Simple Python Scada (continued)
Formation of dynamic objects of the mnemonic scheme
Developing the topic of the previous article , I will describe some functions for the formation of objects of the mnemonic scheme of a simple SCADA program executed in Python.
Objects visually display the status of analog measured values from registers
READ_INPUT_REGISTERS or READ_HOLDING_REGISTERS. Used library Tkinter.
In total, 3 objects were implemented: a horizontal slider, a vertical slider and a dial indicator. Separately describes the construction of a dynamic trend.
Horizontal slider

First you need to create a canvas object and get a link to it.
This object will be placed on the already created root object.
')
from Tkinter import * # root = Tk() canv = Canvas(root,width=1900,height=950,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') canv.place(x=0, y=25) # c = Canvas(root,width=400,height=50,bg="black") # c.place(x=10, y=20) root - reference to the parent object.
width = 400 - width.
height = 50 - height.
bg = "black" - background.
Now you are drawing elements of the slider using graphic primitives.
But in order to execute the correct drawing of elements it is better to create a function.
def hMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) Here are the input variables:
nowValue - the current measured value.
x - X coordinate
y is the y coordinate
widgLen - slider length.
widgHigh - the height of the slider.
maxValue is the maximum allowed value.
outerColor - fill color.
nameValue - the name of the measured value.
hMeterC
def hMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgLen) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(2,2,int(mesureValue),widgHigh-1,fill='red',outline='red') c.create_line(1,widgHigh,1,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/2,widgHigh,1+widgLen/2 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen-widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen-widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(0,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='0') c.create_text(widgLen -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/2))) c.create_text(widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen-widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue-maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh-8,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(nowValue))) c.create_text(1,widgHigh+21,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=nameValue) return (c,'hmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) When executing the code below, a horizontal slider will form on the screen in the window, filled with 25 percent in red and displaying the current measured value in the middle or to the right of the slider.
If this happens, then the code works without errors.
Program code
from Tkinter import * def hMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgLen) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(2,2,int(mesureValue),widgHigh-1,fill='red',outline='red') c.create_line(1,widgHigh,1,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/2,widgHigh,1+widgLen/2 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen-widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen-widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(0,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='0') c.create_text(widgLen -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/2))) c.create_text(widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen-widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue-maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh-8,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(nowValue))) c.create_text(1,widgHigh+21,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=nameValue) return (c,'hmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) root = Tk() canv = Canvas(root,width=1900,height=950,bg="black") canv.place(x=0, y=25) analogFig=hMeterC(250,20,50,300,20,1000,'red','analog Meter') root.mainloop() But this is just a static display of the “horizontal slider” object.
Need to add speakers. To do this, use the root.after method and slightly change the slider display functions.
The function hMeterC takes the form:
def hMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'hmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) That is, the hMeterC function will return an array of parameters of the created object, and another function will perform drawing of graphics.
hMeter:
def hMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgLen) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(2,2,int(mesureValue),widgHigh-1,fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(1,widgHigh,1,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/2,widgHigh,1+widgLen/2 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen-widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen-widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(0,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='0') c.create_text(widgLen -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/2))) c.create_text(widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen-widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue-maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen +10,widgHigh-8,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(int(nowValue))) c.create_text(1,widgHigh+21,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=nameValue) You must add another loop function def jobMeter () for root.after ,
def jobMeter(): hMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) root.after(100, jobMeter) Now the program code has changed a bit.
Program code
import time from Tkinter import * import random def hMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgLen) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(2,2,int(mesureValue),widgHigh-1,fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(1,widgHigh,1,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/2,widgHigh,1+widgLen/2 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen-widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen-widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(0,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='0') c.create_text(widgLen -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/2))) c.create_text(widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen-widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue-maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen +10,widgHigh-8,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(int(nowValue))) c.create_text(1,widgHigh+21,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=nameValue) def hMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'hmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) def jobMeter(): hMeter(analogFig[0],100,analogFig[2],analogFig[3],analogFig[4],analogFig[5],analogFig[6],analogFig[7],analogFig[8]) root.after(100, jobMeter) root = Tk() canv = Canvas(root,width=1900,height=950,bg="black") canv.place(x=0, y=25) analogFig=hMeterC(250,20,50,300,20,1000,'red','analog Meter') root.after(100, jobMeter) root.mainloop() Every 0.1 seconds, the slider object will be updated, but you need to say
that no changes will take place, because the variable nowValue of the hMeter function always has an immutable value of 100.
