Basics of React: everything you need to know to get started
Want to know what React is, but you still don’t have a chance to study it? Or, maybe you have already tried to master React, but could not really understand? Or maybe you understand the basics, but you want to put in order the knowledge? This article is written specifically for those who positively answered at least one of these questions. Today we will create a simple music player, revealing the basic concepts of React as we move towards the goal.

Having dealt with this material, you will learn the following:
This is almost everything you need to know in order to create and maintain React-applications.
Consider this situation: a small startup turns to you for help. They created a nice page, using which users can download music to their service and play it. They want you to do the most difficult thing - breathe life into this page.
')
First, create a new project directory and add three files there. Here they are on GitHub, and here is their code.
To successfully complete this tutorial, you need a fresh version of the Google Chrome browser , otherwise the animation will not work. Thanks to Stephen Fabre for the CSS for the play button and Justin Vindle for the render code (you can see the original here ).
Open
React is a tool for creating user interfaces. Its main task is to provide a display of what can be seen on web pages. React makes it easy to create interfaces by splitting each page into small sections. We call these fragments components.
Here is an example of splitting the page into components:
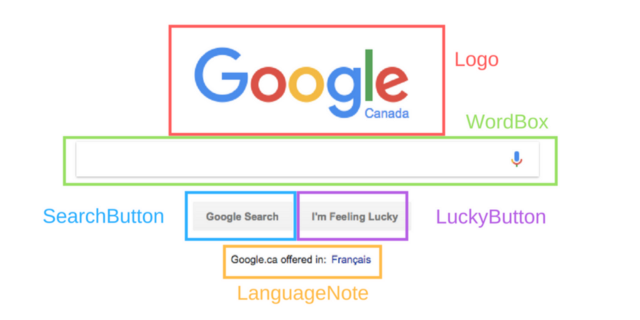
Each selected fragment of the page shown in the figure is considered a component. But what does this mean for a developer?
The React component is, if in simple terms, a piece of code that represents part of a web page. Each component is a JavaScript function that returns a piece of code representing a page fragment.
To form a page, we call these functions in a specific order, collect the results of calls together and show them to the user.
We write the component inside the
When we call the
Functions can be written like this:
React uses a programming language called JSX, which is similar to HTML, but works inside JavaScript, which distinguishes it from HTML.
You can add plain HTML here so that it gets into the user interface:
When we call the
Now the

You can also write your own component on JSX. This is done like this:
This is the standard approach - call components as if you are working with HTML.
Components React can be placed in other components.
Here is what the above code displays:

This is how pages are assembled from fragments written in React - putting components into each other.
So far, we have written components as functions. They are called functional components. However, components can be written differently, in the form of JavaScript classes. They are called component classes.
Component classes must contain a function called
In the event that you are interested in stateless components, preference should be given to functional components, in particular, they are easier to read. The status of the components will be discussed below.
JavaScript variables can be placed in JSX code. It looks like this:
Now the text
In addition, here you can do things more complicated, like function calls:
Here is how the page will look after processing the above code snippet:

Rename
However, here we encounter a problem: the
In order to achieve this, you need to use the
Class-based components can store information about the current situation. This information is called a state, it is stored in a JS object. The following code shows an object representing the state of our component. Its key is
The
So, what should we do with this “state”? Why is it invented?
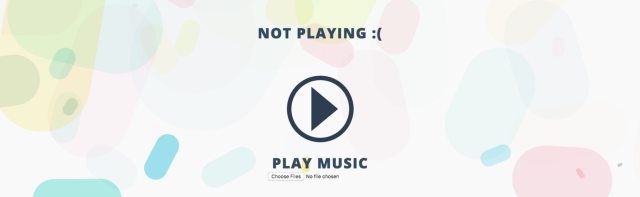
State is a tool to update the user interface based on events. Here we will use the state to change the appearance of the music playback button, based on a click on it. The button can be displayed in one of two options. The first indicates the possibility of starting playback, the second - that the music is playing, and this process can be suspended. When a user clicks a button, the state changes and then the user interface is updated.
This is where we begin. Find out the state of a component using
In the
All this is not particularly useful if we have no way to change
The user can interact with the component by clicking on the play music button. We want to respond to these events. This is done through a function that handles event handling. These functions are called event handlers.
