IntelliJ IDEA 2017.3. What is new and interesting?
If anyone else does not know, today IntelliJ IDEA 2017.3 came out . Continuing the tradition, I tell you that new and interesting things have been added or changed in the release: smart tips, refactorings, navigation, tools for working with Git , databases, support for frameworks and much more.

Go!
')
Type Casting for Call Chains in Smart Completion
In the previous release (IntelliJ IDEA 2017.2), call chains ( method call chains ) began to appear when you first called Smart Completion (before that they were only available on the second call). In this release, these chains also take into account the automatic casting of types depending on the context:

Code flow analysis
A couple of years ago, IntelliJ IDEA learned how to automatically output Nullable and NotNull annotations for parameters and return values of library class methods. This conclusion was made on the basis of analysis of the flow of execution within the methods. In version 2017.3, the output of annotations for parameters works not only for methods of library classes, but also for private or final methods of classes within a project.
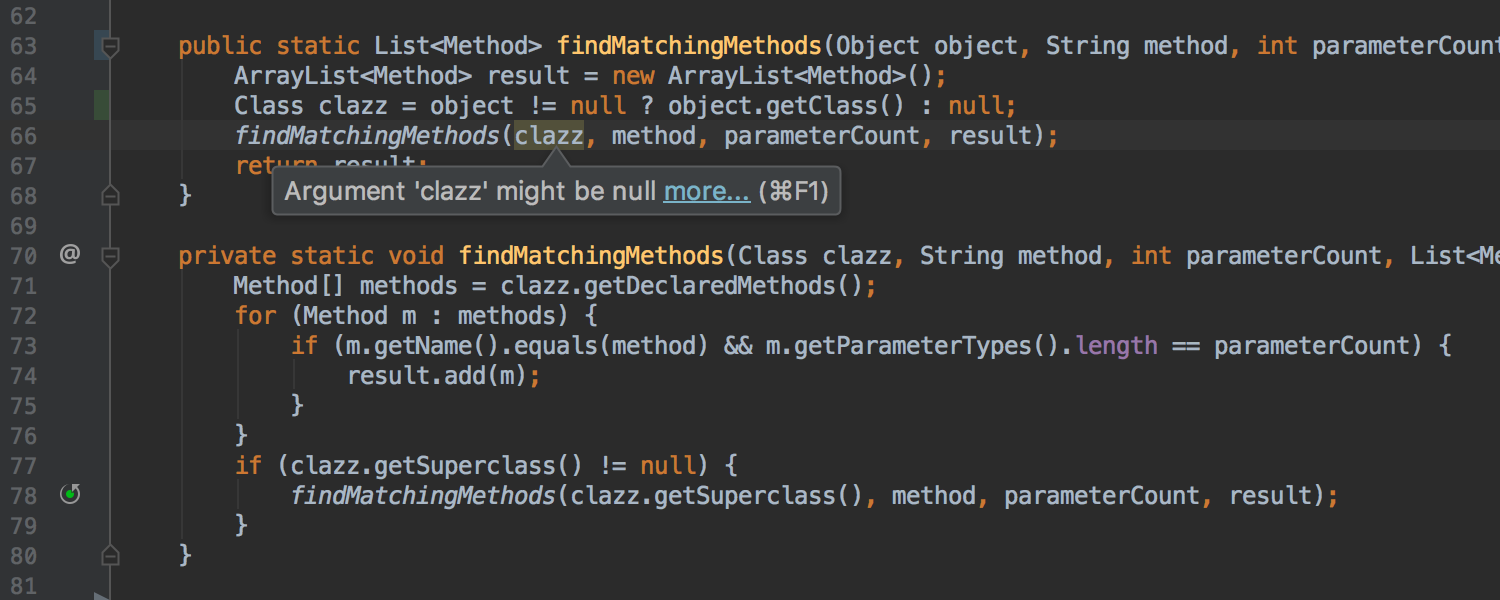
In the case of annotation in a similar method, the IDE offers quick-fix for explicit declaration of the annotation:

