What is DFD (data flow diagrams)
 In the comments to one of my past articles on IDEF0, one of the users asked for more information about what DFD is. The concept is somewhat confusing; many of my clients also ask questions about data flows and charting standards. So I decided to devote this article to DFD.
In the comments to one of my past articles on IDEF0, one of the users asked for more information about what DFD is. The concept is somewhat confusing; many of my clients also ask questions about data flows and charting standards. So I decided to devote this article to DFD.DFD is a common abbreviation for English. data flow diagrams - data flow diagrams. This is the name of the methodology of graphical structural analysis, which describes the sources and data recipients external to the system, logical functions, data streams and data stores that are accessed. Data flow diagram (DFD) is one of the main tools for structural analysis and design of information systems that existed before the wide distribution of UML. Wikipedia
In my opinion, the definition from the Russian-language Wikipedia is somewhat overloaded with information and, as a result, unnecessarily difficult to understand. In addition, I personally believe that DFD and UML are different tools, and therefore it is incorrect to say that DFD is simply a predecessor of UML.
For myself, I derived the following wording:
')
DFD is a notation intended for modeling information systems in terms of storing, processing and transmitting data.
Why do you need DFD notation?
Historically, the syntax of this notation is used in two versions - Jordan (Yourdon) and Gain-Sarson (Gane-Sarson). The differences between them are in the table below:
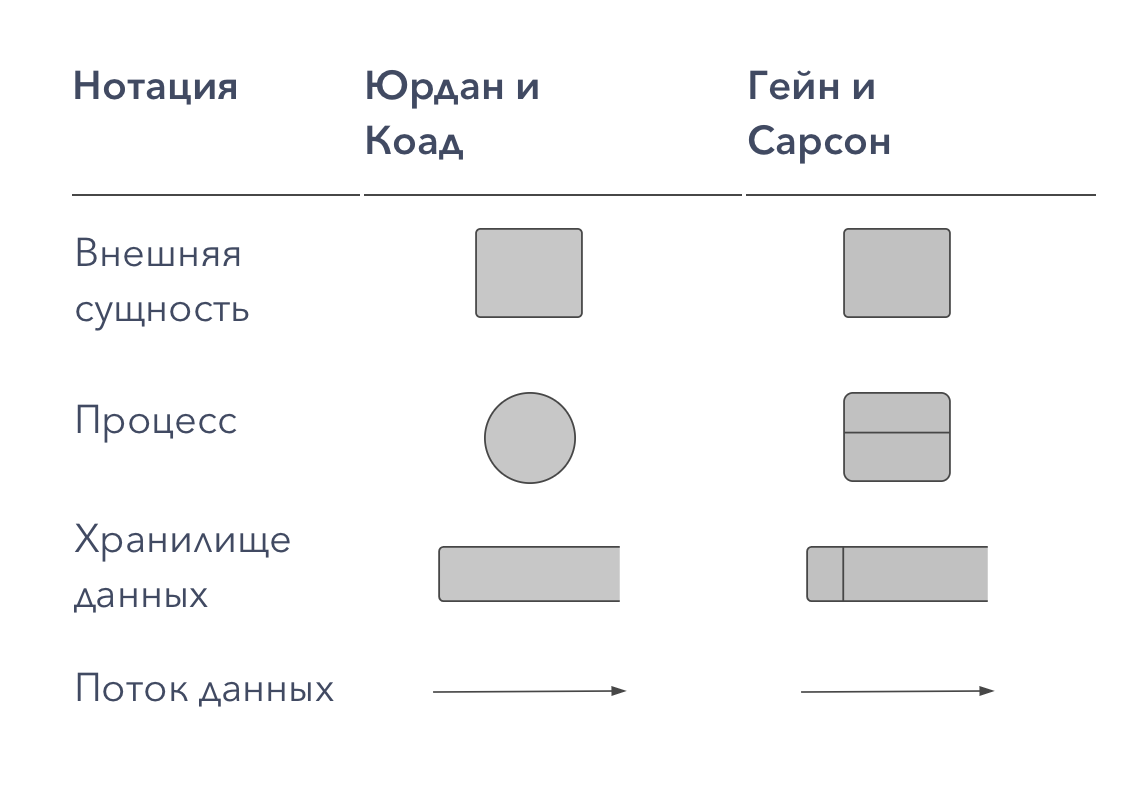
I myself use only one of the options, according to Hein and Sarson. But when I studied the material before writing this article, I saw this comparison table. I believe that it is important not so much for choosing a syntax option, it will depend, rather on the choice of software for creating notations and your personal preferences, as a clear illustration of the fact that there is no hard syntax in DFD, like, for example, BPMN. Here you can use different options, as long as they are clear to you and your customers. DFD notations are a handy tool for creating ad hoc diagrams that can be done quickly and with maximum freedom.