When the user clicks on the text represented by the
We use the
When the state of the component changes, it will call the
Now, having dealt with this mechanism, let's do the processing of clicking on the button.
Components can "communicate" with each other. Let's see how it works. We can tell the
Properties in JSX look the same as HTML properties. We assign a
When the state of the
Inside the
If we change the state to

Properties do not have to be any data. They can be functions.
Now, when we click on the
When you call
Therefore, one should not do this:
If you change the state based on the previous state, you need to do it differently. Namely, you should pass the
It looks like this:
This construction is more complicated, but it is necessary only if you use the old state to form a new state. If not, you can simply pass the
It's time to turn on the music. To begin, add the
We need a way to access the
We assign an attribute to the element, called
This function will be called every time the
Now we can start and pause the music:
Upload the music file to the page (preferably in .mp3 format) using the
As you may have guessed, the React code should not "live" solely inside the
Congratulations! You have taken the first steps in the development of React-applications, have mastered the basics that allow you to start creating your own projects and productively study further.
Dear readers! If today you had your first acquaintance with React, please share your impressions.

Having dealt with this material, you will learn the following:
- React components.
- Rendering ReactDOM.
- Classes of components and functional components.
- Jsx
- State
- Event handling
- Asynchronous setState method.
- Properties (props).
- References (refs).
This is almost everything you need to know in order to create and maintain React-applications.
Preliminary preparation
Consider this situation: a small startup turns to you for help. They created a nice page, using which users can download music to their service and play it. They want you to do the most difficult thing - breathe life into this page.
')
First, create a new project directory and add three files there. Here they are on GitHub, and here is their code.
App.css file
body { background: #f9f9f9; font-family: 'Open Sans', sans-serif; text-align: center; } #container { position: relative; z-index: 2; padding-top: 100px; } .play { display: block; width: 0; height: 0; border-top: 50px solid transparent; border-bottom: 50px solid transparent; border-left: 60px solid #2c3e50; margin: 100px auto 50px auto; position: relative; z-index: 1; transition: all 0.3s; -webkit-transition: all 0.3s; -moz-transition: all 0.3s; left: 10px; } .play:before { content: ''; position: absolute; top: -75px; left: -115px; bottom: -75px; right: -35px; border-radius: 50%; border: 10px solid #2c3e50; z-index: 2; transition: all 0.3s; -webkit-transition: all 0.3s; -moz-transition: all 0.3s; } .play:after { content: ''; opacity: 0; transition: opacity 0.6s; -webkit-transition: opacity 0.6s; -moz-transition: opacity 0.6s; } .play:hover:before, .play:focus:before { transform: scale(1.1); -webkit-transform: scale(1.1); -moz-transform: scale(1.1); } .play.active { border-color: transparent; } .play.active:after { content: ''; opacity: 1; width: 25px; height: 80px; position: absolute; right: 8px; top: -40px; border-right: 20px solid #2c3e50; border-left: 20px solid #2c3e50; } h1 { text-transform: uppercase; color: #34495e; letter-spacing: 2px; font-size: 2em; margin-bottom: 0; } canvas { position: fixed; left: 0; top: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; } audio { position: fixed; left: 10px; bottom: 10px; width: calc(100% - 20px); } App.js file