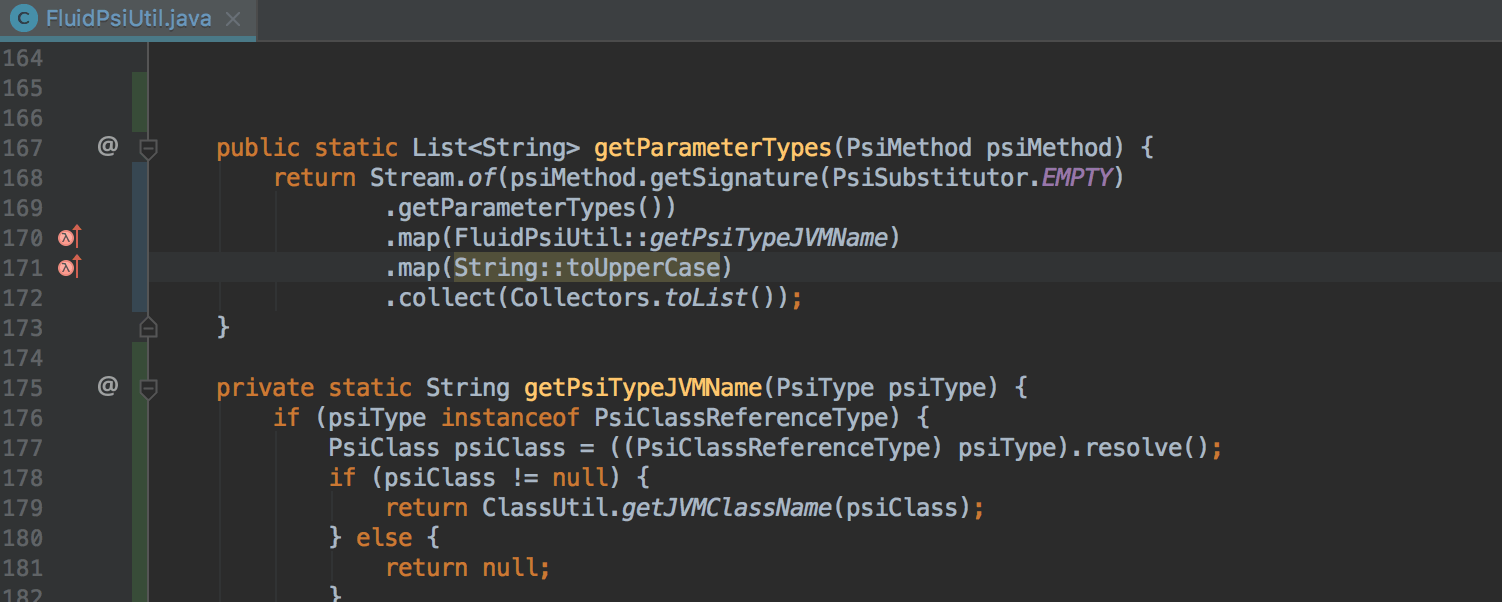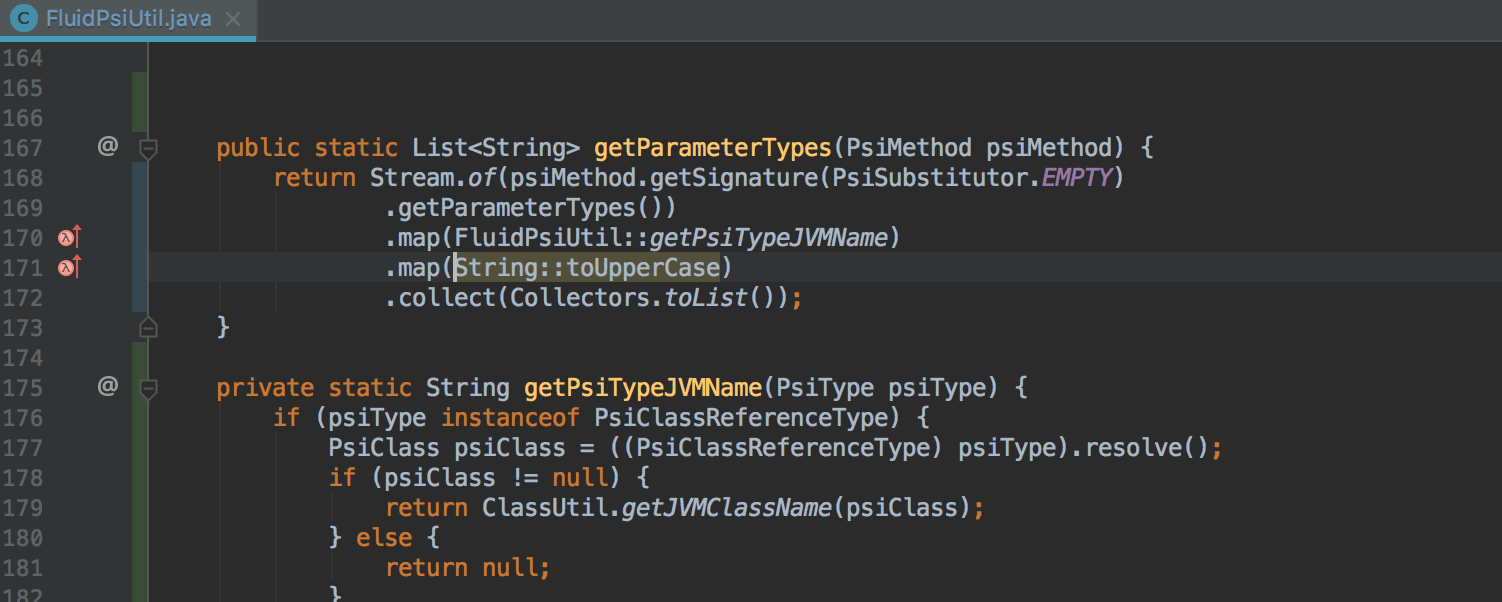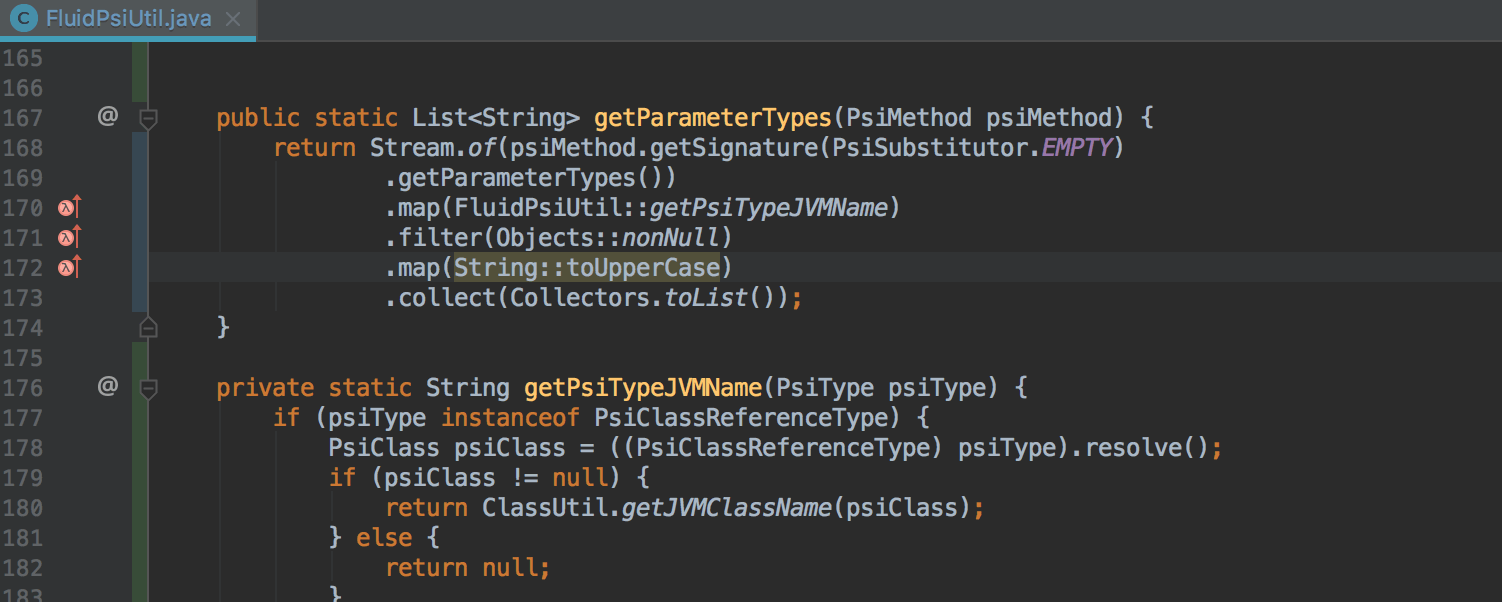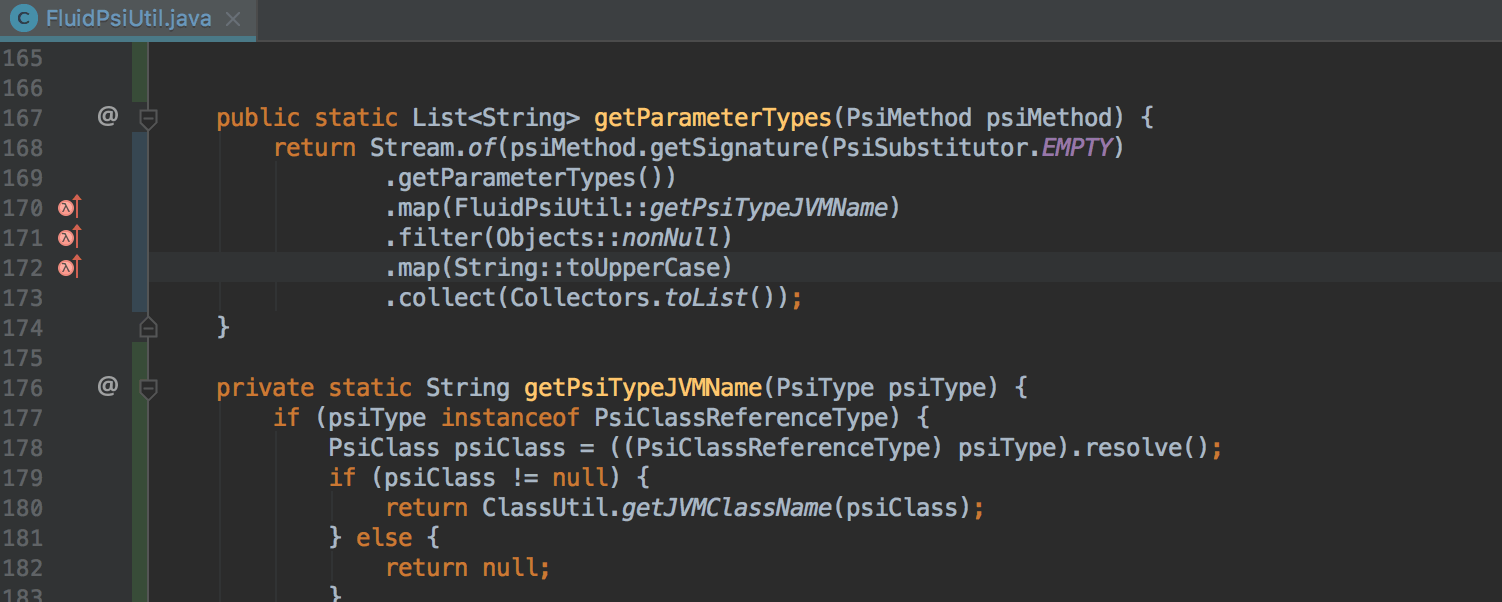
The IDE also learned to detect potential problems with Nullability within calls to Stream API methods. If a potential problem is detected, the IDE reports this and, where possible, offers to automatically make changes to the code to avoid receiving an error during execution:
Transforming a for loop into a Stream API call chain
For loops, the result of which is the addition of strings to StringBuilder , can now be automatically transformed into a chain of calls to the Stream API using Stream.collect and Collectors.joining :
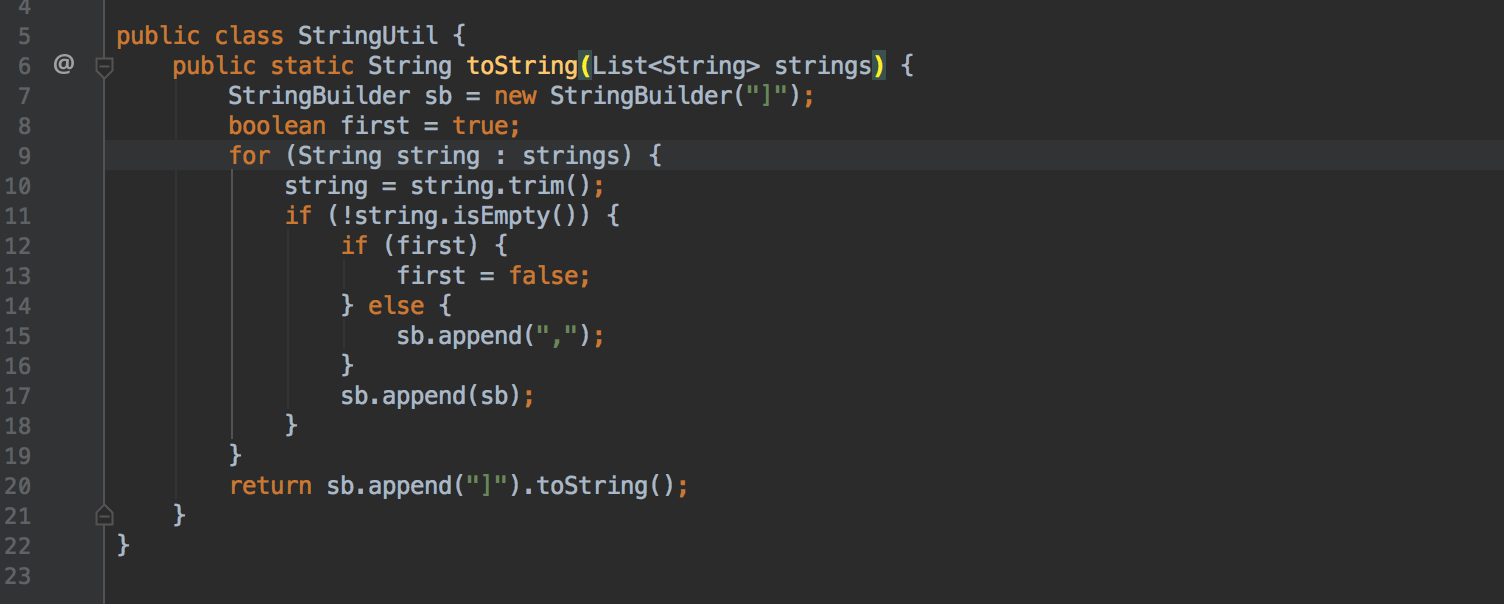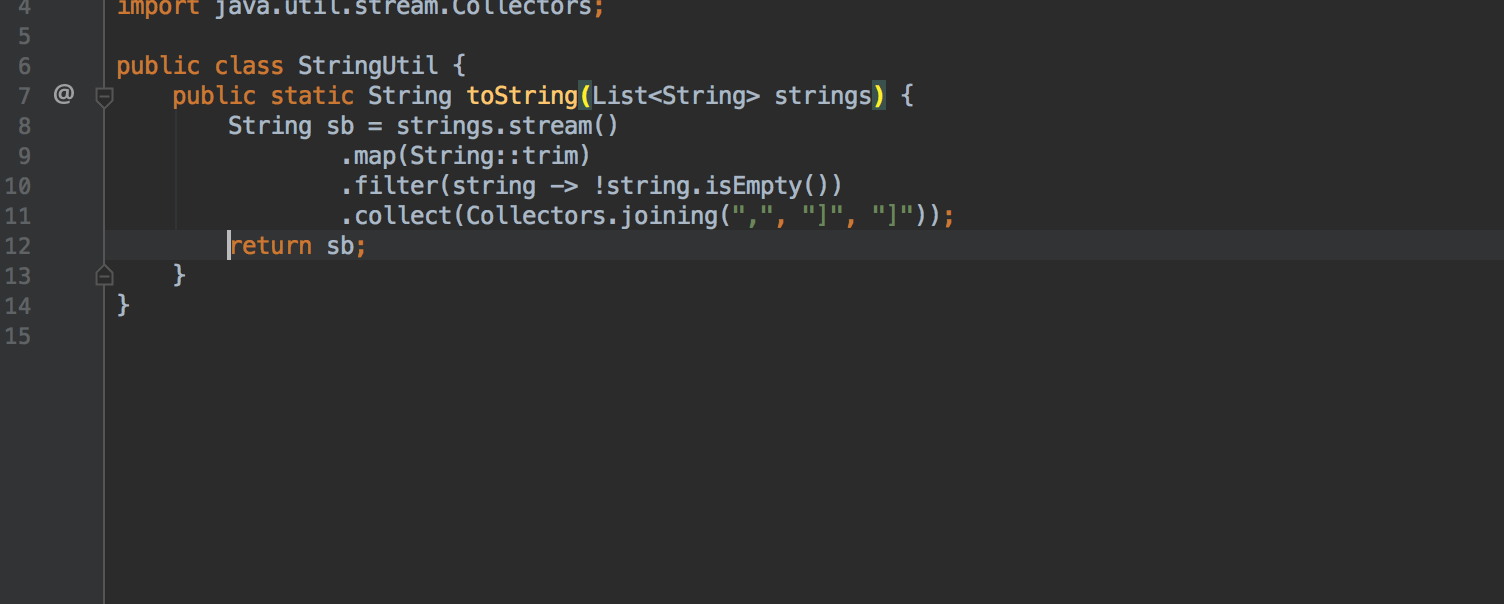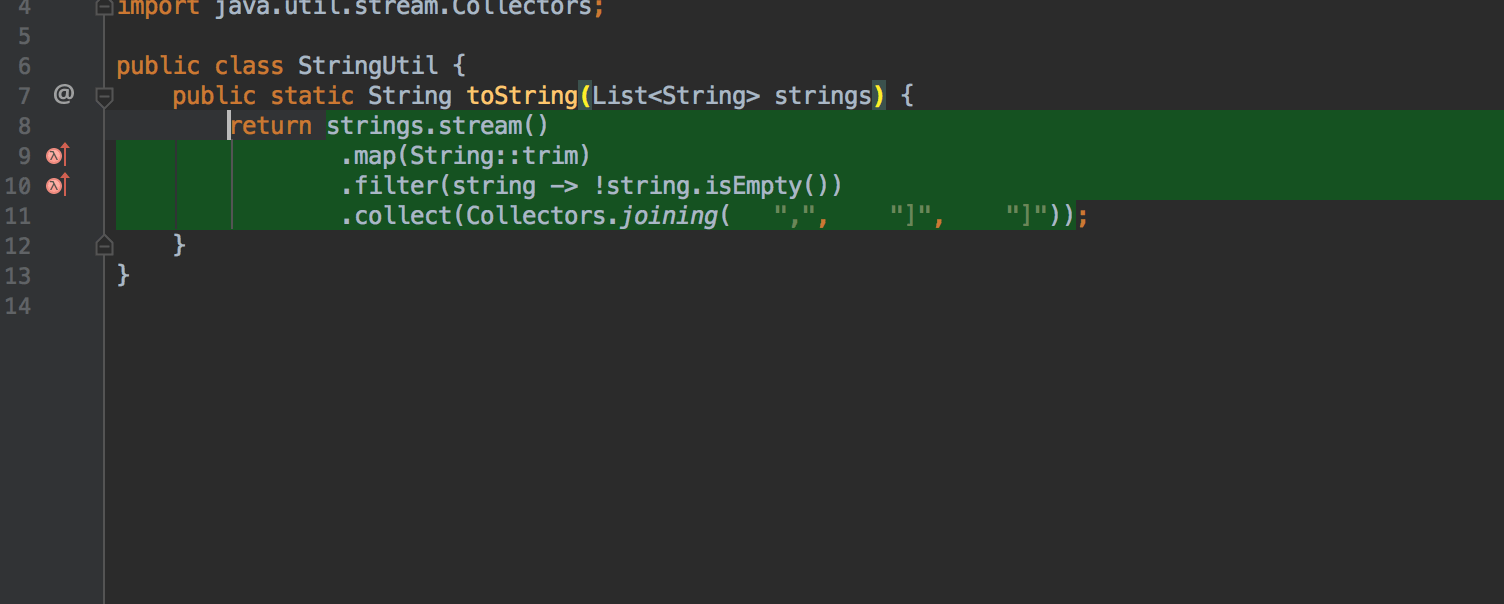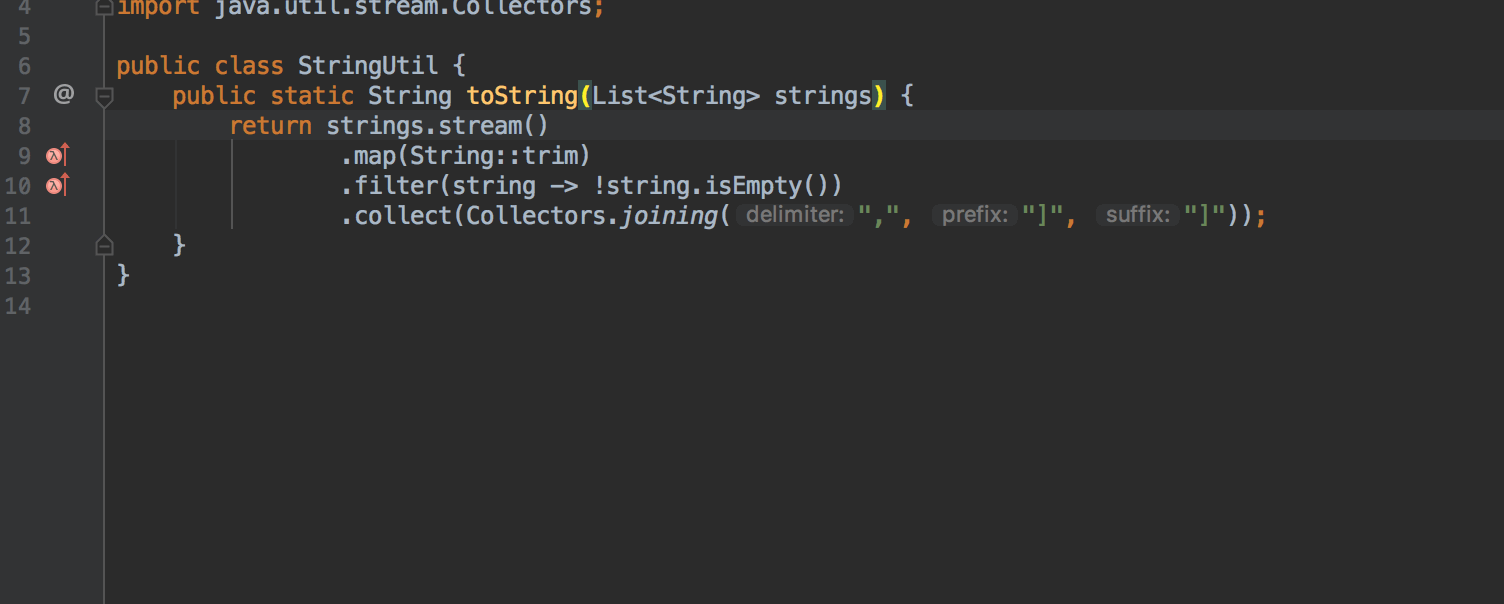
Invert logic boolean methods using quick-fix
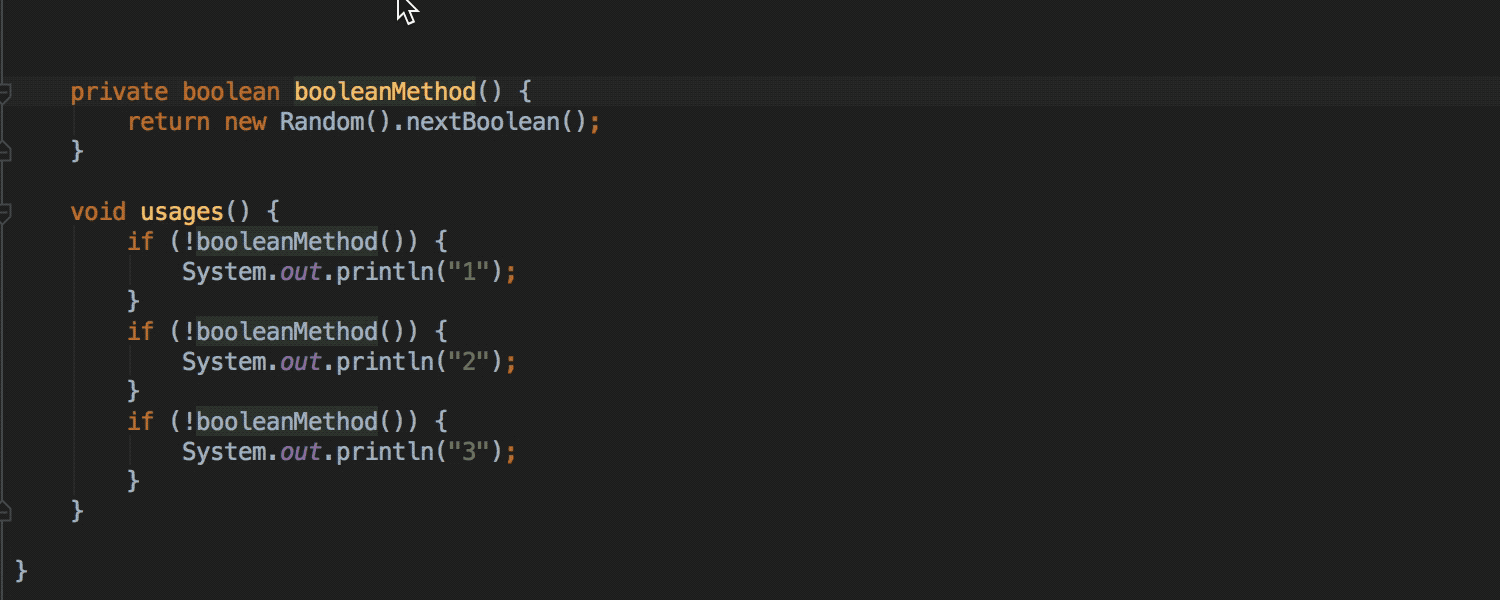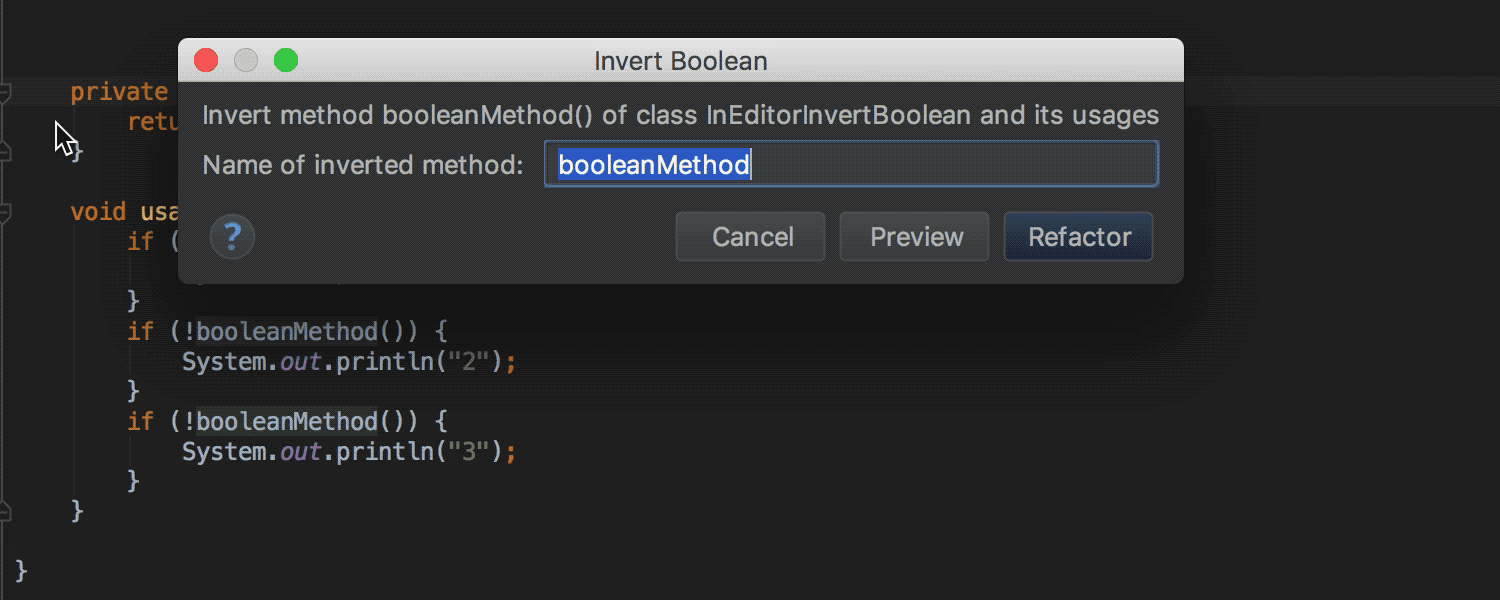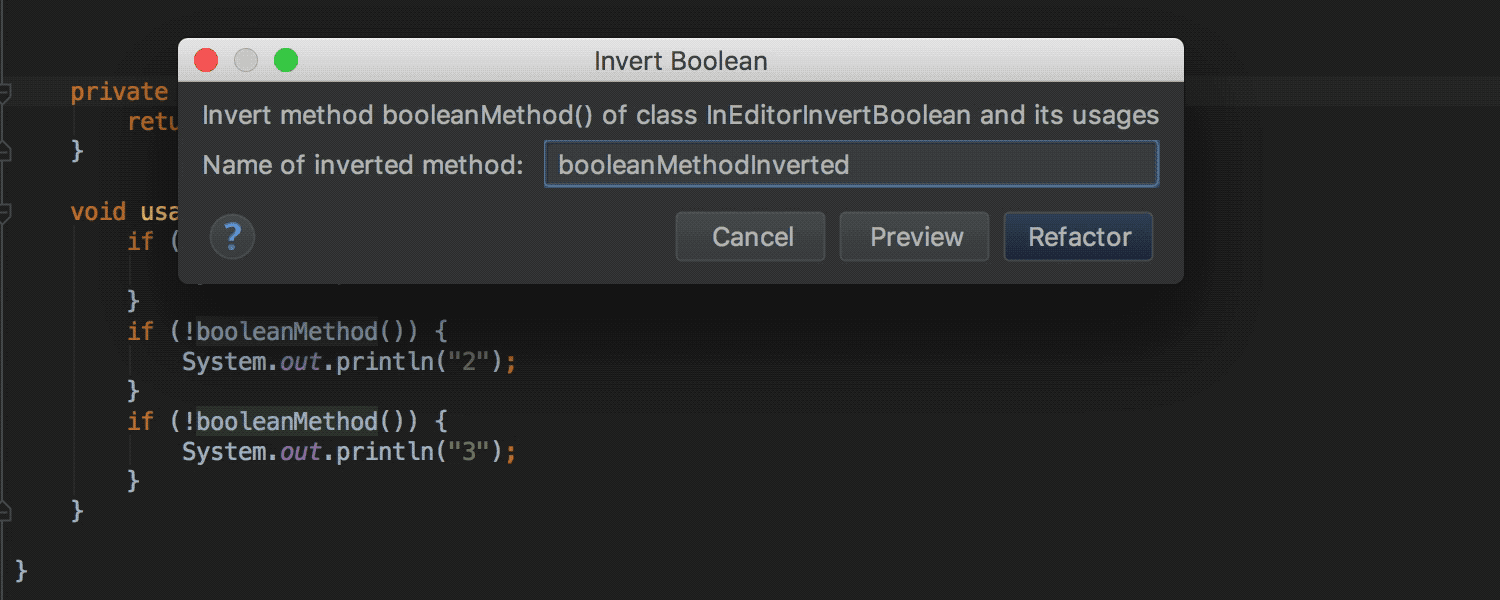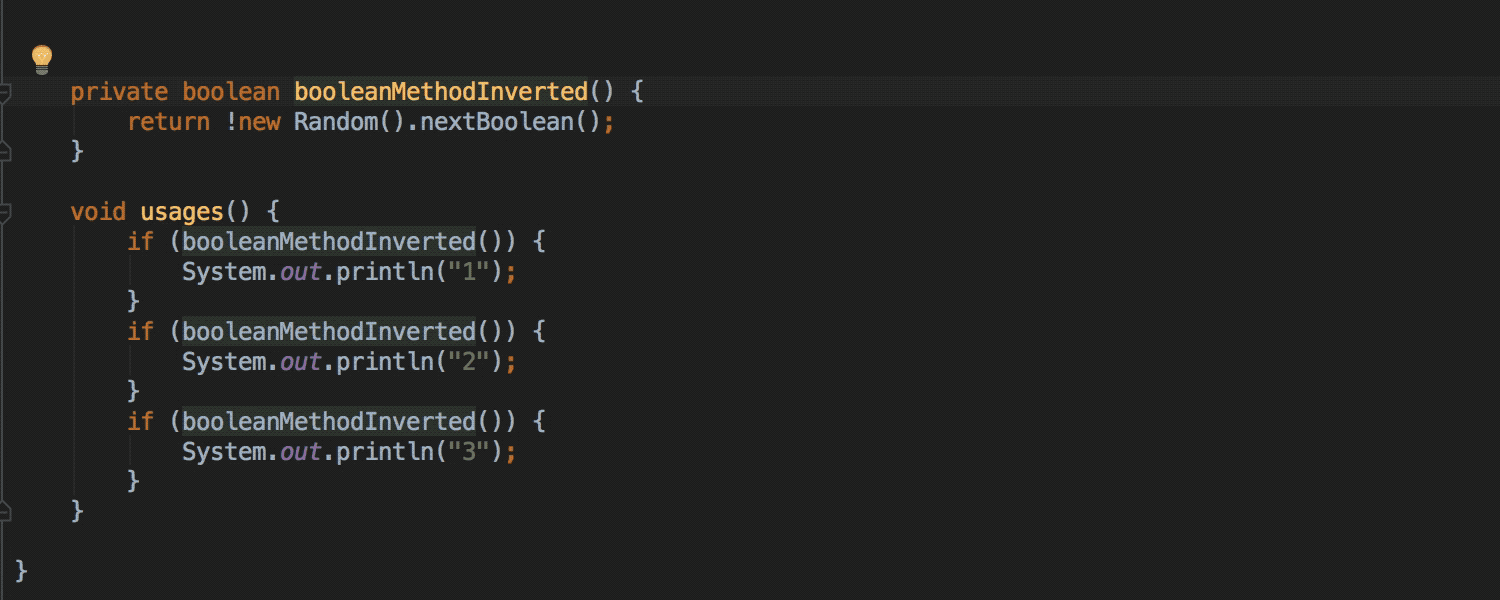