To correct this situation and demonstrate the dynamic properties of an object, it is proposed to use the random library and make changes to the code.
import random def jobMeter(): hMeter(analogFig[0],random.randint(30, 800),analogFig[2],analogFig[3],analogFig[4],analogFig[5],analogFig[6],analogFig[7],analogFig[8]) root.after(100, jobMeter) Now there will be obvious changes in the position of the slider.
But in this case there are two unpleasant facts.
- The script created by volume does not take up much memory, but when executed, the amount of memory used increases.
- Numbers on the right, showing the current value can not be distinguished.
This is all explained simply.
Each time a new measured value is formed on canvas
redrawing of graphic primitives, but at the same time old elements are also preserved.
There is a superposition of new elements on the previous ones.
To get rid of this effect you need to add the canvas cleaning of the old elements.
to the jobMeter () function.
def jobMeter(): analogFig[0].delete("all") hMeter(analogFig[0],100,analogFig[2],analogFig[3],analogFig[4],analogFig[5],analogFig[6],analogFig[7],analogFig[8]) root.after(100, jobMeter) Now the memory does not increase and the numbers are displayed correctly.
Vertical slider

Here, everything is similar to the horizontal, only the configuration of drawing primitives is slightly changed.
Functions.
def vMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'vmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) def vMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgHigh) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(widgLen-1,widgHigh,2,widgHigh-int(mesureValue),fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen+10,widgHigh,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh/4,widgLen+10,widgHigh/4,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh/2,widgLen+10,widgHigh/2,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh-widgHigh/4,widgLen+10,widgHigh-widgHigh/4,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,1,widgLen+10,1,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen+10,widgHigh,widgLen+10 ,widgHigh,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text='0') c.create_text(widgLen+12,10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh/2,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/2)) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh-widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/4)) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue-maxValue/4)) c.create_text(2,widgHigh+15,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nowValue)) Switch device.
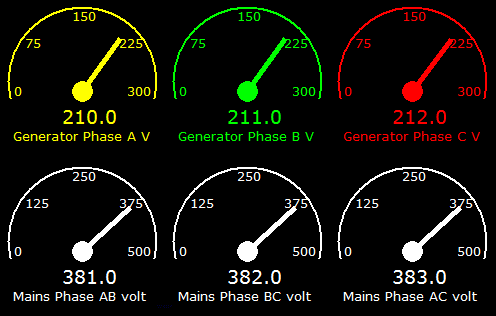
To create this object you will need to import the math library, since
Mathematical functions sin and cos are used.
Functions
def aMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen,height=widgHigh,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'ameter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) def aMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(180) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue x1 = widgLen/2 y1 = widgHigh/2 + 10 x2 = 10 y2 = widgHigh/2 + 10 angle = math.pi * int(mesureValue) / 180; newx = ((x2-x1)*math.cos(angle)-(y2-y1)*math.sin(angle)) + x1 newy = ((x2-x1)*math.sin(angle)+(y2-y1)*math.cos(angle)) + y1 c.create_oval(1 , 1,widgLen-1 ,widgHigh-1,width=2,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_text(7,y1,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text='0') c.create_text(widgLen-30,y1,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2-10,10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/2)) c.create_text(widgLen/8,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/4)) c.create_text(widgLen/2+widgLen/4,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue-maxValue/4)) c.create_text(widgLen/2-20,widgHigh-40,font="Verdana 14",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nowValue)) c.create_rectangle(0,widgHigh/2+18,widgLen ,widgHigh,fill='black',outline='black') c.create_text(widgLen/2-20,widgHigh-40,font="Verdana 14",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nowValue)) c.create_text(6,widgHigh-20,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nameValue)) c.create_oval(x1 - 10, y1 - 10, x1+ 10,y1 + 10,fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(x1,y1,newx,newy,width=5,fill=outerColor) Dynamic chart

The last thing I would like to say is the construction of dynamic graphics. There is a matplotlib library in which many convenient tools for plotting are implemented, as well as a large amount of documentation. But I will describe a simple way to create dynamic graphics using the tkinter library.
