Digital Transformation: Blockchain in a bank
On this wonderful Friday day, we continue to tell you about the technological features of digital transformation. Today we will talk about how blockchain technology can contribute to the development of remote identification using the example of one bank.

The problems of remote identification in one way or another are solved in various ways. In some cases, it is enough to carry out identification using social networks or through a phone number. But its legal significance appears only when personal data operators, defined in 115-FZ, take part in it. At the same time, the specificity of the Russian legislation currently consists in the fact that not all services can be provided using remote identification. Banks are now available only transfers without opening an account.
However, not everything is so bad. For example, the draft law provides for amendments to 115-, which allow banks to open accounts for clients, identifying them remotely. But at the same time, the client must necessarily be primarily identified with a personal presence, and his personal data are placed in the ESIA. Thus, ESIA provides the ability to authenticate (including biometric parameters) and transfer personal data to the service. In this case, there are some risks associated with the consent of the client (and with the withdrawal of this consent) to transfer PD to third parties, as well as centralized storage of PD. Additionally, there are technological difficulties in updating the biometric parameters descriptor.
But let's not go into these details of biometric identification, but rather analyze how blockchain technology can contribute to the development of remote identification.
The main tasks of identification are:
But during the remote identification procedure, there are difficulties with confirming the compliance of personal data with the client who sent them. The difficulties are related to the fact that at the moment there is no convenient tool on the market that would allow a business to carry out this procedure without the personal presence of the client and presenting a passport to them.