var ALPHA, AudioAnalyser, COLORS, MP3_PATH, NUM_BANDS, NUM_PARTICLES, Particle, SCALE, SIZE, SMOOTHING, SPEED, SPIN, TIMES_CALLED, ANALYSER; NUM_PARTICLES = 150; NUM_BANDS = 128; TIMES_CALLED = 0; SMOOTHING = 0.5; MP3_PATH = 'music.mp3'; SCALE = { MIN: 5.0, MAX: 80.0 }; SPEED = { MIN: 0.2, MAX: 1.0 }; ALPHA = { MIN: 0.8, MAX: 0.9 }; SPIN = { MIN: 0.001, MAX: 0.005 }; SIZE = { MIN: 0.5, MAX: 1.25 }; COLORS = [ '#69D2E7', '#1B676B', '#BEF202', '#EBE54D', '#00CDAC', '#1693A5', '#F9D423', '#FF4E50', '#E7204E', '#0CCABA', '#FF006F' ]; function getAnimation(file) { AudioAnalyser = (function() { AudioAnalyser.AudioContext = self.AudioContext || self.webkitAudioContext; AudioAnalyser.enabled = AudioAnalyser.AudioContext != null; function AudioAnalyser(audio, numBands, smoothing) { var src; this.audio = audio != null ? audio : new Audio(); this.numBands = numBands != null ? numBands : 256; this.smoothing = smoothing != null ? smoothing : 0.3; this.audio = document.getElementById('audio'); if (!this.audio) { return; } try { this.audio.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file); } catch (err) { console.log(err); } this.context = new AudioAnalyser.AudioContext(); this.jsNode = this.context.createScriptProcessor(2048, 1, 1); this.analyser = this.context.createAnalyser(); this.analyser.smoothingTimeConstant = this.smoothing; this.analyser.fftSize = this.numBands * 2; this.bands = new Uint8Array(this.analyser.frequencyBinCount); this.audio.addEventListener( 'play', (function(_this) { return function() { if (TIMES_CALLED === 1) { return; } ANALYSER.start(); TIMES_CALLED++; _this.source = _this.context.createMediaElementSource(_this.audio); _this.source.connect(_this.analyser); _this.analyser.connect(_this.jsNode); _this.jsNode.connect(_this.context.destination); _this.source.connect(_this.context.destination); return (_this.jsNode.onaudioprocess = function() { _this.analyser.getByteFrequencyData(_this.bands); if (!_this.audio.paused) { return typeof _this.onUpdate === 'function' ? _this.onUpdate(_this.bands) : void 0; } }); }; })(this) ); } AudioAnalyser.prototype.start = function() { return this.audio.play(); }; AudioAnalyser.prototype.stop = function() { return this.audio.pause(); }; return AudioAnalyser; })(); Particle = (function() { function Particle(x1, y1) { this.x = x1 != null ? x1 : 0; this.y = y1 != null ? y1 : 0; this.reset(); } Particle.prototype.reset = function() { this.level = 1 + floor(random(4)); this.scale = random(SCALE.MIN, SCALE.MAX); this.alpha = random(ALPHA.MIN, ALPHA.MAX); this.speed = random(SPEED.MIN, SPEED.MAX); this.color = random(COLORS); this.size = random(SIZE.MIN, SIZE.MAX); this.spin = random(SPIN.MAX, SPIN.MAX); this.band = floor(random(NUM_BANDS)); if (random() < 0.5) { this.spin = -this.spin; } this.smoothedScale = 0.0; this.smoothedAlpha = 0.0; this.decayScale = 0.0; this.decayAlpha = 0.0; this.rotation = random(TWO_PI); return (this.energy = 0.0); }; Particle.prototype.move = function() { this.rotation += this.spin; return (this.y -= this.speed * this.level); }; Particle.prototype.draw = function(ctx) { var alpha, power, scale; power = exp(this.energy); scale = this.scale * power; alpha = this.alpha * this.energy * 1.5; this.decayScale = max(this.decayScale, scale); this.decayAlpha = max(this.decayAlpha, alpha); this.smoothedScale += (this.decayScale - this.smoothedScale) * 0.3; this.smoothedAlpha += (this.decayAlpha - this.smoothedAlpha) * 0.3; this.decayScale *= 0.985; this.decayAlpha *= 0.975; ctx.save(); ctx.beginPath(); ctx.translate(this.x + cos(this.rotation * this.speed) * 250, this.y); ctx.rotate(this.rotation); ctx.scale( this.smoothedScale * this.level, this.smoothedScale * this.level ); ctx.moveTo(this.size * 0.5, 0); ctx.lineTo(this.size * -0.5, 0); ctx.lineWidth = 1; ctx.lineCap = 'round'; ctx.globalAlpha = this.smoothedAlpha / this.level; ctx.strokeStyle = this.color; ctx.stroke(); return ctx.restore(); }; return Particle; })(); Sketch.create({ particles: [], setup: function() { var analyser, error, i, intro, j, particle, ref, warning, x, y; for (i = j = 0, ref = NUM_PARTICLES - 1; j <= ref; i = j += 1) { x = random(this.width); y = random(this.height * 2); particle = new Particle(x, y); particle.energy = random(particle.band / 256); this.particles.push(particle); } if (AudioAnalyser.enabled) { try { analyser = new AudioAnalyser(MP3_PATH, NUM_BANDS, SMOOTHING); analyser.onUpdate = (function(_this) { return function(bands) { var k, len, ref1, results; ref1 = _this.particles; results = []; for (k = 0, len = ref1.length; k < len; k++) { particle = ref1[k]; results.push((particle.energy = bands[particle.band] / 256)); } return results; }; })(this); analyser.audio = window.audio; ANALYSER = analyser; intro = document.getElementById('intro'); intro.style.display = 'none'; if ( /Safari/.test(navigator.userAgent) && !