Robots in human society
Robots are automated machines that can perform human functions when interacting with the outside world. People have dreamed of them since ancient times, and now these mechanisms are entering our society with great speed. Their main purpose is to make our life more comfortable, improve working conditions, free the “hands” from complex work processes and increase productivity.
Robots are most often found in industry, where they were able to fully automate most production tasks. But, in addition, smart machines are increasingly used in the military industry, medicine, the service sector and the consumer sector.
And if previously they performed only repetitive routine tasks on the program, now their level has reached new heights, allowing them to interact with us, communicating in their machine language, understand our gestures and emotions. In addition, using specialized platforms now everyone has the opportunity to influence the industry, create their own programs and add new functions to robots. Thus, developing from simple auxiliary mechanisms, robots have every chance to join our society and become our friends.
')
Note some interesting facts from the history of the development of robots. The first signs of robotics were observed from antiquity, when people dreamed of giant bronze machines that could help them fight enemies and conquer new lands. There is evidence that the prototype of the current robots were mechanical figures found in the notes of the Arab inventor Al-Jazari around 1136-1206.
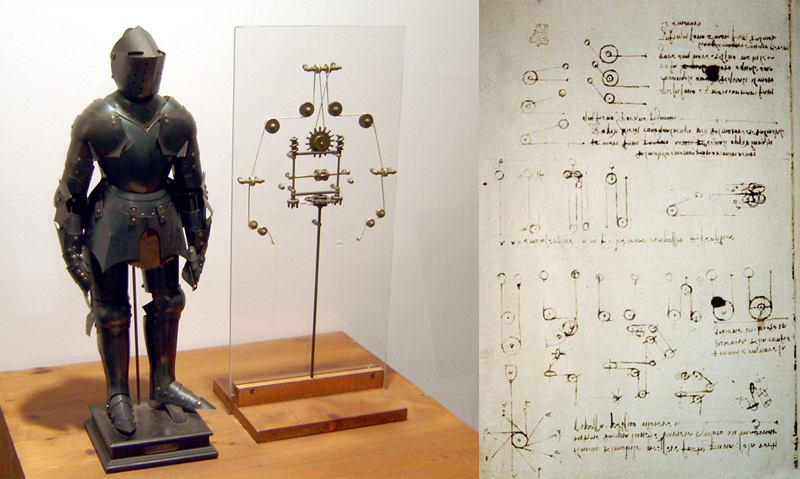
The first who presented a drawing of a humanoid robot was the great Leonardo da Vinci in about 1495. The drawing represented a model of a mechanical knight who can sit, stand, move his arms, his head, and possibly grab objects. But it is not known whether Da Vinci tried to translate this mechanism into reality.
In the 16th and 17th centuries in Western Europe, engineers began to design automata, winding movements, like human beings, that could perform fairly complex operations. The most famous of them is the robot “Spanish monk”, which was invented around 1560 by the mechanic Juanelo Turriano for Emperor Charles V. The automaton was about 40 cm tall, able to walk, beat his chest with his hand, nod his head and even present a wooden cross to lips.
More noticeable progress in robotics was observed in the 18th century. For example, in 1738, French engineer Jacques de Vaucanson assembled the world's first android capable of playing the flute.
Since the 19th century, inventions have become more practical. In 1898, the famous physicist Nikola Tesla presented a miniature radio-controlled vessel to the public. Initially, this invention seemed a bit whimsical. But in the future, his ideas began to be realized and gained wide application.
1921 - the mechanisms finally gained the precise term “robot” thanks to the Czech writer Karl Čapek and his play called “Rossum Universal Robots”. It is noteworthy that apek called this word not machines, but living people, created at a special factory. But the term entrenched in science and gave life to all automated devices.
In the mid-20th century, in particular, in the 1950s, mechanical manipulators were developed to interact with radioactive materials. These robots copied the movements of the hands of a person in a safe place.
In 1968, the Japanese industrial company Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd produced the first industrial robot. Since then, Japan has begun to strive to become the world capital of robotics, and it succeeded. Despite the fact that the robots were originally developed in the United States, they were imported to Japan in small quantities, where engineers studied them and used them in production.

