Highload fwdays conference review

On October 14, in Kiev, the Highload fwdays conference was held, dedicated to high-loaded projects, work with databases and architecture, in particular, microservices, machine learning and Big Data. DataArt sponsored the conference. And our colleagues Igor Masternoy (the leader of the DataArt Kiev Java community) and Anna Kolot (.NET, SharePoint Developer) spoke about the reports they attended.
In detail with the conference program can be found here .
')
Let's start the review with the report by Dmitry Okhonko from Facebook about the Log Device. “Yet another log storage,” you think. You would be right, but this Log Storage stands out against the general background by its creators. Facebook's claimed bandwidth is 1TB / s. And it was interesting to know how they deal with the processing of such a volume of data.
Logdevice

What is Log Device for? The following presents were presented at the presentation:
- Reliable communication between services.
- Write ahead logging.
- State replication.
- Journaling.
- Maintaining secondary indexes on a big distributed data store.
The system is designed to be quickly and reliably available for ages to record a huge number of append only logs, which are the smallest addressable units. In addition, the system must ensure the order of recording the log and the ability to get it if necessary. Let's look at its architecture.

Fig. 1 LogDevice architecture.
The data that is written to the LogDevice, to begin with, is sent to the so-called sequencer nodes (in the figure these are red and green diamonds). Each log has its own sequencer, which generates a number consisting of two numbers: an epoch number and a record sequence number. This combination of identifiers is necessary to ensure the fault tolerance of the sequencer itself. If the sequencer node dies, the new one should continue recording logs whose identifiers will be higher than those previously recorded. For this new node increases the number of the era. Metadata about logs, identifiers of log epochs are stored in zookeeper.
Next, the log with the received identifier is recorded in a certain number of storage nodes. The speaker explained that the key-value Rocks DB database is spinning inside the storage node. Each log in it is a record of the form:
{LOG_ID, LSN, COPYSET, DATE, Payload}- LOG_ID - log type;
- LSN - record identifier;
- COPYSET - a list of node identifiers that contain a record;
- Payload - the body of the log.
How does reading records work? As can be seen in the figure, each Reader client connects to all the nodes that contain records of the necessary logs. Each node issues records starting with the specified identifier or date. The task of the Reader client is to remove duplicates and sort the records received.
You can read more about LogDevice on Facebook . The planned exit to open source is the end of 2017.
ML reports

In the neighborhood with performances about Highload and Big Data it was possible to get more deeply acquainted with the fashionable direction of Machine Learning. We were able to listen to the reports of Sergey Vashchilin (PayMaxi) "Semantic text analysis and plagiarism search" and Alexand Zarichkovy (Ring Ukraine) “Faster than real-time face detection” .
Semantic text analysis
The speaker went through the basic algorithms in the field, but the topic of machine learning remained uncovered. The report presented the SVD , tf-idf algorithms for searching keywords of a document, the shingles algorithm, and using the lzm archiver to compare the similarity of two documents. The system described by the author is a relatively inexpensive way to check documents for matches.
At the entrance to the system, a document is submitted in which keywords are found using SVD, these words are searched for similar documents on the Internet. As a cache, Apache Lucene is used to speed up the search, which allows you to locally save and index documents. The documents found are processed using the shingle algorithm and compared with the incoming document.
The advantages of the system are in its simplicity and low cost of development in comparison with analogues. The lack of a system is the absence of a real semantic analysis of the text and a more intelligent search for keywords.
Faster than real-time face detection
The report provided an overview of machine learning methods for recognizing objects in pictures and determining their location on them (as in Figure 2). The speaker told the history of recognition methods from the Viola-Jones detector to the modern (2015) convolutional neural networks such as YOLO, SSD.

Fig. 2 Recognition of objects and their location.
This report was particularly interested in the fact that he was represented by a Ukrainian startup Ring Ukraine , who is working on the creation of a “smart doorbell” device. As far as is clear from the speech, the described neural networks are widely used to determine the face of a person who calls at your door. The main difficulty, according to the speaker, is the definition of the caller in real time, which requires a high recognition rate itself. Modern neural networks YOLO or SSD have such characteristics, below is a comparative table of architectures of various neural networks.
Table 1. Comparison of neural network architectures
| Model | Train | mAP | Flops | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yolo | BVOC 2007 + 2012 | 40.19 | 40.19 | 45 |
| SSD300 | VOC 2007 + 2012 | 63.4 | - | 46 |
| SSD500 | VOC 2007 + 2012 | 74.3 | - | nineteen |
| YOLOv2 | VOC 2007 + 2012 | 76.8 | 34.90 | 67 |
| YOLOv2 544x544 | VOC 2007 + 2012 | 76.8 | 59.68 | 40 |
| Tiny yolo | VOC 2007 + 2012 | 57.1 | 6.97 | 207 |
As we can see in Table 1, neural networks differ in speed characteristics (FPS - frames per second) and accuracy (mAP - mean average precision) recognition, which allows you to select a neural network for a specific task.
New features in Elastic 6

