Computer vision, cloud development and competition
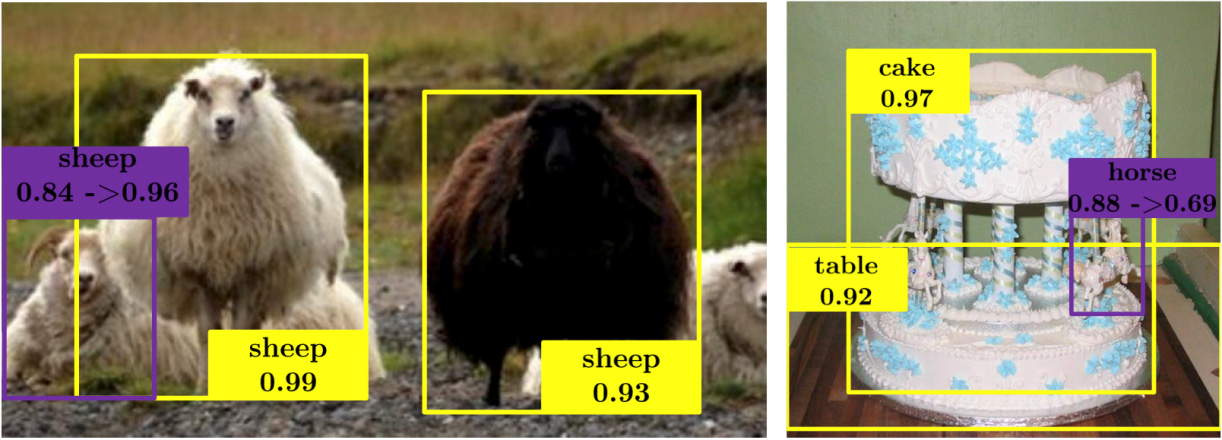

Sudden horse from Spatial Memory for Context Reasoning in Object Detection (presented at ICCV 2017)
We have some news, but it’s boring to just write about a competition where you can win a camera for your home or a vacancy for our cloud team. Therefore, we will begin with information that will be of interest to everyone (ok, almost everyone - this will be a video analytics).
')
Recently, the largest computer vision technology conference, the International Conference on Computer Vision 2017, was completed. Teams of scientists and representatives of research departments of various corporations presented their projects on photo enhancement, image generation by description, peeping around the corner using light analysis, etc. We will talk about several interesting solutions that can be used in the field of video surveillance.
Photos of the quality of "DSLRs" on mobile devices
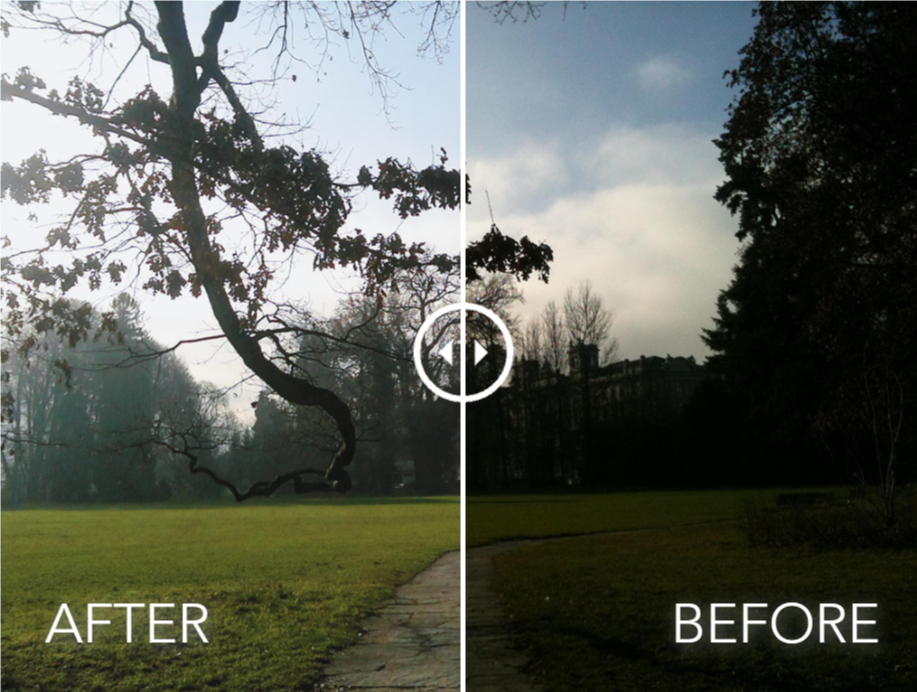

