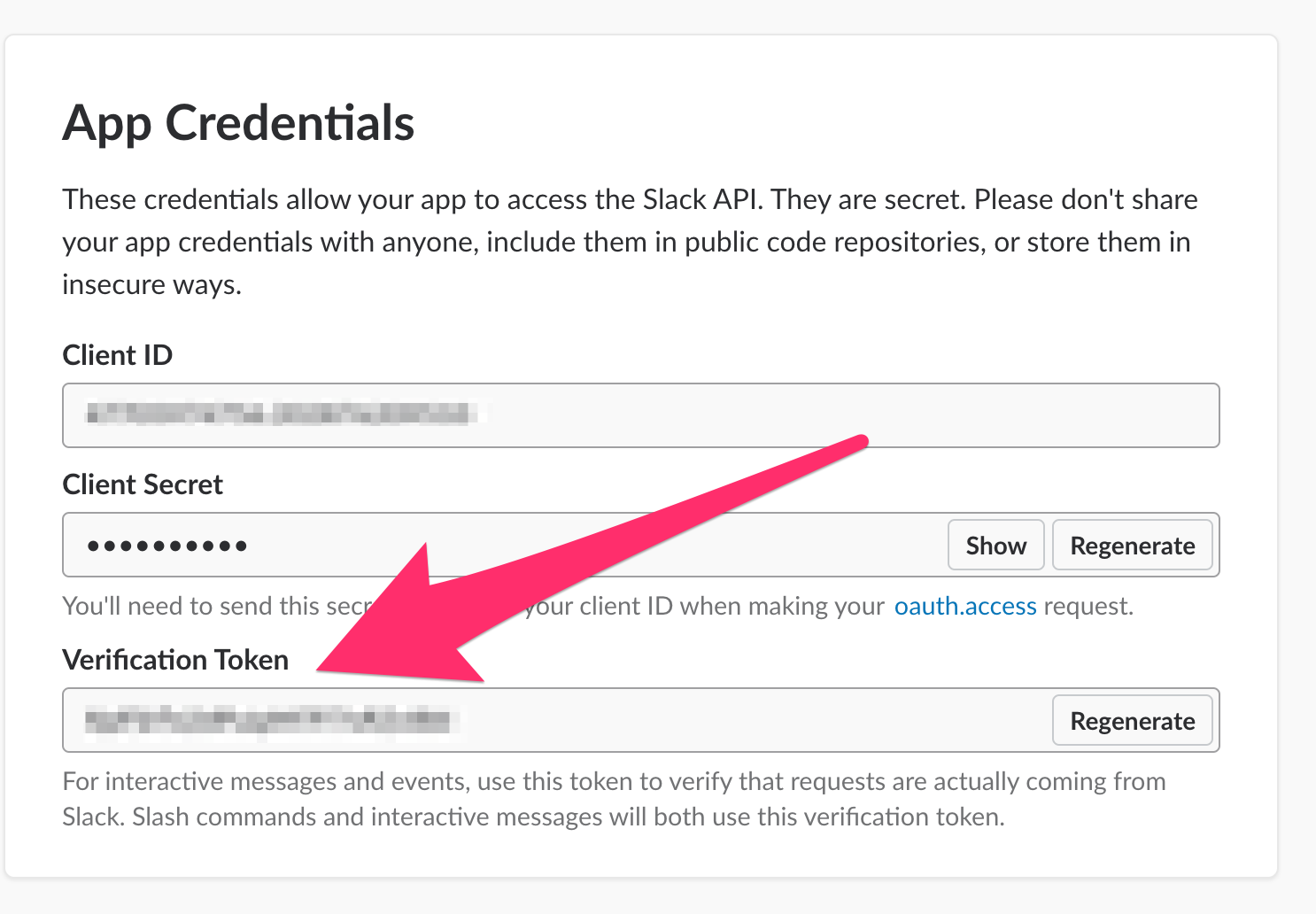
If you installed the Heroku CLI, then you can correctly set the
SLACK_TOKENS property SLACK_TOKENS following command: heroku config:set \ SLACK_TOKENS=<comma separated tokens> \ --app <your heroku app name> Alternatively, go to the Heroku dashboard , go to your application and change the value of
