Simplest RESTful service on Kotlin and Spring boot

More than a year has passed since the release of Kotlin , and the Spring boot has undergone changes. Having come across an article on how to write a simple RESTful service using the Kotlin and Spring boot, I wanted to write about how this can be done today.
This small article is aimed at those who never wrote code on Kotlin and did not use the Spring boot.
Project preparation
We will need:
- MySql DB server
- IDE IntelliJ IDEA
- arms
First, go to the Spring Initializr website to create an application template. Fill out the form and download the resulting blank:
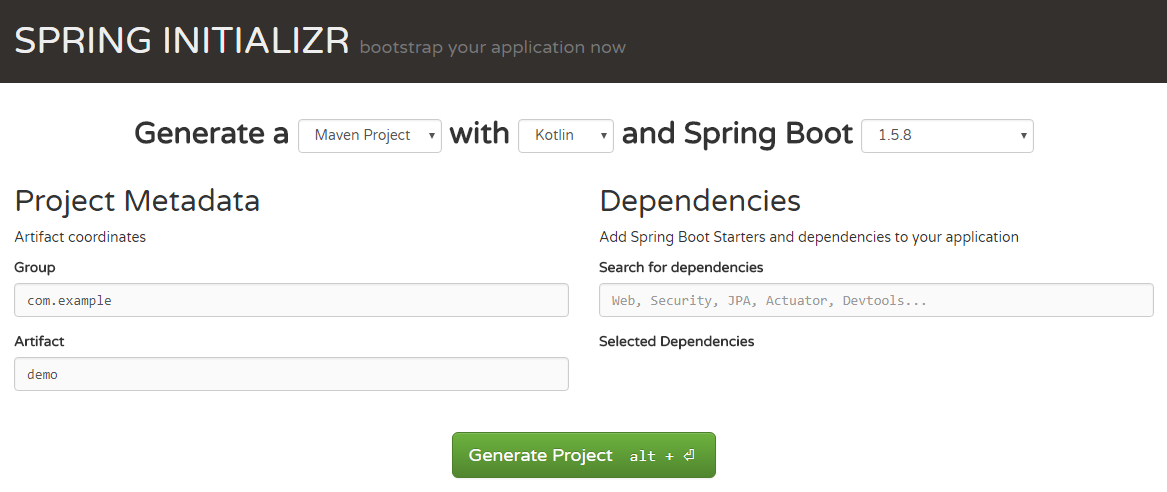
We get a project template with the following structure:
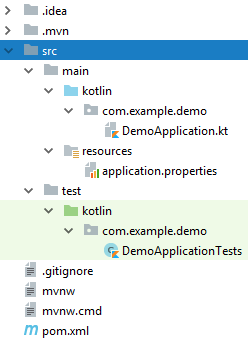
')
Add a couple of dependencies (you can specify when generating an application template) required for the implementation of MVC:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId> </dependency> As well as the database driver (in this case, MySql)
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <version>6.0.6</version> </dependency> Code
Our service will consist of a single Product entity that has the name and description properties. We will also describe the Repository and Controller . All the code is not for "users" will be written in the package com.example.demo.system , and the client code set in com.example.demo.service
Product Entity
Create the models.kt file in the com.example.demo.system com.example.demo.system and add the following code there:
package com.example.demo.system import javax.persistence.* import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.* @Entity // @Table(name = "products") // data class Product( // equals hashCode copy @JsonProperty("name") // JSON @Column(name = "name", length = 200) // val name: String = "", // (, ) name, @JsonProperty("description") @Column(name = "description", length = 1000) val description: String = "", @Id // ORM - Primary Key @JsonProperty("id") @Column(name = "id") @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) // - Autoincrement val id: Long = 0L ) ProductRepository Repository
Create a file repositories.kt in the namespace com.example.demo.system with three lines of code:
package com.example.demo.system import org.springframework.data.repository.* interface ProductRepository : CrudRepository<Product, Long> // CRUD ProductService Service Layer
Create a ProductService.kt file in the com.example.demo.service com.example.demo.service with the following code:
package com.example.demo.service import com.example.demo.system.* import org.springframework.stereotype.Service @Service // IoC class ProductService(private val productRepository: ProductRepository) { // fun all(): Iterable<Product> = productRepository.findAll() // , fun get(id: Long): Product = productRepository.findOne(id) fun add(product: Product): Product = productRepository.save(product) fun edit(id: Long, product: Product): Product = productRepository.save(product.copy(id = id)) // id . Kotlin - ( ) copy ( ) fun remove(id: Long) = productRepository.delete(id) } ProductsController Controller
Now create the controllers.kt file in the com.example.demo.system com.example.demo.system with the following code:
package com.example.demo.system import com.example.demo.service.* import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.* @RestController // http ( JSON ) @RequestMapping("products") // class ProductsController(private val productService: ProductService) { // @GetMapping // GET url fun index() = productService.all() // all . @PostMapping // POST url @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) // HttpStatus fun create(@RequestBody product: Product) = productService.add(product) // Product add @GetMapping("{id}") // GET url (http://localhost/products/{id}) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.FOUND) fun read(@PathVariable id: Long) = productService.get(id) // id Long get @PutMapping("{id}") fun update(@PathVariable id: Long, @RequestBody product: Product) = productService.edit(id, product) // url, PUT edit @DeleteMapping("{id}") fun delete(@PathVariable id: Long) = productService.remove(id) } Application setup