Commercial distribution of robots began in the 1980s. Technical progress was moving towards the improvement of management systems. Such companies as Unimate, Hitachi KUKA, Westinghouse, FANUC developed sensor systems for their robots, making them more sensitive to the tasks they perform.
In the late 90s - early 2000s, the industry began to grow and develop actively using new controllers, programming languages, launching the first robots into space and the emergence of machines that create robots.
At this time, new humanoid robots also appeared, such as Canadian Aiko, imitating human feelings (touch, hearing, speech, vision), ASIMO - humanoid of the Japanese company Honda, robot dog AIBO, created by Sony and others.
The last five years, there has been a broad burst of robotics in all industries, from advanced manipulators to humanoids, which look like living people, have a wide range of emotions and completely copy our facial expressions.
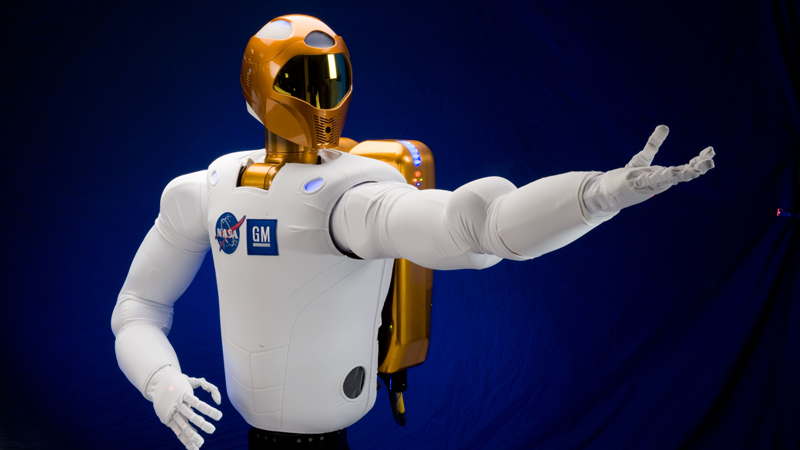

Despite the usefulness of the technology, robots are not yet used everywhere, as is often shown to us in many science fiction films. This is due to a number of factors. Firstly, our infrastructure is simply not ready for this: roads, streets, buildings and our houses. Robots perceive the world differently and are still unable to even distinguish a chair from a table, what can we say about the constantly changing conditions of our life.
Secondly, the legal system of states is not ready: the use of robots requires appropriate laws so that they "coexist" peacefully with us. In the end, if not the robots themselves, then someone else should be responsible for their actions.
Third, some researchers argue that we need to fear these mechanical workers, because with the further active development of artificial intelligence, they will literally enslave us. These fears hold back the study and spread of robotics too much.
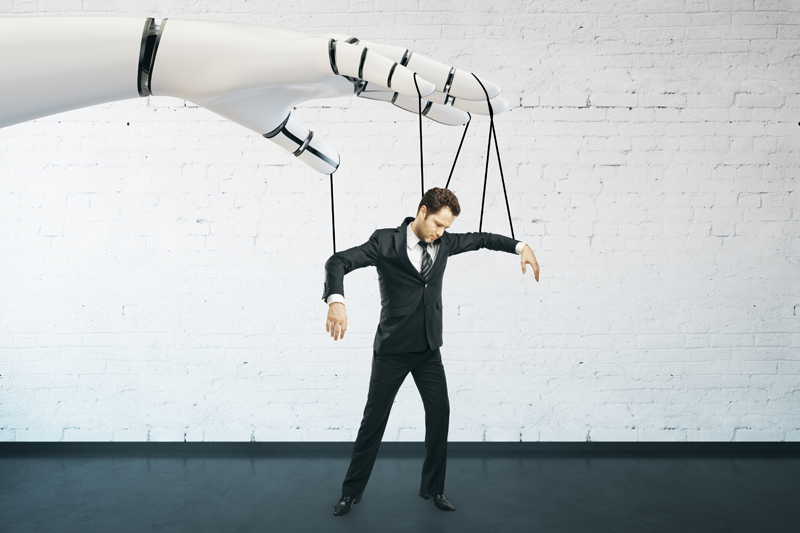