/Chrome/.test(navigator.userAgent) ) { warning = document.getElementById('warning2'); return (warning.style.display = 'block'); } } catch (_error) { error = _error; } } else { warning = document.getElementById('warning1'); return (warning.style.display = 'block'); } }, draw: function() { var j, len, particle, ref, results; this.globalCompositeOperation = 'lighter'; ref = this.particles; results = []; for (j = 0, len = ref.length; j < len; j++) { particle = ref[j]; if (particle.y < -particle.size * particle.level * particle.scale * 2) { particle.reset(); particle.x = random(this.width); particle.y = this.height + particle.size * particle.scale * particle.level; } particle.move(); results.push(particle.draw(this)); } return results; } }); } function handleFileSelect(evt) { var files = evt.target.files; getAnimation(files[0]); } getAnimation(null); document .getElementById('files') .addEventListener('change', handleFileSelect, false); Index.html file
<link rel="stylesheet" href="app.css"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:400,800"> <div id="container"> <div id="hook"></div> <h1>Play Music</h1> <input type="file" id="files" name="files[]" multiple /> </div> <script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react@15/dist/react.js"></script> <script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@15/dist/react-dom.js"></script> <script src="https://npmcdn.com/babel-core@5.8.38/browser.min.js"></script> <script src="https://soulwire.imtqy.com/sketch.js/js/sketch.min.js"></script> <script src="app.js"></script> <script type="text/babel"> // React. </script> To successfully complete this tutorial, you need a fresh version of the Google Chrome browser , otherwise the animation will not work. Thanks to Stephen Fabre for the CSS for the play button and Justin Vindle for the render code (you can see the original here ).
Open
index.html in the code editor and in the browser. It's time to get to know React.What is React?
React is a tool for creating user interfaces. Its main task is to provide a display of what can be seen on web pages. React makes it easy to create interfaces by splitting each page into small sections. We call these fragments components.
Here is an example of splitting the page into components:

Each selected fragment of the page shown in the figure is considered a component. But what does this mean for a developer?
What is the React component?
The React component is, if in simple terms, a piece of code that represents part of a web page. Each component is a JavaScript function that returns a piece of code representing a page fragment.
To form a page, we call these functions in a specific order, collect the results of calls together and show them to the user.
We write the component inside the
<script> the index.html file with the type set to "text/babel" : <script type="text/babel"> function OurFirstComponent() { return ( // , ); } </script> When we call the
OurFirstComponent() function, a page fragment is OurFirstComponent() .Functions can be written like this:
const OurFirstComponent = () => { return ( // , , ); } React uses a programming language called JSX, which is similar to HTML, but works inside JavaScript, which distinguishes it from HTML.
You can add plain HTML here so that it gets into the user interface:
<script type="text/babel"> function OurFirstComponent() { return ( <h1>Hello, I am a React Component!</h1> ); } </script> When we call the
OurFirstComponent() function, it returns a fragment of JSX code. We can use the so-called ReactDOM to output what this code represents to the page: <script type="text/babel"> function OurFirstComponent() { return ( <h1>Hello, I am a React Component!</h1> ); } const placeWeWantToPutComponent = document.getElementById('hook'); ReactDOM.render(OurFirstComponent(), placeWeWantToPutComponent); </script> Now the
<h1> will be inside the element with the ID hook . When you refresh your browser page, it should look like this:
You can also write your own component on JSX. This is done like this:
ReactDOM.render(<OurFirstComponent />, placeWeWantToPutComponent); This is the standard approach - call components as if you are working with HTML.
Component assembly
Components React can be placed in other components.