Phillip Krenna 's report from Elastic began with the table below from db-engines.com, which tracks the popularity of search engines. Elastic is twice ahead of its closest competitor Solr. It is used by organizations such as CERN, Goldman Sachs and Sprint.
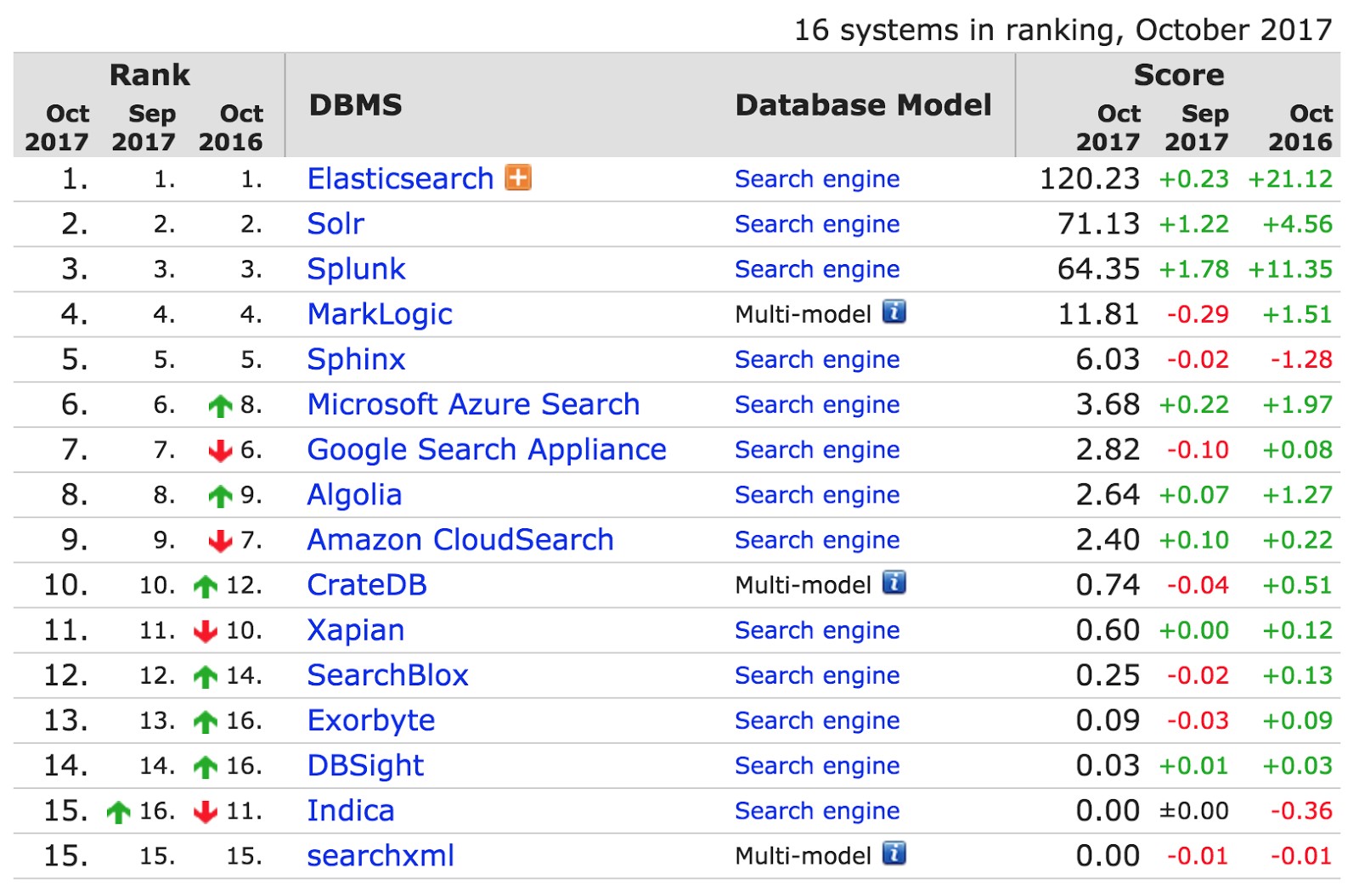
What is so cool about the new Elastic 6, the beta version of which was released in August? The following innovations were presented in the report.
Cross cluster search
Allows you to search for data in several Elastic clusters. This possibility already existed, but it was not optimally realized with the help of the Tribe node. The Tribe kept the merged state of both clusters, accepting any update of the state of each Elastic cluster under control. In addition, the Tribe node that received the request independently determined which indexes, shards and nodes needed to be polled and which top-N documents should be loaded.
ross cluster search does not require a separate dedicated node and merged state of both clusters. Any node can accept cross-cluster requests. A cross cluster request is processed by a coordination node, which communicates with the three configured seed nodes of another cluster. You can also configure the gateway node, which directly accepts the connection from the coordinator and acts as a proxy. For coordination from an API point of view, there is no difference in search queries for indexes on another cluster - the results will be marked with a prefix with the name of the second cluster. Cross cluster search unifies the search API and removes some restrictions compared to the Tribe node (search by indices with the same name on the local and related clusters). Read more here and here .
How to migrate the existing Elastic 5 cluster on Elastic 6? Starting from the sixth version, you will be able to update the version with the help of Rolling Upgrades, without stopping the Elastic cluster (valid for transition from Elastic 5.6 -> Elastic 6).
Sequence numbers
Sequence numbers is another important new feature of Elastic 6. Each update operation, delete, put will be assigned a sequential identifier so that the lagging secondary replica can restore the progress of operations from the Transaction log starting from the i-th, without copying the files. Users are given the opportunity to configure the transaction-log storage time.
Types
Elasticsearch previously represented types (Mapping types) as tables in a database (index). Although the analogy is not entirely accurate. Columns in databases with the same name may not depend on each other, but in Elastic the fields of two different Mapping types must have the same Field type. It is impossible for the field date of one type to be assigned to boolean in another type. This is due to the way Elastic implements types. Apache Lucene under the hood of Elastic stores fields of different types in the same field. Now Elastic decided to gradually abandon the types in the indices. In Elastic 6, each index may contain only one type and may not be specified during indexing. In future versions, type support will be completely discontinued.