The creation of an object is performed in the same way as the previous examples, but here the readings should be transmitted in the form of an array, where each new element is added to the end by the append method.
After this, the object is redrawn.
Suppose at timestamp 0 there is an array with the last measured value (100),
when forming a new time stamp, a new element of the array will be added and a new measured value will be written to it, let it be (110).
It turns out approximately such a table.
0.0 s - (100)
0.1 s - (100,110)
0.2 s - (100.110.90)
0.3 s - (100,110,90,120)
0.4 s - (100,110,90,120,100)
etc.
Upon reaching the number of elements of the array of a given value,
the array is reset and the process is repeated again.
if(len(mesureValue) == 80): mesureValue=None mesureValue=[] Thus, the curve of indications reaches the final border of the canvas of the graph object,
after that, the values are reset and the process of accumulating data in the array is repeated.
Below is a simple example of a program that demonstrates the operation of all the above-described objects of the mnemonic scheme.
Program code
import time from Tkinter import * import random import math def hMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgLen) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(2,2,int(mesureValue),widgHigh-1,fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(1,widgHigh,1,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen/2,widgHigh,1+widgLen/2 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(1+widgLen-widgLen/4,widgHigh,1+widgLen-widgLen/4 ,widgHigh+5,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(0,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='0') c.create_text(widgLen -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2 -10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/2))) c.create_text(widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen-widgLen/4-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue-maxValue/4))) c.create_text(widgLen +10,widgHigh-8,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(int(nowValue))) c.create_text(1,widgHigh+21,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=nameValue) def hMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'hmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) def vMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'vmeter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) def vMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(widgHigh) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_rectangle(widgLen-1,widgHigh,2,widgHigh-int(mesureValue),fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh,widgLen+10,widgHigh,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh/4,widgLen+10,widgHigh/4,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh/2,widgLen+10,widgHigh/2,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,widgHigh-widgHigh/4,widgLen+10,widgHigh-widgHigh/4,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen,1,widgLen+10,1,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_line(widgLen+10,widgHigh,widgLen+10 ,widgHigh,width=1,fill=outerColor) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text='0') c.create_text(widgLen+12,10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh/2,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/2)) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh-widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/4)) c.create_text(widgLen+12,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue-maxValue/4)) c.create_text(2,widgHigh+15,font="Verdana 12",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nowValue)) def aMeterC(nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen,height=widgHigh,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'ameter',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue) def aMeter(c,nowValue,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue): if(nowValue > maxValue): nowValue=maxValue-1 devValue=float(180) / float(maxValue) mesureValue = devValue * nowValue x1 = widgLen/2 y1 = widgHigh/2 + 10 x2 = 10 y2 = widgHigh/2 + 10 angle = math.pi * int(mesureValue) / 180; newx = ((x2-x1)*math.cos(angle)-(y2-y1)*math.sin(angle)) + x1 newy = ((x2-x1)*math.sin(angle)+(y2-y1)*math.cos(angle)) + y1 c.create_oval(1 , 1,widgLen-1 ,widgHigh-1,width=2,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_text(7,y1,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text='0') c.create_text(widgLen-30,y1,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(widgLen/2-10,10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/2)) c.create_text(widgLen/8,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue/4)) c.create_text(widgLen/2+widgLen/4,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(maxValue-maxValue/4)) c.create_text(widgLen/2-20,widgHigh-40,font="Verdana 