Invert Boolean refactoring is now available as quick-fix for methods (earlier quick-fix was available only in batch mode , as well as for variables, constants and class fields):
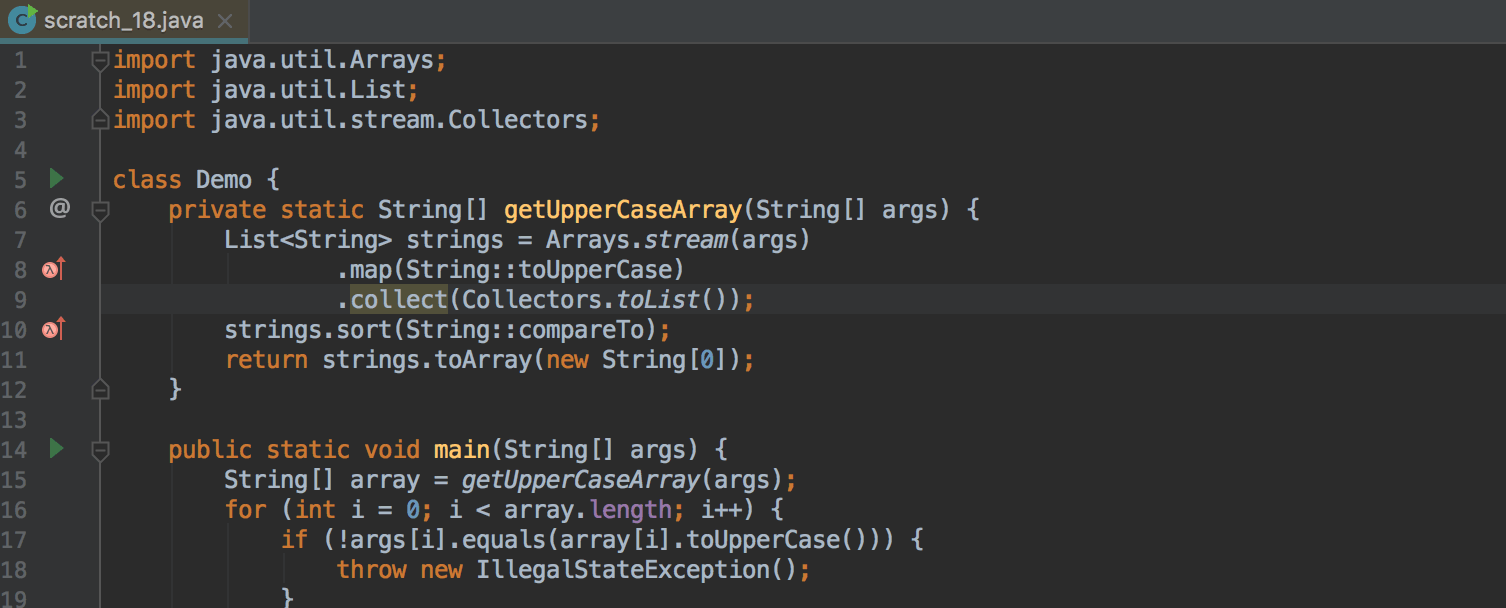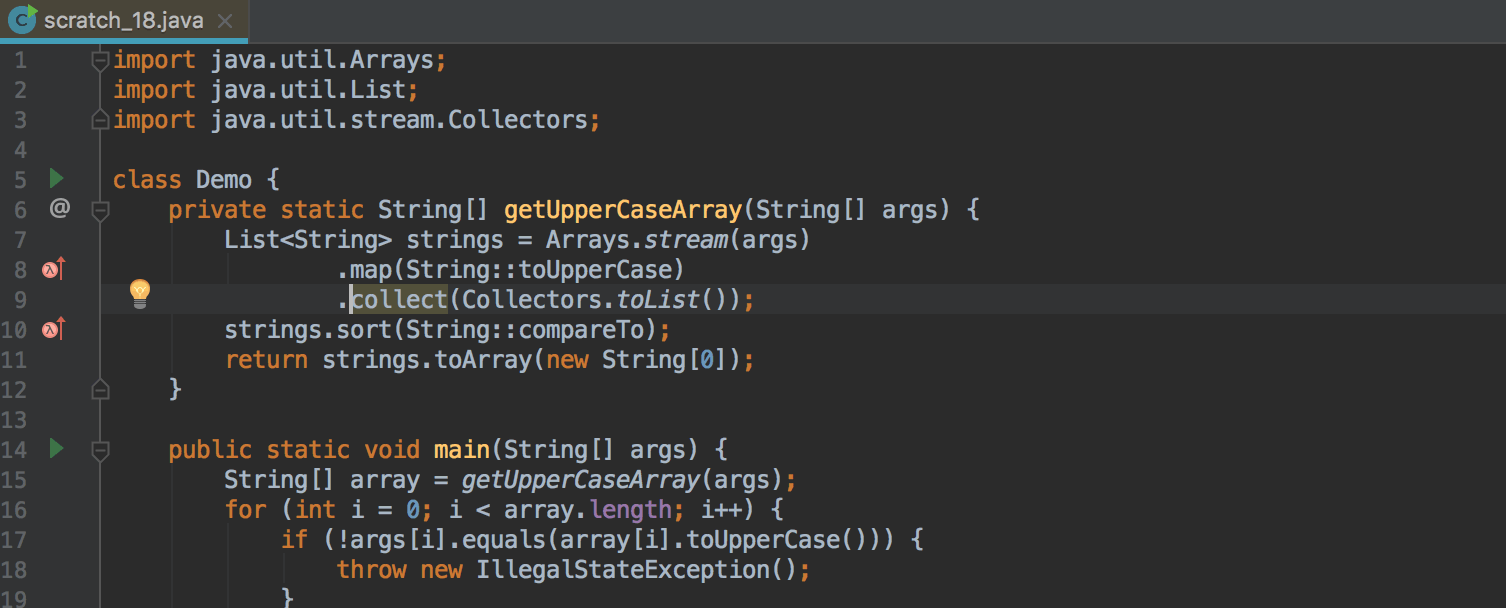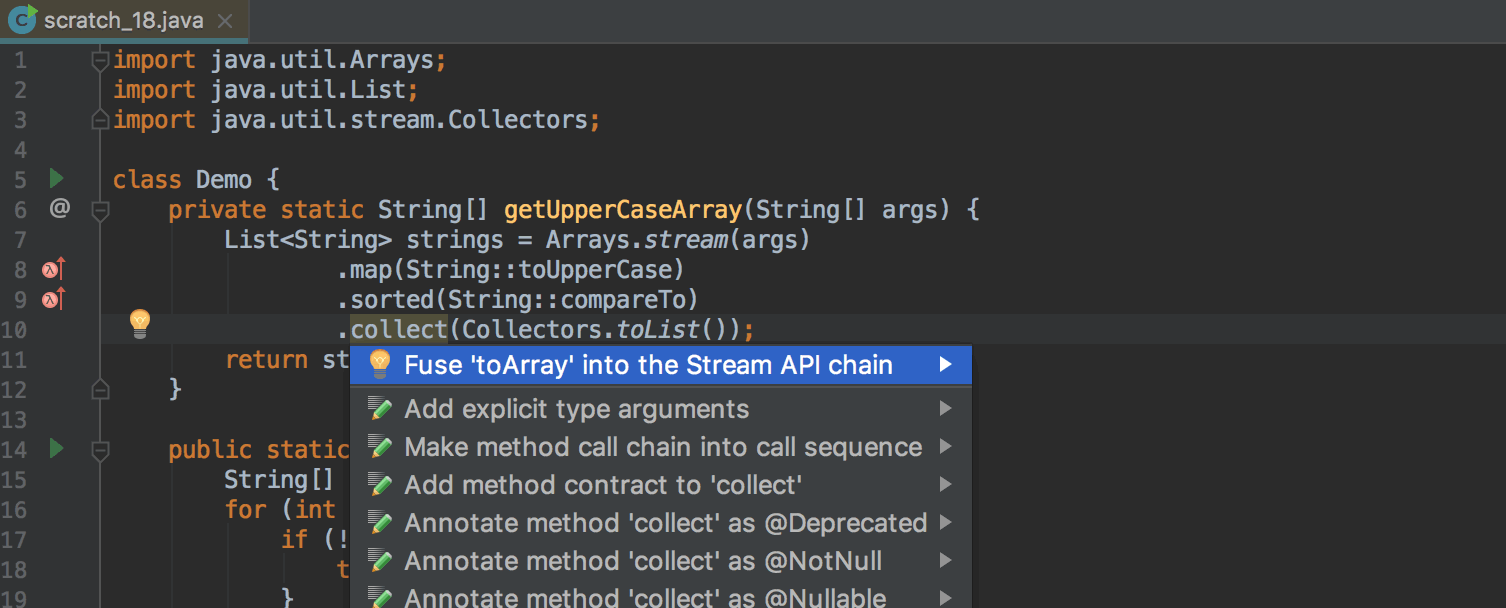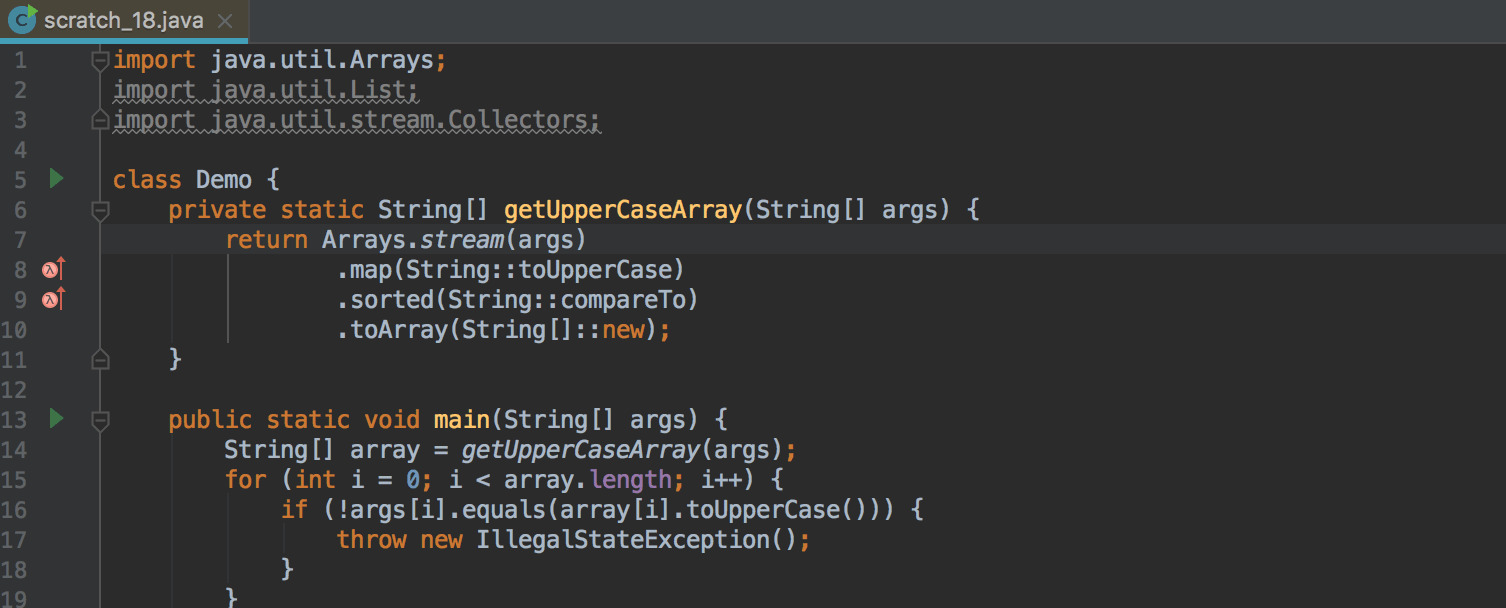
Separate Method Calls on Collections and Stream API Call Chains
Where this makes sense, the IDE now suggests replacing separate sort and toArray calls on collections with corresponding methods on the Stream API call chain:
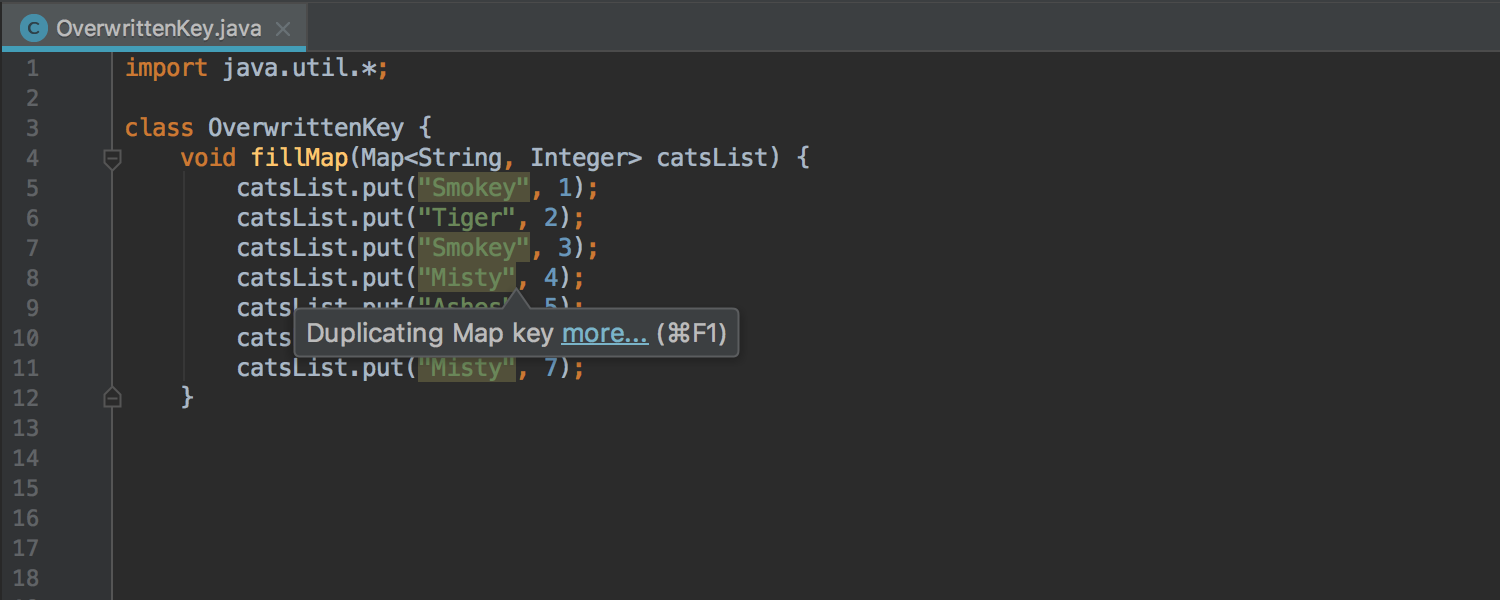
Detection of duplicate keys in Map and Set initialization
If you accidentally specify a value for the same key two or more times or try to add the same element to the Set , now the IDE will warn you about a possible error:
Detect Excess Exception Declarations
Detection of redundant exception declarations previously worked only for final and private methods. Now detection works for any methods:
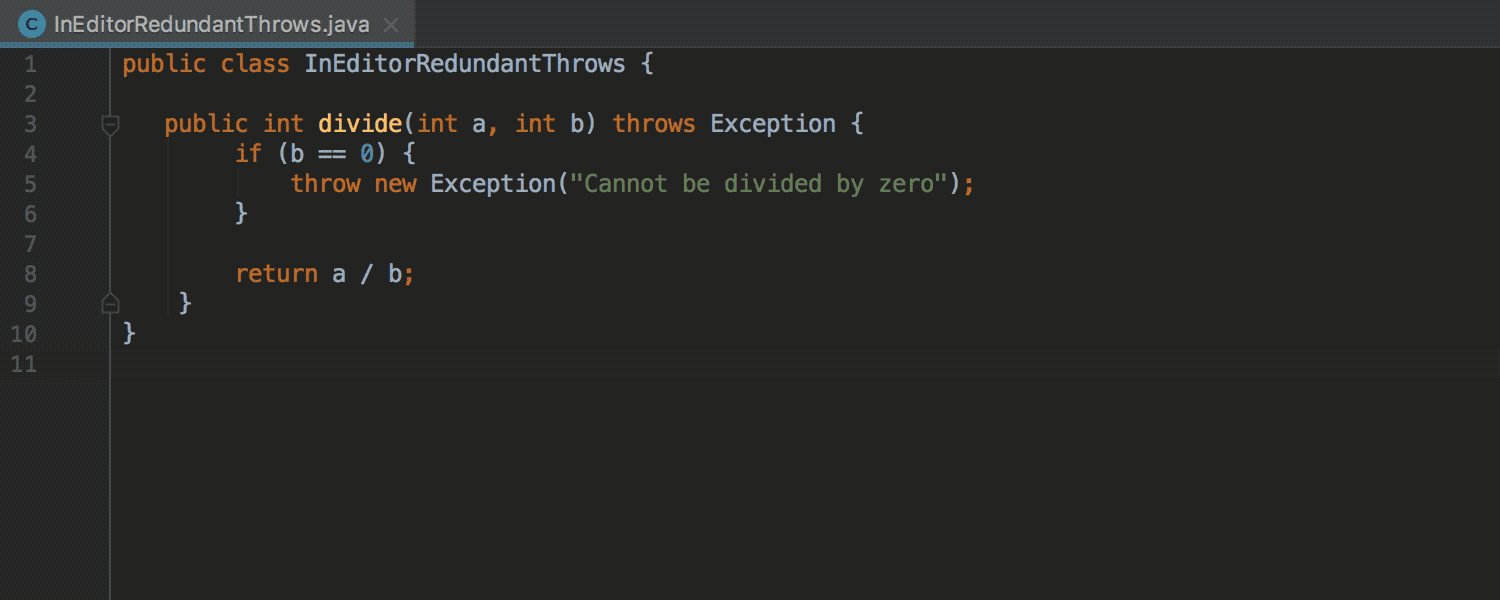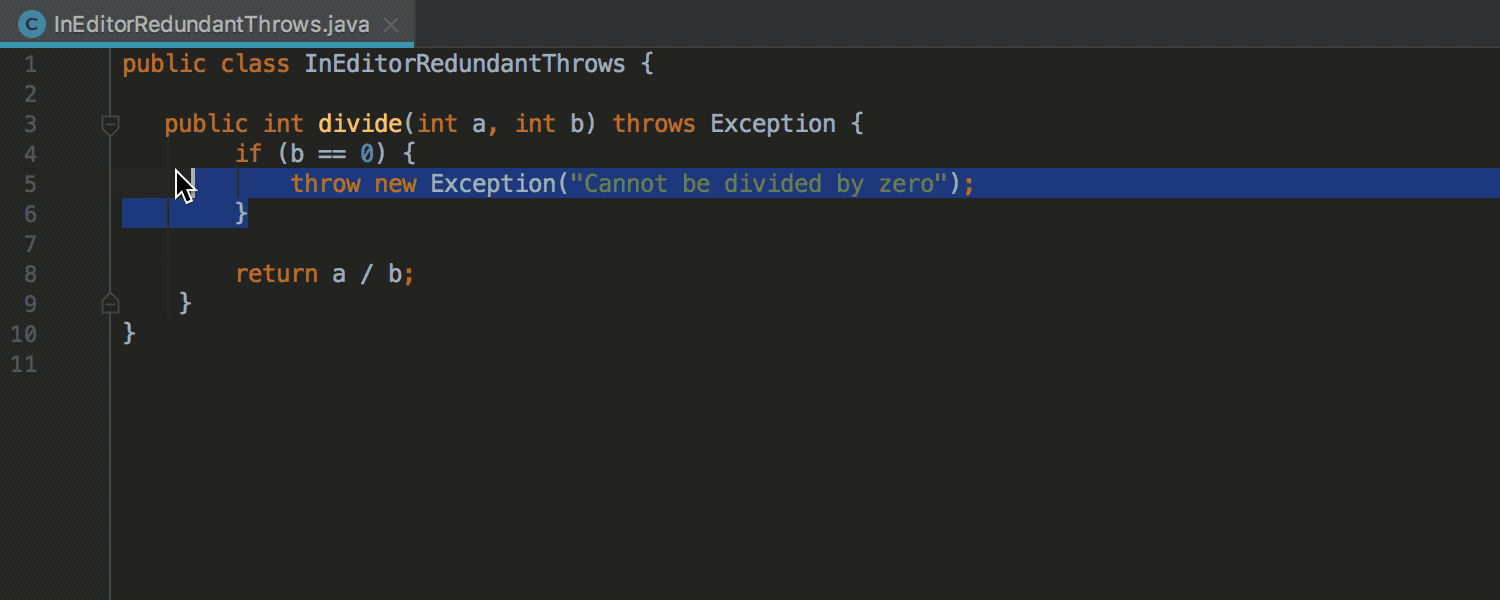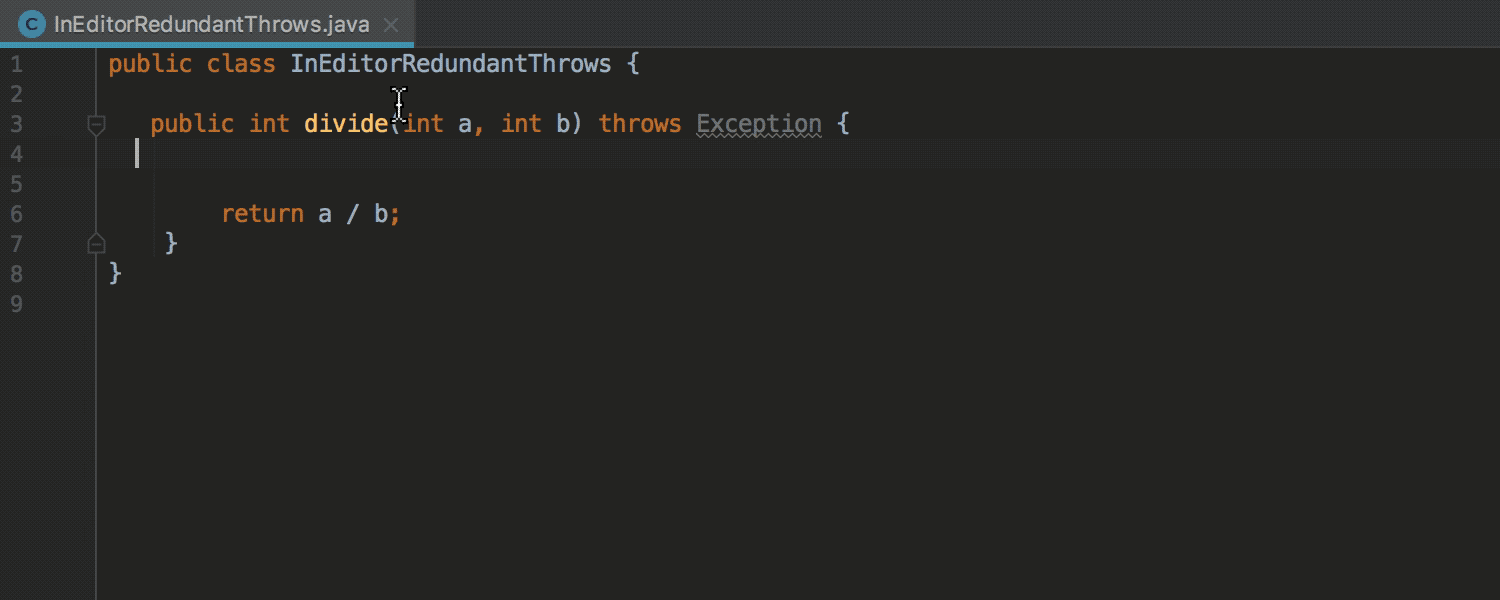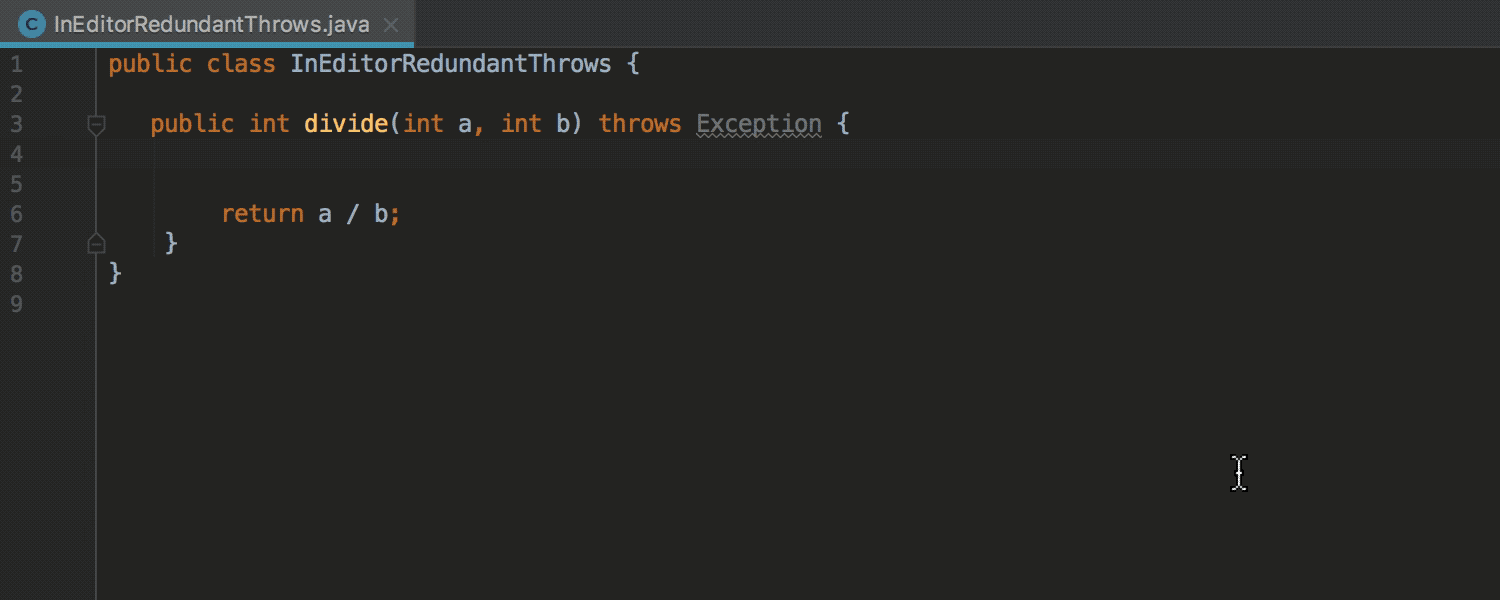
