Basics of information security. Part 2. Information and means of its protection

In the first part of the Basics of Information Security, we reviewed the main types of information security threats . In order for us to proceed to the choice of information security tools, it is necessary to consider in more detail what can be attributed to the concept of information.
Information and its classification
There are many definitions and classifications of "Information". The most concise and at the same time capacious definition is given in Federal Law No. 149-FZ of July 27, 2006 (as amended on July 29, 2017) “On Information, Information Technologies and Information Protection” , Article 2: Information is information ( messages, data) regardless of the form of their presentation ".
Information can be classified into several types and, depending on the category of access to it, is divided into publicly available information , as well as information to which access is restricted — confidential data and state secrets .
')
Information depending on the order of its provision or distribution is divided into information:
- Freely distributed
- Provided by agreement of persons involved in relevant relationships
- Which, in accordance with federal laws, is subject to submission or distribution.
- Distribution to which is restricted or prohibited in the Russian Federation
Information on purpose is the following types:
- Mass - contains trivial information and operates with a set of concepts, understandable to most of the society.
- Special - contains a specific set of concepts that may not be understandable to the majority of society, but are necessary and understandable within a narrow social group where this information is used.
- Secret - access to which is provided to a narrow circle of persons and through closed (protected) channels.
- Personal (private) - a set of information about any person that determines the social status and types of social interactions.
Information security tools should be applied directly to information which access is limited - this is a state secret and confidential data .
According to the law of the Russian Federation of July 21, 1993 N 5485-1 (as amended on March 8, 2015 ) “On State Secrets”, Article 5. “The List of Information Constituting State Secrets ” includes:
- Information in the military field.
- Information in the field of economics, science and technology.
- Information in the field of foreign policy and economics.
- Information in the field of intelligence, counter-intelligence and operational-search activities , as well as in the field of countering terrorism and in the field of ensuring the security of persons in respect of whom a decision has been taken to apply state protection measures.
The list of information that can make confidential information is contained in the presidential decree of March 6, 1997 No. 188 (as amended on July 13, 2015) “On approval of the list of confidential information” .
Confidential data is information, access to which is limited in accordance with the laws of the state and the rules that companies set independently. You can highlight the following types of sensitive data:
- Personal confidential data: Information about the facts, events and circumstances of a citizen’s private life, allowing him to identify his identity (personal data), with the exception of information subject to dissemination in the media in cases established by federal laws. The only exception is information that is distributed in the media.
- Official confidential data: Official information, access to which is restricted by state authorities in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and federal laws (official secrecy).
- Judicial confidential data: On state protection of judges, law enforcement officials and regulatory agencies. On the state protection of victims, witnesses and other participants in criminal proceedings. The information contained in the personal files of convicts, as well as information about the enforcement of judicial acts, acts of other bodies and officials, except for information that is publicly available in accordance with Federal Law of October 2, 2007 N 229-FZ "On Enforcement Proceedings" .
- Commercial confidential data: all types of information that is related to commerce (profit) and access to which is limited by law or information about the invention, utility model or industrial design before the official publication of information about them by the company (secret developments, production technologies, etc.) ).
- Professional confidential data: Information related to professional activities, access to which is restricted in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal laws (medical, notarial, lawyer secrets, confidentiality of correspondence, telephone conversations, mail, telegraph or other messages, etc.)