Top 10 architectural files on a real highload project
By submission, I liked the report by Dmitry Menshikov “Top 10 architectural files on a real highload project”. Dmitry is a born speaker who speaks the word, successfully adds humor to the speech and supports the interest of the audience. The speaker showed ten cases, told him what had caused the problems, and how the situation could be resolved.
For example:
- As an error in the choice of the user ID UUID in the date + time + MAC address format and 128 bits in length, discovered after the project was launched, led to slow work and almost cost two years of development. And as a simple solution to increase the length of the index to 4 bytes saved the day. As you know, the timestamp is 60-bit, and for the UUID version 1, it is presented as a score of 100-nanosecond intervals in UTC, starting at 00: 00: 00.00 on October 15. The problem was that the possible hit of the second fraction at the beginning and the absence of a uniform distribution due to the peculiarities of the generation of identifiers were not taken into account.

- As a new developer decided to fix a long-falling test, he added a check for the existence of a key and about 2 million user letters that did not have a key were lost.
In our opinion, the report was not saturated with complex production details. But the conclusion is unchanged: the implemented solutions need to be tested in practice and to think about how the change will affect the system.
Microservice architecture traps
Nikita Galkin, system architect from GlobalLogic, presented the report “Traps of microservice architecture” . The main problems in the implementation of microservices, according to Nikita, are to develop without using template approaches - when in one case the settings file is called config, in the other case settings, and so on; refusal from daily updating of documentation in the development process; application of microservices where the problem can be solved by means of boxed products already introduced.
High [Page] load
Interesting was the report “High [Page] load” by Dmitry Voloshin, co-founder of Preply.com, a site for searching tutors around the world. Dmitry spoke about the history of the site, how it became necessary to measure and improve the length of the page load with an increase in the number of users from three people to a million and with the release of the site to the intercontinental market.
The main idea of the report is the need for continuous monitoring of factors affecting page loading speed; the need to work to improve performance, as the success of a business is directly dependent on the page loading speed.

Tools used in Preply to increase page loading speed:
- basic: caching, orm optimizations;
- more advanced: replicas, load-balancing;
- current: CDN, microservices.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/341448/
All Articles