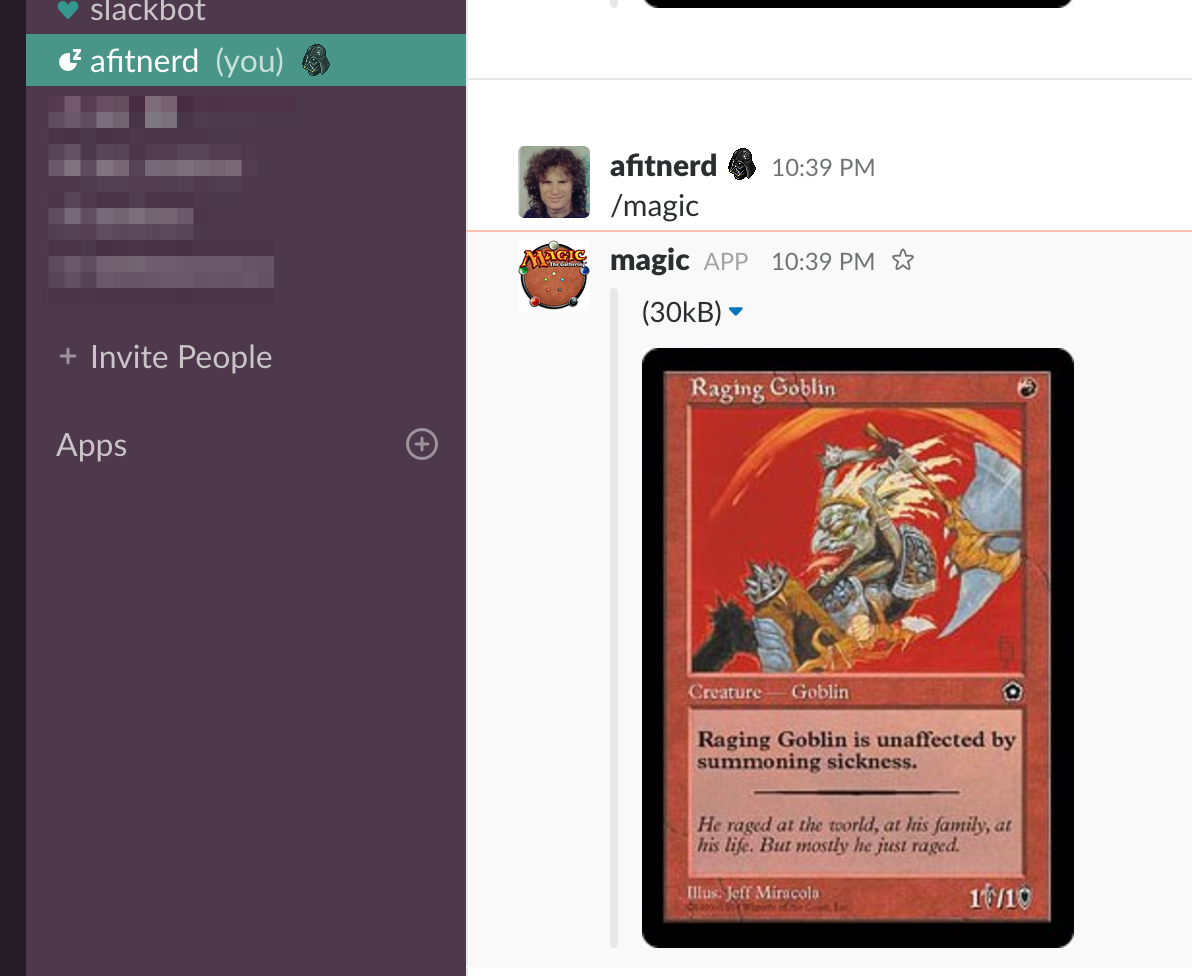
SLACK_TOKENS in the settings.Now the slash command should work on your organization's Slack channel, and in return you will receive a Magic the Gathering card:
Twilio Setup
To configure Twilio integration, go to the Twilio dashboard in the console .