<script type="text/babel"> function OurFirstComponent() { return ( <h1>I am the child!</h1> ); } function Container() { return ( <div> <h1>I am the parent!</h1> <OurFirstComponent /> </div> ); } const placeWeWantToPutComponent = document.getElementById('hook'); ReactDOM.render(<Container />, placeWeWantToPutComponent); </script> Here is what the above code displays:

This is how pages are assembled from fragments written in React - putting components into each other.
Component classes
So far, we have written components as functions. They are called functional components. However, components can be written differently, in the form of JavaScript classes. They are called component classes.
class Container extends React.Component { render() { return ( <div> <h1>I am the parent!</h1> <OurFirstComponent /> </div> ); } } const placeWeWantToPutComponent = document.getElementById('hook'); ReactDOM.render(<Container />, placeWeWantToPutComponent); Component classes must contain a function called
render() . This function returns the JSX code of the component. They can be used in the same way as functional components, for example, referring to them with the help of a construction: <AClassComponent /> In the event that you are interested in stateless components, preference should be given to functional components, in particular, they are easier to read. The status of the components will be discussed below.
Javascript jsx
JavaScript variables can be placed in JSX code. It looks like this:
class Container extends React.Component { render() { const greeting = 'I am a string!'; return ( <div> <h1>{ greeting }</h1> <OurFirstComponent /> </div> ); } } Now the text
«I am a string» will be inside the <h1> .In addition, here you can do things more complicated, like function calls:
class Container extends React.Component { render() { const addNumbers = (num1, num2) => { return num1 + num2; }; return ( <div> <h1>The sum is: { addNumbers(1, 2) }</h1> <OurFirstComponent /> </div> ); } } Here is how the page will look after processing the above code snippet:

JSX pitfalls
Rename
OurFirstComponent() to PlayButton . We need this component to return the following: <a href="#" title="Play video" class="play" /> However, here we encounter a problem: the
class is a JavaScript keyword, so we cannot use it. How do you assign a play class to the <a> element?In order to achieve this, you need to use the
className property: <script type="text/babel"> function PlayButton() { return <a href="#" title="Play video" className="play" />; } class Container extends React.Component { render() { return ( <div> <PlayButton /> </div> ); } } const placeWeWantToPutComponent = document.getElementById('hook'); ReactDOM.render(<Container />, placeWeWantToPutComponent); </script> Features of the created component
Class-based components can store information about the current situation. This information is called a state, it is stored in a JS object. The following code shows an object representing the state of our component. Its key is
isMusicPlaying , and the value false is associated with it. This object is assigned to this.state in the constructor method, which is called when the class is first used. class Container extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isMusicPlaying: false }; } render() { return ( <div> <PlayButton /> </div> ); } } The
constructor method of the React component must always call super(props) before doing anything else.So, what should we do with this “state”? Why is it invented?
Change a React component based on its state
State is a tool to update the user interface based on events. Here we will use the state to change the appearance of the music playback button, based on a click on it. The button can be displayed in one of two options. The first indicates the possibility of starting playback, the second - that the music is playing, and this process can be suspended. When a user clicks a button, the state changes and then the user interface is updated.
This is where we begin. Find out the state of a component using
this.state construction. In the following code, we check the status and use it to decide which text to show to the user. class Container extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isMusicPlaying: false }; } render() { const status = this.state.isMusicPlaying ? 'Playing' : 'Not playing'; return ( <div> <h1>{ status }</h1> <PlayButton /> </div> ); } } In the
render function, the keyword this always refers to the component inside which it is located.
All this is not particularly useful if we have no way to change
this.state.isMusicPlaying .How does the component respond to events?
The user can interact with the component by clicking on the play music button. We want to respond to these events. This is done through a function that handles event handling. These functions are called event handlers.
class Container extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isMusicPlaying: false }; } handleClick(event) { // }; render() { let status = this.state.isMusicPlaying ? 'Playing :)' : 'Not playing :('; return ( <div> <h1 onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>{ status }</h1> <PlayButton /> </div> ); } } When the user clicks on the text represented by the
<h1> , the component calls the handleClick function. The function receives the event object as an argument, which means that it can, if necessary, use it.We use the
handleClick function's .bind method to have the this keyword handleClick to the entire component, not just <h1> .How the component should work
When the state of the component changes, it will call the
render function again. We can change the state with this.setState() , if we pass this object an object representing the new state. The component on the page will always represent its current state. React independently provide this behavior to the components. handleClick() { if (this.state.isMusicPlaying) { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: false }); } else { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: true }); } }; Now, having dealt with this mechanism, let's do the processing of clicking on the button.
