Wi-Fi is over: calculate offenders wireless

To identify attacks and anomalies of wireless air, you can use high-tech solutions (usually expensive), which allow you to monitor wireless networks and detect attacks. In this article I will talk about two free utilities that will allow you to control the wireless broadcast and respond quickly to intruders.
From a security point of view, tracking of wireless devices allows you to immediately inform you about the point at which you need to send employees of the security department. There are many network security threats that are not detected by traditional IDS / IPS systems, since they can only be detected at the radio frequency level. Such threats include wireless bridges that operate in accordance with proprietary protocols, and devices that operate in accordance with earlier standards, such as 802.11FH, which can become an intrusion point in the network.
These threats also include attackers' WiFi devices operating on non-standard operating frequencies or using non-standard modulation. And besides, there are always denial of service attacks that can come from wireless suppression devices.
')
To identify attacks and anomalies of wireless air, you can use high-tech solutions (usually expensive), which allow you to monitor wireless networks and detect attacks. These solutions include Cisco CleanAir. We will use two free solutions - waidps and nzyme.
Important note: for the utilities to work, it is necessary that your Wi-Fi adapter can work in monitor mode.
Waidps
You can use the waidps utility to detect anomalies of a wireless broadcast in “home” conditions. It is a multipurpose tool designed to audit (penetration testing) networks, detect wireless intrusion (WEP / WPA / WPS attacks) and prevent intrusion (stop communication of a station with an access point). In addition, the program will collect all WiFi information in the area and save it in databases.