Click on the ellipsis and select
Programmable SMS :
Select
Messaging Services :
Create a new messaging service by clicking on the red plus button (or click “Create new Messaging Service” if there are no services yet):
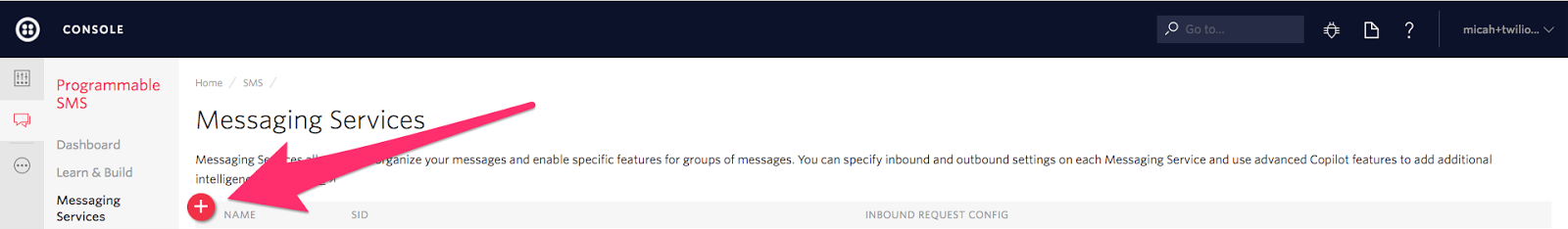
Enter
Friendly Name , select Notifications, 2-Way in the Use Case column and click the Create button: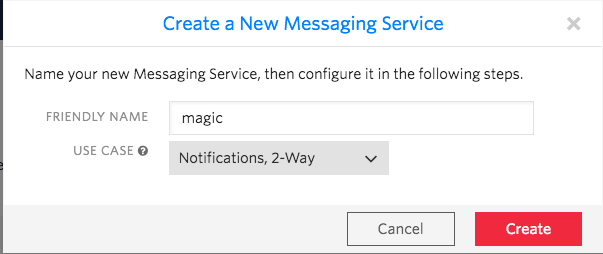
Check the
Process Inbound Messages in Process Inbound Messages and enter the Request URL for your Heroku application (for example, https://<your app name>.herokuapp.com/api/v1/twilio ):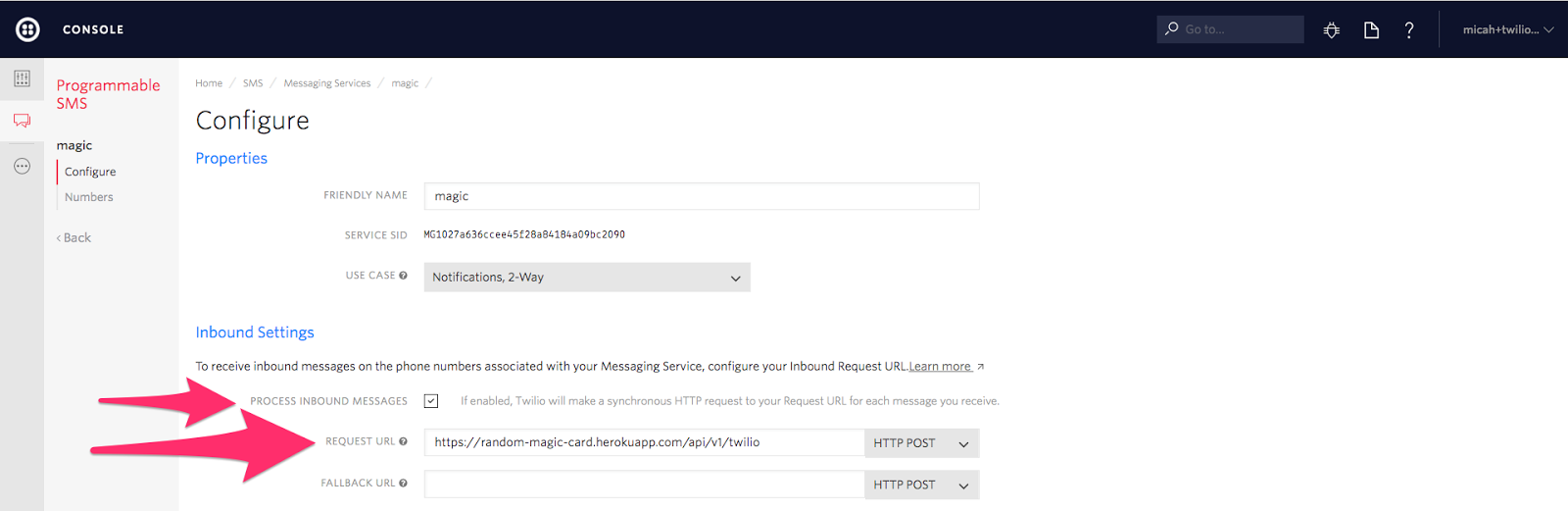
Click the
Save button to save the changes.Go to the
Numbers section in the left menu and make sure that your Twilio number has been added to the messaging service: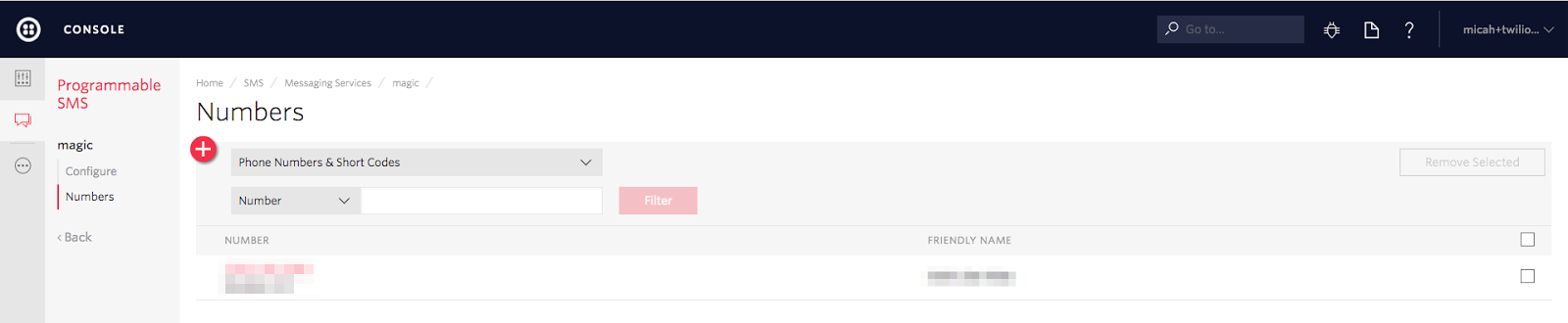
Now you can test the Twilio service by sending
magic to your number as a text message:
** Note: ** If you send anything other than the word
magic (regardless of case), the error message shown above will pop up.Summary of SOLID
Once again we publish the SOLID table, this time with the Github project tags that correspond to each principle:
- S - SRP - The principle of sole responsibility. Tag:
twilio-fixes-srp. Splits theTwilioControllercontroller into two parts, where each controller has only one function. - O - OCP - The principle of openness / closeness. Tag:
master. TheSlackResponseclassSlackResponsesolid and cannot be changed. It can be expanded without changing the code of the existing service. - L - LSP - Barbara Liskov substitution principle. Tag:
master. None of theSlackResponsechild classes returnnull, it does not contain unnecessary classes or annotations. - I - ISP - The principle of interface separation. Tag:
slack-first-passthroughmaster. TheMagicCardServiceandSlackResponseServiceperform different functions and therefore are separated from each other. - D - DIP - The principle of dependency inversion. Tag:
slack-first-passthroughmaster. Dependent services are automatically associated with controllers. Implementing a controller is the “best practice” of dependency injection.
There are some difficulties in developing this application. I have already spoken above about the problem with TwiML. But with Slack, there are special problems that I have outlined in this article. TL; DR: Slack accepts for slash commands * only * POST requests
application/x-www-form-urlencoded, not more modern ones application/json. Because of this, there are difficulties with processing incoming JSON data with Spring Boot.The basic idea is that the SOLID principles have made the code much easier to work with and to further expand.
This concludes our review of the SOLID principles. I hope it was more useful than the usual simple Java examples.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343966/
All Articles