Of course, one should not deny that there are a lot of global risks that can arise when using superhuman mind, which is not programmed for unconditional loyalty to man. But the future is still in our hands, and we have the power to change it, especially since the programming of robots is now becoming more and more open and accessible to the public. It is only necessary to learn how to properly use these features.
As already mentioned, the largest industry where robotics is used is the industry, in particular, the automotive industry. Manipulators working in factories vary in size and functionality depending on the type of task they perform - assembly, welding, cutting, painting. Along with them in production, you can find unloading and loading robots, packers, sorters, molders and other mechanisms that replace people in routine repetitive tasks. The leading companies in industrial automation are KUKA (Germany), Fanuc (Japan), Kawasaki (Japan), ABB (Switzerland), Denso (Japan) and others.
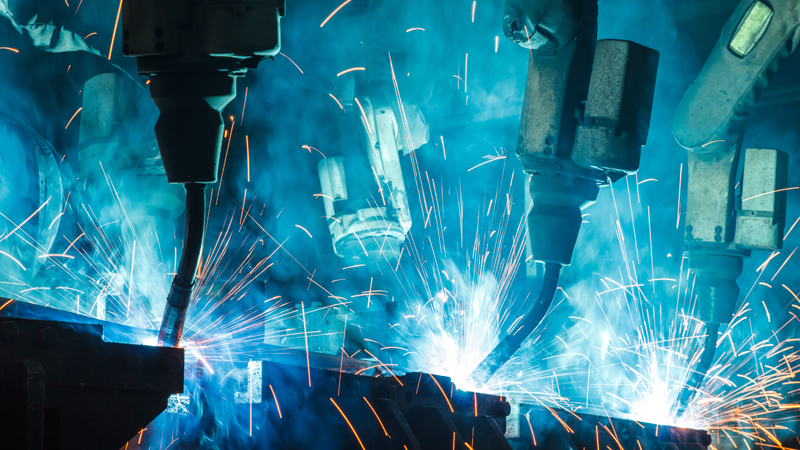

Along with this, the market is gaining new scale of joint robots that can work with people on the same production line without harming them. These are manipulators of Universal Robots, as well as industrial robots of the new generation Baxter and Sawyer from Rethink Robotics.
In recent years, the whole world is closely following the development of autonomous cars that will transport people without their participation in the process. Now the closest to the unmanned vehicles is a taxi service Uber. But progress in technology development is regularly demonstrated by manufacturers such as Ford, Mercedes, Toyota, BMW and Tesla.
Robots are also widely used in agriculture. Frequently, these are radio-controlled tractors and plows, but more and more widespread use is acquired by unmanned aerial vehicles, which farmers use to map their land and regularly inspect crops.
And what robots serve in everyday life? Of course, the first place here belongs to vacuum cleaning robots, which have become indispensable cleaning assistants in the house. The leader among the manufacturers of these devices is the American company iRobot and its Roomba vacuum cleaners. The latest models of the manufacturer have improved navigation and pairing with the smartphone. This addition opens up new opportunities for ordinary users who can add more functions to robots through special applications.
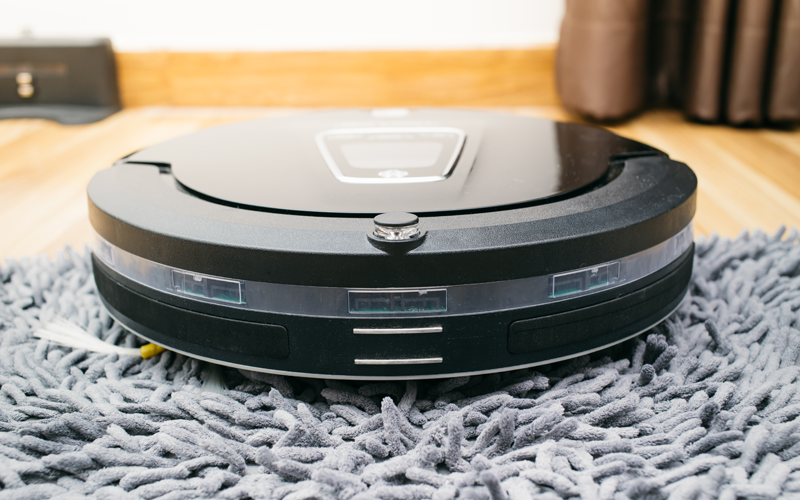