Waidps is able to detect massive deauthentication, which can signal a possible attack on WPA (to intercept a handshack), detect attacks using ARP requests, using Rogue AP and Evil_Twin, possible attacks through WPS pin, and much more.
The utility itself raises the interfaces it needs and starts monitoring the broadcast. An interesting feature is that the utility can be used not only to detect attacks, but also with its help you can audit the AP of interest to us.
For the utility to work, you must additionally install the aircrack-ng and wireshark package.
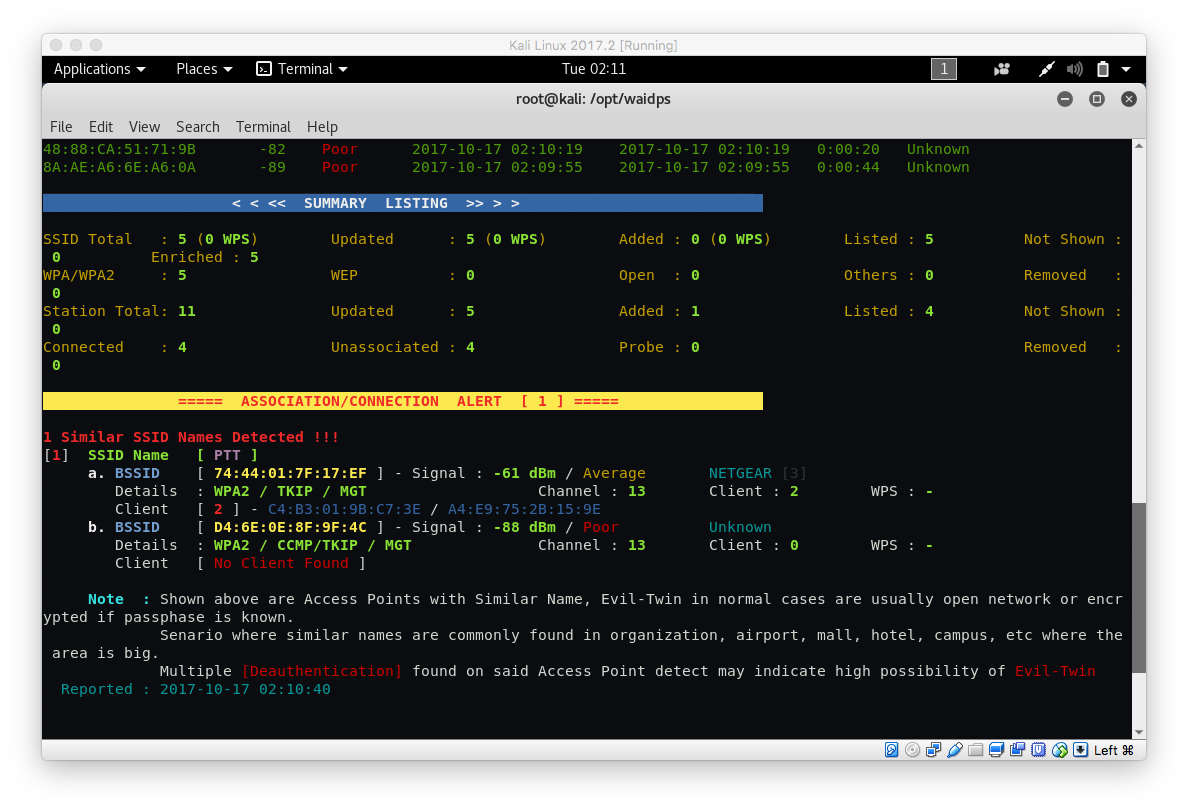
The utility monitors the wireless air and signals anomalies - common attacks on the wireless network, as well as the appearance of fraudulent access points - RogueAP.
Although the utility has not been updated since 2014, until recently it had no alternatives. With the help of several waidps points, you can set up perimeter monitoring by checking the physical location of each station to determine the approximate location of the intruder.
The best option is to run the utility for several hours in order to take a “clean” picture of the ether for comparison.
→ Download utility
nzyme
Nzyme collects 802.11 frames directly from the air and sends them to Graylog's journal management system (open source), which allows it to be used as IDS WiFi, monitoring and incident response. All you need is a JVM and a WiFi adapter that supports monitoring mode.

A distinctive feature of this tool is the initial "sharpened" to run on weak machines, such as the Raspberry Pi. It is also possible to run nzyme out of the box on your MacBook.
First you need to configure the system to work by installing the deb package or using the jar file. You also need to configure the config file to connect to Graylog:
nzyme_id = nzyme
channels = en0:1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11
channel_hop_command = sudo /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport {interface} channel {channel}
channel_hop_interval = 1
graylog_addresses = %graylog IP%:12000
beacon_frame_sampling_rate = 0