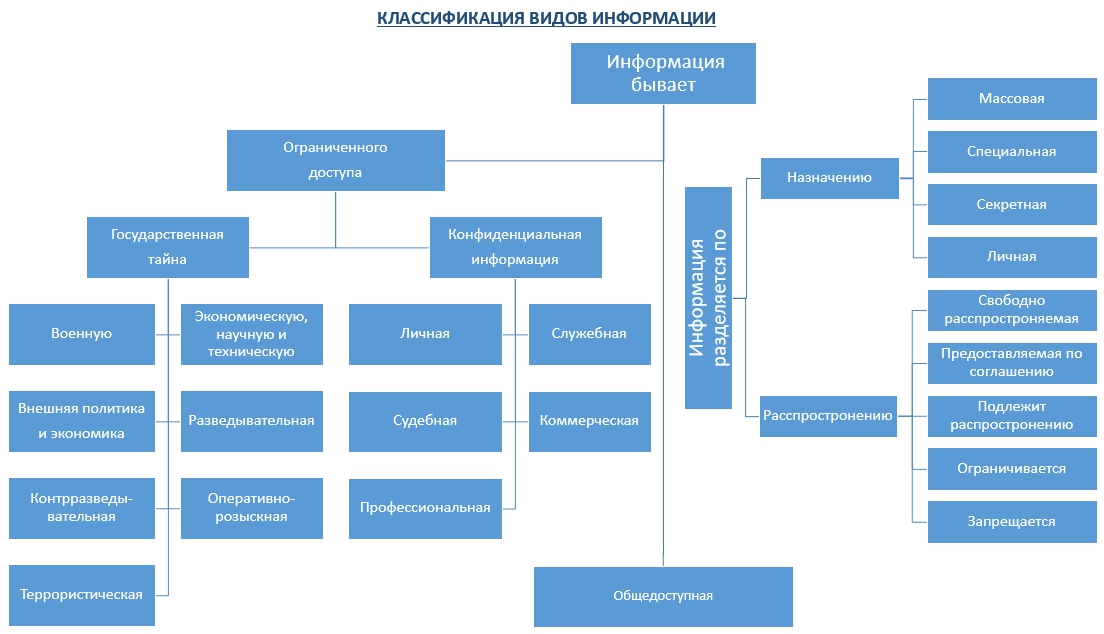
Figure 1. Classification of types of information.
Personal Information
We should also pay attention to and consider personal data. According to the federal law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ (as amended on July 29, 2017) “On personal data” , article 4: Personal data is any information relating to a directly or indirectly determined or determined individual (subject of personal data) .
The operator of personal data is a state body, municipal body, legal or natural person, independently or jointly with other persons organizing and (or) processing personal data, as well as determining the purposes of personal data processing, the composition of personal data to be processed, actions (operations ) committed with personal data.
Personal data processing - any action (operation) or a set of actions (operations) performed with the use of automation tools or without the use of such tools with personal data, including the collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, refinement (update, change), retrieval, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of personal data.
The rights to the processing of personal data are enshrined in the regulations on state bodies, federal laws, licenses to work with personal data, which are issued by Roskomnadzor or FSTEC.
Companies that professionally work with personal data of a wide range of people, for example, hosting virtual server companies or telecom operators, should be included in the register, it is maintained by Roskomnadzor.
For example, our hosting of virtual servers VPS.HOUSE operates within the framework of the legislation of the Russian Federation and in accordance with the licenses of the Federal Service for Supervision in the Field of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications No. 139322 dated December 25, 2015 (Telematic Communication Services) and No. 139323 dated December 25 .2015 (Communication services for data transmission, with the exception of communication services for data transmission for the purposes of voice transmission) .
Based on this, any site on which there is a user registration form in which information relating to personal data is indicated and subsequently processed is the operator of personal data.
Taking into account Article 7, Law No. 152- “On Personal Data” , operators and other persons who have access to personal data are obliged not to disclose to third parties and not to distribute personal data without the consent of the subject of personal data, unless otherwise provided by federal law. Accordingly, any personal data operator is obliged to ensure the necessary security and confidentiality of this information.
In order to ensure the security and confidentiality of information, it is necessary to determine what kind of information carriers are, access to which is open and closed. Accordingly, the methods and means of protection are selected as well depending on the type of carrier.
The main information carriers:
- Printed and electronic media, social networks, other resources on the Internet;
- Employees of the organization who have access to information on the basis of their friendly, family, professional connections;
- Communication facilities that transmit or store information: telephones, PBX, other telecommunications equipment;
- Documents of all types: personal, official, government;
- Software as an independent information object, especially if its version was developed specifically for a particular company;
- Electronic storage media that process data automatically.
Having determined what information is to be protected, information carriers and possible damage in case of its disclosure, you can select the necessary means of protection.