Lawn mowers serve as lawn mowers that are equipped with an array of sensors for safe driving and cutting grass in large areas. The pools are looked after by small wheeled robots, which independently move along the bottom of the reservoir, clean the walls, steps and filter the water.
In addition, a growing number of gaining unmanned aerial vehicles, which have long since moved from exclusively military to civilian use. Drones are used for a variety of tasks - from entertainment to observation and professional video. Leadership in this sector for the Chinese manufacturer DJI. Their latest Spark device is considered the most perfect selfie drone launched and controlled by gestures.
Increasing distribution is also becoming a smart home system. If earlier this “automation” consisted in clapping with its hands to turn on the light, nowadays a person doesn’t need to follow anything at all - all power is in the hands of the electronic house manager, the robotic control center, which controls all home devices from security systems and lighting to the coffee maker and washing cars.
Moreover, the user can add functions to the system that he needs. For example, he needs to adjust the operation of the washing machine at a time when the meters work in the “night” mode in order to save energy costs. To do this, you need to design an appropriate application for your smartphone that will help you stay in touch with your home and manage home automation from virtually anywhere.

An auxiliary gadget can be an echo column (Amazon Echo, Google Home and others), which allows you to control all the equipment in your house using voice commands. Or helper robots that act as an organizer, alarm clock, multimedia player. Being connected to the Internet, they report weather, tell the news, provide information about traffic jams in your city and so on. And thanks to the open access to programming, one can make excellent assistants for studying children, entertaining the elderly and even toys for pets.
As you can see, robots have already entered our lives in the form of a variety of smart gadgets, home appliances and smart systems. However, smart cars are still very far from the ideal image created by human imagination. All they can do is execute commands that are programmed by a person. But engineers persistently strive to make machines truly capable, and interaction with them easier, natural, and most importantly, accessible to the common man.
Every year, experts and analysts represent us a new world, where faith in science and technology will replace faith in the supernatural. A world in which you can learn and work without leaving your home. The Internet will blur the boundaries between countries, and robots will do almost everything for us.
According to the statistics of the organization Tractica, the number of robots consumed by mankind will reach 31.2 million units worldwide by 2020. At the same time, domestic robots will take the lead in the market, having overtaken industrial and military.

Scientists predict that by 2018 the Internet of Things will have about 6 billion connected devices. These devices will access services and data on the Web, allowing people to build new business plans to service these connected devices. By 2020, 40% of interactions with mobile devices will be through smart agents. This prediction is based on the fact that our world is moving toward an era of applications in which services such as Amazon Alexa, Microsoft Cortana and Apple Siri will play the role of a universal interface for human interaction with devices.
Google Technical Director Ray Kurzweil, in his predictions about the development of robotics and information technology, suggests that personal robots capable of fully autonomous complex actions will become as familiar as refrigerators or washing machines in 2027. And unmanned vehicles will fill the roads completely in 2033.
No matter how consoling or, on the contrary, frightening predictions, scientists and engineers face some other problems. The main one is the severe restrictions of governments in the adoption of robotics, which are accompanied by a lack of quality standards and product safety.
Another problem that needs to be solved before robots are massively implemented is the availability of software and hardware. The high cost of materials and equipment for production does not allow manufacturers to reduce prices for their robots. For example, medical devices such as exoskeletons, which would help many people with disabilities to live and move, are very expensive.
So far, only cleaning robots, drones and personal assistants are available to us, but we are pleased with the fact that we will soon be able to make these devices more functional, independent of the manufacturers.
Plus, ordinary people are not yet morally ready to accept robots like them. This is primarily due to the lack of information about the achievements made by scientific and technical progress. In addition to this, people had an erroneous opinion about robots, which were repeatedly presented in science fiction films. Some still perceive the word “robot” as something like a “Terminator” or a droid from Star Wars. But in fact, now even a child can assemble and program a robot.