Graylog is used for display (can be used as a virtual machine), which allows you to display information in a beautiful interface:
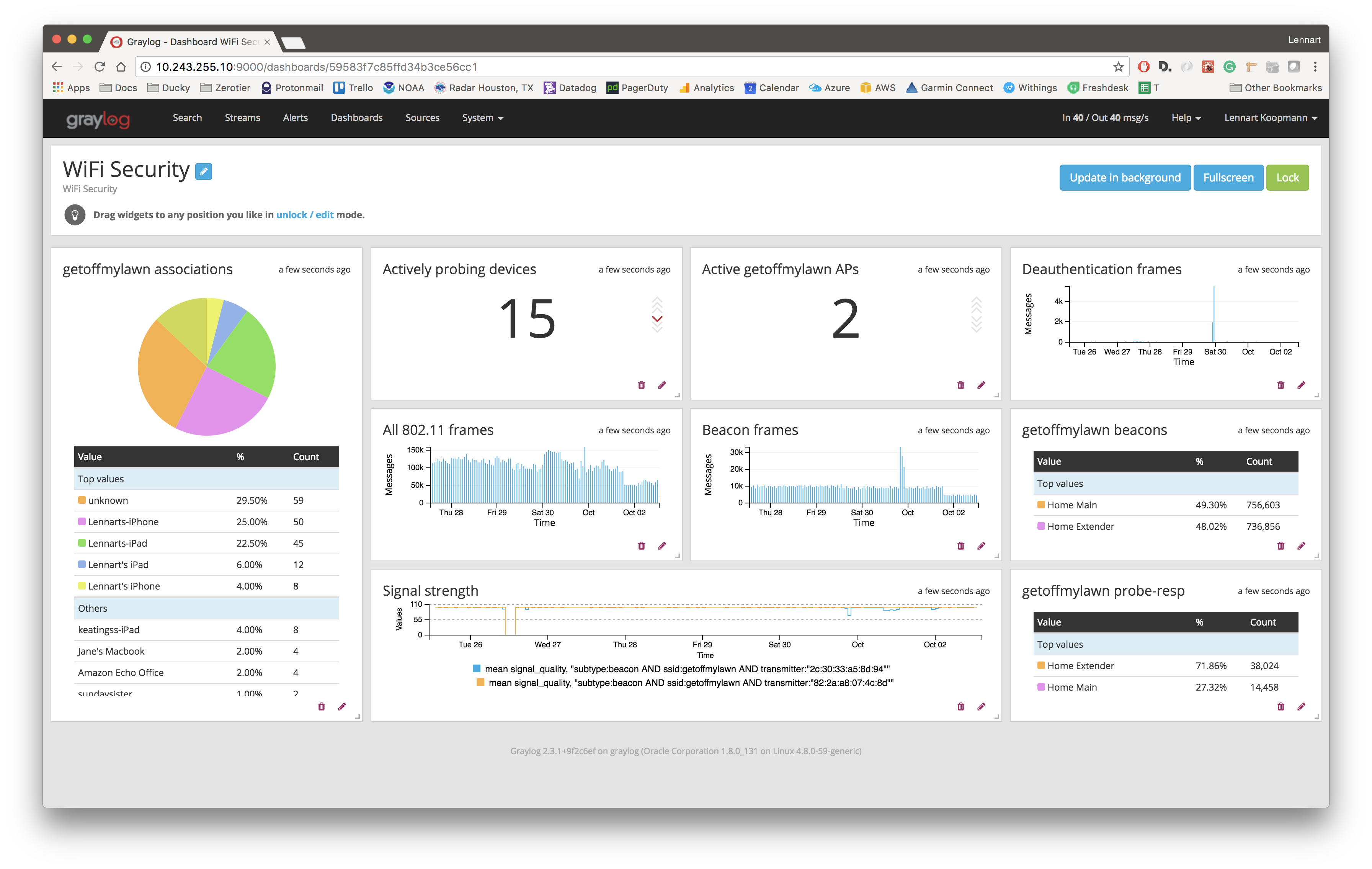
The undoubted advantage of the utility is the ability to view devices, probably compromised by hackers - nzyme will show which devices were imprudent to connect to a fake access point.
→ Download utility
Conclusion
These utilities will not in any way replace the "professional" solutions for the protection of wireless air, but will nevertheless be able to give information about its "purity."
Modern equipment allows you to conduct constant active listening on all channels, to check the appeared points by various criteria allows you to quickly identify the points of intruders. After detection, the corresponding notifications are generated. Management Frame Protection (MFP) technology neutralizes attacks such as Evil Twin, because when it is used, a special signature is inserted into each wireless frame, and the client with this feature will simply not authenticate with the attacker’s access point.
In addition, you can enable active restraint mode (Active Rogue Containment) and then upon detecting an attacker's point, de-authentication packets will be sent to it en masse, which will prevent anyone from connecting to it.
In order to detect new points connected directly to the local network of the enterprise, it is necessary to use the switchport tracing technology, as a result of which the port on the switch is detected and blocked and the attacker's point loses access to the local network.
Also, in addition to the built-in basic IDS, there are also adaptive wIPS. wIPS can detect, among other things, the use of tools (karma, aircrack), off-traffic traffic bursts, attackers' DHCP servers, WEP key picking, etc.
Addition: it is currently unknown whether professional equipment is able to detect a new type of attack - Key Reinstallation Attacks.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/339270/
All Articles