How we did a huge amount of communication for a rather big security structure
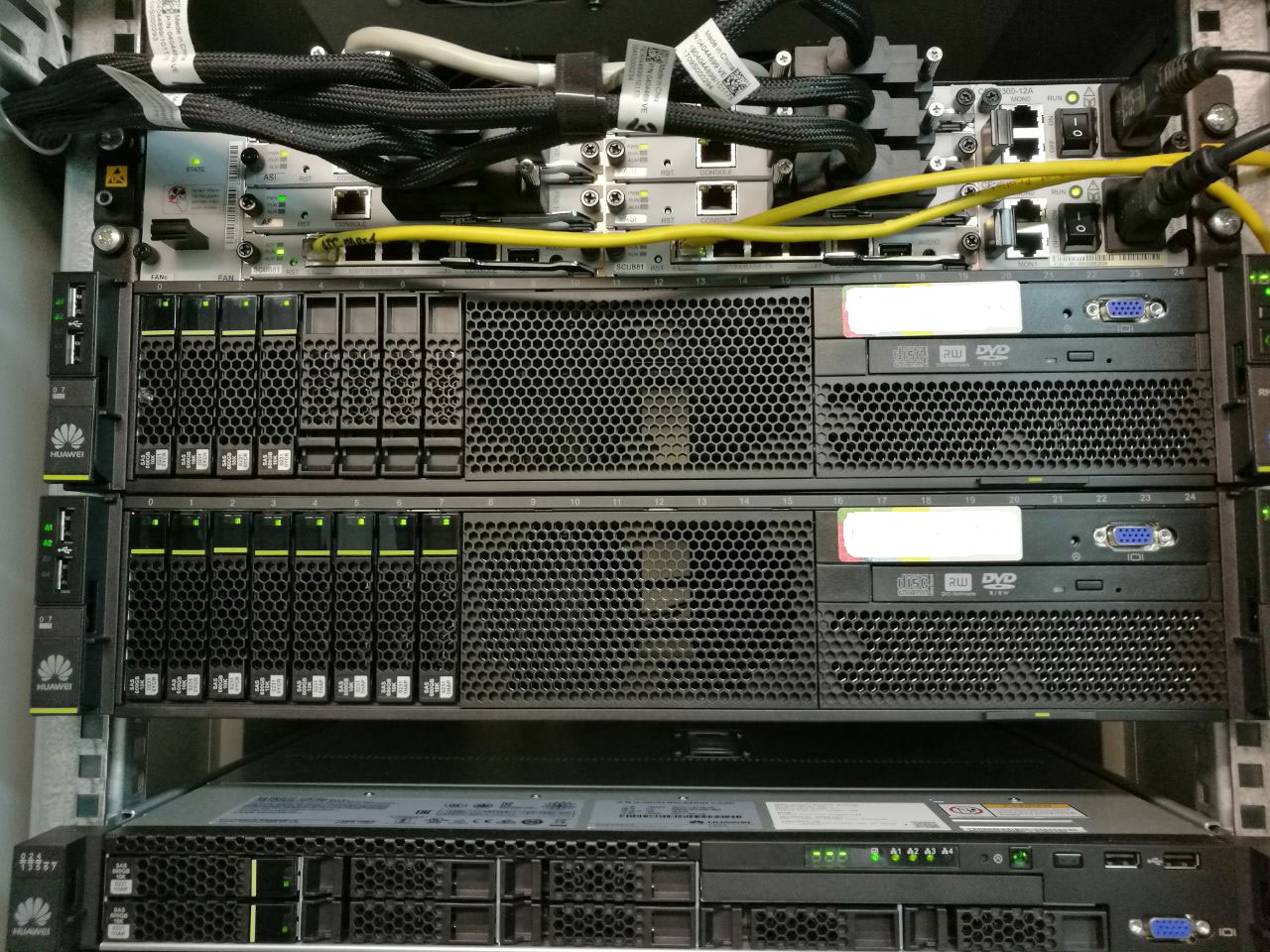