It is necessary to expand the boundaries of knowledge, read more and watch interesting videos about devices from the real world, which can be of great importance in our daily life.
Robotics also affects the area of the now highly acclaimed direction - the Internet of Things. This is a single network that connects the surrounding objects of the real world with virtual ones.
How it happens: sensors are introduced into all devices connected to the network, which allows them to interact with the outside world. For example, "smart" curtains, which themselves regulate their transparency depending on the levels of external and internal lighting. Or a refrigerator, which independently regulates the temperature in different compartments, based on what products you take most often. Thus, the technique begins to adapt to the user's daily life and is controlled based on his needs.
The Internet of Things is not just a combination of various devices and sensors through wired and wireless channels. This is a closer integration of the real and virtual worlds, in which communication between people and devices takes place.

Scientists are confident that in the future these systems will become active participants in information and social processes, as well as businesses, where they can interact with each other, exchange information about the environment, respond and influence external processes without human intervention.
Against this background, the concept of Social IoT appears, which involves the unification of people, robots and devices into one information-legal field. But what is needed to implement this concept? The fact is that the most important problem in this area today is the lack of state standards, which makes it difficult to apply the solutions offered on the market, and also holds back the emergence of new ones.
But besides safety standards, it is necessary to create accessible mechanisms of interaction between robots and humans for control and monitoring. This will make it possible to fully control not one robot, but to safely introduce another civilization of machines into our society and live in harmony with them.
Such user software services, fortunately, will soon appear and be available, allowing even a beginner to add new interesting tasks to his robot. Want a robot vacuum to sing your favorite songs? Why not. To do this, it will be enough to use a set of ready-made basic tools.
With the help of the API program, anyone can quickly create and combine many of their solutions. At the same time, you will not need to spend your resources on creating basic tools, but only focus on the main task.
In the near future, you will be able to connect the program, select the finished application and make your robot vacuum speaking and singing. And if you equip it with a video camera, he will be able to act as a security guard. But the most important thing is that with the help of a large set of software tools you will have the opportunity to write your own unique applications in order to add more new functions to household robots.

It is also worth noting that each individual third-party product on the presented base will be able to attract users of the entire system and distribute its product. Thus, a large ecosystem of tools and opportunities will be created that will be used daily by people from all over the world.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that as our world is filled with robots, the skills of communication with them will be no less useful than the skills of communication with people. We see how modern technologies gradually unite people and smart machines into one big social and hardware network. And this is only the beginning of a difficult, but very exciting journey into the future.

Robots are most often found in industry, where they were able to fully automate most production tasks. But, in addition, smart machines are increasingly used in the military industry, medicine, the service sector and the consumer sector.
And if previously they performed only repetitive routine tasks on the program, now their level has reached new heights, allowing them to interact with us, communicating in their machine language, understand our gestures and emotions. In addition, using specialized platforms now everyone has the opportunity to influence the industry, create their own programs and add new functions to robots. Thus, developing from simple auxiliary mechanisms, robots have every chance to join our society and become our friends.
')
The history of development
Note some interesting facts from the history of the development of robots. The first signs of robotics were observed from antiquity, when people dreamed of giant bronze machines that could help them fight enemies and conquer new lands. There is evidence that the prototype of the current robots were mechanical figures found in the notes of the Arab inventor Al-Jazari around 1136-1206.
The first who presented a drawing of a humanoid robot was the great Leonardo da Vinci in about 1495. The drawing represented a model of a mechanical knight who can sit, stand, move his arms, his head, and possibly grab objects. But it is not known whether Da Vinci tried to translate this mechanism into reality.

