Security Week 37: Together we turn off Bluetooth, a hole in Tor for a million, botnets on Elasticsearch servers
 BlueBorne. Remember this name. This is not even a vulnerability, it is a whole bunch of holes in Bluetooth implementations on Windows, Linux, Android, and even a little bit in iOS. The researchers from Armis Labs revealed this abscess, and they also estimated the number of potential victims in ... 5.3 billion devices.
BlueBorne. Remember this name. This is not even a vulnerability, it is a whole bunch of holes in Bluetooth implementations on Windows, Linux, Android, and even a little bit in iOS. The researchers from Armis Labs revealed this abscess, and they also estimated the number of potential victims in ... 5.3 billion devices.In short, this is a serious matter. BlueBorne allows you to attack a Bluetooth-enabled device from another bluetooth device. Moreover, both devices do not have to be paired. Moreover, the victim does not even need to be “on the radar” of Bluetooth-fellows in the district. In other words, if you have a blue tooth, you are at risk.
A bag of discovered vulnerabilities looks like this:
')
- CVE-2017-1000251. RCE in the Linux kernel;
- CVE-2017-1000250. The vulnerability of data leakage in the Bluetooth stack;
- CVE-2017-0785. Android data leakage vulnerability;
- CVE-2017-0781. RCE on Android;
- CVE-2017-0782. RCE on Android;
- CVE-2017-0783. Logical vulnerability in Android (Bluetooth Pineapple);
- CVE-2017-8628. Logical vulnerability in Windows (Bluetooth Pineapple);
- So fierce that so far without CVE. RCE-vulnerability of the proprietary protocol Apple Low Energy Audio Protocol.
There are those two bluetooth pineapple so named not by chance. This is a reference to the well-known hacker (officially, of course, Penterster, but we all understand;) the Wi-Fi Pineapple device. This piece can be left in any public place, where it mimics the favorite home networks of all available devices. The same will ingenuously cling to supposedly native networks, well, then MiTM will happen with all the consequences. Something similar, only via Bluetooth allow you to rotate the CVE-2017-0783 and CVE-2017-8628.
The original study shows a very picturesque picture with “nesting sites” of vulnerabilities in the Bluetooth stack.
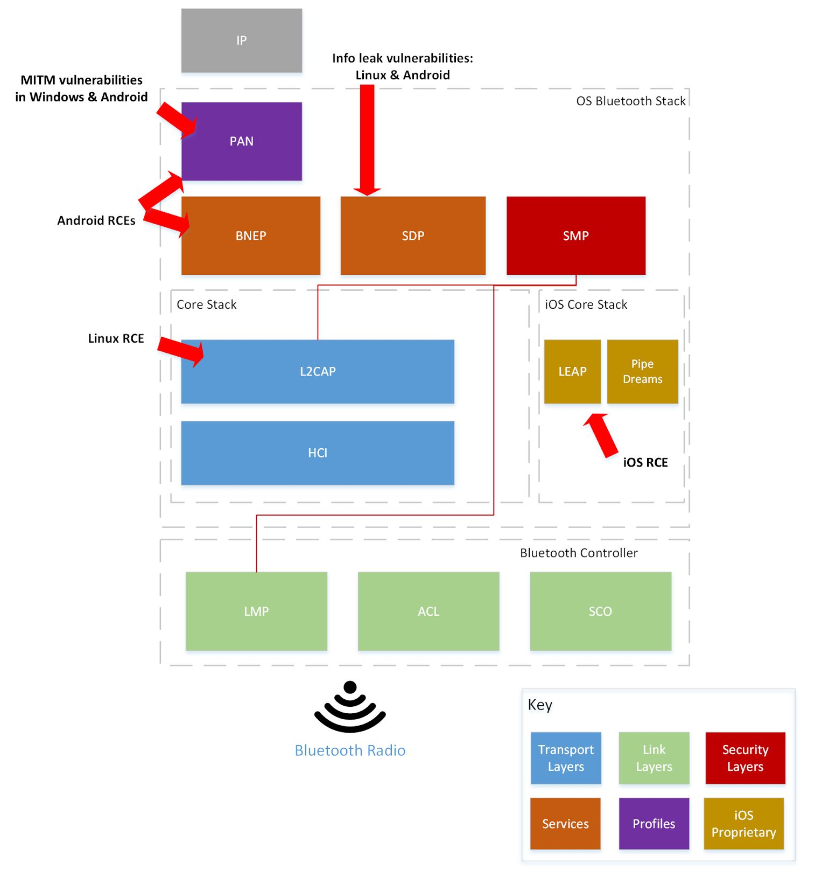
Due to the fact that the holes are heterogeneous and belong to all sorts of Bluetooth implementations, an attacker must first determine the OS family and version on the attacked device and then apply the appropriate exploit. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that Bluetooth processes have very high privileges, so with a successful attack, a hacker can do almost anything with the victim's device. For example, to lure the device to the dark side, including in your botnet or intercept communications, steal data, download software and distribute filth in the radius of a Bluetooth connection.
The guys from Armis Labs acted responsibly and published their discoveries only after Google, Microsoft and Apple rolled out patches. But we must bear in mind that there is a bug in all Windows, starting with Vista, in Linux on the 3.3-rc1 kernel with BlueZ (including Tizen) and in unnamed iOS versions. Prorva devices with these OSes will not get their patches ever.