Matrix surveillance cameras and smartphones are being improved from year to year, but it seems they never catch up with SLR cameras. And one reason - the physical limitations of mobile devices.
Researchers from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich presented an algorithm that transforms the image obtained on the camera is not the highest quality, correctly "correcting" the details and colors. The algorithm cannot create something in the image that is not there, but it can help improve photos not only by adjusting the brightness and contrast.
Photographs are processed using a neural network, which improves both color reproduction and image sharpness. The grid was trained on objects that were photographed simultaneously on the camera of a smartphone and on a digital camera. Understanding what quality is optimal for a conditional object, the grid seeks to change the parameters of the image so as to correspond as closely as possible to the “ideal” image.
The sophisticated image error perception function combines color, tonality and texture data. The study shows that the enhanced images demonstrate quality comparable to photographs taken with SLR cameras, while the method itself can be applied to any type of digital camera.
The current version of the image quality improvement algorithms can be tested on phancer.com - just upload any image.
Creating photo-realistic images from scratch

A large team of scientists — 7 people on two continents from Rutgers University, Lihai University, China University of Hong Kong, and Baidu Research’s research unit — proposed a way to use meshes to create photorealistic images based on text descriptions. Something similar to the work of this artist, who creates a picture based on the images in his head - first a rough sketch appears on the canvas, and then more and more precise details.
The computer first makes the first attempt to create an image based on the text description of the specified objects (and the knowledge base of the images known to it), and then a separate algorithm evaluates the resulting picture and makes suggestions for improving the image. At the entrance, for example, there is a “green bird”, a base of flowers and a base of famous birds. There are a large number of images that correctly correspond to this textual description - and this is one of the problems.
To generate images from textual descriptions, several folded generative-contention networks (SGAN) are used. GAN Stage-I sketches a primitive sketch and adds the primary colors of the objects based on the text description data. GAN Stage-II accepts Stage-I results and text descriptions as input and generates high-resolution images and photo-realistic details. GAN Stage-II is able to correct defects and add interesting details. Samples created by StackGAN are more plausible than those generated by other existing approaches.
Since GAN Stage-I generates sketches for objects and for the background, GAN Stage II only needs to focus on the details and fix the defects. GAN Stage-II learns to process textual information that GAN Stage-I did not take to work, and draws more detailed information about the object.
Handling complex interrelated events in video
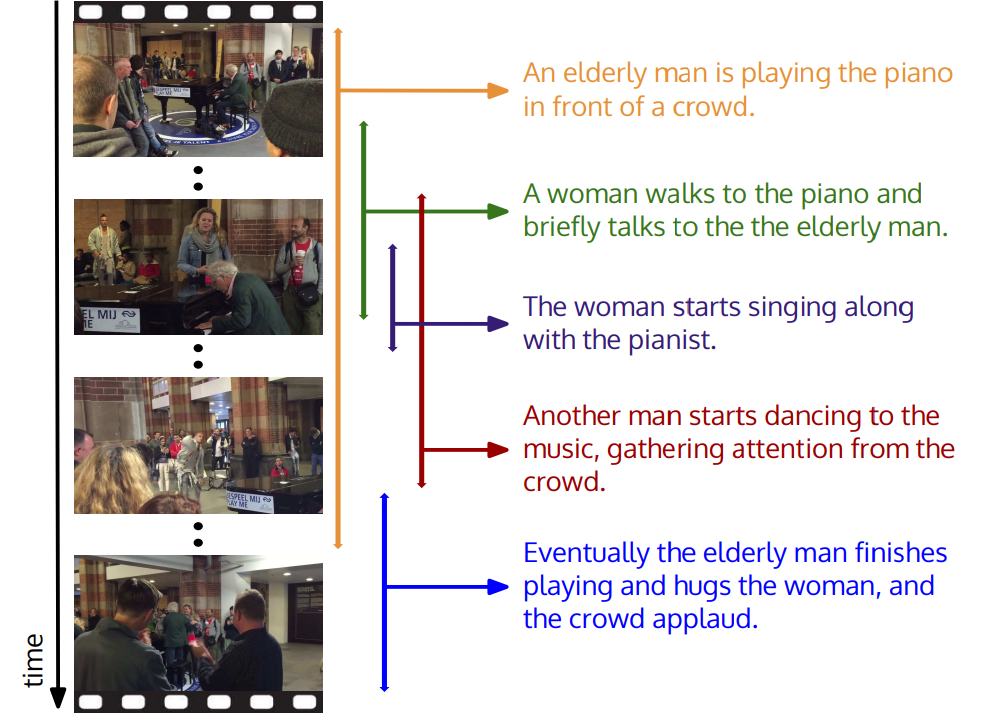
At Stanford University, they thought that there were too many events happening in the commercials. For example, in the video “a person plays the piano”, the video may also contain “a dancing person” or “applauding a crowd of people”. The new study proposed a model that allows you to identify all events and give them a description in natural language.
The model is based on the basis of space-time descriptions . In fact, the computer was first trained on thousands of videos containing detailed descriptions of the context.
Interestingly, in DeepMind, in order to solve a similar problem, they went the other way and began to correlate the video sequence with sound in order to recognize objects without first understanding what is in the frame. The Google algorithm consists of three parts: the first neural network processes images taken from the video, the second - the audio corresponding to these images, the third part learns to correlate images with a specific sound.
Similar technologies in video surveillance can be used for convenient and fast search in the data archive.
Description of images in natural language