This type of notation is used when a description of the system as a data warehouse is required. Those. The notation should visually answer the following questions:
- What does an information system consist of?
- What you need to process information?
Directly DFD notation consists of the following elements:
- Process (eng. Process) , i.e. the function or sequence of actions to be taken in order for the data to be processed. This could be order creation, customer registration, etc. In the names of processes it is customary to use verbs, i.e. “Create customer” (not “create customer”) or “process order” (and not “carry out an order”). There is no strict requirements system, as, for example, in IDEF0 or BPMN, where the notations have rigidly defined syntax, since they can be executable. But still, certain rules should be adhered to in order to avoid confusion when other people read the DFD.
- External Entities (eng. External Entity). These are any objects that are not included in the system itself, but are for it the source of information or the recipients of any information from the system after data processing. This may be a person, an external system, any storage media and data storage.
- Data storage (English Data store) . Internal data storage for processes in the system. Received data before processing and the result after processing, as well as intermediate values should be stored somewhere. This is a database, a table or any other way of organizing and storing data. It will store customer data, customer requests, expenditure invoices and any other data that entered the system or is the result of processing processes.
- Data flow . The notation is displayed in the form of arrows, which show what information is included, and which comes from a particular block in the diagram.
The DFD notation can describe any actions, including the process of selling or shipping goods, working with requests from customers or purchasing materials, in terms of describing the system. This notation helps to understand what the system should consist of, what is needed to automate the business process. But DFD is not a description of the business process itself. Here, for example, there is no such important parameter as time. Also in this notation are not provided for the conditions and "fork". In DFD, we consider where data comes from, what data is needed, processing it and where to send the results. Those. this notation describes not so much the process itself, as the movement of data streams. To work with processes, I recommend using BPMN or IDEF3 (I'll talk about it another time).
How to create DFD notations
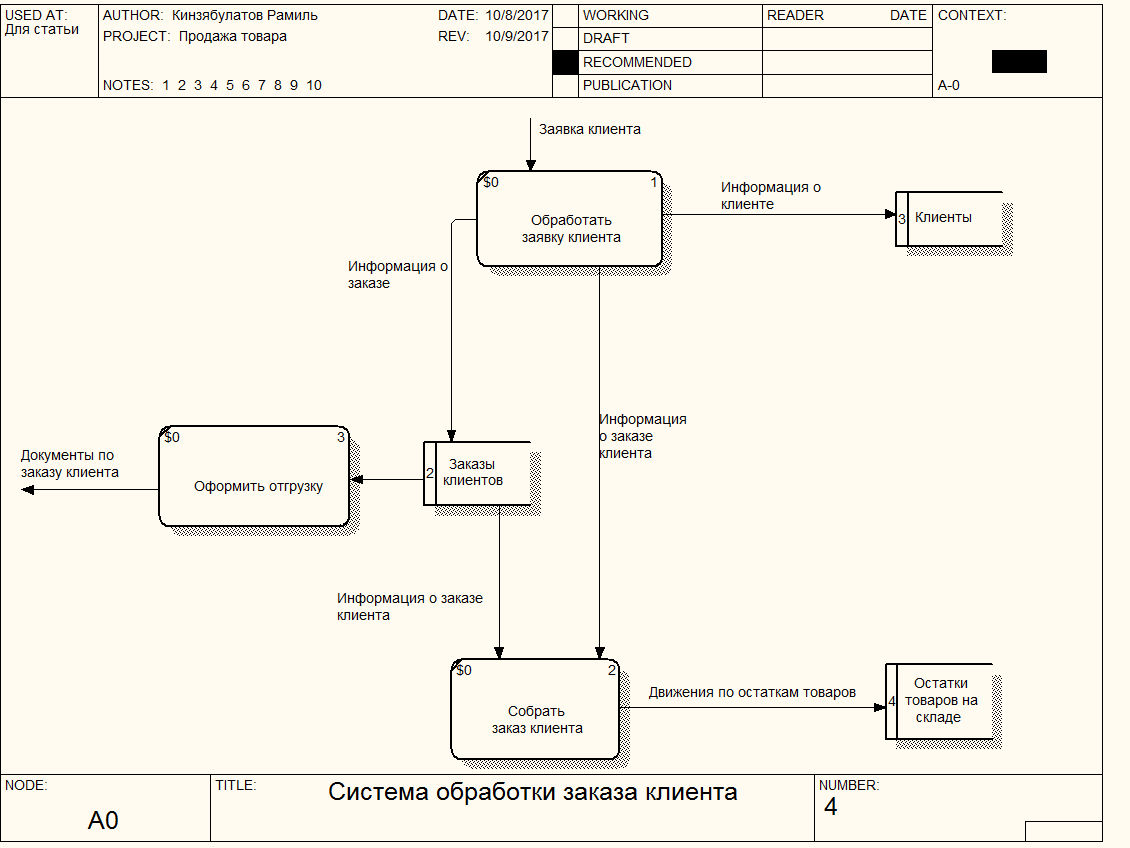
Let's take a look at the sales automation notation for example. Suppose we have a client who makes a request through the website or by telephone. There is a manager who registers this application. Thus, data appears in the system - the client and his order. The warehouse worker must see and ship the goods with all necessary documents and send the documents to the client.