There are categories of organizations whose services are received by almost the entire population of the country - these are banks, mobile operators. By signing a contract with a client, these organizations carry out primary identification, that is, they receive personal data of the client in his personal presence and upon presentation of a passport. Accordingly, in the future, these organizations can confirm the correctness of personal data and the identity of this information to the person who provided it.
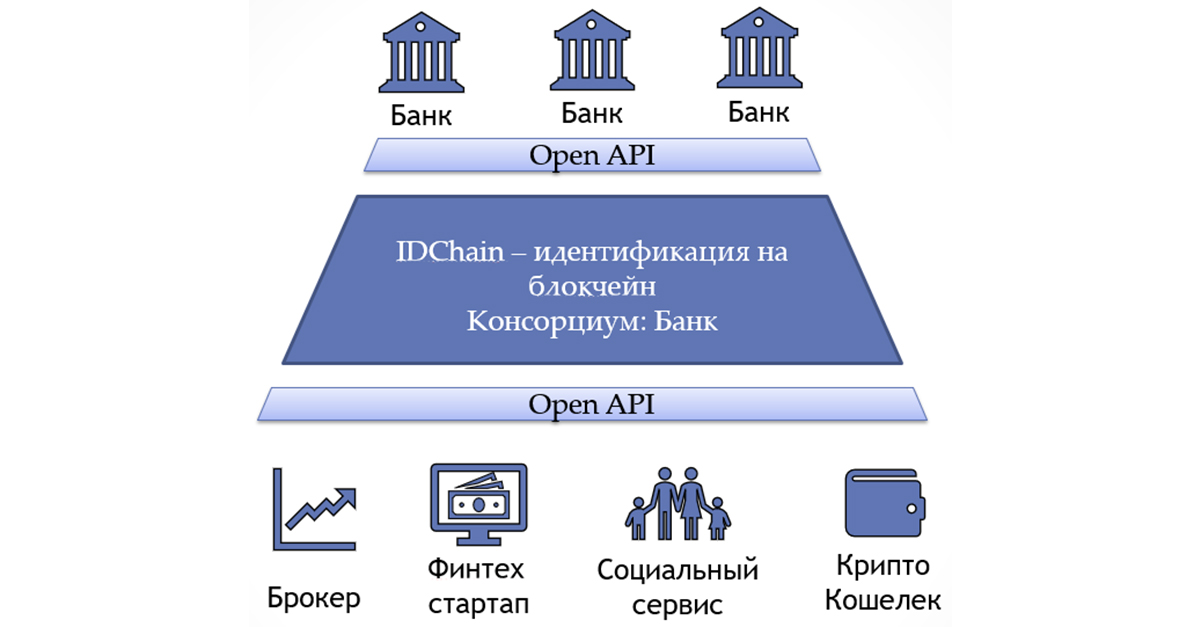
Three parties are involved in the remote identification process:
The remote identification process can be organized with full transfer of personal data from the donor to the recipient using the OAuth 2.0 protocol. But this solution has a number of problems:
The first problem is that this process will require a third party who will record the fact of data transfer. This entails additional costs for the creation of an intermediary, which will be trusted by both parties, and the cost of the commission to the intermediary for conducting remote identification.
The second problem is related to the fact that in the presence of a large number of personal data providers, service consumers need to build relationships with each of them.
The third problem is connected with the risks of non-compliance with Federal Law No. 152 “On Personal Data”.
However, applying the principle of interoperability of systems of a consortium of organizations, which assumes the availability of products or systems with open interfaces, and using the blockchain technology, these problems can be solved. At the same time, there are ample opportunities for financial companies to access banking audiences and banking infrastructure. And this is only at first glance.
