UX-design: common misconceptions and myths
What does the user see in the product? Interface. It does not matter to him how many nights you have not slept, building the architecture of the application, how beautiful the written code is. The main thing is that everything is intuitive and work. In one of the past publications, we talked about what we are doing to create a unified user experience. This is an interesting topic, now we are preparing new cases for publication, but for now the material on the editorial board, we propose to read and talk about popular myths and misconceptions about UX design. Thanks for the material Miklos Philips .

It seems that even now “UX” is still a buzzword in many companies - “We don’t need just a designer,” says the vice president for new products. “We need a UX designer!” All those present at the meeting gasp, according to nod and secretly googling "What is UX-design?" And "What does the UX-designer do?".
Of course, today most people already know that UX stands for “user experience”, i.e. "User experience". But this does not mean that everyone really understands what it is made of and how it works. Moreover, it’s often difficult to explain what a design is based on user experience or what a UX designer actually does.
')
In short, UX is the perception of users of all aspects of the system (site, application, product, service, community, etc.). Companies strive to achieve positive, consistent, predictable and desired results using user experience, which may include interface, industrial design, physical interaction, and more.
UX design is a special discipline dedicated to what UX designers do, and user-centered design (UCD) is a UX design process . Another widely used term is design thinking. As a rule, this practice includes the study of user behavior, the creation of sketches, frame modeling, interaction design, visual design, development of prototypes, user testing and an iterative approach to design.

Understanding UX design — what it is and what it is not — will help everyone associated with it create superior products with superior user experience. To this end, I would like to consider some common misconceptions and myths about UX-design:
The interface is not a solution . UI-design, as a rule, plays an important role in the work of the UX-designer, but this is not its only element. Speaking figuratively, UX-design is a journey , and UI is a destination .
UX-design is a multi-stage strategic design process whose goal is to create a product or site that consumers / users find attractive, user-friendly and understandable. And using the UX-design, we end up with the optimal user interface for us.
In the complex process of UX-design, you can select at least 10 steps necessary to create a ready user interface.
And finally, we get the final user interface design and arrive at our desired destination .

Illustration: Shane Rounds
Aesthetics alone is not enough to ensure a high degree of usability. Aesthetics is only an appearance , and UX-design is both an appearance , and general sensations , and quality of work .
A great user experience is a prerequisite for creating a successful digital product design. Of course, visual appeal and aesthetics in general are very important, but they represent only the final touch in creating an easy-to-use product, which is also very pleasant to use. Some people compare them with paint, which is applied to an already constructed building. Striving for aesthetic perfection without attention to usability will ultimately lead to failure.
If the user experience was associated only with aesthetics, the usability of the product should have been relegated to the background. But usability is a crucial quality indicator, determining how easy it is to use the product. The consumer will hardly be greatly concerned with what the product looks like if he cannot use it .
Whether a product is useful is defined in terms of functionality (utility) , as well as usability. The first of these elements provides the necessary functions for people, and it depends on the second how easy and pleasant it is to use these functions. Design based solely on aesthetics and ignoring the basic principles of usability ultimately turns out to be useless by definition.

UX-design is not just any checkbox (check box). It must be integrated into everything the company does.
UX-design is not just a stage in the design process, but repeated, continuous use of design thinking regarding the interaction of consumers with the services and products of a company. This process never ends.
For example, the Interaction Design Foundation gives the following definition of UX design: “This is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and deeply personal experience. It involves increased attention to both the usability of the product and the pleasure that consumers receive using it. In addition, UX-design is related to the overall process of acquiring and integrating a product, including such aspects as branding, design, usability and functionality. ”

UX-design is not limited to the screen owned by the user of the computer and is not any separate layer or component in the composition of the product or service. This is a holistic experience , contextually acting at all levels as a whole.
UX design takes into account the human factor in a specific context and covers all aspects of the ecosystem that uses the relevant products. It is associated with a holistic development of experience, when “the whole is considered as something more than just the sum of its constituent parts”, and with maintaining a similar focus throughout the time of interaction with the consumer, as well as with all points of contact of the user with the product.

Undoubtedly, usability — or usability — is essential to the success of any user experience. However, under the UX umbrella many different things are hidden, and usability is just one of them. The user interface can be very convenient to use, but it does not achieve the goal, for example, when it comes to providing what the consumer needs, at the right time and in the right way.
As we have already mentioned, the user interface can be aesthetically appealing and pleasant to use, but at the same time it looks completely pitiful under the microscope of a heuristic analysis for a detailed check of all elements that provide a high level of usability.