The sequence is as follows:
- The client provides their data and application.
- The manager checks and brings the data into the system.
- The warehouse worker forms the documents, for example, the expenditure invoice, and ships the goods.
- The client receives the goods and a package of documents to him.
We need to see this sequence of actions in terms of data storage and working with them in the IT system.
From the point of view of the DFD, we have:
- A customer is an external entity that is a source of data and a result.
- Order processing process (confirmation and data posting in the system by the manager).
- Collection of order in stock (after receiving the application).
- Registration of shipment (creating the necessary documents).
What rules you need to know to create a DFD diagram:
- Each process must have at least one input and one output. The meaning of the processes here is in data processing, and therefore the process must receive data (incoming arrow) and give it somewhere after processing (outgoing arrow);
- The data processing process must have an external incoming arrow (data from an external entity). In order for any such process to start working, little use of data from the repository must be received new information for further processing;
- The arrows can not directly bind the data warehouse, all links go through the processes. There is no point in simply moving data from one place to another, and this is how the direct connection between the two storages is read with an arrow. The data comes in order to make some actions, in our example - the sale process is carried out. And this is only possible through the process (process);
- All processes must be associated with either other processes or other data repositories. Processes do not exist by themselves, and therefore the result must be transferred somewhere;
- Decomposition. DFD diagrams provide the ability to create large processes and decompose them into subprocesses with a detailed description of actions. For example, we can create the process of “creating an application”, which we then decompose into a sequence of actions, for example, to receive an application, and check and receive customer data separately; from the supplier about the availability of the necessary names, etc. And then in the upper diagram we will have the “processing of the application” block, and when decomposing we get a diagram with a detailed sequence of actions at this stage. At the same time, there will be no conditions or branching at any stage. There will be a process and its decomposition to a depth of 3-4 levels.
How the diagram will look (without decomposition, top level):

And the decomposition of the main element of our diagram:
Where are DFD notations used
DFD diagrams are actively used in software development. Wherein:
- data warehouses are spreadsheets and databases
- external entities - clients or other databases, including those from other programs (integration and data exchange),
- Processes are functions performed and modules in the system.