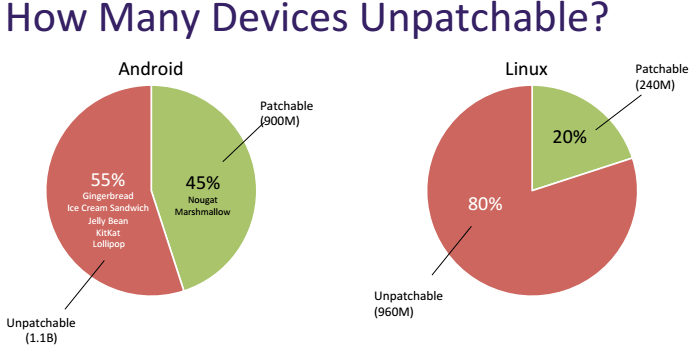
Well, let's say, smart TVs are in relative safety - they are rarely taken out of the house (although how about an advanced neighbor behind a wall who is not averse to watching your weekdays through a webcam? ..). But for mobile devices somehow quite alarming.
Zerodium Offers One Million Dollars for the Zerodey in Tor
 News The exploit provider Zerodium again announced a beautiful seven-digit reward for a zero-day exploit - this time in the Tor browser. A fully functional exploit for a hitherto unknown vulnerability in Tor under Tails Linux and Windows will cost the office a million dollars.
News The exploit provider Zerodium again announced a beautiful seven-digit reward for a zero-day exploit - this time in the Tor browser. A fully functional exploit for a hitherto unknown vulnerability in Tor under Tails Linux and Windows will cost the office a million dollars.$ 250 thousand will be paid for the combined RCE exploit plus escalation of privileges on Tails and Windows, and $ 200 thousand if the exploit turns out to be only RCE or if it only works when JavaScript is enabled in the browser. The exploit is received with full documentation, and the attack vector must be a website.
Zerodium demonstrates such generosity, obviously, not at its own expense - there is a specific order. Moreover, if you believe the company, this is an order from some government agencies that want to get to the terrible criminals hiding with Tor. The states are not named, but in August Zerodium already announced the peak of requests from "democratic states, as well as states that are not under sanctions." That is, the circle is narrowing - this is definitely not North Korea and Mother Russia. One way or another, someone seriously burns about Tor, as evidenced by the amounts and the deadline: increased bounty is valid only until November 30, so hurry.
The Tor project has already been asked what they think about it, and they classically chatted out, saying that, firstly, such awards testify to Tor’s high security level, and, secondly, all this is not good, since a successful Tor hack can become threatening the lives of some users. It is they who hint at the inhabitants of non-democratic countries and states under international sanctions, and there are no such clients among Zerodium customers, as we were told.
Thousands of Elasticsearch servers are infected with a POS Trojan
News Research Researcher from Kromtech decided to probe the public server Elasticsearch - a free search engine. He found there something very curious - the control panel of POS Trojans JackPOS and AlinaPOS. This is a pretty old man who made a lot of noise a few years ago.
POS Trojans specialize in intercepting bank card billing data, for which they infect terminals in retail chains, restaurants and hotels. Stolen dumps in encrypted form are sent to the server, from where they go straight to the card stores online.
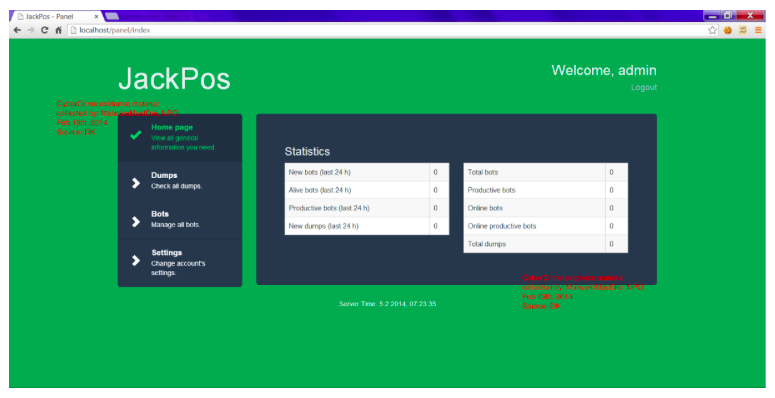
As it turned out, someone got hold of the source of these old Trojans (AlinaPOS - 2012, JackPOS - 2014) and put it up for sale. Accordingly, the command infrastructure was also needed, which Kromtech eventually exposed. Scanning with Shodan found 15,000 Elasticsearch servers on the Web, four thousand of which were captured by POS bot-drivers.
Tellingly, almost all hacked servers are hosted by Amazon. Researchers attribute this to the features of the server configuration system. More precisely, the system itself is reasonably secure, but during a quick installation, users often click through the security setting - and here is the result.

Antiquities
"Pentagon"
Dangerous virus, using the “Brain” method, affects the boot sector of floppy disks when accessing them. If at the same time the diskette was already affected by the “Brain” virus, then “Pentagon” treats the Boot sector of this disk, changes its label and then infects it with its copy. The file PENTAGON.TXT is created on the infected disk. The virus "survives" with a warm reboot. Part of the virus is encrypted. Intercepts int 9 and int 13h. Contains texts "© 1987 The Pentagon, Zorell Group", "first sector in segment".
Quote from the book "Computer viruses in MS-DOS" Eugene Kaspersky. 1992 Page 102.
Disclaimer: This column reflects only the personal opinion of its author. It may coincide with the position of Kaspersky Lab, or it may not coincide. Then how lucky.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/338050/
All Articles