This particular inspection may be disabled for so-called entry points, for example for tests.
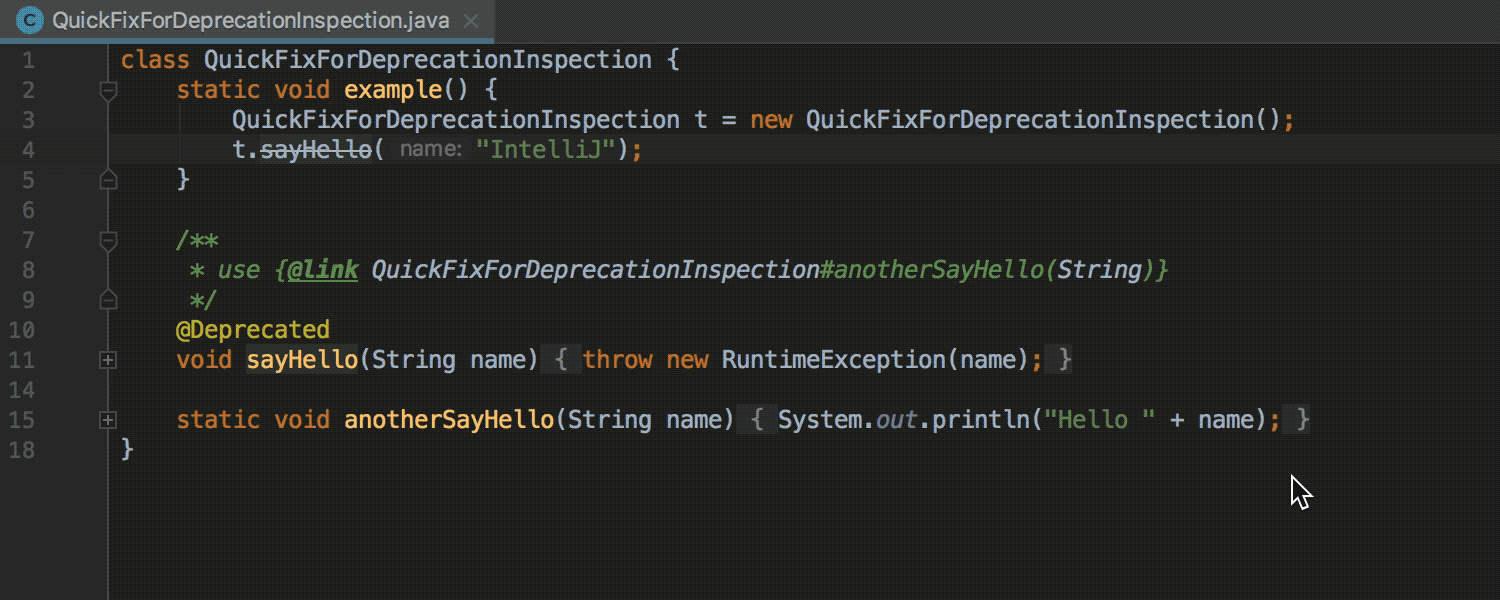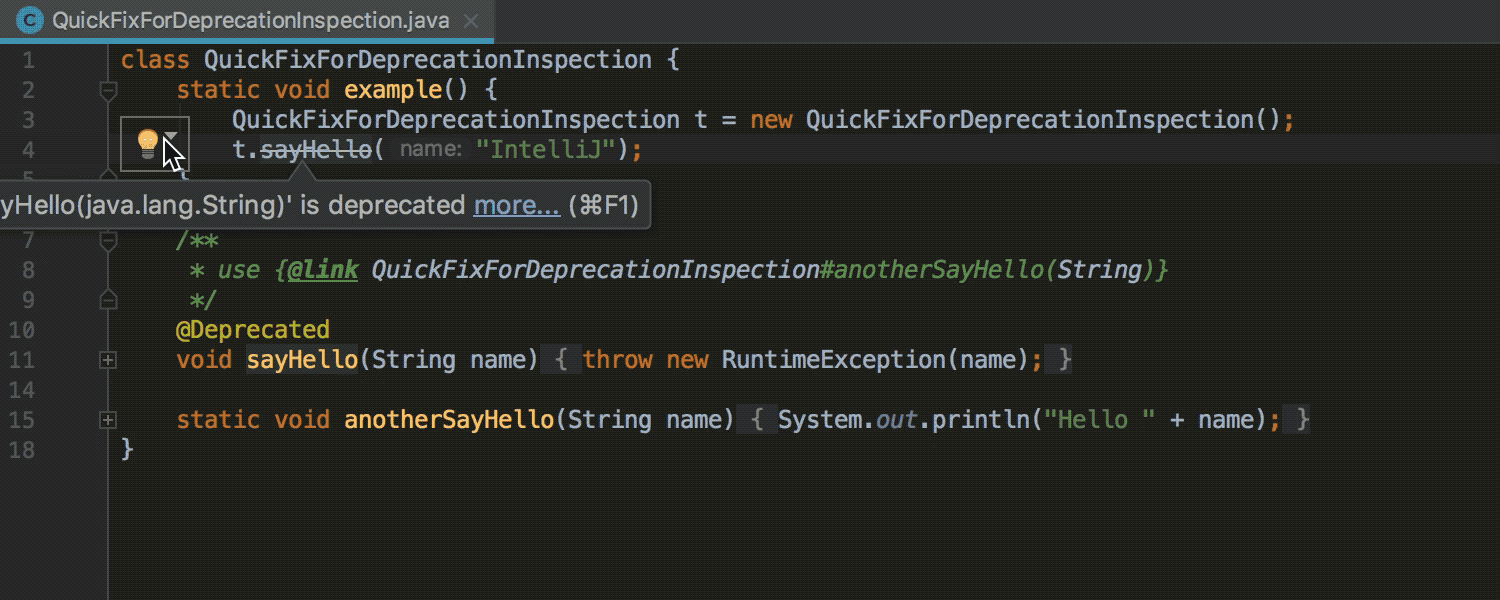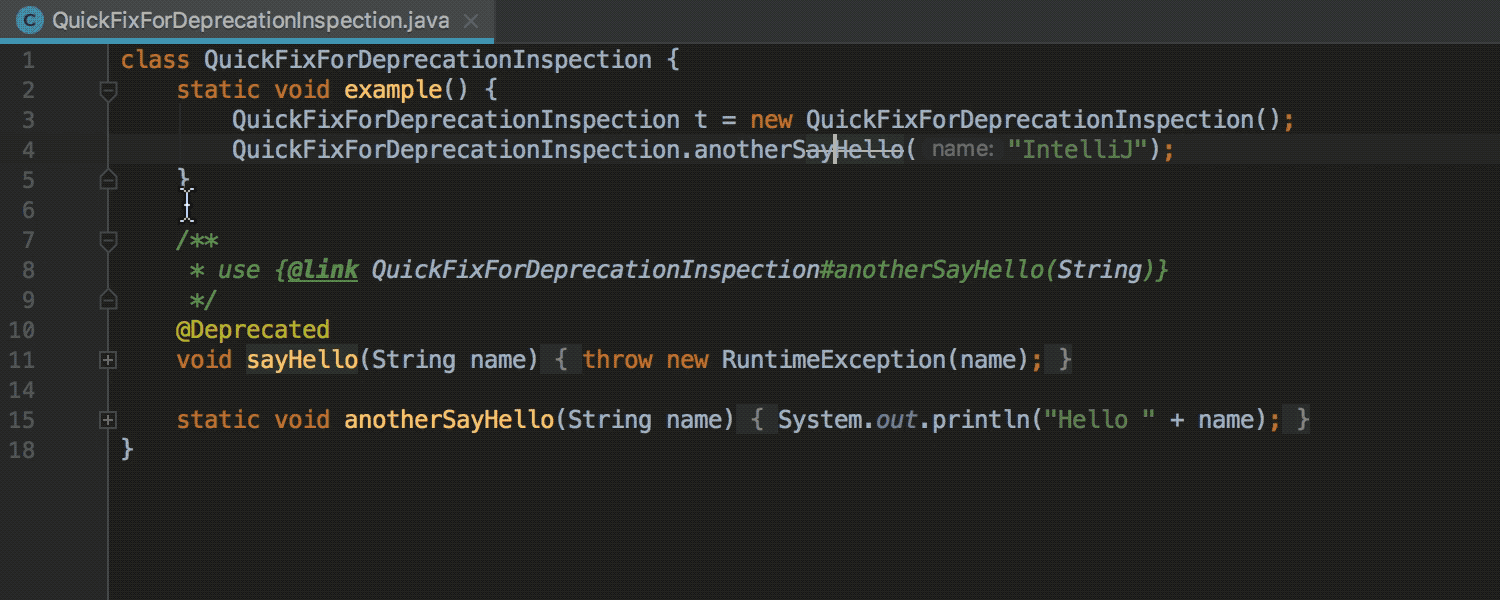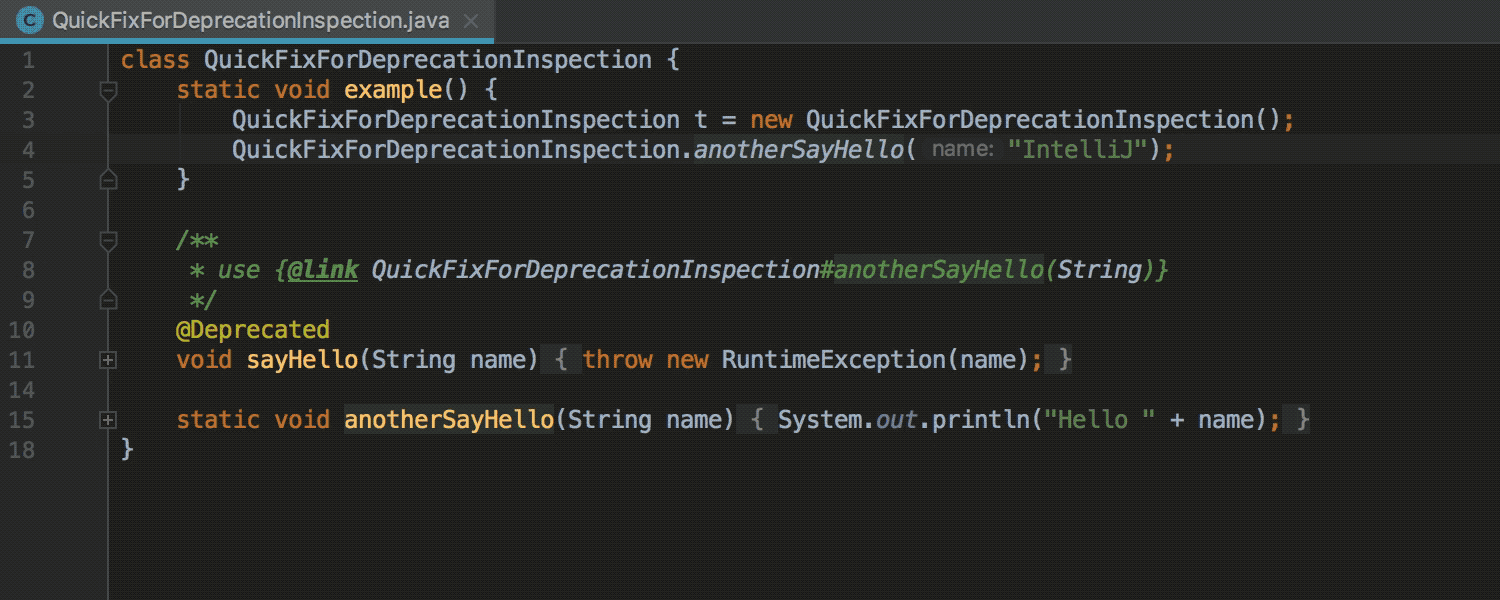
Migration of deprecated methods
When the explicit alternative is specified for the deprecated method, the IDE offers quick-fix for autochange:
Migration from JUnit 4 to JUnit 5
If the module contains both the JUnit 4 and JUnit 5 libraries, the IDE offers quick-fix for automatic migration from JUnit 4 to JUnit 5 :
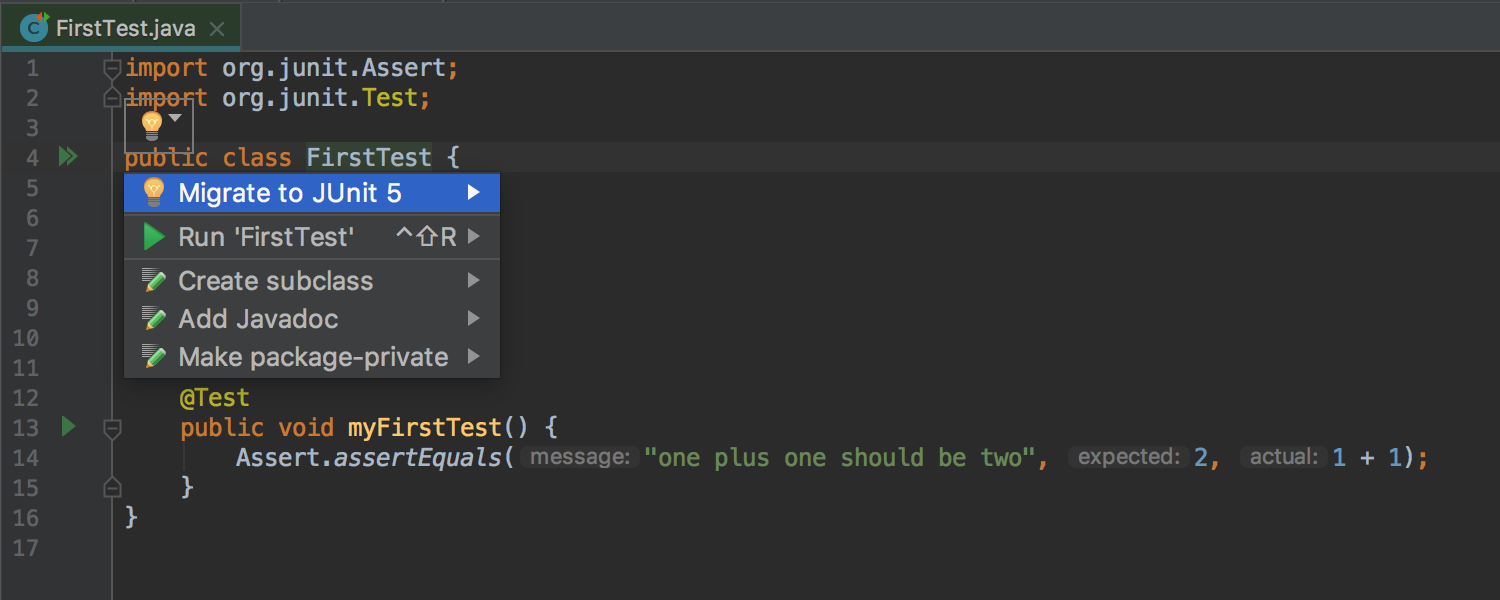
Run Dashboard for any type of Run Configuration
Run Dashboard was previously only available for Spring Boot applications, and now can be used for any type of Run Configuration . To do this, open the Edit Run Configurations dialog, select the Defaults item and add the appropriate configuration types to the Run Dashboard Types list:
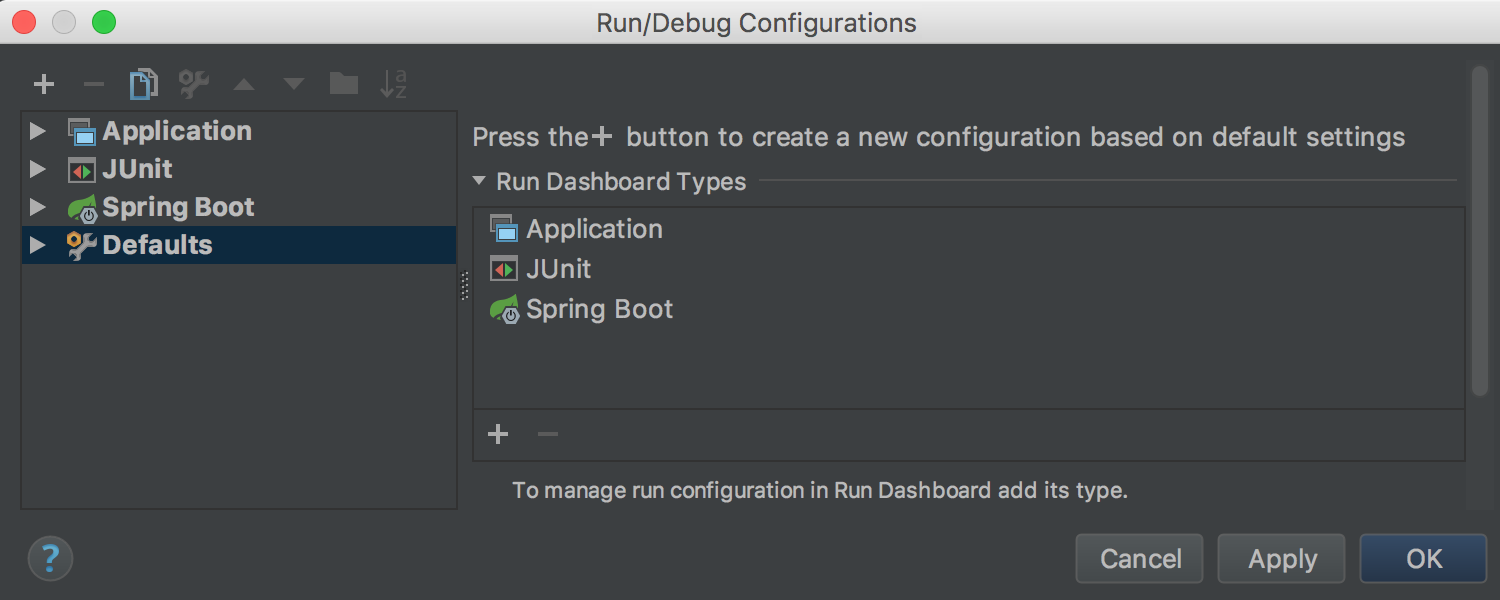
Run Dashboard offers a convenient interface for launching and managing multiple Run Configurations :