If you think more broadly, then smart contracts significantly expand the capabilities of the technology to build trust. You can fasten a certifying center to the blockchain either with the help of a trusted oracle, or by implementing Russian kernel-level cryptography. Then participants will be able to receive a qualified electronic digital signature (which by default is an analogue of a handwritten signature) and enter into legally significant contracts.
This solution implements the mechanism of remote identification using Blockchain technology. Thanks to him, organizations do not need to share personal data, and each operation will be recorded in an unchangeable blockchain chain.
Participants in the process (see figure):
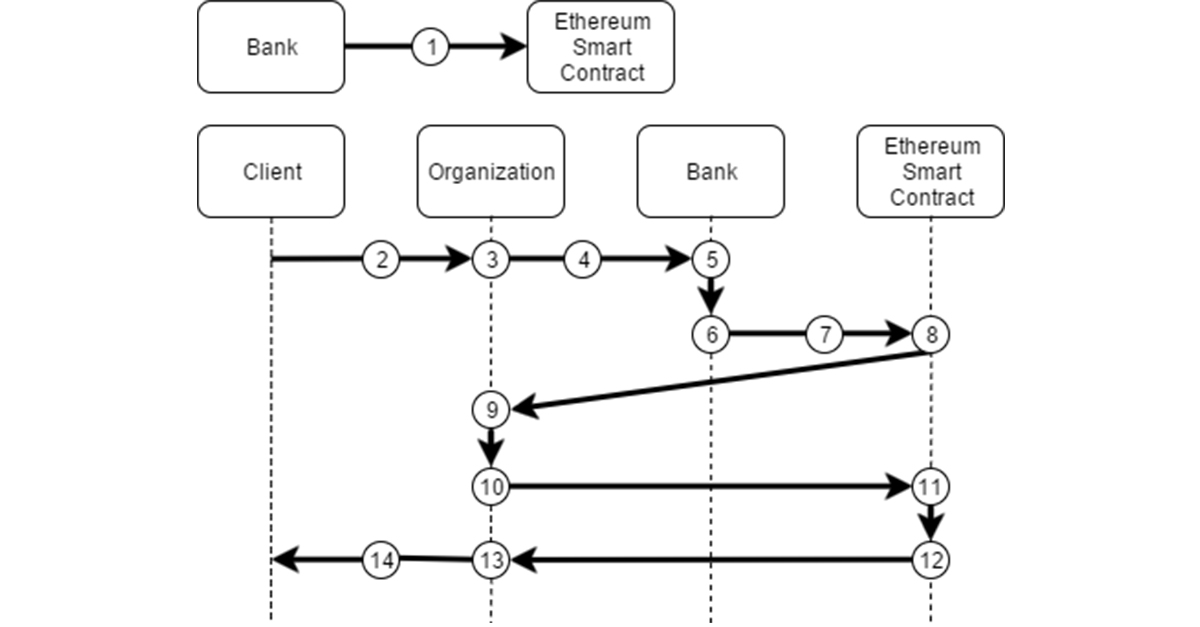
Process:
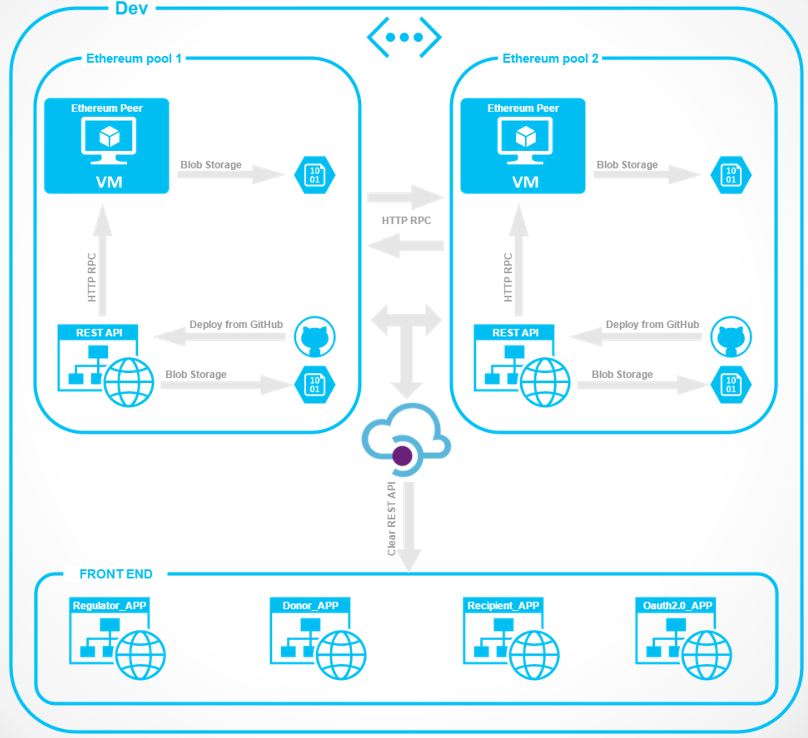
This system will make it possible to radically change the market for distribution of services in digital channels, open to the clients of banks wide access to products and services of third-party organizations - participants of the consortium without the need for a personal visit for identification. The prototype of the solution is based on the Microsoft Azure Blockchain as a Service cloud platform.
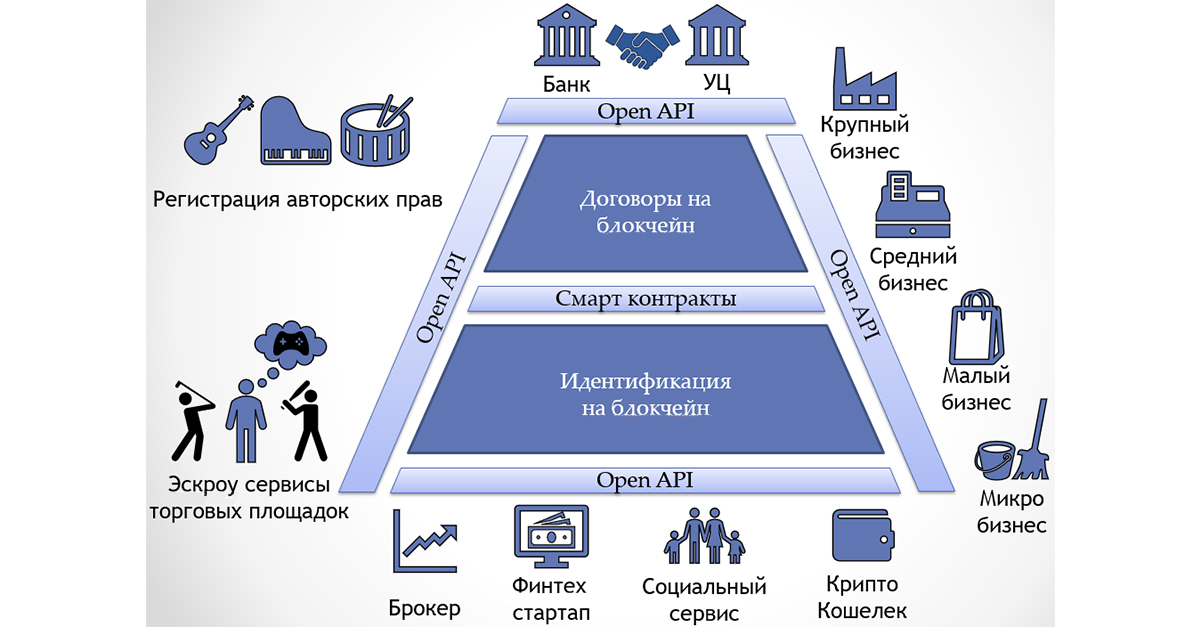
The consortium allows to ensure the implementation of the basic processes required for identification:
Personal data in this process are not transferred to a third party (they remain only with the donor and the recipient). At the same time, the use of the blockchain technology not only ensures the storage and immutability of information on all identification procedures performed. The principle of smart contracts allows you to build a transparent monetization of the service and improve the efficiency of interaction between participants. And due to decentralization, the risk of compromising personal data is reduced, and the fault tolerance of the system is also increased.

