Clouds from an unknown country. Cloud FAQ
Straight above them floated a light cloud.
- Listen, let's go to Tili-mili-straightened! - suggested Little Bear. - We can speak in their language. Look, what a good word: “Try”!
- Try it? Very good word, said the Hedgehog. - What does it mean?
- Straight - tili-mili-trache means “hello!”

Cloud experts use numerous terms that describe the features of virtualized solutions. These terms were included in the lexicon gradually and to describe technical or marketing specifics. At the same time, their meaning was initially described, and then names were assigned to them. A decade after the beginning of the rapid development of “clouds,” professional slang makes it difficult to understand the essence of cloud products for businesses and people who previously did not know or perceive cloud technologies as a news background, without delving into the content.
In the article we will try to act as a translator from the marketing-technical language of the cloud provider to a more comprehensible language, limiting the use of words that are on the periphery of the vocabulary of the language and do not have the quality of communicative general significance.
')
Why is cloud computing?
In 1993, Eric Schmidt came to the conclusion that the network and computer were related, this idea became widely known later on from the motto of Sun Microsystems “The network is a computer”. “When the network becomes as fast as the processor, the computer as such ceases to exist, it will spread throughout the network,” said Schmidt about 25 years ago. In August 2006, Schmidt was the first to use the term cloud computing in an interview after the end of the Search Engine Strategies Conference:
“A new model of computer systems is emerging before our eyes, and it seems to me that there are not so many people who are able to understand the emerging perspective. Its essence is that the services that support the data and architecture are hosted on remote servers. The data is located on these servers, and the necessary calculations are performed on them ... And if you have the appropriate browser and corresponding access rights at your disposal, then you can access this cloud regardless of the device you use. ”
Back in 1959, science fiction writer Kurt Vonnegut mentions a cloud that “thinks of everything and for everyone together” in the book “Sirens of Titan”.

There is also an opinion that the Internet in computer network and system diagrams was often designated as a cloud image, and so the name became popular for using computers over the Internet. But we believe that it is the comment of Eric Schmidt that can be taken as the beginning of using the term “cloud” in the narrow sense in which it is used in IT, since it is the remoteness of servers that the user accesses through the Internet that characterizes the cloud consumption model.
We give our definition:
A cloud is a pool of resources from which a user, interacting via the Internet, can obtain the necessary volume and composition of IT services and, if necessary, independently change these consumption characteristics.
Everything as a Service or what you can get from the cloud
Much depends on the responsibility and rights that you want to keep when using the cloud. The initial level is the program-as-service model (saas - software as a service). With such a business model, the provider creates and configures the infrastructure itself, giving the client access to the finished program / application, for example, corporate email or antivirus. This type of cloud service is well known even to people far from IT due to solutions for cloud storage of photos and documents. However, it should be understood that this is not the only application of the model and the functionality and purpose of the program in the cloud can be anything.
For customers who want to set up their own “cloud servers”, install the necessary software on them and, importantly, link them over the network, services are provided according to the Infrastructure-as-a-Service model (IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service).
Since the cloud is only a consumption model in which you can get any IT-resource with access to it via the Internet, marketers have come up with an infinite number of abbreviations like Everything a Service (XaaS), corresponding to each type of service.
How it works?
The network has become fast enough to allow full interaction with a computer via the Internet. This created new business opportunities. So cloud providers appeared. To provide their services, they use physical servers, the resources of which are pooled, and then using the program (hypervisor), it is “sliced” into virtual machines (cloud servers, vds / vps). This process of emulating software-defined or virtual machines underlies the virtualization technology. In Cloud4Y the virtualization platform from VMware is used and we will describe the work of the cloud in our example.
Below, in the first two photos are examples of servers that we use. These are HP ProLiant BL460c Gen8 Server Blades. Each blade (blade) is combined with a chassis, which is responsible for power supply, network connection, and other processes.