JVM Debugger
In this release, more attention was paid to accounting and optimizing the cost of computational resources ( overhead ), which Debugger contributes to the running process due to processing breakpoints and displaying values (using Data Renderers ) in the tabs Variables , Watches , Evaluate Expression , Inspect and other places.
To account for these resource costs, a new Overhead tab has been added to the Debug tools window. This tab displays the cumulative number of calls to Breakpoints and Data Renderers (considering the option Enable 'toString ()' object view , which is used by default if no specific Data Renderer is specified):
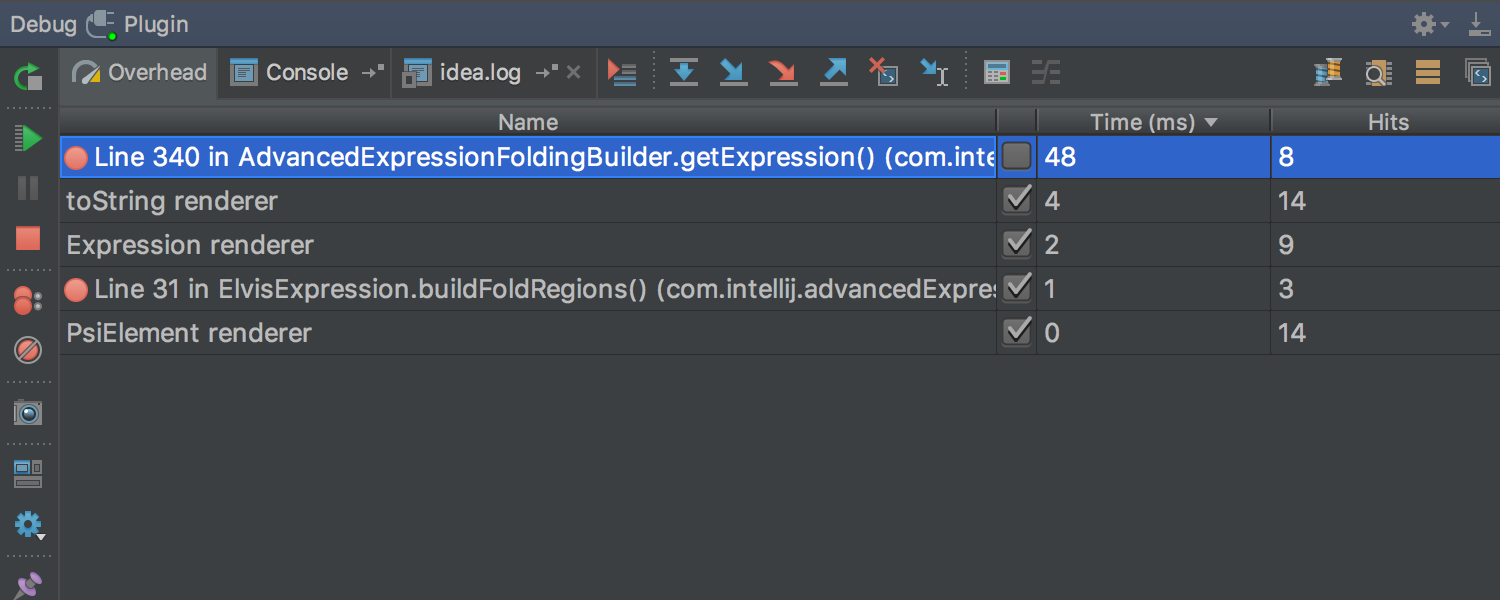
In addition, any Data Renderer can be marked as On-demand . This will mean that the value will be calculated and displayed only if necessary (by clicking):
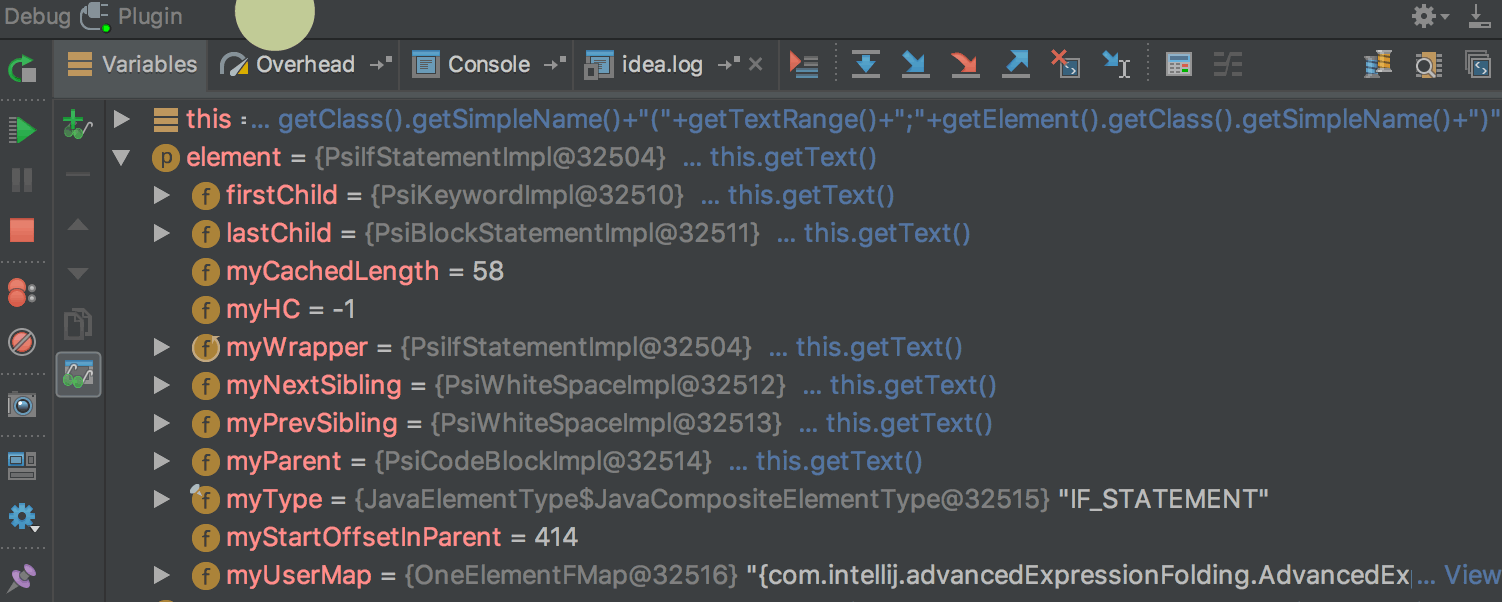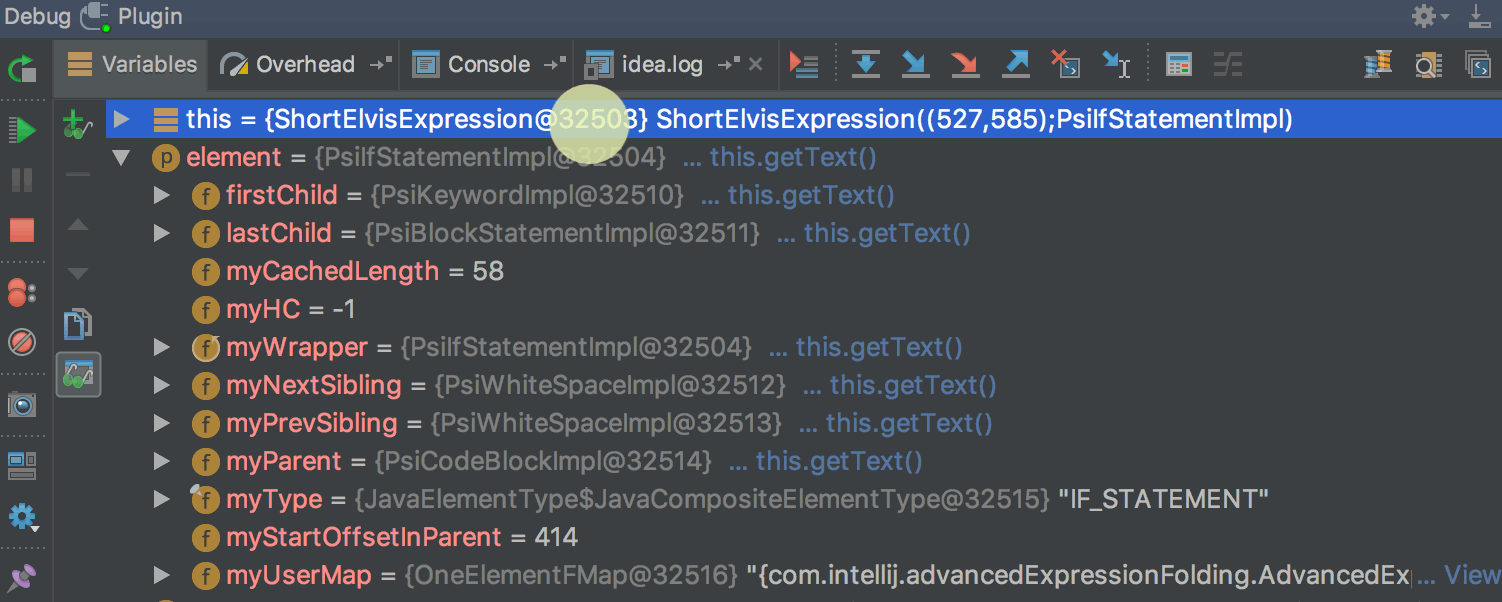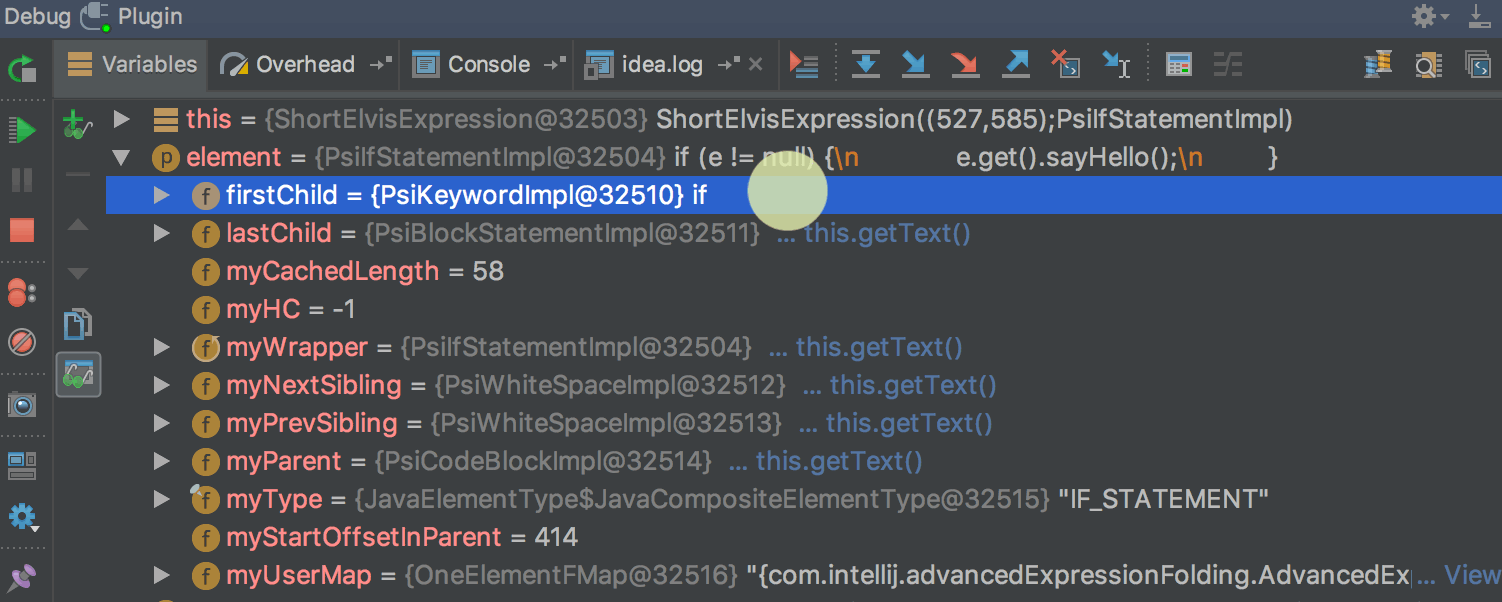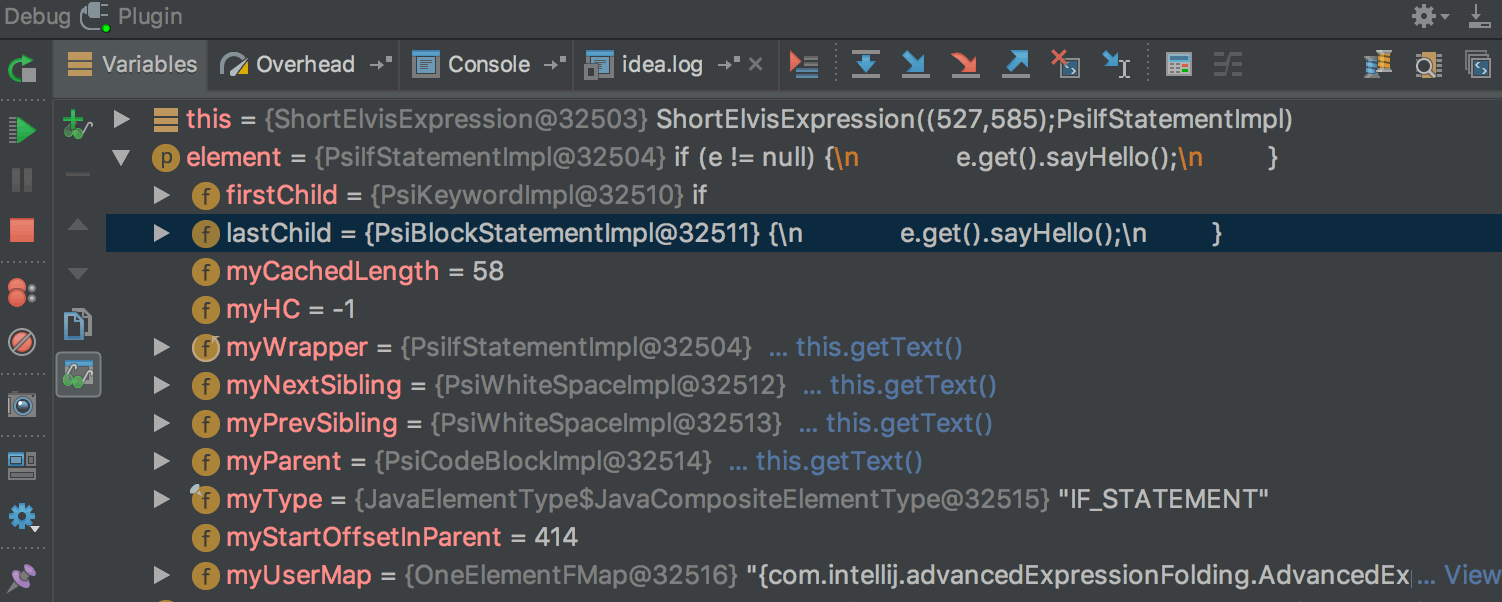
You can mark Data Renderer as On-demand in the Java Type Renderers settings:
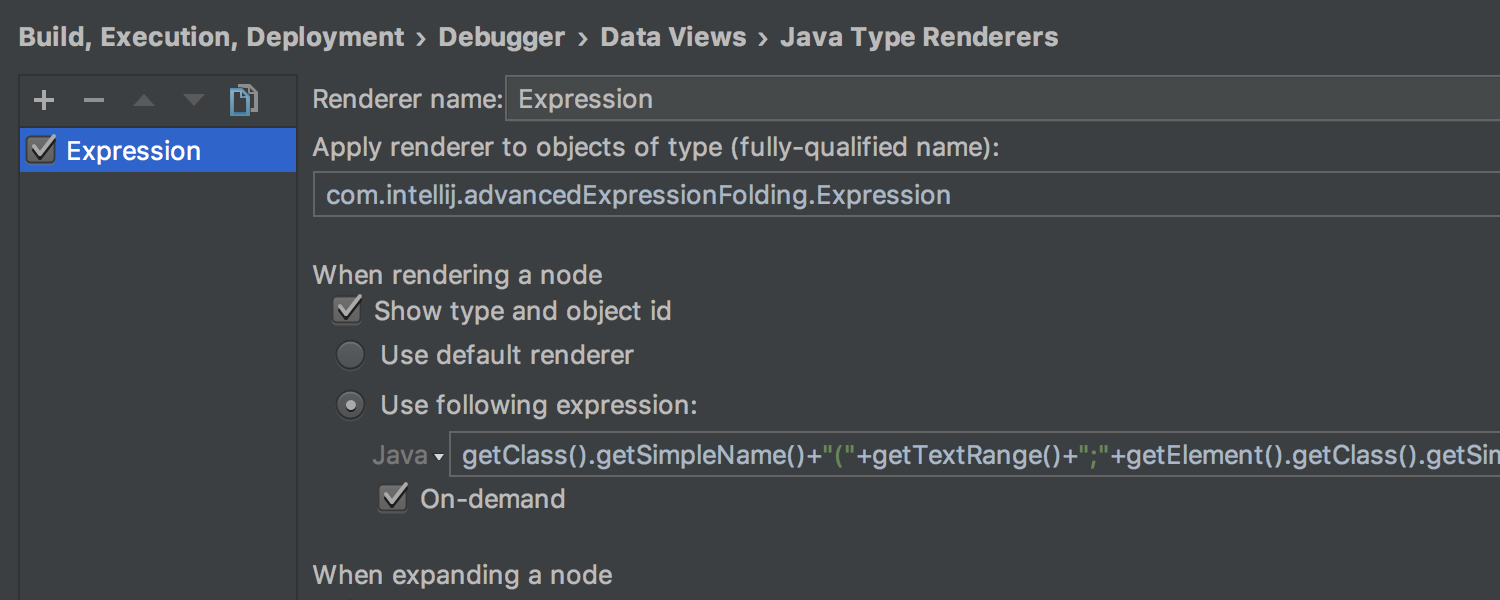
Or by selecting Mute Renderers in the context menu on a specific value:
We also optimized the cost of resources for the calculation of Async Stacktraces . In addition, Async Stacktraces do not need to be further configured. Now they work immediately, out of the box.
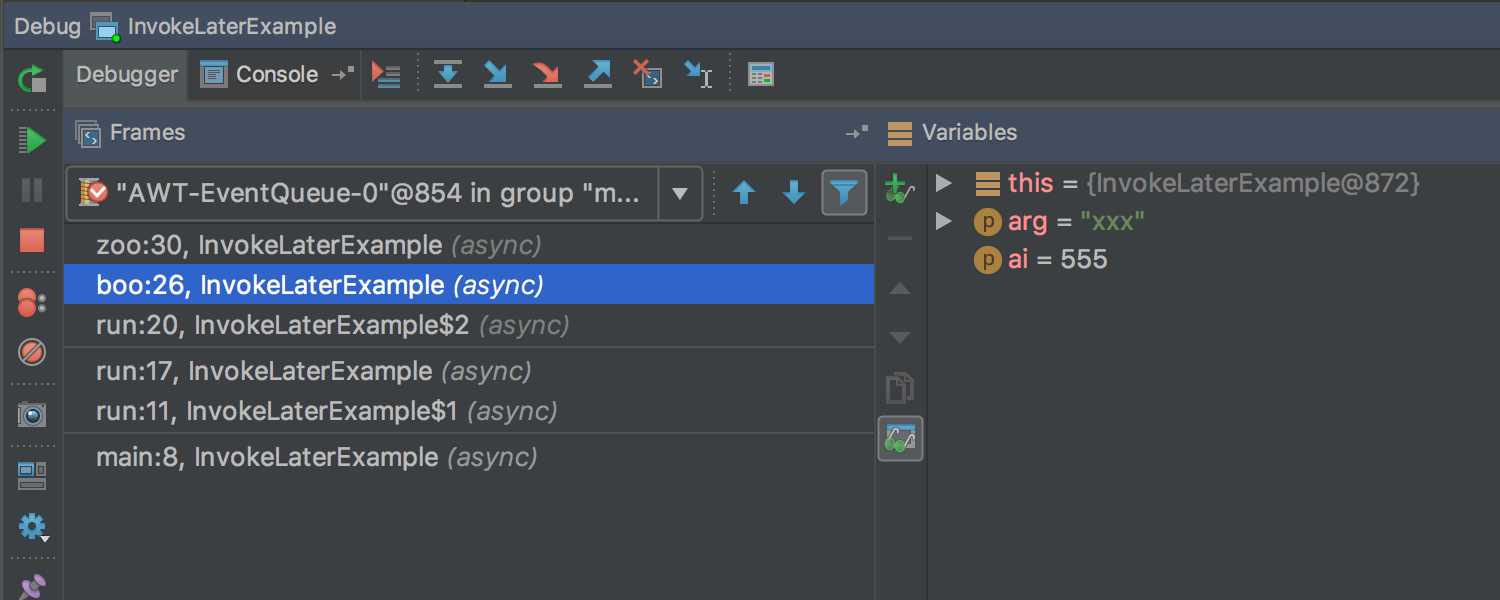
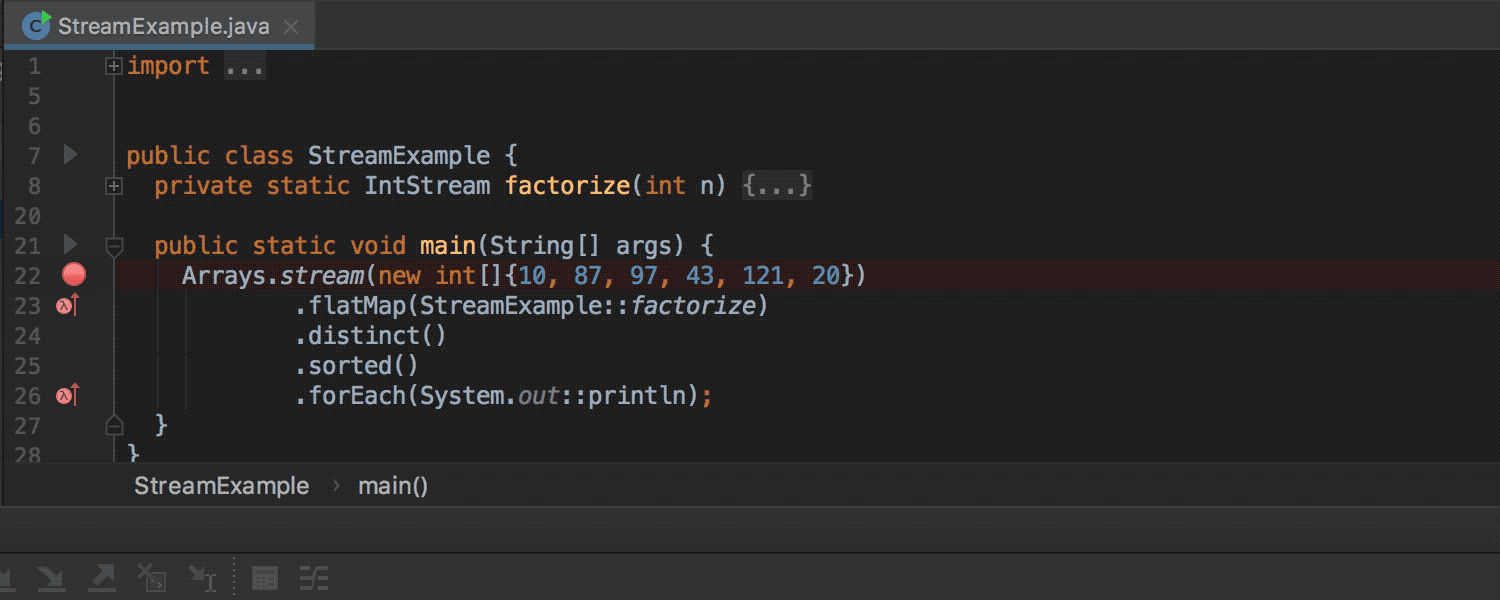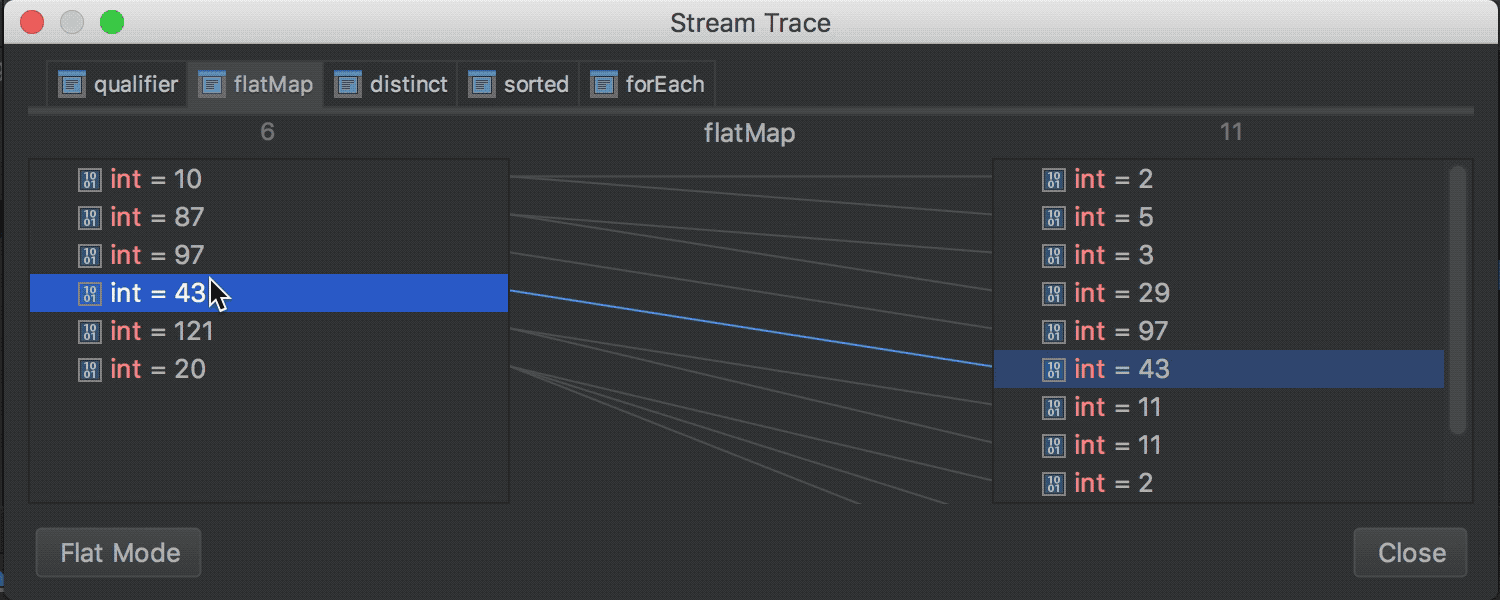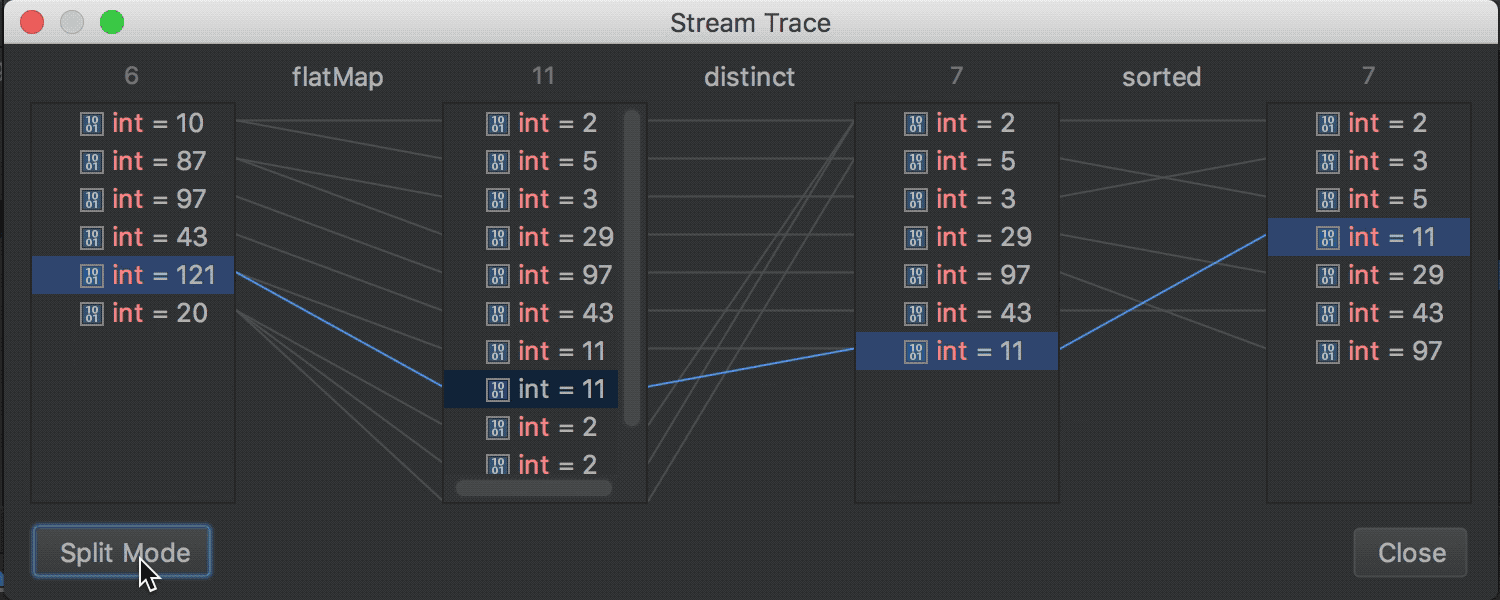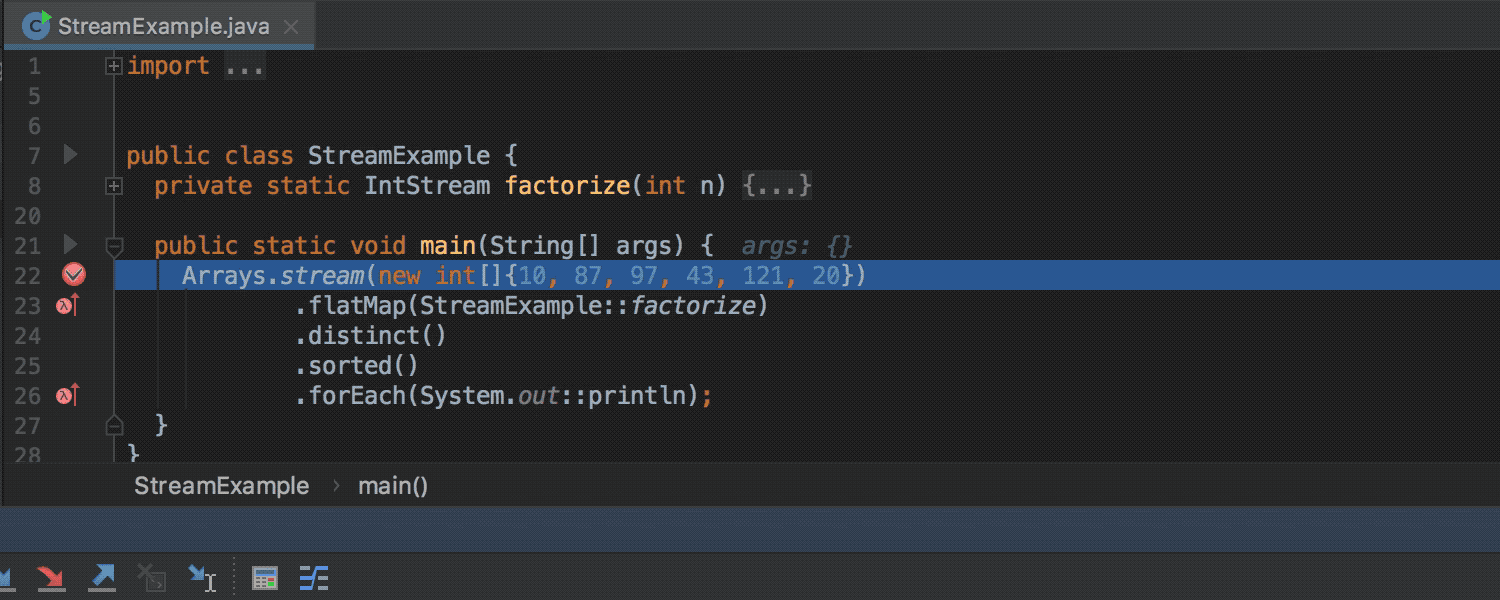
The Java Stream Debugger plugin, which helped debug the Stream API call chains, is now part of the IDE and is available during debugging (the Trace Current Stream Chain button in the Debug toolbox):
Java EE 8 Tips and Navigation
The new release fully supports the Java EE 8 standard and offers additional prompts, navigation, and other nice features for Asynchronous CDI Events , CDI Bean Injection , PushBuilder , Disposes, and Produces :
Spring and Spring Boot support
Now the IDE can automatically detect and configure the MVC Context in the Spring Facet preferences for Spring Boot applications:

The Endpoints tab in the Spring Boot application launch and debug window, which helps to monitor the running application, now supports Spring Boot 2.0 Actuator Endpoints .
Highlighting in the Spring Boot application configuration files now takes into account the type of values:

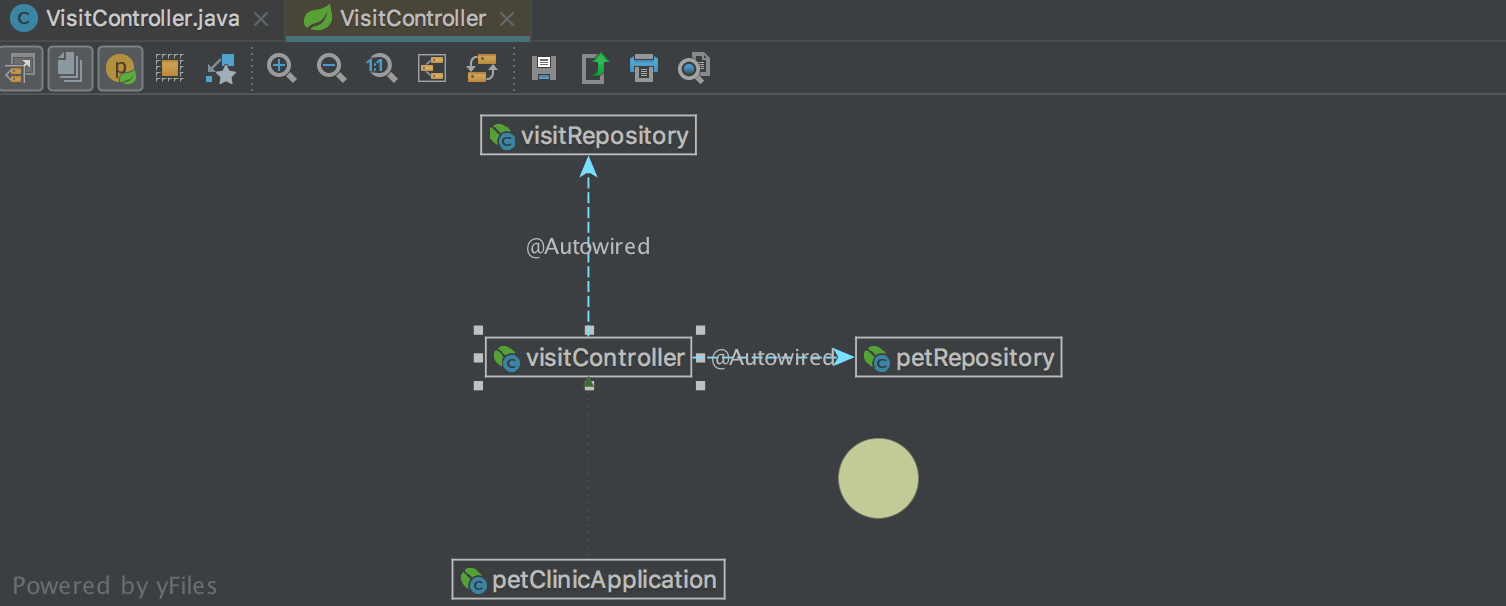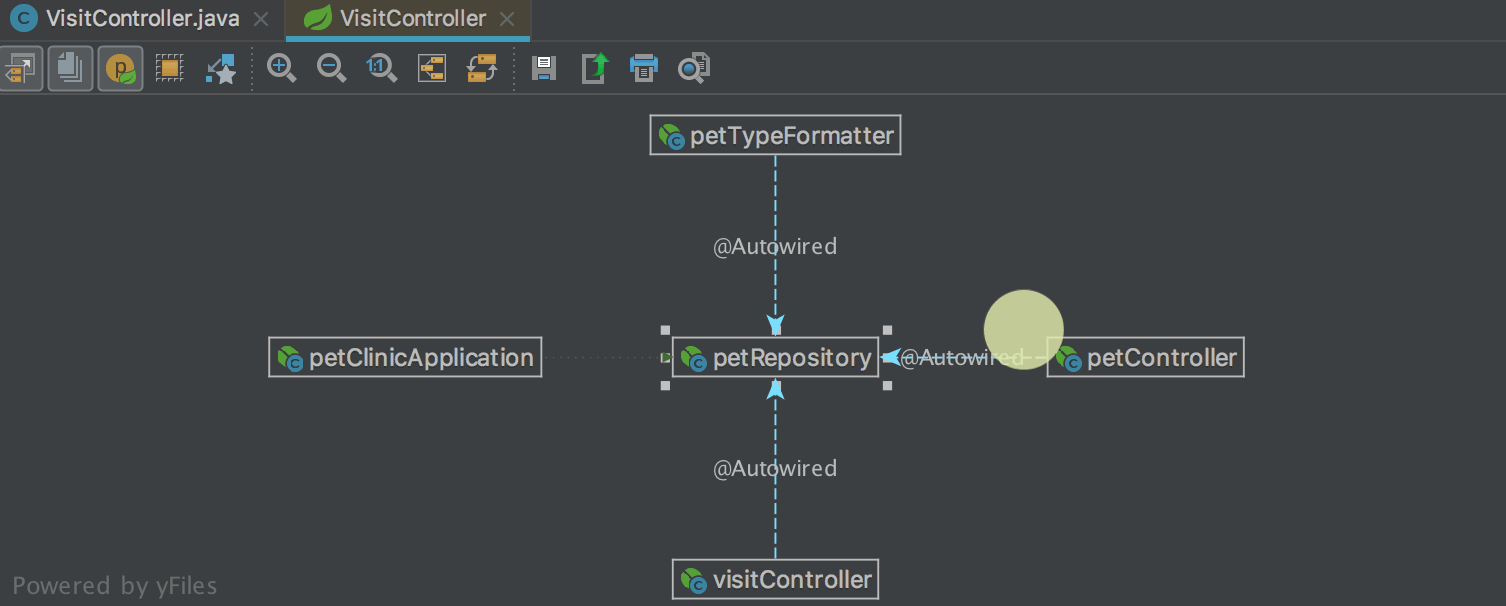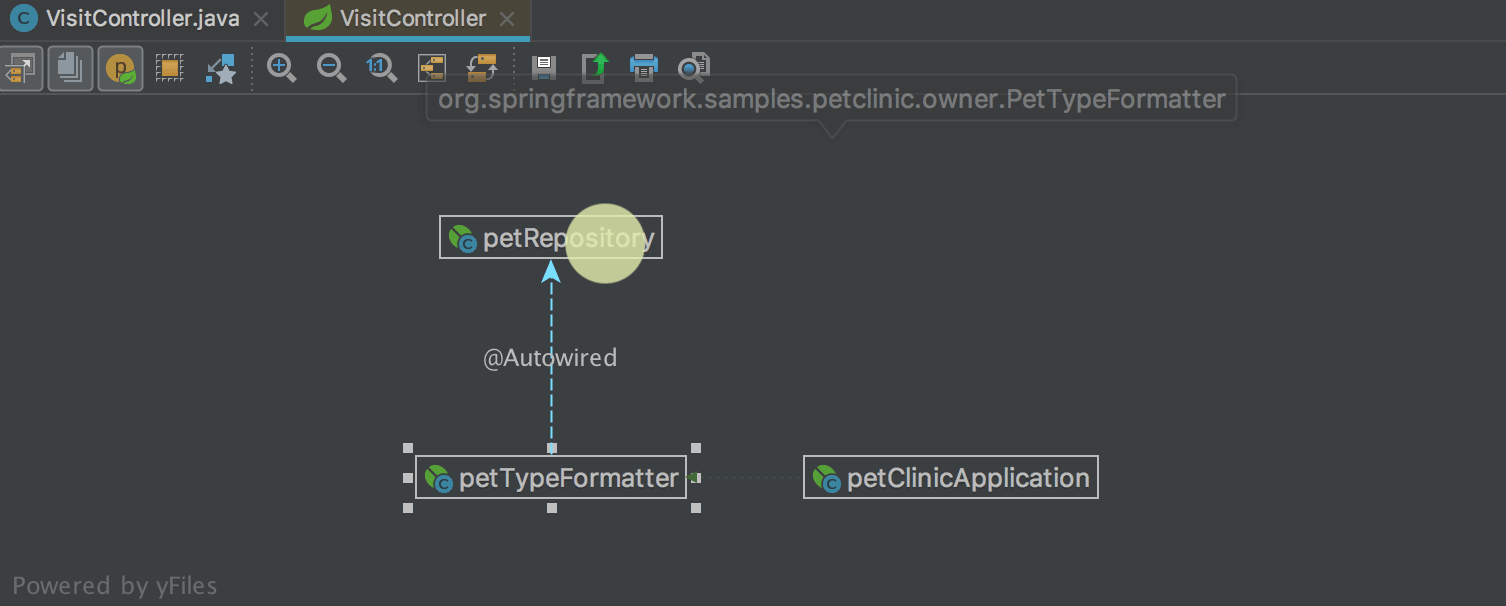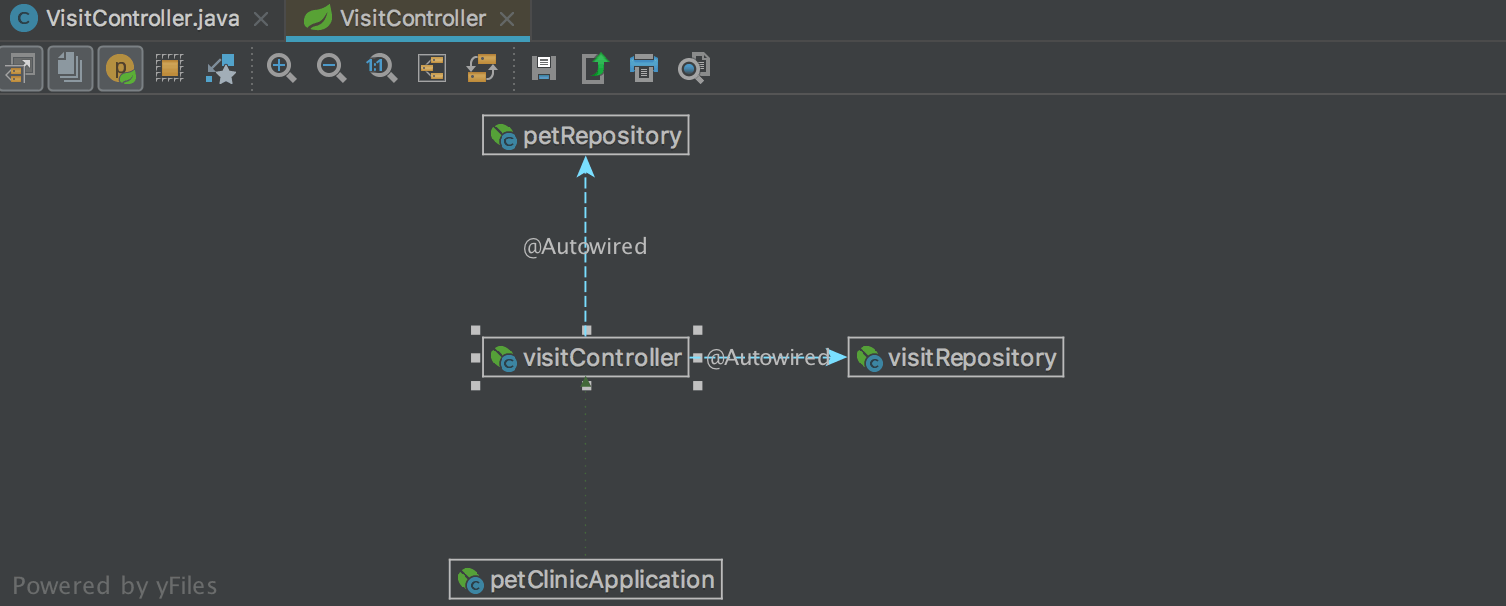
In the dependency diagrams between the bins ( Spring Beans Diagram ) a new interesting mode has appeared: Neighborhood . In this mode, only direct dependencies are displayed. When you select one of the dependencies, you will see direct dependencies for the selected bean, etc. Thus, it is convenient to navigate between dependencies:
Work with modules
If you marked some modules as “unloaded” ( unloaded ) and when updating a VCS project, new modules were created, they were previously marked as “loaded” ( loaded ). Now, in those cases when modules marked as “loaded” are not dependent on these modules, these modules are automatically marked as “unloaded”.
Also, before the commit, the IDE now checks that the “unloaded” modules are compiled without errors.
In addition, the way the modules are grouped during display has changed. Previously, this was done using groups of modules that could be created in the Project Structure . Now the same mechanism is used that is used to group the package structure: the module name is broken up by a dot symbol and forms a tree:
Build project
Previously, when using Gradle, launching applications and tests in the mode of collecting statistics on code coverage ( Run with Coverage ) did not work if the Delegate IDE option to Gradle or Gradle Test Runner was enabled. Now Run with Coverage works in all cases.
The process of importing, compiling and building a project for Gradle , Android / Gradle and SBT can now be seen in a new window of the Build tools:

Work with REST requests
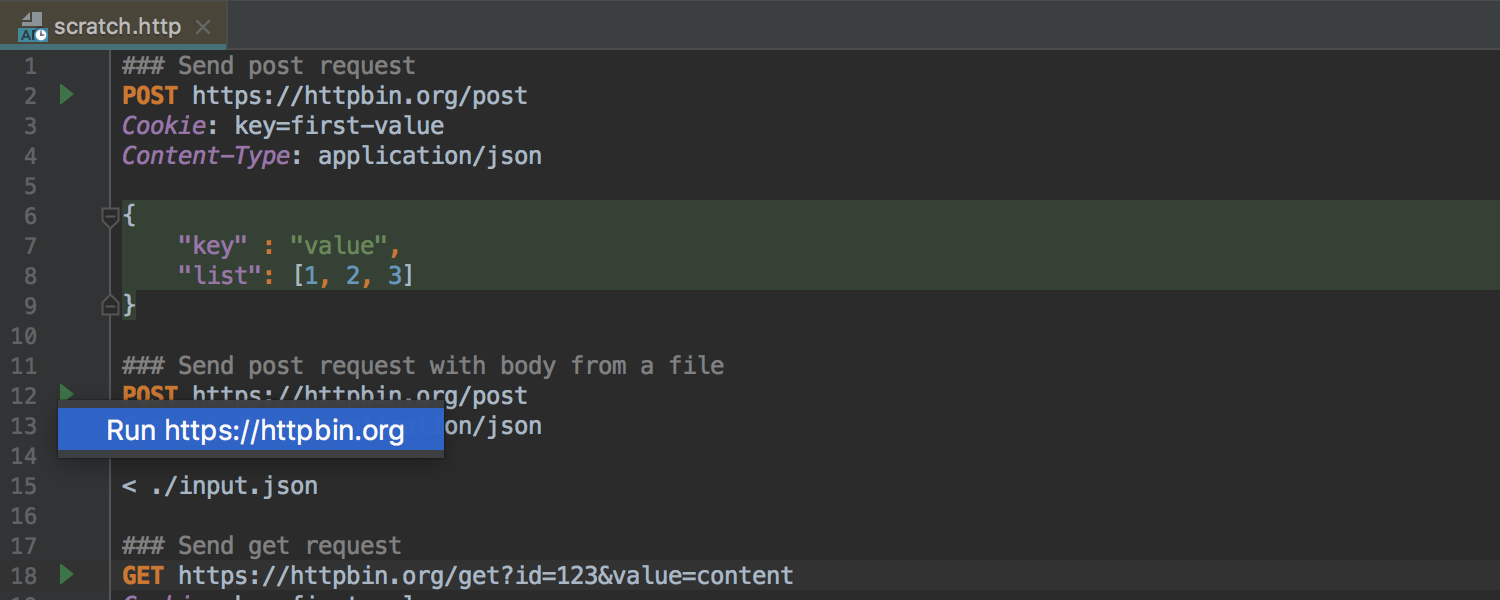
Now you can work with REST requests using a new tool based on the editor. To do this, simply create a file in the project with the permission . Http and open it in the editor. If you do not want to create a file in the project, you can use the Scratch File :
Kotlin
Following the release of Kotlin 1.2 , which happened yesterday, language support was updated in the IDE. The main innovation of the update is the experimental possibility of “re-using code” between JVM and JavaScript :
With the expect keyword, any class or method can now be declared as “generic.” An implementation of this class or method for a specific platform can be declared using the actual keyword in the module for the corresponding platform. The IDE checks that the implementation exists for the configured platforms, and allows you to move from declaration to implementation and vice versa:
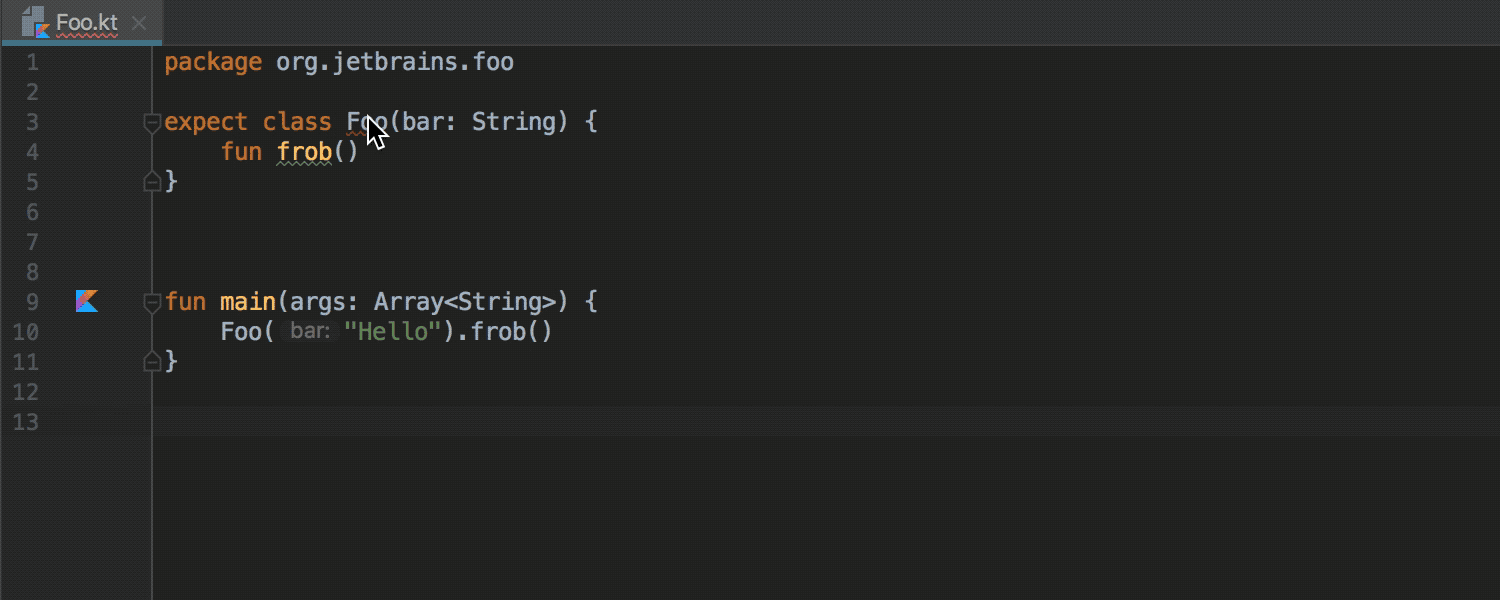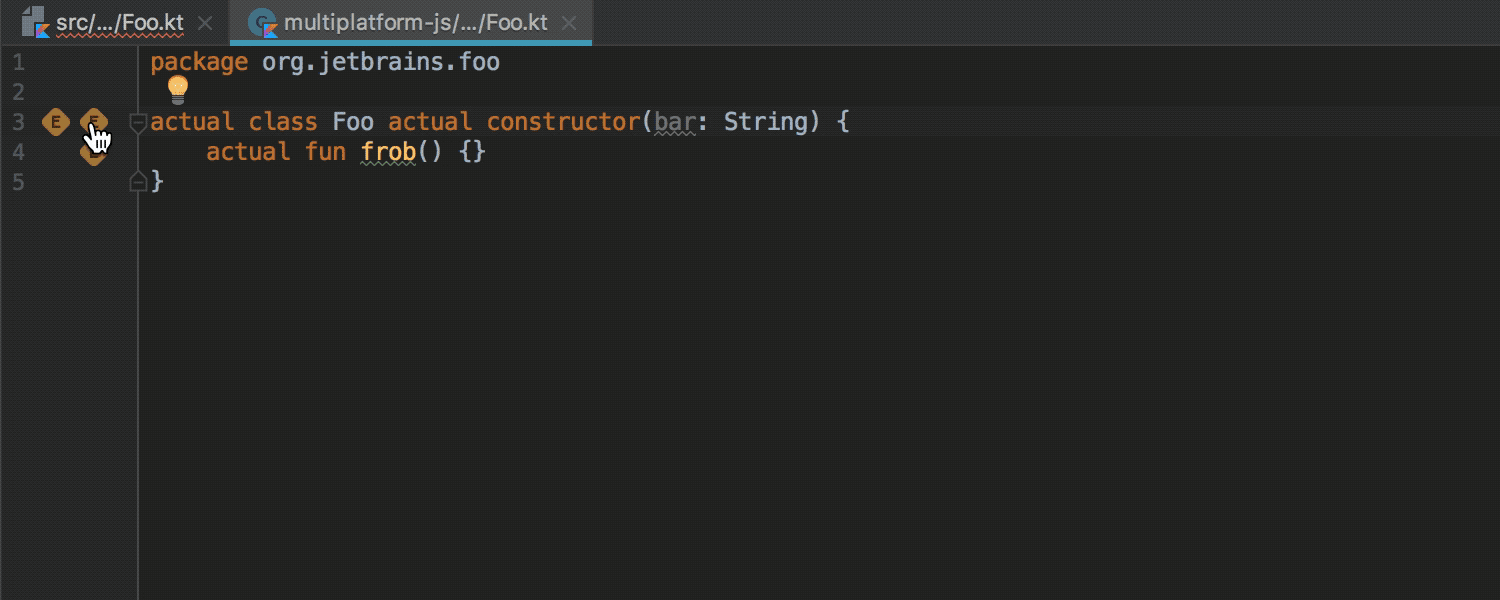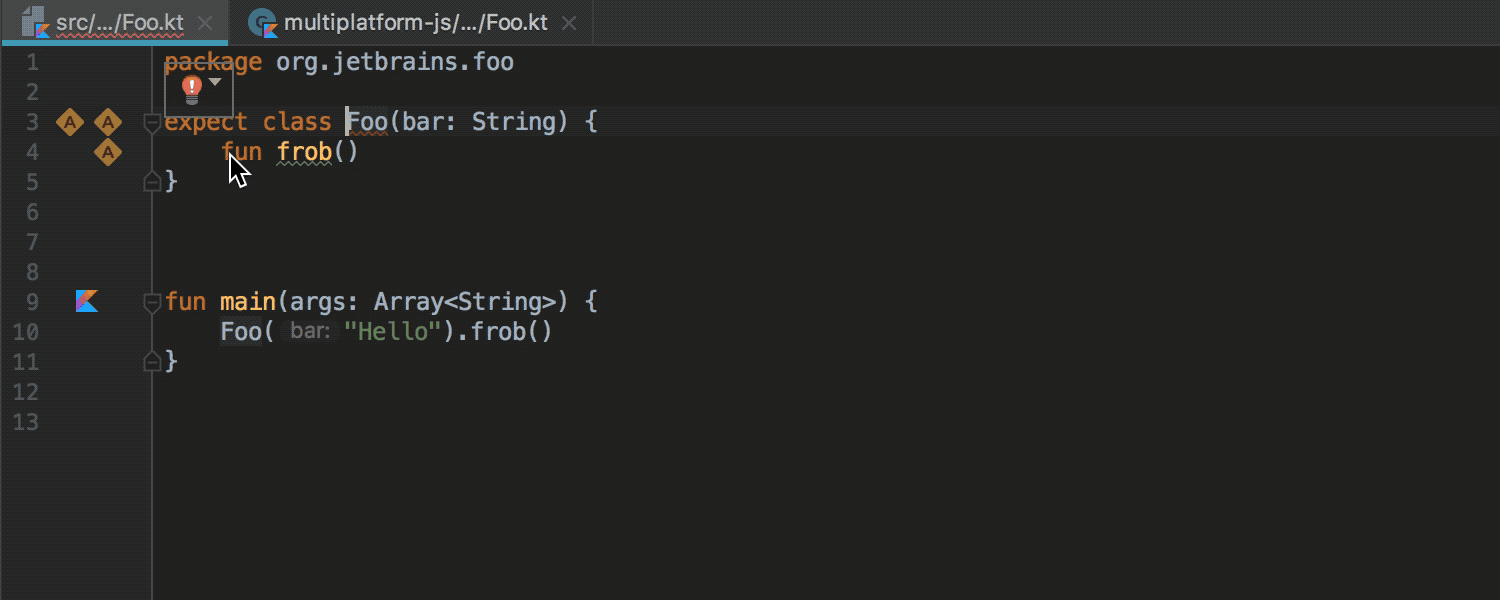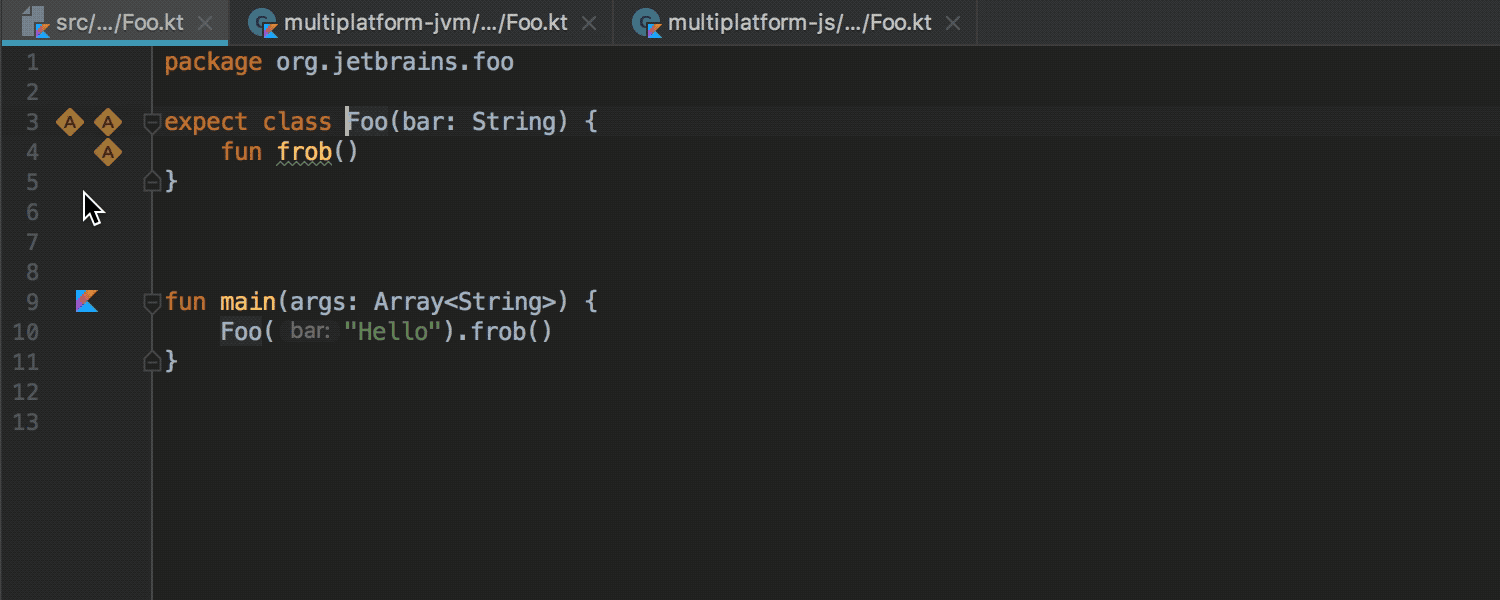
More information about the work of "common modules» ( common modules ) can be found in this habraposta or in the official documentation (in English). A prerequisite for the work of such modules is the assembly of the Gradle project.
Scala
The highlighting of the symbol under the carriage (which is enabled by default, like the one that is available by pressing Shift + Ctrl / Cmd + F7 ) now also highlights the implicit use of the symbol:
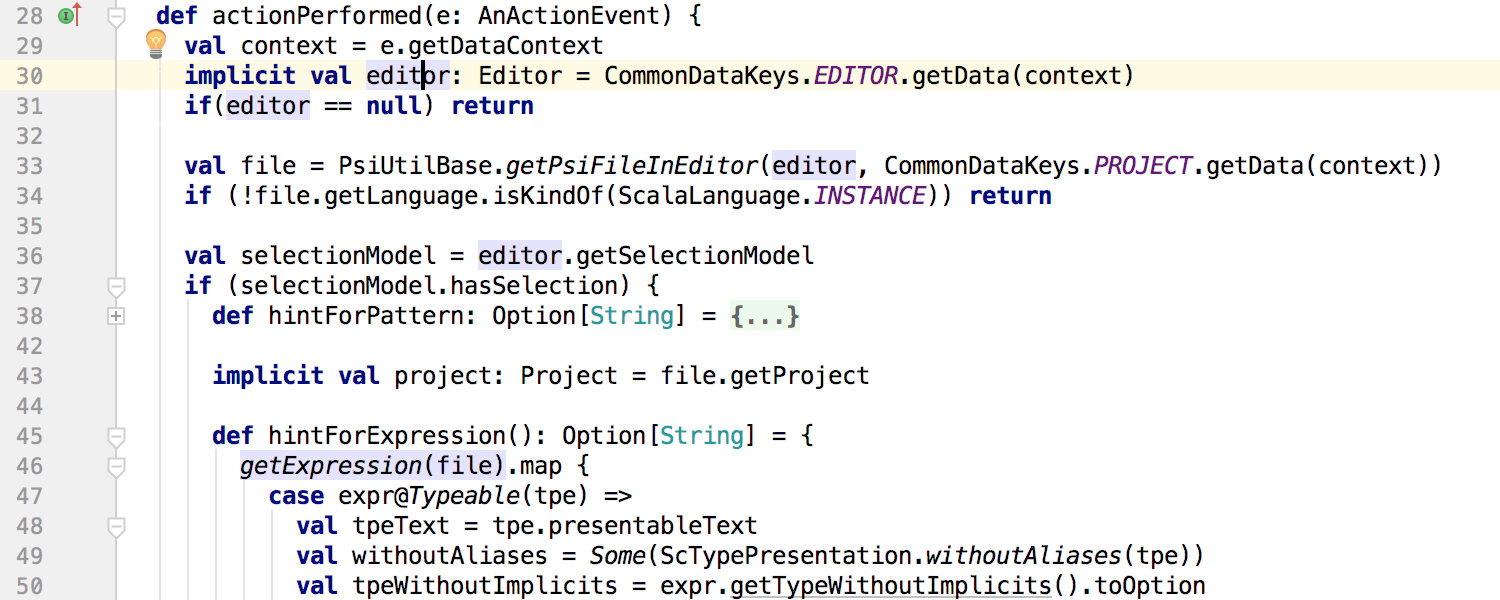
Building and running an application or tests is no longer tied to indexing and works even if the indexing is not over.
In SBT projects, when a plugin notices a dependency import expression that is not specified in the SBT configuration but present in the local Ivy Cache , the IDE suggests adding it to the SBT configuration:
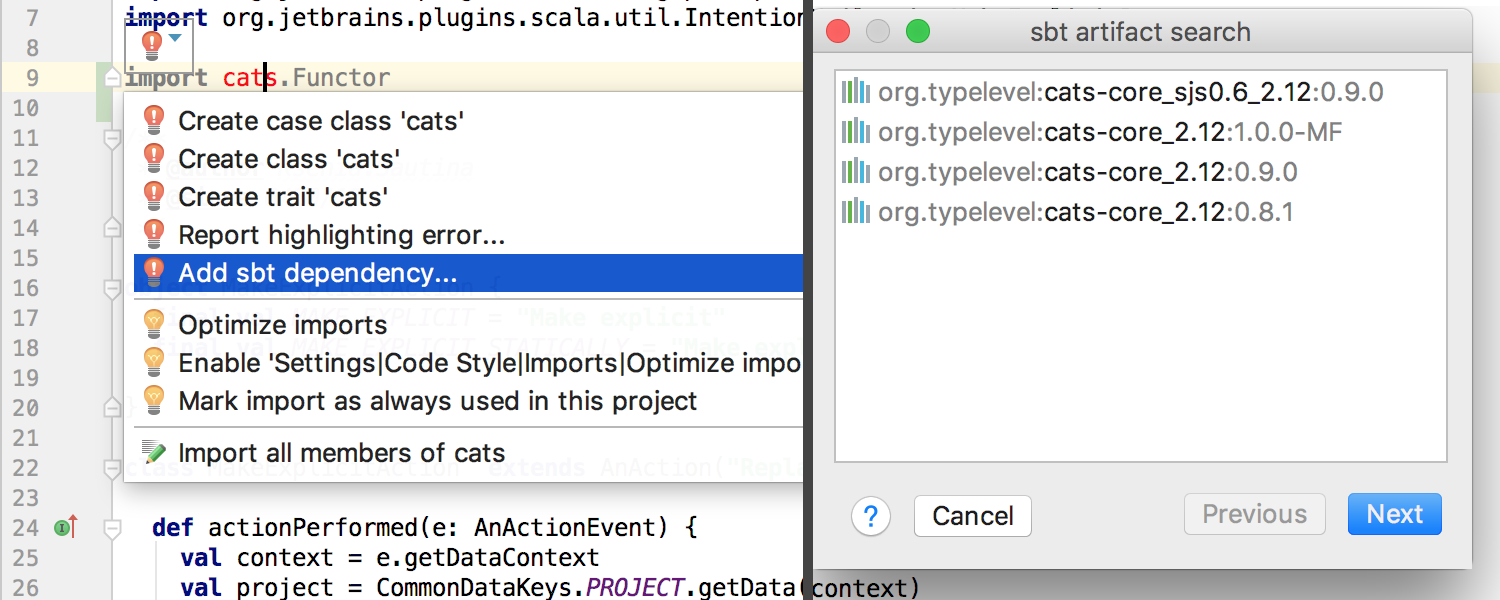
The new version of the plugin supports Ammonite and offers syntax highlighting, hints, navigation, and a separate type of Run Configuration :
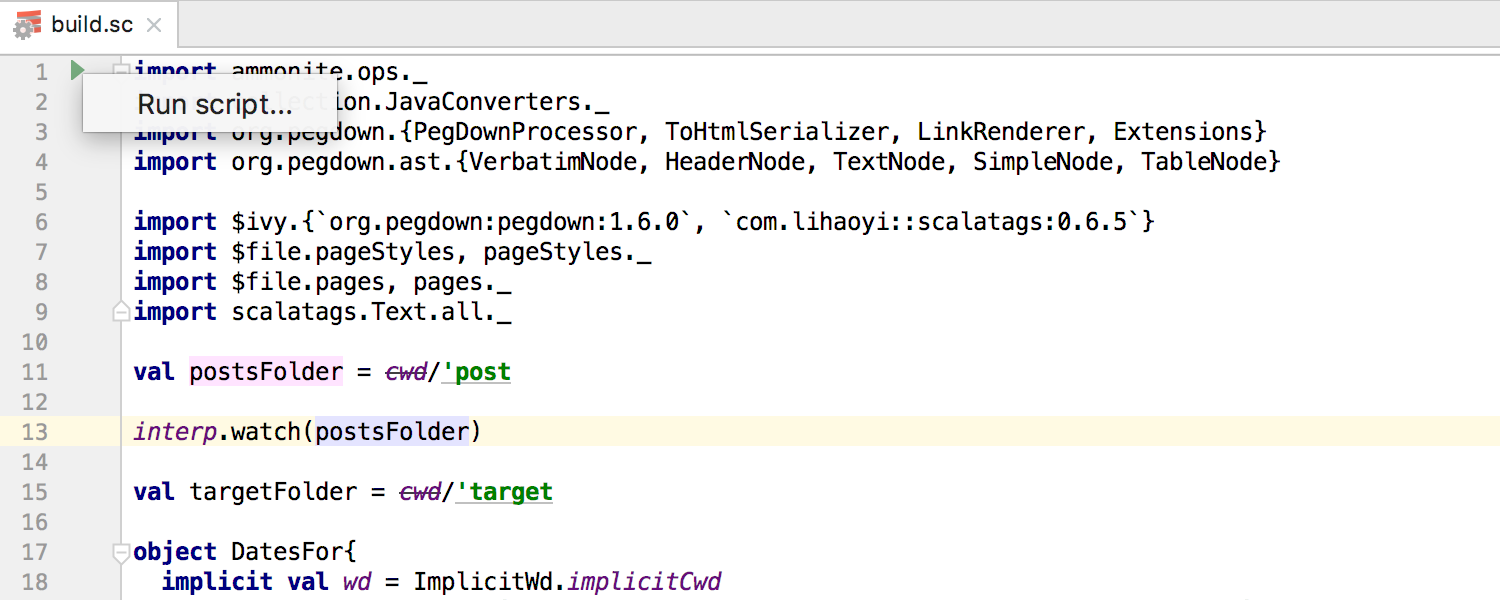
Scala project creation has changed. Now, instead of Lightbend Activator (which ceased to exist in the middle of this year), the plugin suggests using Tech Hub Project Starter project templates.
Work with Git and Mercurial
You can now interactively rebase the latest changes in Git by invoking Interactively Rebase from Here from Log :
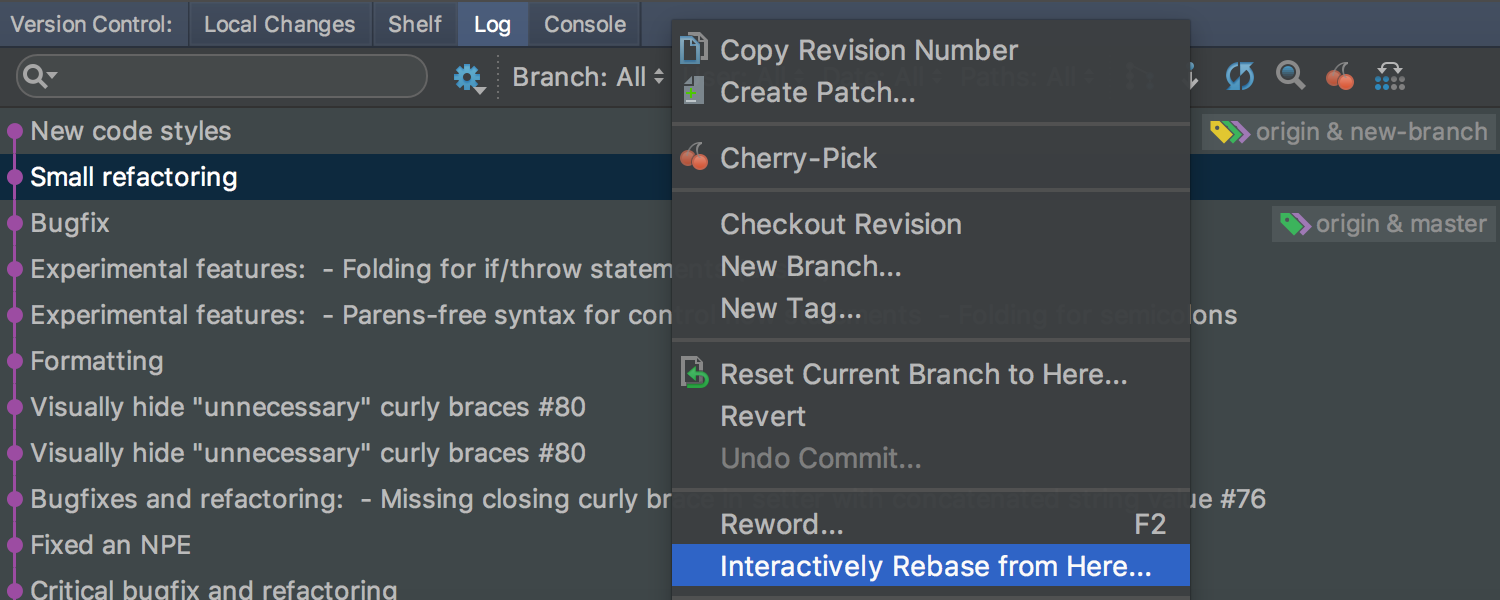
When switching between branches, the IDE saves the state of the workspace : the location of the editor tabs, tool windows, etc.:
For convenience, changes to participate in the merge ( merge ), in Log added a new mode: Show Changes to Parents . In this mode, the right pane in Log shows not only changes in files with conflicts, but also separately non-conflicting changes for each branch participating in the merge:

The mode can be activated in the context menu.
To view conflicting changes for Git in the Log IDE now offers a three-pane interface.
When sending changes from the patch, the IDE automatically inserts the name, the mail of the author, and a description of the change, if they were in the patch:

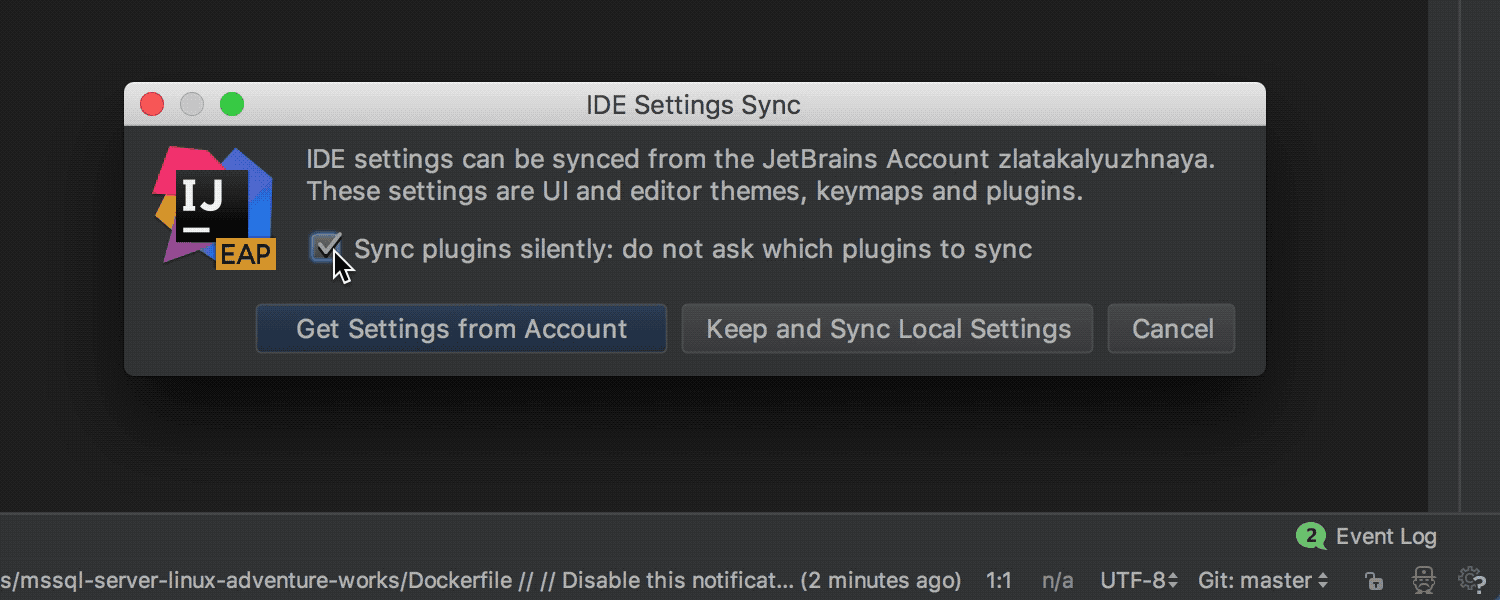
Synchronize IDE settings between different computers
Sometimes it happens that IDE is installed at work and at home, on a stationary computer and on a laptop, etc. Previously, you had to configure IDE on each computer. Some time ago, to automate this process, you could use the plugin. When using this plugin, the settings were stored in the specified Git repository. IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate 2017.3 has a new mechanism that does not require a Git repository: all settings are stored securely on the JetBrains server. Another advantage of the new mechanism is the synchronization of not only the settings, but also directly installed plug-ins. To use the new mechanism requires a JetBrains Account .
Changes in Docker plugin
In this release, we continue to improve the plugin for Docker. Of the most notable:
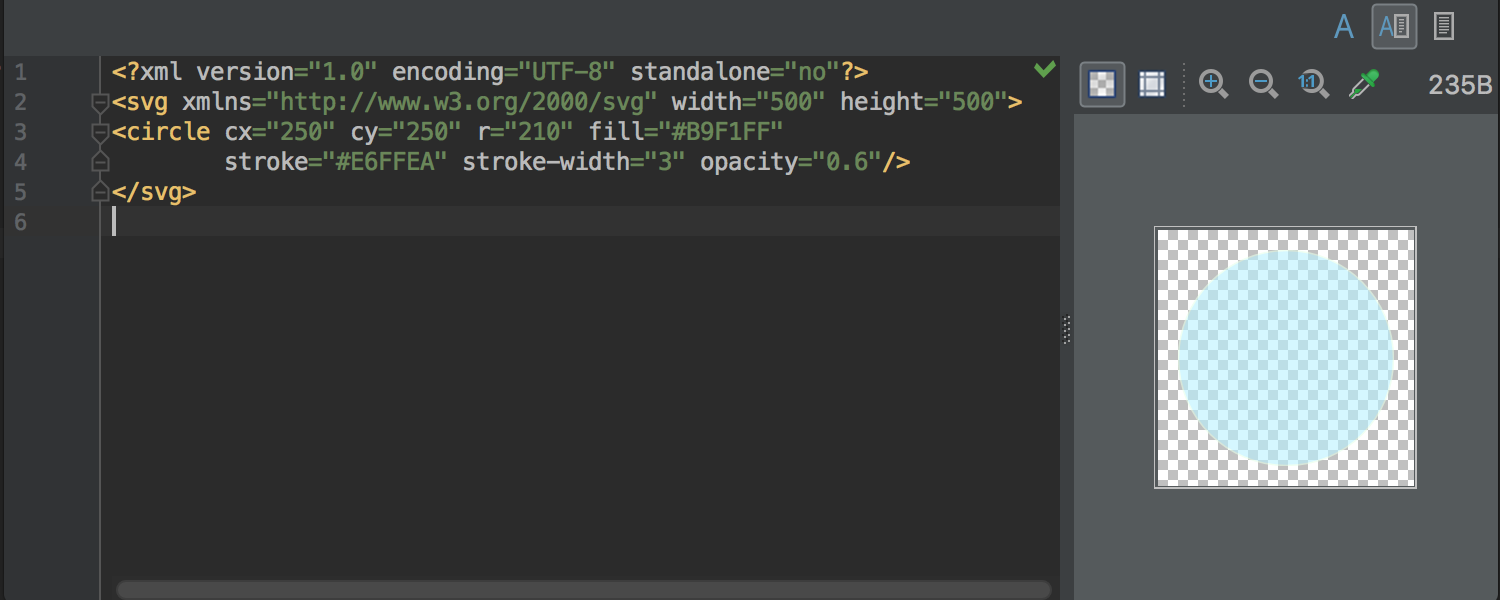
Preview for SVG files
Now, when opening the SVG file in the editor, the IDE will offer on the right side a visual preview of this file:
Visual borders in the editor
Previously, the IDE was setting Right margin , which is displayed in the editor and taken into account in the rules of code design ( code styles ). In the new release, this setting was renamed to Hard wrap at , and in addition to it a new Visual guides option was added. With its help, you can specify values for several visual borders at once, separated by commas. These borders will also be displayed in the editor:
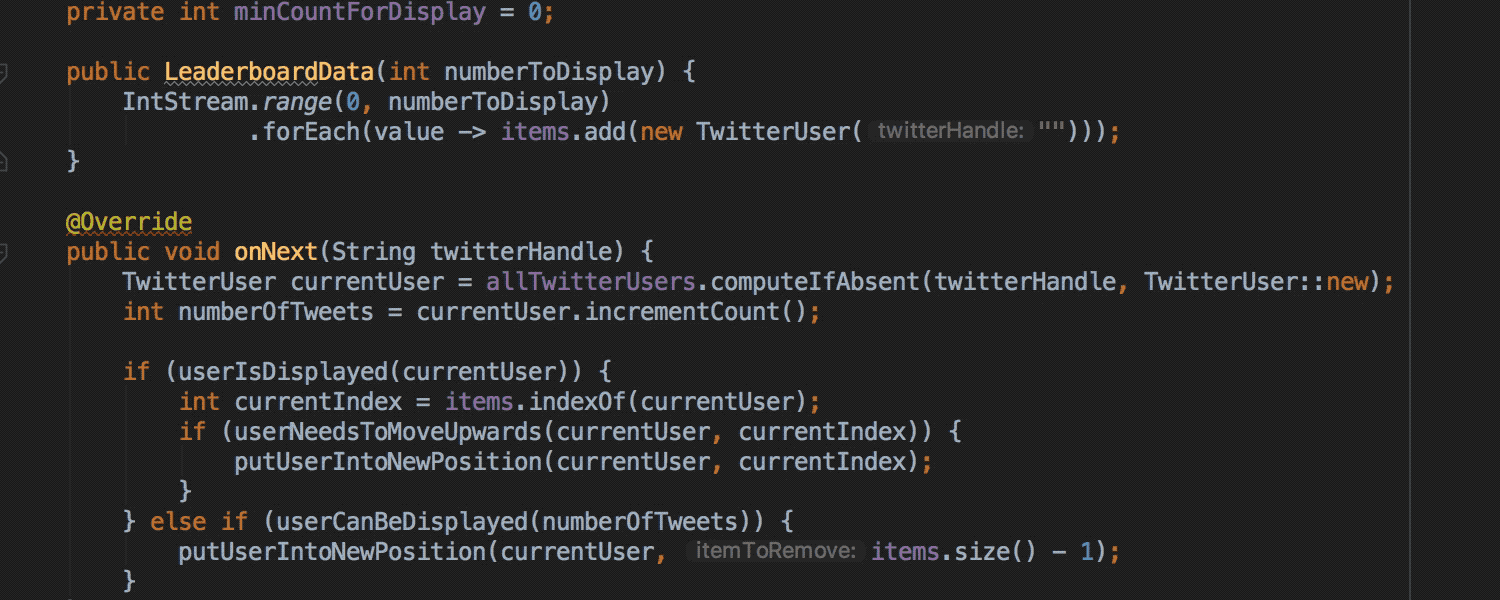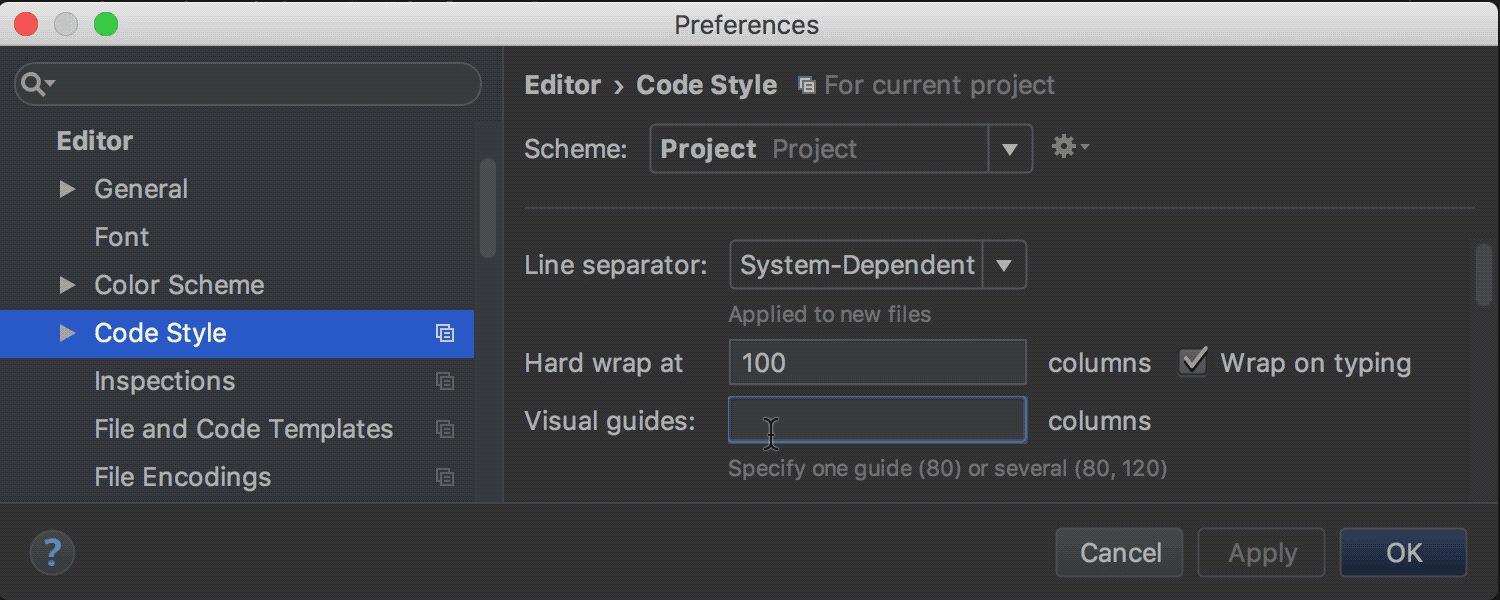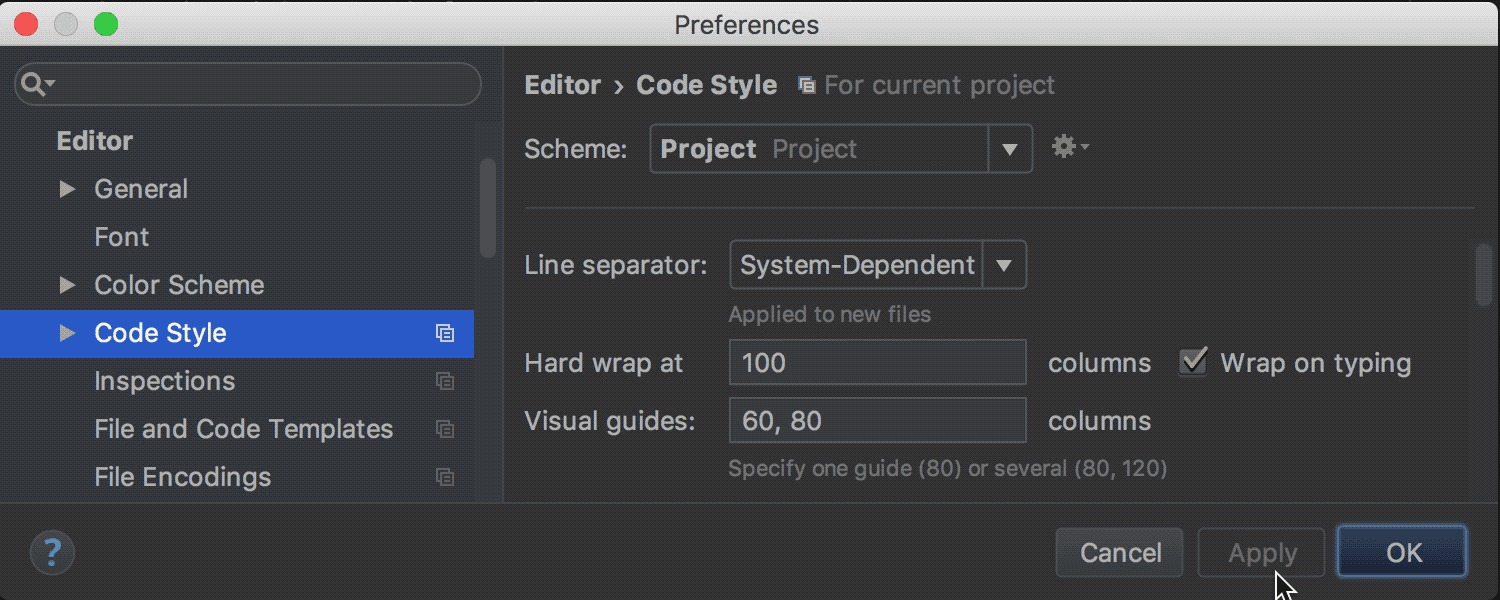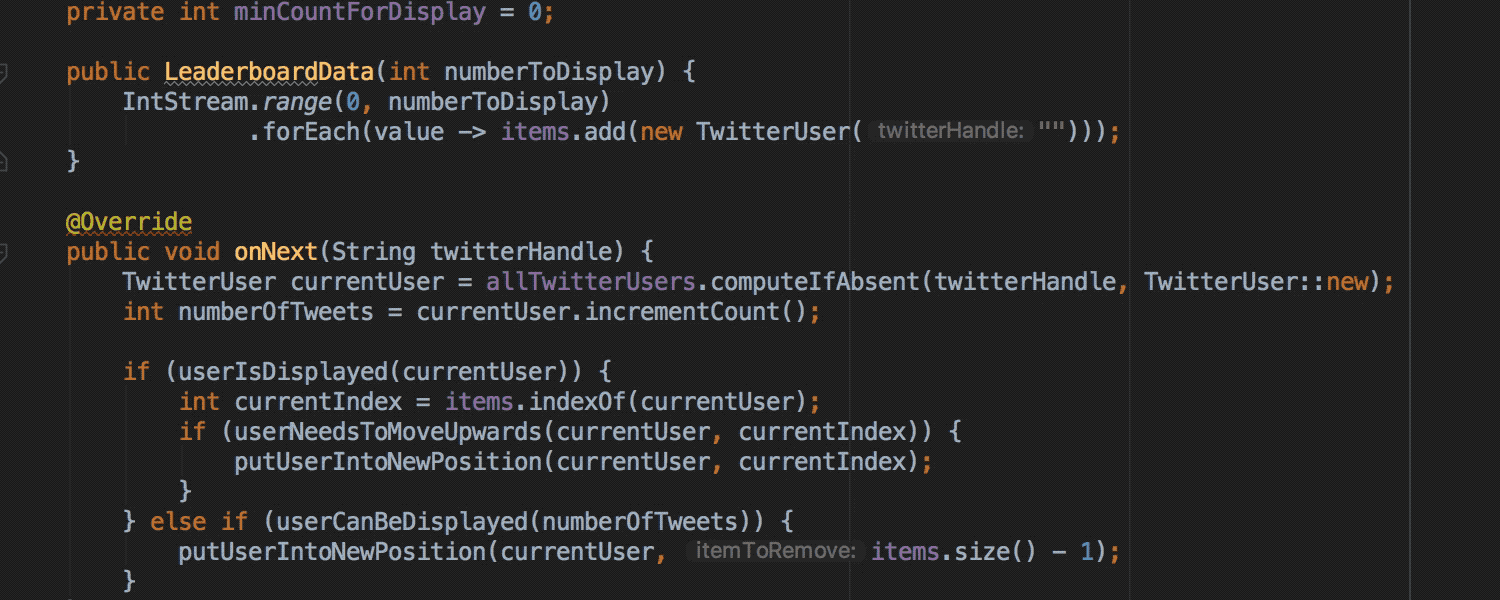
Mainly, this is necessary in cases where the code design rules refer to several such boundaries (this is possible, for example, in Python and in PHP).
Tools for working with databases (DataGrip 2017.3)
JavaScript and TypeScript support (WebStorm 2017.3)
As you can see from this post, in IntelliJ IDEA 2017.3 there are a lot of new and interesting things, not counting several hundred bug fixes and smaller features that simply would not fit in one post.
You can download the update through the Toolbox App or from the official site . I will be glad to answer any questions. Questions that I can not answer myself, send the team.
UPDATE: GoLand 2017.3 was released, and now you can buy it. IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate users get GoLand functionality for free using the plugin: plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/9568-go
Program with pleasure!

Go!
')
Type Casting for Call Chains in Smart Completion
In the previous release (IntelliJ IDEA 2017.2), call chains ( method call chains ) began to appear when you first called Smart Completion (before that they were only available on the second call). In this release, these chains also take into account the automatic casting of types depending on the context:

Code flow analysis
A couple of years ago, IntelliJ IDEA learned how to automatically output Nullable and NotNull annotations for parameters and return values of library class methods. This conclusion was made on the basis of analysis of the flow of execution within the methods. In version 2017.3, the output of annotations for parameters works not only for methods of library classes, but also for private or final methods of classes within a project.

In the case of annotation in a similar method, the IDE offers quick-fix for explicit declaration of the annotation:

The IDE also learned to detect potential problems with Nullability within calls to Stream API methods. If a potential problem is detected, the IDE reports this and, where possible, offers to automatically make changes to the code to avoid receiving an error during execution:

Transforming a for loop into a Stream API call chain
For loops, the result of which is the addition of strings to StringBuilder , can now be automatically transformed into a chain of calls to the Stream API using Stream.collect and Collectors.joining :

Invert logic boolean methods using quick-fix
Invert Boolean refactoring is now available as quick-fix for methods (earlier quick-fix was available only in batch mode , as well as for variables, constants and class fields):

Separate Method Calls on Collections and Stream API Call Chains
Where this makes sense, the IDE now suggests replacing separate sort and toArray calls on collections with corresponding methods on the Stream API call chain:

Detection of duplicate keys in Map and Set initialization
If you accidentally specify a value for the same key two or more times or try to add the same element to the Set , now the IDE will warn you about a possible error:

Detect Excess Exception Declarations
Detection of redundant exception declarations previously worked only for final and private methods. Now detection works for any methods:

This particular inspection may be disabled for so-called entry points, for example for tests.
Migration of deprecated methods
When the explicit alternative is specified for the deprecated method, the IDE offers quick-fix for autochange:

Migration from JUnit 4 to JUnit 5
If the module contains both the JUnit 4 and JUnit 5 libraries, the IDE offers quick-fix for automatic migration from JUnit 4 to JUnit 5 :

Run Dashboard for any type of Run Configuration
Run Dashboard was previously only available for Spring Boot applications, and now can be used for any type of Run Configuration . To do this, open the Edit Run Configurations dialog, select the Defaults item and add the appropriate configuration types to the Run Dashboard Types list:

Run Dashboard offers a convenient interface for launching and managing multiple Run Configurations :

JVM Debugger
In this release, more attention was paid to accounting and optimizing the cost of computational resources ( overhead ), which Debugger contributes to the running process due to processing breakpoints and displaying values (using Data Renderers ) in the tabs Variables , Watches , Evaluate Expression , Inspect and other places.
To account for these resource costs, a new Overhead tab has been added to the Debug tools window. This tab displays the cumulative number of calls to Breakpoints and Data Renderers (considering the option Enable 'toString ()' object view , which is used by default if no specific Data Renderer is specified):

In addition, any Data Renderer can be marked as On-demand . This will mean that the value will be calculated and displayed only if necessary (by clicking):

You can mark Data Renderer as On-demand in the Java Type Renderers settings:

Or by selecting Mute Renderers in the context menu on a specific value:

We also optimized the cost of resources for the calculation of Async Stacktraces . In addition, Async Stacktraces do not need to be further configured. Now they work immediately, out of the box.

The Java Stream Debugger plugin, which helped debug the Stream API call chains, is now part of the IDE and is available during debugging (the Trace Current Stream Chain button in the Debug toolbox):

Java EE 8 Tips and Navigation
The new release fully supports the Java EE 8 standard and offers additional prompts, navigation, and other nice features for Asynchronous CDI Events , CDI Bean Injection , PushBuilder , Disposes, and Produces :

Spring and Spring Boot support
Now the IDE can automatically detect and configure the MVC Context in the Spring Facet preferences for Spring Boot applications:

The Endpoints tab in the Spring Boot application launch and debug window, which helps to monitor the running application, now supports Spring Boot 2.0 Actuator Endpoints .
Highlighting in the Spring Boot application configuration files now takes into account the type of values:

In the dependency diagrams between the bins ( Spring Beans Diagram ) a new interesting mode has appeared: Neighborhood . In this mode, only direct dependencies are displayed. When you select one of the dependencies, you will see direct dependencies for the selected bean, etc. Thus, it is convenient to navigate between dependencies:

Work with modules
If you marked some modules as “unloaded” ( unloaded ) and when updating a VCS project, new modules were created, they were previously marked as “loaded” ( loaded ). Now, in those cases when modules marked as “loaded” are not dependent on these modules, these modules are automatically marked as “unloaded”.
Also, before the commit, the IDE now checks that the “unloaded” modules are compiled without errors.
In addition, the way the modules are grouped during display has changed. Previously, this was done using groups of modules that could be created in the Project Structure . Now the same mechanism is used that is used to group the package structure: the module name is broken up by a dot symbol and forms a tree:

Build project
Previously, when using Gradle, launching applications and tests in the mode of collecting statistics on code coverage ( Run with Coverage ) did not work if the Delegate IDE option to Gradle or Gradle Test Runner was enabled. Now Run with Coverage works in all cases.
The process of importing, compiling and building a project for Gradle , Android / Gradle and SBT can now be seen in a new window of the Build tools:

Work with REST requests
Now you can work with REST requests using a new tool based on the editor. To do this, simply create a file in the project with the permission . Http and open it in the editor. If you do not want to create a file in the project, you can use the Scratch File :

Kotlin
Following the release of Kotlin 1.2 , which happened yesterday, language support was updated in the IDE. The main innovation of the update is the experimental possibility of “re-using code” between JVM and JavaScript :

With the expect keyword, any class or method can now be declared as “generic.” An implementation of this class or method for a specific platform can be declared using the actual keyword in the module for the corresponding platform. The IDE checks that the implementation exists for the configured platforms, and allows you to move from declaration to implementation and vice versa:

More information about the work of "common modules» ( common modules ) can be found in this habraposta or in the official documentation (in English). A prerequisite for the work of such modules is the assembly of the Gradle project.
Scala
The highlighting of the symbol under the carriage (which is enabled by default, like the one that is available by pressing Shift + Ctrl / Cmd + F7 ) now also highlights the implicit use of the symbol:

Building and running an application or tests is no longer tied to indexing and works even if the indexing is not over.
In SBT projects, when a plugin notices a dependency import expression that is not specified in the SBT configuration but present in the local Ivy Cache , the IDE suggests adding it to the SBT configuration:

The new version of the plugin supports Ammonite and offers syntax highlighting, hints, navigation, and a separate type of Run Configuration :

Scala project creation has changed. Now, instead of Lightbend Activator (which ceased to exist in the middle of this year), the plugin suggests using Tech Hub Project Starter project templates.
Work with Git and Mercurial
You can now interactively rebase the latest changes in Git by invoking Interactively Rebase from Here from Log :

When switching between branches, the IDE saves the state of the workspace : the location of the editor tabs, tool windows, etc.:

For convenience, changes to participate in the merge ( merge ), in Log added a new mode: Show Changes to Parents . In this mode, the right pane in Log shows not only changes in files with conflicts, but also separately non-conflicting changes for each branch participating in the merge:

The mode can be activated in the context menu.
To view conflicting changes for Git in the Log IDE now offers a three-pane interface.
When sending changes from the patch, the IDE automatically inserts the name, the mail of the author, and a description of the change, if they were in the patch:

Synchronize IDE settings between different computers
Sometimes it happens that IDE is installed at work and at home, on a stationary computer and on a laptop, etc. Previously, you had to configure IDE on each computer. Some time ago, to automate this process, you could use the plugin. When using this plugin, the settings were stored in the specified Git repository. IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate 2017.3 has a new mechanism that does not require a Git repository: all settings are stored securely on the JetBrains server. Another advantage of the new mechanism is the synchronization of not only the settings, but also directly installed plug-ins. To use the new mechanism requires a JetBrains Account .

Changes in Docker plugin
In this release, we continue to improve the plugin for Docker. Of the most notable:
- The Docker Deployment Run Configuration is divided into 3 separate Run Configurations : Dockerfile (build the image from the Dockerfile and launch the container based on the resulting image), Docker Image (start the image, equivalent to the “ docker run ” command ) and Docker Compose (start the services).
- In the Docker Image Run Configuration, you can now specify the command line directly (previously, the IDE required the creation of a special JSON file).
- In the Dockerfile Run Configuration, you can now only build an image and not run it as a container.
- You can now build an image or launch a container based on this image directly from the Dockerfile editor (by clicking on the panel to the left of the editor).
- IDE supports alternate names for Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml files.
- The Docker toolbar is now hidden by default, until the Docker settings are added to Settings .
Preview for SVG files
Now, when opening the SVG file in the editor, the IDE will offer on the right side a visual preview of this file:

Visual borders in the editor
Previously, the IDE was setting Right margin , which is displayed in the editor and taken into account in the rules of code design ( code styles ). In the new release, this setting was renamed to Hard wrap at , and in addition to it a new Visual guides option was added. With its help, you can specify values for several visual borders at once, separated by commas. These borders will also be displayed in the editor:

Mainly, this is necessary in cases where the code design rules refer to several such boundaries (this is possible, for example, in Python and in PHP).
Tools for working with databases (DataGrip 2017.3)
- If you work with a large number of data sources ( data sources ), these data sources can now be organized into groups.
- For convenience of working with numerical data in the table, they are now aligned to the right.
- For PostgreSQL , the Database toolbar displays Users and Roles , and also supports Foreign Data Wrappers .
- Data in the table can now be inserted from Excel.
- Several table values can now be compared with each other.
- Export to DDL now supports more options and is available via ( Context menu | SQL Scripts | SQL Generator ).
- Autocompletions for JOIN have become even a bit smarter.
- Support Exasol database.
- Backlight for XQuery and XPath for Sql Server via Language Injection .
JavaScript and TypeScript support (WebStorm 2017.3)
- For Vue.js , code autocompletion and navigation for props, properties and methods, as well as a new collection of code templates appeared.
- New refactorings Pull member up and Extract superclass for JavaScript - and TypeScript -classes.
- New refractorings Extract type alias and Extract interface for TypeScript .
- Updated documentation and improved autocompletion for standard JavaScript methods and objects. Opening projects has become faster thanks to pre-built indexes for these methods.
- Watch mode support for Jest and Mocha , reports on code coverage by tests for Jest and the ability to easily update Jest snapshots in one click.
- Imports to JavaScript and TypeScript files are now automatically added when copying and pasting code from one file to another.
- Debugging client applications in WebStorm no longer requires the installation of an additional extension for Chrome . But the extension is still needed for Live Editing , which is now disabled by default.
As you can see from this post, in IntelliJ IDEA 2017.3 there are a lot of new and interesting things, not counting several hundred bug fixes and smaller features that simply would not fit in one post.
You can download the update through the Toolbox App or from the official site . I will be glad to answer any questions. Questions that I can not answer myself, send the team.
UPDATE: GoLand 2017.3 was released, and now you can buy it. IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate users get GoLand functionality for free using the plugin: plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/9568-go
Program with pleasure!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343382/
All Articles