Heuristic evaluation reveals a low level of usability. An example of identifying usability problems with heuristic analysis (figure author: Corey Haggard ).
A quality product must satisfy users on many levels. It should be:
If the product is inconvenient to use, the consumer simply passes by it, regardless of how good the visual design is - how awesome the micro-animation is - and your UX-design goes to the cat's tail. If it is done correctly, you will be on your way to a very significant improvement in user experience. The product will have a much better chance of success, which, in turn, will contribute to the final indicators.

In addition to all the above, UX-design must meet commercial goals and objectives. It all starts with an understanding of the concept of the product, the reasons for its existence from a commercial point of view. This should take into account the needs of the target market, solve problems and develop effective solutions.
If the UX designer only focuses on creating an optimal user experience, forgetting commercial goals, he will fail. This mistake is made by many newcomers to the UX profession, who often make totally unrealistic recommendations. The existence of companies is ensured by their profitability.
Business needs can be addressed, for example, by using a SMART scheme when defining business goals for a UX project:
Specific
Measurable (measurable),
Actionable (implementable)
Realistic (realistic),
Time-based (time controlled).
Designers should consider their work from a business point of view, think strategically, take into account priorities and work not only for users, but also to achieve commercial goals.

Of course, theoretically, someone can spend a lot - “go all-in” - and use the whole range of methods and tools that make up the entire UX process. In reality, no one does. Most companies refer to the high costs (myth) and time constraints when trying to justify the refusal to implement the most important elements of UX design, such as the study of user behavior and user testing. In fact, especially when it comes to researching user behavior, companies cannot afford not to.
In reality, the best UX designers have a specific set of methods that can be used for a wide variety of projects and a wide variety of budgets. For example, without very high costs, you can find very broad design possibilities and get a lot of important analytical information as a result of a study in which only five users participate. Similarly, completely inexpensive testing of a simple prototype by the same five users reveals most of the problems associated with usability, and demonstrates to product developers what works and what does not.
Another method is heuristic analysis . Only five experts can identify more than 80% of the problems associated with the usability of the product - and this is completely inexpensive, especially considering the costs that may not entail such testing.
A bad user experience is much more expensive than a good one. The consequences of poor UX design always create additional user interference. Interference also leads to irritation, and when irritation reaches a certain limit, people simply refuse the corresponding product.
In this animated video , Dr. Susan Weinshenk shows how user-centered design leads to a significant increase in return on investment.
Responsibility for the user experience should be borne by the entire company. If a company does not use a customer-centric design methodology when developing its products and services, it will undoubtedly be surpassed by competitors who do not neglect this technique. Companies in which specialists in UX-design are forced to work in isolation and only “preening” the already created product make a big mistake.
The integration of user-centered design (UCD) into the company's strategic concept, mission and culture is a vital moment. All the most successful companies do it. At the same time, UX-design has many different definitions: it is called “user-oriented design” (definition adopted by Amazon), “consumer experience” (CX) or “service design”