The provider infrastructure tenant can create virtual machines with the necessary characteristics (CPU, RAM, etc.) and quickly change them. Of course, for this you do not need to select the corresponding physical server each time and “move” to it. The physical resources of the data center servers, such as computing power, disks, and networks, are combined into large pools of virtual resources. In the future, parts of these resources are provided in the form of "prefabricated" virtual data centers (data centers), which are allocated to tenants. It provides the flexibility and scalability that are advantages of the cloud infrastructure.

To support a large number of virtual machines on one physical server, more memory, more connections for data warehouses and more network connections are required, so we chose HP servers certified for VMware and built with virtualization in mind. VMware certification enables stable use of VMware virtualization platform with all cluster options , which significantly increase the efficiency and reliability of the entire cloud:
What is a cluster on VMware and how is it arranged?
At the beginning we mean that in this article we will mean by cluster a group of hosts (physical servers) under the control of a single service for the joint performance of certain functions as an integral system communicating through a network.
On the VMware vSphere virtualization platform, two types of clusters can be built: High-availability cluster (HA) and Distributed Resource Scheduler cluster (DRS).
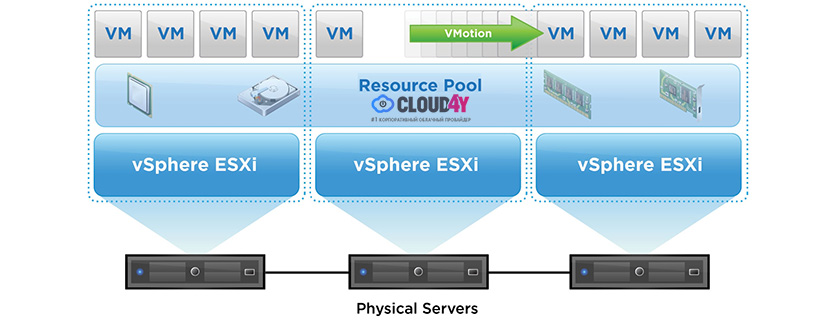
HA-cluster will mean that a certain number of physical servers are combined into a cluster and they run virtual machines. In case of failure of one of the hosts, virtual machines are started on other servers from the group on which space was previously allocated for this. As a result, the idle time is equal to the boot time of the virtualka operating system.
If you need to reduce downtime to a minimum, we recommend using VMware Fault Tolerance technology. The main idea of the option can be described as creating a synchronously working replica of a virtual machine on another server and instantly switching to it when the primary host fails.
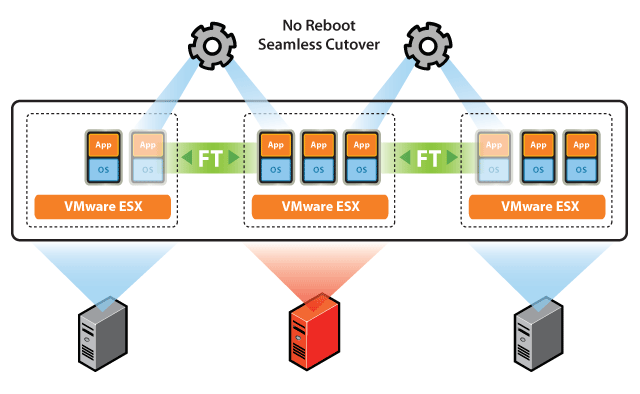
Fault tolerance
VMware DRS technology is used for load balancing in a cluster. To do this, at the initial stage cluster resources are pooled and then load balancing between the hosts occurs by moving the virtual machines. DRS can recommend moving with the necessary confirmation from the administrator or do it automatically. This happens with the use of the “live migration” utility vMotion, due to which the migration does not require stopping the VM. Users continue to work with one VM instance until the data is transferred to another host. At the last moment, the latest changes are copied from the RAM, the user sees a slight short-term decrease in system performance and after a moment is already working with the same VM, which in fact is already on another physical server.