Classification of information security tools
In accordance with the federal law of July 27, 2006 No. 149-FZ (as amended on July 29, 2017) “On Information, Information Technologies and Protection of Information” , article 7, paragraph 1. and clause 4:
1. Information protection is the adoption of legal, organizational and technical measures aimed at:
- Ensuring the protection of information from unauthorized access, destruction, modification, blocking, copying, providing, distributing, as well as from other illegal actions in relation to such information;
- Compliance with confidential information of limited access;
- The exercise of the right of access to information.
4. The information owner, the information system operator, in the cases established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, must provide :
- Preventing unauthorized access to information and (or) its transfer to persons who do not have the right to access information;
- Timely detection of unauthorized access to information;
- Prevention of the possibility of adverse consequences of violation of the procedure for access to information;
- Non- admission of influence on technical means of information processing, as a result of which their functioning is disrupted;
- The possibility of immediate recovery of information modified or destroyed due to unauthorized access to it;
- Constant monitoring of the level of information security;
- The presence on the territory of the Russian Federation of databases of information that are used to collect, record, systematize, accumulate, store, refine (update, change), extract personal data of citizens of the Russian Federation (clause 7 was introduced by Federal Law of July 21, 2014 No. 242- FZ ).
Based on the law No. 149-FZ, information security can also be divided into several levels:
- The legal level ensures compliance with state standards in the field of information protection and includes copyright, decrees, patents and job descriptions.
Properly built protection system does not violate the rights of users and data processing standards. - The organizational level allows you to create regulations for the work of users with confidential information, to select personnel, to organize work with documentation and data carriers.
The rules for working with confidential information are called access control rules. The rules are established by company management in conjunction with the security service and the supplier who implements the security system. The goal is to create conditions for access to information resources for each user, for example, the right to read, edit, transmit a confidential document.
Access control rules are developed at the organizational level and are implemented at the stage of work with the technical component of the system. - The technical level is conventionally divided into physical, hardware, software and mathematics (cryptographic).
Information Security Tools
Information security tools are usually divided into regulatory (informal) and technical (formal) .
Informal means of protecting information
Informal means of protecting information - are regulatory (legislative), administrative (organizational) and moral and ethical means, which include: documents, rules, events.
The legal basis ( legislative means ) of information security is provided by the state. Information protection is governed by international conventions, the Constitution, federal laws "On Information, Information Technologies and Information Protection", laws of the Russian Federation "On Security", "On Communications", "On State Secrets" and various secondary legislation.
Also, some of the listed laws were cited and considered by us above, as legal bases of information security. Failure to comply with these laws entails threats to information security, which can lead to significant consequences, which in turn is punishable under these laws in the flesh to criminal responsibility.
The state will also determine the measure of responsibility for violation of the provisions of the legislation in the field of information security. For example, Chapter 28, “Computer Crime Offenses” in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, includes three articles:
- Article 272 "Wrongful access to computer information";
- Article 273 "Creation, use and distribution of malicious computer programs";
- Article 274 "Violation of the rules of operation of the means of storage, processing or transmission of computer information and information and telecommunication networks."
Administrative (organizational) measures play an essential role in creating a reliable information protection mechanism. Since the possibility of unauthorized use of confidential information is largely determined not by technical aspects, but by malicious acts. For example, negligence, carelessness and negligence of users or protection personnel.
To reduce the impact of these aspects, a set of organizational, legal, and organizational and technical measures is necessary, which would exclude or minimize the possibility of threats of confidential information.
In this administrative and organizational activity for the protection of information for security officers, there is room for creativity.
This includes architectural and planning solutions that protect the meeting rooms and management rooms from listening, and the establishment of various levels of access to information.
From the point of view of the regulation of personnel activities, it will be important to design a system of requests for access to the Internet, external e-mail, and other resources. A separate element will be the receipt of an electronic digital signature to enhance the security of financial and other information, which is transmitted to government agencies via e-mail.
Moral and ethical means include the moral norms or ethical rules that have been established in a society or a given group, observance of which contributes to the protection of information, and their violation is equated with non-observance of the rules of behavior in a society or a collective. These norms are not obligatory, as legislatively approved norms, however, their non-observance leads to a decline in the authority, prestige of a person or organization.
Formal information security tools
Formal security tools are special hardware and software that can be divided into physical, hardware, software, and cryptographic.