Create a database schema named demo and modify the application.properties file as follows:
#------------------------- # Database MySQL #------------------------- # spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver # spring.datasource.username=**** # spring.datasource.password=**** # , spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false #------------------------- # ORM settings #------------------------- # spring.jpa.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect # (, , ...) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create # SQL spring.jpa.show-sql=true Everything is ready you can test
Testing
DemoApplicationTests file in the com.example.demo com.example.demo as follows:
package com.example.demo import org.junit.* import org.junit.runner.RunWith import org.junit.runners.MethodSorters import org.springframework.http.MediaType import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders.* import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.* import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.* @SpringBootTest @RunWith(SpringRunner::class) @FixMethodOrder(MethodSorters.NAME_ASCENDING) // class DemoApplicationTests { private val baseUrl = "http://localhost:8080/products/" private val jsonContentType = MediaType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON.type, MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON.subtype) // http private lateinit var mockMvc: MockMvc // mock @Autowired private lateinit var webAppContext: WebApplicationContext // @Before // fun before() { mockMvc = webAppContextSetup(webAppContext).build() // } @Test fun `1 - Get empty list of products`() { // val request = get(baseUrl).contentType(jsonContentType) // GET http://localhost:8080/products/ http Content-Type: application/json mockMvc.perform(request) // .andExpect(status().isOk) // http 200 OK .andExpect(content().json("[]", true)) // JSON } // @Test fun `2 - Add first product`() { val passedJsonString = """ { "name": "iPhone 4S", "description": "Mobile phone by Apple" } """.trimIndent() val request = post(baseUrl).contentType(jsonContentType).content(passedJsonString) val resultJsonString = """ { "name": "iPhone 4S", "description": "Mobile phone by Apple", "id": 1 } """.trimIndent() mockMvc.perform(request) .andExpect(status().isCreated) .andExpect(content().json(resultJsonString, true)) } @Test fun `3 - Update first product`() { val passedJsonString = """ { "name": "iPhone 4S", "description": "Smart phone by Apple" } """.trimIndent() val request = put(baseUrl + "1").contentType(jsonContentType).content(passedJsonString) val resultJsonString = """ { "name": "iPhone 4S", "description": "Smart phone by Apple", "id": 1 } """.trimIndent() mockMvc.perform(request) .andExpect(status().isOk) .andExpect(content().json(resultJsonString, true)) } @Test fun `4 - Get first product`() { val request = get(baseUrl + "1").contentType(jsonContentType) val resultJsonString = """ { "name": "iPhone 4S", "description": "Smart phone by Apple", "id": 1 } """.trimIndent() mockMvc.perform(request) .andExpect(status().isFound) .andExpect(content().json(resultJsonString, true)) } @Test fun `5 - Get list of products, with one product`() { val request = get(baseUrl).contentType(jsonContentType) val resultJsonString = """ [ { "name": "iPhone 4S", "description": "Smart phone by Apple", "id": 1 } ] """.trimIndent() mockMvc.perform(request) .andExpect(status().isOk) .andExpect(content().json(resultJsonString, true)) } @Test fun `6 - Delete first product`() { val request = delete(baseUrl + "1").contentType(jsonContentType) mockMvc.perform(request).andExpect(status().isOk) } } PS
Tutorial only describes one of the many options for implementing such applications and does not claim anything at all. Any criticism is welcome, I will be glad to know where I was wrong.
Thanks to all!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343364/
All Articles