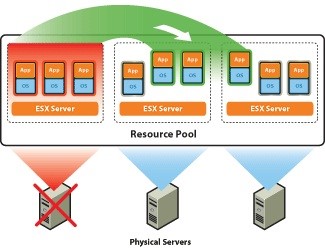
How VMware HA + DRS works
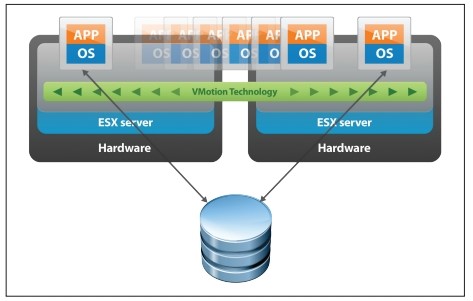
vmotion
In the case of a VMware cluster, a group of 2 or more ESXi servers is under centralized management of VMware vCenter Server. Actually, you can create virtual machines on the same host with the VMware ESXi hypervisor installed, but HA, DRS, and others will not. You can simply “chop” your physical server into several virtual ones, and its inoperability will mean idle time for all VMs.
To use all the cluster capabilities, you need to use the VMware vSphere platform, which includes an ESXi-host management server and storage, the so-called vCenter Server. Also, building a cluster will require a storage system connection. It has a special VMFS cluster file system that stores partitions with virtual machine files that can be read and written by all ESXi hosts in the cluster. Due to the storage in one place and the independence of the virtual machine from the physical platform, fast movement and recovery is achieved using HA, DRS, FT, vMotion.
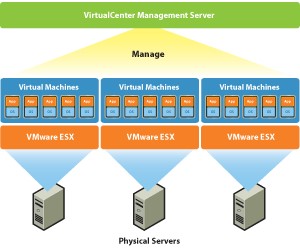
VMware vSphere Platform
VMware vCenter Server, to put it simply, is a set of services and a database. Each service deals with its specific task list and interacts with other services and / or ESXi hosts. The vCenter Server is a kind of command center that obeys the ESXi hypervisors on the hosts. Communication between them takes place through the VPXA host agents. From the vCenter Server Control Panel, you can do even more than connecting directly to ESXi. If you can create / delete virtual machines in ESXi, then using the vCenter Server you can additionally create and configure a cluster for them and all the necessary cluster options, some of which are described above. VMware vCenter Server can work both on a separate physical server and inside a virtual machine on the same host, which it controls itself.
The topic is certainly interesting and extensive, but the deployment of such infrastructures requires large material costs. If you want to use all the features that increase the fault tolerance and reliability of the system, you need to purchase at least two servers and storage, as well as buy a license for the VMware vSphere platform from one of the distributors. Installing, configuring and administering a VMware cluster will also require a temporary and financial investment.
In cases where the IT infrastructure requires high reliability, which is provided by the VMware vSphere platform, but there is no possibility or sense to carry significant capital investments, many corporate clients choose the infrastructure rental service (IaaS).
Clients do not use VMware vCenter Server. The provider is responsible for managing the clusters and the physical equipment. Customers get a significant amount of control over their virtual data center using the convenient VMware vCloud Director self-service portal , about which we wrote a separate article . Creating a data center for the client takes place as soon as possible, and it can create the required number of virtual machines with the necessary characteristics and operating systems, routed and isolated networks with any topology, flexible Firewall rules and much more.
Is it possible to build your own cloud? The main differences between public, hybrid and private clouds?
The public cloud is a business model of service provision in which all the physical resources of a data center, such as computing power, disks, and networks, are combined into large pools of virtual resources, and then some of these resources are provided as “composite” vODCs that are allocated tenants. Virtual machines of different tenants are isolated from each other, so you should not understand the publicity of such a cloud as the lack of data security. Cloud publicity means that data can be physically stored on the same physical server with data from other companies, but they do not have access to your data. It is impossible to unequivocally tell which physical equipment your virtual machines will be in, since, when stored in a cluster, virtual machines move between servers for load balancing and increasing fault tolerance. It is the allocation of “private” resources from the general “public” pool that makes the cloud public, but user data is protected by modern organizational, technical and software tools and solutions.