Part of the equipment of the central node of the network, which according to the survival scenario can be completely destroyed, and the network will retain the main functionality
There is one state enterprise whose employees protect more than 2,000 different objects, including strategically important ones. IT, and indeed communications, is not in the sphere of their main interests, therefore, he has few specialists in networks and telephony.
')
Within the framework of the project, two tasks were accomplished in parallel: the separation of the departmental network from the channels and the savings in communication. If you are engaged in IP-telephony, perhaps our experience will be interesting for you.
Situation
As part of a comprehensive project, we built a corporate data network for this customer on Huawei routers. Plus, the customer wanted to provide all the same objects with a telephone connection, simultaneously reducing the costs of it. Objects of about 500, for a start, took up 270 of them. Objects are large - this is the management of regional offices, guiding the work, respectively, at the regional level. Local departments are subordinate to them, and small sites are already subordinate to branches.
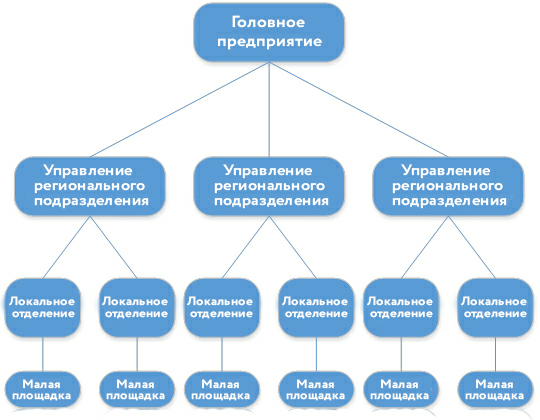
At each of the sites there was a local area network on the equipment that they could afford. The existing telephony at the facilities was implemented either on small PBXs connected to external telephone networks using conventional two-wire lines, or these same two-wire lines were routed directly to offices and workplaces. Some regional divisions had E1 flows. There was no single standard for equipment and settings for telephony. There was one unit-exception - there was already built a full-fledged piece of CSFD based on Cisco DMVPN and telephony based on Avaya. Currently, Avaya PBXs are integrated with Huawei-based telephony and a general numbering plan.
Decision making
By telephony, we looked at key market players. The customer needed only basic telephone functionality - call routing, transfer, call forwarding, etc., scalability and disaster recovery. This functionality is easy to close all vendors. The scope of the project was big - all of Russia, so the choice was made for the price. In terms of price-quality ratio, the Huawei solution turned out to be the best.
How to build CSFD
To build a CSFD, we simply selected performance routers for each type of object. Here's what we got:
The parent company. Huawei AR2240:

Office of regional offices. Huawei AR2240, Huawei 2220E or Huawei 1220 (depending on the size of the unit).
Local branches. Huawei AR1220:

Huawei 2220E Router:

Small sites: Huawei AR151:

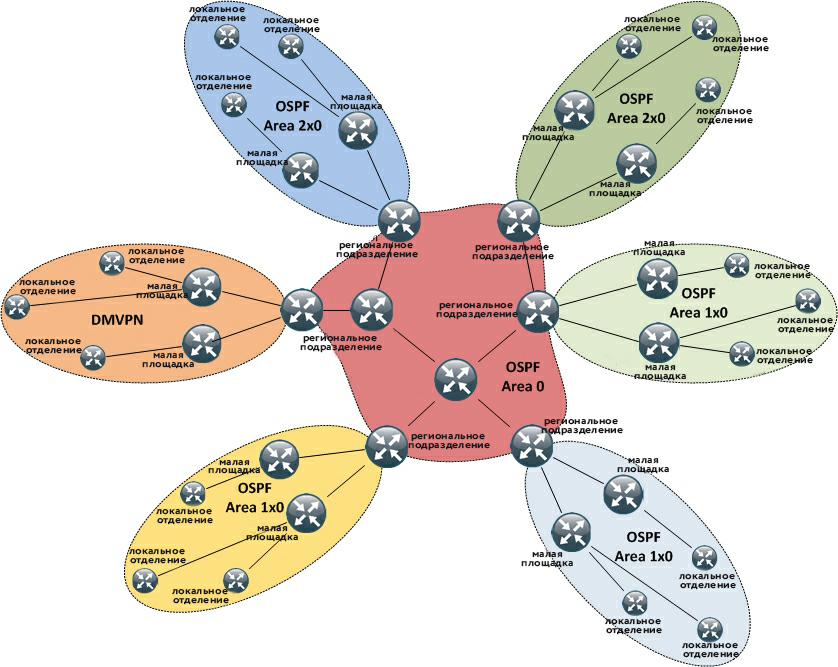
From the point of view of the network building logic, between objects, repeating their hierarchy, we build GRE / IPSec tunnels, within which we transmit routing information using OSPF. It turns out such a tree structure. Routing scheme in the corporate data network:
Telephony
First, the vendor, following the usual design schemes, offered to carry out all call processing at one central point. In our case, this is the parent company.
Having estimated the size of the territory over which customer objects are scattered, and the reliability of communication channels, we came to the conclusion that it is better to make the processing distributed. In the adopted architecture, it occurs independently in the management of each of the regional divisions. The equipment of local offices is connected to the equipment of divisions in the Local Regeneration Mode. In this mode, call management between SIP phones and analog lines of the local branch is managed by the regional department, and when the connection with it is broken, it is automatically transferred to the local branch equipment. Small sites, in turn, receive analog voice gateways — devices that register with SIP on the regional unit's control equipment and provide a number of analog ports.
Distributed call handling solved another problem: in the corporate network there were satellite transitions and tricky joints of several providers, thanks to which, for example, traffic between the cities of the Far East cut a loop through Moscow. On the part of the nodes, the network delay reached 1 second. With such a delay, telephones from distant points could not register at all at the central facility.
Equipment mounted in the local branch:

As an alternative to the old PBX, regional office divisions received eSpace U1960 devices. These are chassis with E1, FXO and FXS interface modules and SIP support. The eSpace U1911, similar devices of smaller size, went to the small platforms.
PBX Huawei eSpace U1960:

eSpace U1911:

At the parent company installed eSpace U1981, U1960 older brother. In addition, the regional offices have deployed a server to register softphones. They are used by employees of the customer who spend a lot of time on business trips.
External telephone lines, in most cases analog or ISDN PRI interfaces and subscribers, are connected to the PBX eSpace. Auto attendant with extension dialing is supported.
At small sites, external telephone lines are not connected, small analog line adapters are used. They are called iad. IAD 104H analog line adapter:

In most cases, analog telephone sets were used as subscriber devices. This made the decision cheaper at the initial stage compared to the mass installation of SIP phones, since telephone lines, unlike Ethernet cables, have already been installed at all workstations. Now the customer himself is testing SIP devices from other manufacturers, in order to enable regional units to buy their own phones to choose from the list of tested.
Heads of regional divisions received SIP-devices with Android inside and video support. Huawei eSpace 8950 SIP Phone:

Secretaries - devices with expansion panel. Huawei eSpace 7950 SIP Phone:

Some of the other employees are basic eSpace 7910 devices. In the photo, he is already “in work”. Huawei eSpace 7910 SIP Phone:

Result
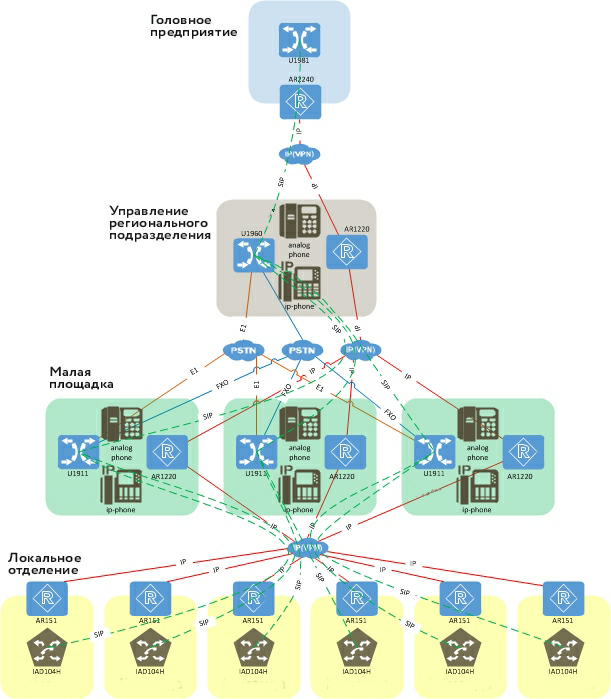
The whole solution looks like this. Architecture of PSTN and IP-telephony solutions:
What did the customer end up with?
The corporate data transmission network allowed to integrate local networks of objects into the general infrastructure. This is the basis for the work of application services, including telephony. In part of the same telephony:
- Communication is now organized uniformly (you no longer need to think about which PBX where it is and whether it is at all), at the facilities of one level of hierarchy (regional division management / local branch / small platform) the same equipment is installed
- All use a single numbered plan - employees have four-digit internal numbers, each regional unit has a two-digit prefix
- In all local branches and offices, the same telephone functionality is available - connecting analog and SIP subscribers, external interfaces FXO and PRI for connecting to the city networks
- Everywhere there was an auto attendant for the extension of internal numbers. It is no longer necessary to start an external city line for each employee who receives calls from the city.
- Finally, the classic of IP-telephony - savings due to the reduction of long-distance calls through public networks - both in the payment of calls and in the payment of urban lines, the number of which can now be reduced.
Project Features
Totally 5 thousand subscribers are covered. The first part of the implementation - 10 months.
One of the main difficulties was the installation. Business trips to all necessary points of our country would cost more than work. Therefore, we acted differently: we received the equipment at the customer’s Moscow warehouse, unpacked it, set it up, then packed it back and sent it to places. On the ground, the customer’s employees turned on the equipment in the socket and the local network, embroidered analog lines on the patch panels, after which we connected and tuned everything we needed. Often, some of the settings did not coincide with the survey data - somewhere not the same IP, somewhere not such a mask. A separate topic is analog telephone lines. Adventures never end with them. For situations where parameters like pulse / tone dialing or “busy” signal did not match, they got used quickly, but there were moments and more interesting. On one of the objects, the line, when dialed from the telephone, did not accept the number "9". All other numbers at the same time were typed normally. It was solved only by laying a new cable.
ESpace has quite good means of analogue telephony switching - from the web interface, you can see the graphs of current and voltage in the line and even something like an oscillogram of sound. It helped us a lot, but the main tools for solving problems, as in the old days, were a telephone receiver and a piercer in the hands of an employee of a customer working on site. The project in general was more about interacting with people than about working with technology. Once, for example, after long attempts to defeat voltage fluctuations on external communication lines during lengthy consultations and dialogues, we went out to a person who told us that these lines were near the power plant on the way to the customer’s site, and everyone was used to them for a long time. The same person helped his colleagues in the field competently organize the grounding and eventually solved the problem.
Well, yes, even for IVR, we gave texting to the employees of the customer, and they called the special number and recorded greetings. Not Levitan, of course, but someone discovered the talent of the announcer.
At one of the sites, we initially incorrectly downloaded localization files, because of which the station told the external subscriber that it would be transferred to the extension number in Chinese. The customer told us that he heard a “speech that was alien to his ear,” and suggested rewriting the voice file on his own. Showed him how to do it. After 5 minutes, we make a test call and hear: "From the sober in the office, only the communications personnel, so we transfer the call to the IT department."
Links
- Pro features of brake lines
- Alteration of the Aeroexpress network
- VCS in ECE
- My mail is ASigachev@croc.ru
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343352/
All Articles