14",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nowValue)) c.create_rectangle(0,widgHigh/2+18,widgLen ,widgHigh,fill='black',outline='black') c.create_text(widgLen/2-20,widgHigh-40,font="Verdana 14",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nowValue)) c.create_text(6,widgHigh-20,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill=outerColor,text=str(nameValue)) c.create_oval(x1 - 10, y1 - 10, x1+ 10,y1 + 10,fill=outerColor,outline=outerColor) c.create_line(x1,y1,newx,newy,width=5,fill=outerColor) def hTrendC(x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue,trendKoef): c = Canvas(root,width=widgLen+50,height=widgHigh+40,bg="black",bd=0, highlightthickness=0, relief='ridge') c.place(x=x, y=y) return (c,'htrend',x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue,trendKoef) def hTrend(arrayData,arrayValue): c,markErr,x,y,widgLen,widgHigh,maxValue,outerColor,nameValue,trendKoef=arrayData c.create_rectangle(1,1,widgLen,widgHigh,fill='black',outline=outerColor) c.create_line(50,widgHigh/2,widgLen-5,widgHigh/2,width=0.1,fill='white',dash=(4, 2)) c.create_line(50,widgHigh/4,widgLen-5,widgHigh/4,width=0.1,fill='white',dash=(4, 2)) c.create_line(50,widgHigh - widgHigh/4,widgLen-5,widgHigh -widgHigh/4,width=0.2,fill='white',dash=(4, 2)) c.create_text(10,widgHigh-10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=0) c.create_text(10,12,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(maxValue)) c.create_text(10,widgHigh/2,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/2))) c.create_text(10,widgHigh/4,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue-maxValue/4))) c.create_text(10,widgHigh - widgHigh/4 ,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(int(maxValue/4))) c.create_text(1,widgHigh+25,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=nameValue) c.create_text(widgLen/10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='1') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*2,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='2') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*3,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='3') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*4,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='4') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*5,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='5') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*6,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='6') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*7,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='7') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*8,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='8') c.create_text((widgLen/10)*9,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='9') c.create_text(widgLen-10,widgHigh+10,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text='100') oldy=widgHigh - float(widgHigh)/float(maxValue) * arrayValue[0] * int(trendKoef) oldx=5 xval=0 for counter in range(0,len(arrayValue)): val=arrayValue[counter] yval=widgHigh - float(widgHigh)/float(maxValue) * val * int(trendKoef) xval+=10 c.create_line(oldx,oldy,xval,yval,width=1.5,fill='green') oldy=yval oldx=xval mesureValue = arrayValue[len(arrayValue)-1 ] * int(trendKoef) c.create_line(xval,widgHigh-10,xval,0,width=0.5,fill='white') c.create_text(xval+10,yval,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=str(mesureValue)) c.create_text(xval+10,yval+20,font="Verdana 10",anchor="w",justify=CENTER,fill='white',text=time.strftime('%H:%M:%S')) def jobMeter(): global mesureValue analogFig[0].delete("all") analogVertical[0].delete("all") analogString[0].delete("all") hMeter(analogFig[0],random.randint(30, 800),analogFig[2],analogFig[3],analogFig[4],analogFig[5],analogFig[6],analogFig[7],analogFig[8]) vMeter(analogVertical[0],random.randint(30, 800),analogVertical[2],analogVertical[3],analogVertical[4],analogVertical[5],analogVertical[6],analogVertical[7],analogVertical[8]) aMeter(analogString[0],random.randint(30, 800),analogString[2],analogString[3],analogString[4],analogString[5],analogString[6],analogString[7],analogString[8]) lenVal = len(mesureValue)+1 mesureValue.append(lenVal) mesureValue[lenVal-1] = random.randint(30, 800) trend[0].delete("all") hTrend(trend,mesureValue) if(len(mesureValue) == 80): mesureValue=None mesureValue=[] root.after(100, jobMeter) root = Tk() canv = Canvas(root,width=1900,height=950,bg="black") canv.place(x=0, y=25) analogFig=hMeterC(250,20,50,300,20,1000,'red','analog Meter') analogVertical=vMeterC(250,42,150,30,200,1000,'red','analog Meter') analogString=aMeterC(250,200,150,150,150,1000,'green','analog Meter') global mesureValue mesureValue=[] trend=hTrendC(450,28,800,400,1000,'green','analog', '1') root.after(1, jobMeter) root.mainloop() More examples can be found here.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/339678/
All Articles