In the 16th and 17th centuries in Western Europe, engineers began to design automata, winding movements, like human beings, that could perform fairly complex operations. The most famous of them is the robot “Spanish monk”, which was invented around 1560 by the mechanic Juanelo Turriano for Emperor Charles V. The automaton was about 40 cm tall, able to walk, beat his chest with his hand, nod his head and even present a wooden cross to lips.
More noticeable progress in robotics was observed in the 18th century. For example, in 1738, French engineer Jacques de Vaucanson assembled the world's first android capable of playing the flute.
Since the 19th century, inventions have become more practical. In 1898, the famous physicist Nikola Tesla presented a miniature radio-controlled vessel to the public. Initially, this invention seemed a bit whimsical. But in the future, his ideas began to be realized and gained wide application.
1921 - the mechanisms finally gained the precise term “robot” thanks to the Czech writer Karl Čapek and his play called “Rossum Universal Robots”. It is noteworthy that apek called this word not machines, but living people, created at a special factory. But the term entrenched in science and gave life to all automated devices.
In the mid-20th century, in particular, in the 1950s, mechanical manipulators were developed to interact with radioactive materials. These robots copied the movements of the hands of a person in a safe place.
In 1968, the Japanese industrial company Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd produced the first industrial robot. Since then, Japan has begun to strive to become the world capital of robotics, and it succeeded. Despite the fact that the robots were originally developed in the United States, they were imported to Japan in small quantities, where engineers studied them and used them in production.

Commercial distribution of robots began in the 1980s. Technical progress was moving towards the improvement of management systems. Such companies as Unimate, Hitachi KUKA, Westinghouse, FANUC developed sensor systems for their robots, making them more sensitive to the tasks they perform.
In the late 90s - early 2000s, the industry began to grow and develop actively using new controllers, programming languages, launching the first robots into space and the emergence of machines that create robots.
At this time, new humanoid robots also appeared, such as Canadian Aiko, imitating human feelings (touch, hearing, speech, vision), ASIMO - humanoid of the Japanese company Honda, robot dog AIBO, created by Sony and others.
- In 2005, the humanoid robot RoboThespian of the British company Engineered Arts. Passing several modifications, it became the best platform for communication and entertainment. In the same year, the world saw BigDog, a four-legged combat robot created by Boston Dynamics.
- In 2008, a humanoid, friendly robot, NAO, came out to work in homes, universities, and laboratories, offering assistance in research and education.
- In 2011, NASA's first robot astronaut Robonaut-2 was sent to the ISS.
The last five years, there has been a broad burst of robotics in all industries, from advanced manipulators to humanoids, which look like living people, have a wide range of emotions and completely copy our facial expressions.

Obstacles
Despite the usefulness of the technology, robots are not yet used everywhere, as is often shown to us in many science fiction films. This is due to a number of factors. Firstly, our infrastructure is simply not ready for this: roads, streets, buildings and our houses. Robots perceive the world differently and are still unable to even distinguish a chair from a table, what can we say about the constantly changing conditions of our life.
Secondly, the legal system of states is not ready: the use of robots requires appropriate laws so that they "coexist" peacefully with us. In the end, if not the robots themselves, then someone else should be responsible for their actions.
Third, some researchers argue that we need to fear these mechanical workers, because with the further active development of artificial intelligence, they will literally enslave us. These fears hold back the study and spread of robotics too much.