You can find out more about the project implementation on GitHub .

Alexander Vasiliev - RosEvroBank, Deputy Director of IT for Innovations, looks to the future, listens to Nightwish, believes in the blockchain.
We remind you that you can try Azure for free .
Minute advertising . If you want to try new technologies in your projects, but do not reach the hands, leave the application in the program Tech Acceleration from Microsoft. Its main feature is that together with you we will select the required stack, we will help to realize the pilot and, if successful, we will spend maximum efforts so that the whole market will know about you.
 PS We thank Kostya Kichinsky ( Quantum Quintum ) for the illustration of this article and Kostya Goldstein for help in creating the material.
PS We thank Kostya Kichinsky ( Quantum Quintum ) for the illustration of this article and Kostya Goldstein for help in creating the material.

Series of Digital Transformation articles
Technological articles:
1. Start .
2. Blockchain in the bank .
3. We learn the car to understand human genes .
4. Machine learning and chocolates .
5. Loading ...
')
A series of interviews with Dmitry Zavalishin on DZ Online :
1. Alexander Lozhechkin from Microsoft: Do we need developers in the future?
2. Alexey Kostarev from “Robot Vera”: How to replace HR with a robot?
3. Fedor Ovchinnikov from Dodo Pizza: How to replace the restaurant director with a robot?
4. Andrei Golub from ELSE Corp Srl: How to stop spending a lot of time on shopping trips?
Remote Identification: Legal Features
The problems of remote identification in one way or another are solved in various ways. In some cases, it is enough to carry out identification using social networks or through a phone number. But its legal significance appears only when personal data operators, defined in 115-FZ, take part in it. At the same time, the specificity of the Russian legislation currently consists in the fact that not all services can be provided using remote identification. Banks are now available only transfers without opening an account.
However, not everything is so bad. For example, the draft law provides for amendments to 115-, which allow banks to open accounts for clients, identifying them remotely. But at the same time, the client must necessarily be primarily identified with a personal presence, and his personal data are placed in the ESIA. Thus, ESIA provides the ability to authenticate (including biometric parameters) and transfer personal data to the service. In this case, there are some risks associated with the consent of the client (and with the withdrawal of this consent) to transfer PD to third parties, as well as centralized storage of PD. Additionally, there are technological difficulties in updating the biometric parameters descriptor.
But let's not go into these details of biometric identification, but rather analyze how blockchain technology can contribute to the development of remote identification.
Identification problems
The main tasks of identification are:
- obtaining customer identification information;
- validation of the data provided by the client;
- confirmation that the data provided correspond to the person who transmitted it.
But during the remote identification procedure, there are difficulties with confirming the compliance of personal data with the client who sent them. The difficulties are related to the fact that at the moment there is no convenient tool on the market that would allow a business to carry out this procedure without the personal presence of the client and presenting a passport to them.
There are categories of organizations whose services are received by almost the entire population of the country - these are banks, mobile operators. By signing a contract with a client, these organizations carry out primary identification, that is, they receive personal data of the client in his personal presence and upon presentation of a passport. Accordingly, in the future, these organizations can confirm the correctness of personal data and the identity of this information to the person who provided it.