A UX designer is a “practicing specialist in design thinking ”, a “jack of all trades” in the field of user experience, whose main task is to ensure customer satisfaction with the product. The structure of UX-design includes many different disciplines, approaches, methods and tools: analysis of commercial goals, competitive analysis , character development, research of user behavior , mapping empathy, learning "ways of users", information architecture, content strategy, interaction design , interface design, visual design, prototyping , heuristic analysis , user testing ... and much more.
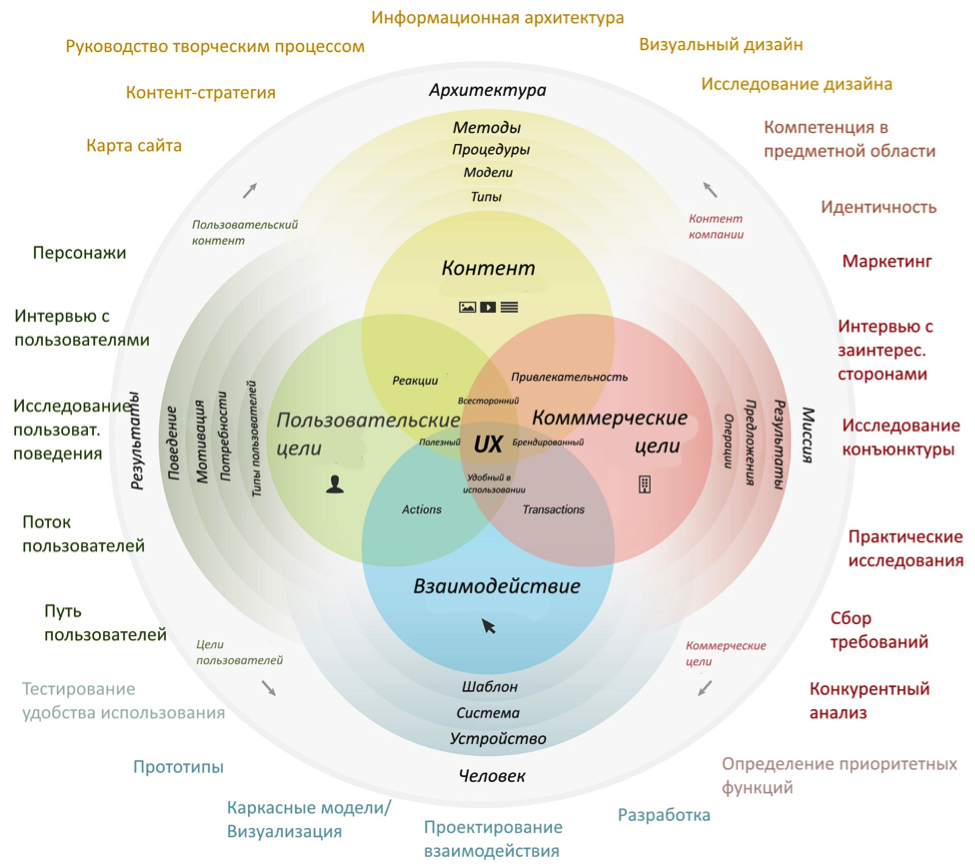
User Experience Model (circuit author: Corey Stern )
In the modern world, UX-design simply cannot be some kind of “supplement” to which companies turn after they have done “all the most important” types of defining business goals, analyzing the market, drawing up requirements for the product, engineering developments, sales and marketing. Nowadays, UX design should be integrated into everything the company does.
Products are not only their characteristics and functionality. Sites, applications or B2B SaaS products are not just utilities. Companies can not get the full return from their investments, if their result is only a short-term emotional reaction of consumers, caused by the efforts of designers who were focused solely on functionality and aesthetics. In any long-term positive emotional reaction, there must necessarily be a value component, and product design - to constantly give pleasure to users. Thus, UX-design is required for long-term success.
UX-design is primarily associated with increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty by providing a positive experience in all points of their interaction with the brand or company.
Recent research conducted by Forrester Research shows that a high-quality interface with the potential can increase the site’s performance by 200% or even 400% (with further improvement). With numbers you can not argue - they speak for themselves.
Once these myths have been dispelled, and erroneous ideas about UX design are refuted, it becomes clear that it can have a huge impact on the overall development of the company, provide benefits, and the UX process should be integrated into everything that it does. And what other misconceptions and myths encountered?

It seems that even now “UX” is still a buzzword in many companies - “We don’t need just a designer,” says the vice president for new products. “We need a UX designer!” All those present at the meeting gasp, according to nod and secretly googling "What is UX-design?" And "What does the UX-designer do?".
Of course, today most people already know that UX stands for “user experience”, i.e. "User experience". But this does not mean that everyone really understands what it is made of and how it works. Moreover, it’s often difficult to explain what a design is based on user experience or what a UX designer actually does.
')
In short, UX is the perception of users of all aspects of the system (site, application, product, service, community, etc.). Companies strive to achieve positive, consistent, predictable and desired results using user experience, which may include interface, industrial design, physical interaction, and more.
UX design is a special discipline dedicated to what UX designers do, and user-centered design (UCD) is a UX design process . Another widely used term is design thinking. As a rule, this practice includes the study of user behavior, the creation of sketches, frame modeling, interaction design, visual design, development of prototypes, user testing and an iterative approach to design.

Understanding UX design — what it is and what it is not — will help everyone associated with it create superior products with superior user experience. To this end, I would like to consider some common misconceptions and myths about UX-design:
User Experience (UX) is not a user interface (UI)
The interface is not a solution . UI-design, as a rule, plays an important role in the work of the UX-designer, but this is not its only element. Speaking figuratively, UX-design is a journey , and UI is a destination .
UX-design is a multi-stage strategic design process whose goal is to create a product or site that consumers / users find attractive, user-friendly and understandable. And using the UX-design, we end up with the optimal user interface for us.
In the complex process of UX-design, you can select at least 10 steps necessary to create a ready user interface.
- Analysis of commercial objectives and technical characteristics
- Competitive Analysis Results Reports
- Character development and user experience learning
- Sitemap and information architecture
- User Experience Maps, Paths and User Flows
- Sketches and frame models
- Mockups and interaction design
- Interactive Prototypes
- Usability testing
- Visual design
And finally, we get the final user interface design and arrive at our desired destination .