Of course, one should not deny that there are a lot of global risks that can arise when using superhuman mind, which is not programmed for unconditional loyalty to man. But the future is still in our hands, and we have the power to change it, especially since the programming of robots is now becoming more and more open and accessible to the public. It is only necessary to learn how to properly use these features.
Robots today
As already mentioned, the largest industry where robotics is used is the industry, in particular, the automotive industry. Manipulators working in factories vary in size and functionality depending on the type of task they perform - assembly, welding, cutting, painting. Along with them in production, you can find unloading and loading robots, packers, sorters, molders and other mechanisms that replace people in routine repetitive tasks. The leading companies in industrial automation are KUKA (Germany), Fanuc (Japan), Kawasaki (Japan), ABB (Switzerland), Denso (Japan) and others.

Along with this, the market is gaining new scale of joint robots that can work with people on the same production line without harming them. These are manipulators of Universal Robots, as well as industrial robots of the new generation Baxter and Sawyer from Rethink Robotics.
In recent years, the whole world is closely following the development of autonomous cars that will transport people without their participation in the process. Now the closest to the unmanned vehicles is a taxi service Uber. But progress in technology development is regularly demonstrated by manufacturers such as Ford, Mercedes, Toyota, BMW and Tesla.
Robots are also widely used in agriculture. Frequently, these are radio-controlled tractors and plows, but more and more widespread use is acquired by unmanned aerial vehicles, which farmers use to map their land and regularly inspect crops.
And what robots serve in everyday life? Of course, the first place here belongs to vacuum cleaning robots, which have become indispensable cleaning assistants in the house. The leader among the manufacturers of these devices is the American company iRobot and its Roomba vacuum cleaners. The latest models of the manufacturer have improved navigation and pairing with the smartphone. This addition opens up new opportunities for ordinary users who can add more functions to robots through special applications.

Lawn mowers serve as lawn mowers that are equipped with an array of sensors for safe driving and cutting grass in large areas. The pools are looked after by small wheeled robots, which independently move along the bottom of the reservoir, clean the walls, steps and filter the water.
In addition, a growing number of gaining unmanned aerial vehicles, which have long since moved from exclusively military to civilian use. Drones are used for a variety of tasks - from entertainment to observation and professional video. Leadership in this sector for the Chinese manufacturer DJI. Their latest Spark device is considered the most perfect selfie drone launched and controlled by gestures.
Increasing distribution is also becoming a smart home system. If earlier this “automation” consisted in clapping with its hands to turn on the light, nowadays a person doesn’t need to follow anything at all - all power is in the hands of the electronic house manager, the robotic control center, which controls all home devices from security systems and lighting to the coffee maker and washing cars.
Moreover, the user can add functions to the system that he needs. For example, he needs to adjust the operation of the washing machine at a time when the meters work in the “night” mode in order to save energy costs. To do this, you need to design an appropriate application for your smartphone that will help you stay in touch with your home and manage home automation from virtually anywhere.

An auxiliary gadget can be an echo column (Amazon Echo, Google Home and others), which allows you to control all the equipment in your house using voice commands. Or helper robots that act as an organizer, alarm clock, multimedia player. Being connected to the Internet, they report weather, tell the news, provide information about traffic jams in your city and so on. And thanks to the open access to programming, one can make excellent assistants for studying children, entertaining the elderly and even toys for pets.
As you can see, robots have already entered our lives in the form of a variety of smart gadgets, home appliances and smart systems. However, smart cars are still very far from the ideal image created by human imagination. All they can do is execute commands that are programmed by a person. But engineers persistently strive to make machines truly capable, and interaction with them easier, natural, and most importantly, accessible to the common man.
Future forecasts
Every year, experts and analysts represent us a new world, where faith in science and technology will replace faith in the supernatural. A world in which you can learn and work without leaving your home. The Internet will blur the boundaries between countries, and robots will do almost everything for us.
According to the statistics of the organization Tractica, the number of robots consumed by mankind will reach 31.2 million units worldwide by 2020. At the same time, domestic robots will take the lead in the market, having overtaken industrial and military.