A private or private cloud is the opposite of a public cloud, which means that a pool of physical resources (physical server) will be provided to only one tenant / organization. At the same time exactly where the private cloud equipment is located does not matter. The cloud will be considered private not only if the equipment is located on the company's territory, but options are also possible when the equipment is located in the data center and is adjacent to the equipment of other customers. A private cloud can also provide a cloud provider. For example, Cloud4Y has a solution called “ Private Cloud 2.0 ”.
Pros of a Private Cloud:
- high level of security;
- complete isolation of the infrastructure;
- equipment control;
- possibility of placement on the customer’s site.

Summing up, it can be noted that in both cases the model is cloudy, which means there is no equipment linking to the site, all resources are available via the Internet or the network where it is needed. However, in the private cloud, the customer receives completely isolated equipment, and in the public only its virtual resources are isolated. Often, when equipment is placed in a data center, customers who are particularly sensitive to the security of their data or fulfill the requirements of certain standards order server racks with a perimeter enclosing structure, the so-called “cell”. In this case, a private cloud is probably the only solution, however, even without a separate “cell”, the equipment in the modern TIER III data center is safe and monitored around the clock, including video recording.
A hybrid cloud is a model of consumption of IT resources, in which an organization part of the system is placed in a public cloud, based on the equipment of a cloud provider, and partly in a private cloud, on servers owned by the company or rented as a whole. The concept of a hybrid “cloud” (hybrid cloud) allows you to combine into a single cloudy space the internal (onsite) corporate cloud and the external (offsite) cloud service provider. The main idea of the “hybrid cloud” is that when your own capacity is not enough, you can use external resources. Hybrid clouds are used as an opportunity to go beyond the company's cloud capacity in case of peak loads or in order to avoid capital expenditures in favor of operating expenses.
Cloud is not a luxury
The cloud on the VMware platform has three types of models through which resources are allocated.
- ALLOCATION POOL -% of the resource is guaranteed, and the maximum possible limit is set in the resource pool.
- PAY-AS-YOU-GO - there are no guaranteed resources and maximum limits set in the reservation pool. Resource limits are set at the virtual machine level.
- RESERVATION POOL- guaranteed resources and maximum limits are equal, all resources are allocated. At the virtual machine level, the resource parameters are not set, however, the user can change the limits and reserve resources to the virtual machine.
A customer who needs a fixed set of resources can work with guaranteed resources, or choose PAY-AS-YOU-GO when there is no information about how many resources they will consume in the cloud. The provider, due to the elasticity of the pool, can avoid redundancy of physical data centers and reduce capital expenditures by adding physical hosts only as needed without stopping work. For the customer, payment may occur upon consumption at the end of the month, which also allows you to abandon capital expenditures in favor of operating expenses.
The agreement with the provider (SLA) should provide for the level of availability of services of a certain quality. In the case of Cloud4Y, this figure is 99.982%. In addition, we set the minimum acceptable performance indicators for the CPU and system RAM. The number of MIPS per vCPU is at least 2900, which guarantees customers the claimed processor speed. Also, “re-signing” of physical RAM is not allowed, RAM Swaped is 0%. This means that the Configured Virtual RAM allocated during creation of the virtual machine, which the guest OS will see, is 100% allocated physical memory that is available to the virtual machine at any time. This approach in practice allows you to avoid performance degradation of cloud servers in cases where the operating system accesses blocks in RAM and expects a quick response, but these blocks are read and written to the hard disk, which is significantly inferior in speed, due to the load of other clients.
This creates conditions under which cloud servers can fully replace a physical server with appropriate characteristics for clients at any time, and due to reliable equipment in the TIER III data center network, cluster virtualization and round-the-clock technical support, proper quality of services and fault tolerance are ensured.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/342022/
All Articles