Physical information security tools are any mechanical, electrical, and electronic mechanisms that function independently of information systems and create barriers to accessing them.
Locks, including electronic, screens, blinds are designed to create obstacles to the contact of destabilizing factors with systems. The group is supplemented by means of security systems, for example, video cameras, video recorders, sensors, detecting movement or exceeding the degree of electromagnetic radiation in the area of location of technical means for removing information.
Hardware information security tools are any electrical, electronic, optical, laser and other devices that are embedded in information and telecommunication systems: special computers, employee control systems, server protection and corporate networks. They prevent access to information, including through its disguise.
The hardware includes: noise generators, network filters, scanning radios and many other devices that “block” potential channels of information leakage or allow them to be detected.
Information security software is a simple and comprehensive program designed to solve problems associated with ensuring information security.
An example of integrated solutions are the DLP-system and SIEM-system.
DLP systems (Data Leak Prevention, literally “data leakage prevention”), respectively, serve to prevent information leakage, reformatting and redirecting information flows.
SIEM systems (“Security Information and Event Management”, which means “Event and Information Security Management”) provide real-time analysis of security events (alarms) from network devices and applications. SIEM is represented by applications, appliances, or services, and is also used to log data and generate reports for compatibility with other business data.
The software is demanding on the power of the hardware devices, and additional resources must be provided for during installation.
Mathematical (cryptographic) - the introduction of cryptographic and shorthand data protection methods for secure transmission over a corporate or global network.
Cryptography is considered one of the most reliable ways to protect data, because it protects the information itself, and not access to it. Cryptographically transformed information has a high degree of protection.
The introduction of cryptographic protection of information provides for the creation of software and hardware complex, the architecture and composition of which is determined based on the needs of a particular customer, the requirements of the legislation, the tasks and necessary methods, and encryption algorithms.
This may include encryption software components (crypto-providers), VPN organization tools, authentication tools, key generation and verification tools, and electronic digital signature.
Encryption tools can support GOST encryption algorithms and provide the necessary classes of cryptographic protection, depending on the required degree of protection, the regulatory framework and compatibility requirements with other, including external systems. At the same time, encryption tools protect the entire set of information components, including files, file directories, physical and virtual storage media, servers and storage systems entirely.
In conclusion of the second part, having reviewed briefly the main methods and means of protecting information, as well as classifying information, we can say the following: The fact that the well-known thesis is once again confirmed that ensuring information security is a whole set of measures that includes all aspects of protection information, the creation and maintenance of which must be approached most carefully and seriously.
It is necessary to strictly observe and under no circumstances violate the “Golden Rule” - this is an integrated approach.
For a more visual representation of information protection means, namely, as an indivisible set of measures, are presented below in Figure 2, each of the building blocks of which represents the protection of information in a certain segment, remove one of the building blocks and there will be a security threat.
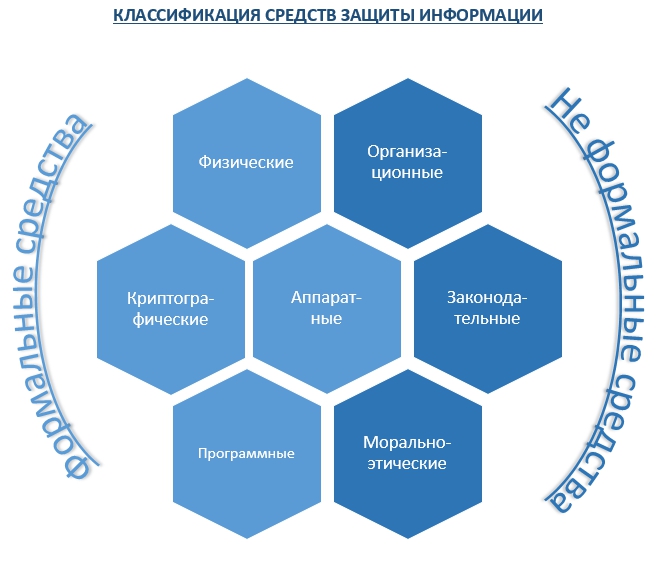
Figure 2. Classification of information security tools.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343498/
All Articles