Scientists predict that by 2018 the Internet of Things will have about 6 billion connected devices. These devices will access services and data on the Web, allowing people to build new business plans to service these connected devices. By 2020, 40% of interactions with mobile devices will be through smart agents. This prediction is based on the fact that our world is moving toward an era of applications in which services such as Amazon Alexa, Microsoft Cortana and Apple Siri will play the role of a universal interface for human interaction with devices.
Google Technical Director Ray Kurzweil, in his predictions about the development of robotics and information technology, suggests that personal robots capable of fully autonomous complex actions will become as familiar as refrigerators or washing machines in 2027. And unmanned vehicles will fill the roads completely in 2033.
No matter how consoling or, on the contrary, frightening predictions, scientists and engineers face some other problems. The main one is the severe restrictions of governments in the adoption of robotics, which are accompanied by a lack of quality standards and product safety.
Another problem that needs to be solved before robots are massively implemented is the availability of software and hardware. The high cost of materials and equipment for production does not allow manufacturers to reduce prices for their robots. For example, medical devices such as exoskeletons, which would help many people with disabilities to live and move, are very expensive.
So far, only cleaning robots, drones and personal assistants are available to us, but we are pleased with the fact that we will soon be able to make these devices more functional, independent of the manufacturers.
Plus, ordinary people are not yet morally ready to accept robots like them. This is primarily due to the lack of information about the achievements made by scientific and technical progress. In addition to this, people had an erroneous opinion about robots, which were repeatedly presented in science fiction films. Some still perceive the word “robot” as something like a “Terminator” or a droid from Star Wars. But in fact, now even a child can assemble and program a robot.

It is necessary to expand the boundaries of knowledge, read more and watch interesting videos about devices from the real world, which can be of great importance in our daily life.
IoT concept robots
Robotics also affects the area of the now highly acclaimed direction - the Internet of Things. This is a single network that connects the surrounding objects of the real world with virtual ones.
How it happens: sensors are introduced into all devices connected to the network, which allows them to interact with the outside world. For example, "smart" curtains, which themselves regulate their transparency depending on the levels of external and internal lighting. Or a refrigerator, which independently regulates the temperature in different compartments, based on what products you take most often. Thus, the technique begins to adapt to the user's daily life and is controlled based on his needs.
The Internet of Things is not just a combination of various devices and sensors through wired and wireless channels. This is a closer integration of the real and virtual worlds, in which communication between people and devices takes place.

Scientists are confident that in the future these systems will become active participants in information and social processes, as well as businesses, where they can interact with each other, exchange information about the environment, respond and influence external processes without human intervention.
Against this background, the concept of Social IoT appears, which involves the unification of people, robots and devices into one information-legal field. But what is needed to implement this concept? The fact is that the most important problem in this area today is the lack of state standards, which makes it difficult to apply the solutions offered on the market, and also holds back the emergence of new ones.
But besides safety standards, it is necessary to create accessible mechanisms of interaction between robots and humans for control and monitoring. This will make it possible to fully control not one robot, but to safely introduce another civilization of machines into our society and live in harmony with them.
Such user software services, fortunately, will soon appear and be available, allowing even a beginner to add new interesting tasks to his robot. Want a robot vacuum to sing your favorite songs? Why not. To do this, it will be enough to use a set of ready-made basic tools.
With the help of the API program, anyone can quickly create and combine many of their solutions. At the same time, you will not need to spend your resources on creating basic tools, but only focus on the main task.
In the near future, you will be able to connect the program, select the finished application and make your robot vacuum speaking and singing. And if you equip it with a video camera, he will be able to act as a security guard. But the most important thing is that with the help of a large set of software tools you will have the opportunity to write your own unique applications in order to add more new functions to household robots.

It is also worth noting that each individual third-party product on the presented base will be able to attract users of the entire system and distribute its product. Thus, a large ecosystem of tools and opportunities will be created that will be used daily by people from all over the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is worth noting that as our world is filled with robots, the skills of communication with them will be no less useful than the skills of communication with people. We see how modern technologies gradually unite people and smart machines into one big social and hardware network. And this is only the beginning of a difficult, but very exciting journey into the future.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/337902/
All Articles