Illustration: Shane Rounds
UX design is not only aesthetic
Aesthetics alone is not enough to ensure a high degree of usability. Aesthetics is only an appearance , and UX-design is both an appearance , and general sensations , and quality of work .
A great user experience is a prerequisite for creating a successful digital product design. Of course, visual appeal and aesthetics in general are very important, but they represent only the final touch in creating an easy-to-use product, which is also very pleasant to use. Some people compare them with paint, which is applied to an already constructed building. Striving for aesthetic perfection without attention to usability will ultimately lead to failure.
If the user experience was associated only with aesthetics, the usability of the product should have been relegated to the background. But usability is a crucial quality indicator, determining how easy it is to use the product. The consumer will hardly be greatly concerned with what the product looks like if he cannot use it .
Whether a product is useful is defined in terms of functionality (utility) , as well as usability. The first of these elements provides the necessary functions for people, and it depends on the second how easy and pleasant it is to use these functions. Design based solely on aesthetics and ignoring the basic principles of usability ultimately turns out to be useless by definition.

UX design is not just one of the steps of a large process.
UX-design is not just any checkbox (check box). It must be integrated into everything the company does.
“Most customers believe that UX-design is a separate line of business that can solve all problems by defining functional requirements or conducting some kind of research. In fact, this is a permanent job, an ongoing process of obtaining new information about users, responding to their behavior and developing a product or service, ”- Dan Brown, co-founder and director of EightShapes .
UX-design is not just a stage in the design process, but repeated, continuous use of design thinking regarding the interaction of consumers with the services and products of a company. This process never ends.
For example, the Interaction Design Foundation gives the following definition of UX design: “This is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and deeply personal experience. It involves increased attention to both the usability of the product and the pleasure that consumers receive using it. In addition, UX-design is related to the overall process of acquiring and integrating a product, including such aspects as branding, design, usability and functionality. ”

UX design is not just digital product design.
UX-design is not limited to the screen owned by the user of the computer and is not any separate layer or component in the composition of the product or service. This is a holistic experience , contextually acting at all levels as a whole.
UX design takes into account the human factor in a specific context and covers all aspects of the ecosystem that uses the relevant products. It is associated with a holistic development of experience, when “the whole is considered as something more than just the sum of its constituent parts”, and with maintaining a similar focus throughout the time of interaction with the consumer, as well as with all points of contact of the user with the product.
As Don Norman says: "User experience covers all aspects of the end-user interaction with the company, its services and its products."
“UX design is not limited to computer. It doesn't even need a screen ... User experience is any interaction with any product, any artifact, any system, ”- Bill Derushi, Director of Interaction Design at Ziba Design.

UX design is not only about usability
Undoubtedly, usability — or usability — is essential to the success of any user experience. However, under the UX umbrella many different things are hidden, and usability is just one of them. The user interface can be very convenient to use, but it does not achieve the goal, for example, when it comes to providing what the consumer needs, at the right time and in the right way.
As we have already mentioned, the user interface can be aesthetically appealing and pleasant to use, but at the same time it looks completely pitiful under the microscope of a heuristic analysis for a detailed check of all elements that provide a high level of usability.

Heuristic evaluation reveals a low level of usability. An example of identifying usability problems with heuristic analysis (figure author: Corey Haggard ).
A quality product must satisfy users on many levels. It should be:
Useful
Why should I use it? Does it serve any purpose? Does any need meet?
Convenient to use
Is it intuitive? Is it easy to use? Is it available?
Attractive
Is it aesthetically appealing? Is he different from others? Is it remembered?
Sustainable
Can I save it? Is he capable of development? Can I support it? Does it scale?
Social
Does he facilitate communication? Does sharing support? Does community encouragement?
If the product is inconvenient to use, the consumer simply passes by it, regardless of how good the visual design is - how awesome the micro-animation is - and your UX-design goes to the cat's tail. If it is done correctly, you will be on your way to a very significant improvement in user experience. The product will have a much better chance of success, which, in turn, will contribute to the final indicators.
“Although usability is very important, a focus on efficiency seems to obscure other important factors in the user experience — for example, ease of learning, as well as unconscious and behavioral emotional responses to the products and services we use,” David Maloof, a professor of design. Interactions, Savanna College of Art and Design