Which of the two descriptions of the top photo seems more human to you: “A cow standing in a field with houses” or “A gray cow walking along a large green field in front of houses”? Last probably. But computers have no natural understanding of what makes a person intuitively choose the right (from our point of view) option.
In the Towards Diverse and Natural Image Descriptions via a Conditional GAN project, one neural network creates a description of the scene in the image, while the other compares this description with human-made and evaluates elements that better fit our own style of speech.
A system was proposed that included several generative competitive neural networks, one of which selected a description for the image, and the second assessed how well the description corresponded to the visual content. It was possible to achieve a level of recognition of objects and the relationships between them, that the context of the events being processed had no meaning. Although the system has never seen a cow drinking milk through a straw, it can recognize this image because it has an idea of what a cow looks like, milk, a straw, and what it means to drink.
The camera looks around the corner.

A few years ago, engineers and physicists from Scotland created a camera that literally looked around the corner and tracked the movements of people and objects behind it.
The solution consisted of a set of two devices - a “photon gun”, which scientists fired at the floor and wall, located on the opposite side of the corner, and a special light-sensitive matrix based on avalanche photodiodes , capable of recognizing even single photons.
The photons from the gun beam, reflecting from the surface of the wall and the floor, collide and are reflected from the surface of all the objects that are behind the wall. Some of them fall into the detector, reflecting again from the wall, which allows, based on the time of the beam, to determine the position, shape and appearance of what is hiding around the corner.
The system worked extremely slowly - it took about three minutes to form the initial image. In addition, the result was issued in the form of an image of 32 by 32 pixels, which actually did not allow to see anything in the picture, except for a rough silhouette.
There have been several attempts to improve the quality, but the decision came from an unexpected side. Experts from MIT and Google Research have suggested looking around the corner with the help of reflected light. Looking very carefully at the light, which is visible from different angles, you can get an idea of the color and spatial arrangement of objects hidden around the corner.
It looks like a scene from the American procedure. The new image processing system does not require any special equipment; it will even work with the smartphone's camera, using only reflected light to detect objects or people and measure their speed and trajectory — all in real time.
Most objects reflect a small amount of light on the ground in your line of sight, creating a fuzzy shadow, which is called a "penumbra." Using video of the penumbra, the CornerCameras system can sew a number of images, getting rid of superfluous noise. Although the objects are not actually visible on the camera, you can see how their movements affect the penumbra to determine where they are and where they go.
***
If you are interested in these projects, have your own ideas or want to get acquainted with our developments - come yourself or bring friends. We need new people in the Cloud team to work on products based on cloud-based video surveillance and computer vision.
For a successful recommendation after the developer’s design in the state - we give the iPhone X. And if the developer is with us going to paintball too, then the recommendation is also a protective glass for iPhone! ;) More about the job (respond there).
And the last for today: until November 19 (inclusive), follow the link . You need to answer one question, leave your mail, throw a link to the competition to any social network and wait - a random number generator based on the entropy of atmospheric noise will select several participants whom we will award to a home Wi-Fi camera with Oco2.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/342618/
All Articles