Data exchange between components
Components can "communicate" with each other. Let's see how it works. We can tell the
PlayButton music is playing or not using so-called properties (props). Properties are information shared by the parent component and its descendant components.Properties in JSX look the same as HTML properties. We assign a
PlayButton property called isMusicPlaying , which is the same as isMusicPlaying in this.state . class Container extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isMusicPlaying: false }; } handleClick() { if (this.state.isMusicPlaying) { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: false }); } else { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: true }); } }; render() { return ( <div> <PlayButton isMusicPlaying={this.state.isMusicPlaying} /> </div> ); } } When the state of the
Container changes, the PlayButton property also changes, and the PlayButton function PlayButton called again. This means that the appearance of the component on the screen will be updated.Inside the
PlayButton we can react to changes, since the PlayButton takes properties as an argument: function PlayButton(props) { const className = props.isMusicPlaying ? 'play active' : 'play'; return <a href="#" title="Play video" className={className} />; } If we change the state to
this.state = { isMusicPlaying: true }; and reload the page, the pause button should appear on it:
Events as properties
Properties do not have to be any data. They can be functions.
function PlayButton(props) { const className = props.isMusicPlaying ? 'play active' : 'play'; return <a onClick={props.onClick} href="#" title="Play video" className={className} />; } class Container extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isMusicPlaying: false }; } handleClick() { if (this.state.isMusicPlaying) { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: false }); } else { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: true }); } }; render() { return ( <div> <PlayButton onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)} isMusicPlaying={this.state.isMusicPlaying} /> </div> ); } } Now, when we click on the
PlayButton button, it changes the state of the Container , which will change the props PlayButton , which will lead to an update of the button on the page.Unpleasant feature setState
When you call
setState the state change is not performed instantly. React waits a bit to see if it is necessary to make some other changes, and only then makes a state change. This means that you cannot know exactly what the state of the component will be after calling setState .Therefore, one should not do this:
handleClick() { this.setState({ isMusicPlaying: !this.state.isMusicPlaying }); }; If you change the state based on the previous state, you need to do it differently. Namely, you should pass the
setState function, not the object. This function takes the old state as an argument and returns an object representing the new state.It looks like this:
handleClick() { this.setState(prevState => { return { isMusicPlaying: !prevState.isMusicPlaying }; }); }; This construction is more complicated, but it is necessary only if you use the old state to form a new state. If not, you can simply pass the
setState object.What are links?
It's time to turn on the music. To begin, add the
<audio> : class Container extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isMusicPlaying: false }; } handleClick() { this.setState(prevState => { return { isMusicPlaying: !prevState.isMusicPlaying }; }); }; render() { return ( <div> <PlayButton onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)} isMusicPlaying={this.state.isMusicPlaying} /> <audio id="audio" /> </div> ); } } We need a way to access the
<audio> and call either its play() method or pause() . You can do this with the document.getElementById('audio').play() construct, but React offers something better.We assign an attribute to the element, called
ref , which takes a function. This function takes the <audio> element as the first argument, and assigns it to this.audio .<audio id="audio" ref={(audioTag) => { this.audio = audioTag }} />This function will be called every time the
Container is displayed, that is, this.audio will always be up to date and will point to the <audio> .Now we can start and pause the music:
handleClick() { if (this.state.isMusicPlaying) { this.audio.pause(); } else { this.audio.play(); } this.setState(prevState => { return { isMusicPlaying: !prevState.isMusicPlaying }; }); }; Upload the music file to the page (preferably in .mp3 format) using the
Choose files button, click on the play button and listen to the music.React outside index.html
As you may have guessed, the React code should not "live" solely inside the
<script> . React supports many build configurations. Fortunately, using tools like the Create React App, you can automate all the routine work of building an application framework. Install create-react-app , create a new project, look at the manual and start working with JS-files in the src project folder, applying all the knowledge of React you received today.Results
Congratulations! You have taken the first steps in the development of React-applications, have mastered the basics that allow you to start creating your own projects and productively study further.
Dear readers! If today you had your first acquaintance with React, please share your impressions.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/343022/
All Articles