Three parties are involved in the remote identification process:
- organization (recipient) that wants to remotely identify its client;
- the organization (donor) that conducted the primary identification, for example, a bank;
- an individual who wants to receive a service from a recipient.
The remote identification process can be organized with full transfer of personal data from the donor to the recipient using the OAuth 2.0 protocol. But this solution has a number of problems:
- distrust of participants to each other in terms of fixing the fact of identification;
- the need to build interfaces "every with each";
- transfer, processing and storage of personal data.
The first problem is that this process will require a third party who will record the fact of data transfer. This entails additional costs for the creation of an intermediary, which will be trusted by both parties, and the cost of the commission to the intermediary for conducting remote identification.
The second problem is related to the fact that in the presence of a large number of personal data providers, service consumers need to build relationships with each of them.
The third problem is connected with the risks of non-compliance with Federal Law No. 152 “On Personal Data”.
However, applying the principle of interoperability of systems of a consortium of organizations, which assumes the availability of products or systems with open interfaces, and using the blockchain technology, these problems can be solved. At the same time, there are ample opportunities for financial companies to access banking audiences and banking infrastructure. And this is only at first glance.
If you think more broadly, then smart contracts significantly expand the capabilities of the technology to build trust. You can fasten a certifying center to the blockchain either with the help of a trusted oracle, or by implementing Russian kernel-level cryptography. Then participants will be able to receive a qualified electronic digital signature (which by default is an analogue of a handwritten signature) and enter into legally significant contracts.

Decision
This solution implements the mechanism of remote identification using Blockchain technology. Thanks to him, organizations do not need to share personal data, and each operation will be recorded in an unchangeable blockchain chain.
Participants in the process (see figure):
- a client is an individual who wants to receive a service from an organization;
- A bank is a credit institution in which a client has undergone a primary identification procedure with a personal presence;
- organization - an organization to which the client has applied and which wants to receive the remote identification service from the bank in order to provide the service to the client.

Process:
- the bank forms for the client a pair of values, which consists of the hash of the token and the hash of the client's personal data and the token combined between them, and then places this pair of values in the smart contract;
- the client applies for the service in the organization;
- the organization provides the client with an interface for entering personal data and choosing the organization in which the client would like to identify (in our case, it is a bank);
- client redirection to the remote banking service interface (Internet bank is assumed) for authentication (authorization);
- the bank performs authentication using its own mechanism (two-factor, biometrics, etc.);
- if the client successfully passes the authentication, the bank encrypts the client's token with the public key of the organization;
- sending an encrypted client token to the organization via a smart contract to record the fact of the transfer of the token;
- forming a message with an encrypted token and sending it to the organization;
- receiving and decryption using the token's private key;
- generation and sending of a request with a token hash and a hash of the personal data that has been stored between them, provided by the client through the organization's interface, and the token;
- reconciliation of data placed by the bank in a smart contract and the data transmitted to the organization;
- in case of successful reconciliation, the smart contract records the fact of successful reconciliation and sends the response to the organization;
- the organization receives a response on successful customer identification;
- organization provides service to the client.
Conclusion
This system will make it possible to radically change the market for distribution of services in digital channels, open to the clients of banks wide access to products and services of third-party organizations - participants of the consortium without the need for a personal visit for identification. The prototype of the solution is based on the Microsoft Azure Blockchain as a Service cloud platform.

The consortium allows to ensure the implementation of the basic processes required for identification:
- “Receipt of identification information about the client” - obtaining personal data directly from the client;
- “Confirmation of the reliability of the information received” - a comparison of the values of the hash functions stored in the blockchain, with those calculated in the moment;
- “Identification (verification) of the client’s identity” - authentication with the bank that conducted the primary identification of the client.
Personal data in this process are not transferred to a third party (they remain only with the donor and the recipient). At the same time, the use of the blockchain technology not only ensures the storage and immutability of information on all identification procedures performed. The principle of smart contracts allows you to build a transparent monetization of the service and improve the efficiency of interaction between participants. And due to decentralization, the risk of compromising personal data is reduced, and the fault tolerance of the system is also increased.

You can find out more about the project implementation on GitHub .
about the author

Alexander Vasiliev - RosEvroBank, Deputy Director of IT for Innovations, looks to the future, listens to Nightwish, believes in the blockchain.
We remind you that you can try Azure for free .
Minute advertising . If you want to try new technologies in your projects, but do not reach the hands, leave the application in the program Tech Acceleration from Microsoft. Its main feature is that together with you we will select the required stack, we will help to realize the pilot and, if successful, we will spend maximum efforts so that the whole market will know about you.
 PS We thank Kostya Kichinsky ( Quantum Quintum ) for the illustration of this article and Kostya Goldstein for help in creating the material.
PS We thank Kostya Kichinsky ( Quantum Quintum ) for the illustration of this article and Kostya Goldstein for help in creating the material.Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/342364/
All Articles