Also, DFD notation is convenient for analysis, when the system is considered from the point of view of workflow. In this case, you can visually see where the data is stored, how the documentation is exchanged, where business process errors are made in this process, etc. But here the use of DFD diagrams requires special care. Yet this is not a description of the business process itself, but rather a diagram of data movement during the implementation of business processes. But as an auxiliary option, including, for a visual demonstration to the client of the existing problems and methods of optimizing work, this type of notation is quite suitable.
For example, to identify problems of workflow, duplication of documents or, conversely, missing documentation or electronic data in the system, it is very convenient to create a separate description of the business process, and then DFD notation for it. Or vice versa, DFD-notation is created in advance for understanding the basics of the business and the features of the implementation of the workflow. It helps to identify, for example, the absence in the automation system of important documents that are actually created (on paper), but are not displayed in the system at all. And then an optimized business process is built taking into account the identified nuances of the workflow.
DFD notation is easy!
I believe that DFD notation is really much simpler than it seems at first glance. The main thing is to clearly understand the limitations of constructing this type of diagrams (lack of conditions, time, etc.) and apply them where exactly this approach will be more convenient. You may find your own DFD applications that I haven’t described above. In my list there are only those options that I use in practice.
What is particularly convenient in DFD notations is that it is not necessary to adhere to strict rules and syntax, as, for example, in BPMN. These notations will not be executable, they are necessary for understanding the features of the workflow, structure and subsequent work with the data. Therefore, if your diagram is clear to both you and the customer, some deviations from the DFD standards are quite acceptable.
You can draw DFD diagrams, in principle, where and how you are more comfortable. But if you want to work with decomposition, build a system at different levels of detail, then you will have to forget the “drawing tools” (Visio, Paint, and the like). You will need specialized programs for modeling.
I personally use the ERwin program and recommend it to everyone. One of the reasons for my choice is the features of the decomposition. In ERwin, as in some other similar systems, it is possible to decompose DFD processes in IDEF3 format, i.e. The main diagram will be in DFD format, and at the most general level you will see the main data streams and the “nodes” of their processing. And with decomposition, you can use the process approach, which is also very convenient for developing large systems or working with different business units.
Questions and answers
What is the difference between DFD and UML?
There is a language for creating UML notation, which also positions itself as a notation based on working with data. But at the same time, UML is already a programming language, there is a hard syntax, requirements, but there are also many more possibilities for describing various functions. DFD is a notation that is used more freely, more suitable for planning, studying possible solutions, discussions with the customer, etc.
If you are a developer, and you know UML, it is possible that even preliminary solutions will be more convenient for you to create in this notation. And for a business consultant DFD will always be more convenient as a tool, since a business consultant does not need a detailed description of the functions in terms of automation, this is the task of technical specialists. But time and effort DFD saves much.
You should not consider DFD as a simplified version of UML. In spite of the similarity in the approach, these are different tools designed for different purposes.
How many elements can be used in DFD?
Unlike systems with strict syntax and regulations, DFD does not limit the number of elements that can be on a single diagram. For comparison: in IDEF0 the number of such elements, then only detailing (decomposition) or different notations.
On the one hand, this is a big plus, since the absence of restrictions gives a maximum of freedom and comfort when drawing up the notation. On the other hand, this freedom is not recommended to abuse. Remember, the more items you have in a diagram, the harder it is to read.
Can I use DFD notations for working with clients?
In principle, no one can forbid it. Moreover, in limited quantities, as an illustration to some of your explanations, such notations are perfect for discussing the project’s features with the client. But still, customers usually have little knowledge of automation, storage structure, processing capabilities, etc. This is all in the hands of the developers. And the DFD notations are built taking into account the peculiarities of working with data, so I still recommend using them primarily when discussing a project by experts, when creating a technical description and task for developers, to increase the understanding of the developers of the project’s essence and features. It may be difficult for an unprepared customer to even explain the features of DFD notations.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/340064/
All Articles