UX design is not only about the user
In addition to all the above, UX-design must meet commercial goals and objectives. It all starts with an understanding of the concept of the product, the reasons for its existence from a commercial point of view. This should take into account the needs of the target market, solve problems and develop effective solutions.
If the UX designer only focuses on creating an optimal user experience, forgetting commercial goals, he will fail. This mistake is made by many newcomers to the UX profession, who often make totally unrealistic recommendations. The existence of companies is ensured by their profitability.
Business needs can be addressed, for example, by using a SMART scheme when defining business goals for a UX project:
Specific
Measurable (measurable),
Actionable (implementable)
Realistic (realistic),
Time-based (time controlled).
Designers should consider their work from a business point of view, think strategically, take into account priorities and work not only for users, but also to achieve commercial goals.
“We simply cannot always do what is best for users. In addition, we also need to achieve certain commercial goals - and our design work is focused on that too, ”- Russ Unger, director of user experience planning, DraftFCB

UX-design does not require large expenses
Of course, theoretically, someone can spend a lot - “go all-in” - and use the whole range of methods and tools that make up the entire UX process. In reality, no one does. Most companies refer to the high costs (myth) and time constraints when trying to justify the refusal to implement the most important elements of UX design, such as the study of user behavior and user testing. In fact, especially when it comes to researching user behavior, companies cannot afford not to.
In reality, the best UX designers have a specific set of methods that can be used for a wide variety of projects and a wide variety of budgets. For example, without very high costs, you can find very broad design possibilities and get a lot of important analytical information as a result of a study in which only five users participate. Similarly, completely inexpensive testing of a simple prototype by the same five users reveals most of the problems associated with usability, and demonstrates to product developers what works and what does not.
Another method is heuristic analysis . Only five experts can identify more than 80% of the problems associated with the usability of the product - and this is completely inexpensive, especially considering the costs that may not entail such testing.
“Bad design creates interference”, - Jared M. Spoole, founder of User Interface Engineering
A bad user experience is much more expensive than a good one. The consequences of poor UX design always create additional user interference. Interference also leads to irritation, and when irritation reaches a certain limit, people simply refuse the corresponding product.
Return on investment in UX-design from the point of view of user experience
In this animated video , Dr. Susan Weinshenk shows how user-centered design leads to a significant increase in return on investment.
UX design is not just the role of one person or department
Responsibility for the user experience should be borne by the entire company. If a company does not use a customer-centric design methodology when developing its products and services, it will undoubtedly be surpassed by competitors who do not neglect this technique. Companies in which specialists in UX-design are forced to work in isolation and only “preening” the already created product make a big mistake.
The integration of user-centered design (UCD) into the company's strategic concept, mission and culture is a vital moment. All the most successful companies do it. At the same time, UX-design has many different definitions: it is called “user-oriented design” (definition adopted by Amazon), “consumer experience” (CX) or “service design”

UX design is not one discipline.
A UX designer is a “practicing specialist in design thinking ”, a “jack of all trades” in the field of user experience, whose main task is to ensure customer satisfaction with the product. The structure of UX-design includes many different disciplines, approaches, methods and tools: analysis of commercial goals, competitive analysis , character development, research of user behavior , mapping empathy, learning "ways of users", information architecture, content strategy, interaction design , interface design, visual design, prototyping , heuristic analysis , user testing ... and much more.

User Experience Model (circuit author: Corey Stern )
UX design required
In the modern world, UX-design simply cannot be some kind of “supplement” to which companies turn after they have done “all the most important” types of defining business goals, analyzing the market, drawing up requirements for the product, engineering developments, sales and marketing. Nowadays, UX design should be integrated into everything the company does.
Products are not only their characteristics and functionality. Sites, applications or B2B SaaS products are not just utilities. Companies can not get the full return from their investments, if their result is only a short-term emotional reaction of consumers, caused by the efforts of designers who were focused solely on functionality and aesthetics. In any long-term positive emotional reaction, there must necessarily be a value component, and product design - to constantly give pleasure to users. Thus, UX-design is required for long-term success.

UX-design is primarily associated with increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty by providing a positive experience in all points of their interaction with the brand or company.
Recent research conducted by Forrester Research shows that a high-quality interface with the potential can increase the site’s performance by 200% or even 400% (with further improvement). With numbers you can not argue - they speak for themselves.
Once these myths have been dispelled, and erroneous ideas about UX design are refuted, it becomes clear that it can have a huge impact on the overall development of the company, provide benefits, and the UX process should be integrated into everything that it does. And what other misconceptions and myths encountered?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343366/
All Articles