Professional penetration testing: the fate of real geeks, fans of the command line or not?
When it comes to hacking, no matter if it is ethical or not, many of us present a dark room with monitors and a bespectacled professional with red eyes from constant lack of sleep. Is a geek really able to hack the system, and is it really necessary to involve only such experts in order to test the security of their systems? Is it possible to equip a competent IT specialist with hacking tools and logical methodology and get a quality result? Let's try to figure it out.

In order to understand the components of the modern methodology of testing security, we need to consider its main "building blocks" - the basic approaches: the classic penetration test, scanning for vulnerabilities and configuration analysis.
Penetration test
During the penetration test, the security tester acts like a real hacker: finds those vulnerabilities that are easiest to exploit, exploits them, and gets access to the right information. As a rule, the goal is the need to obtain administrative access or access to specific information (for example, data on salaries of top managers).
The key feature of penetration testing is that not all of the existing vulnerabilities are searched for, but only those that are necessary to achieve the chosen goals (as in the case of a real hack). Since the combat exploitation of vulnerabilities occurs, there may be negative consequences in the form of frozen services, server reboot, headaches for system administrators, listening to the security manager of the company by the management of the company.
Vulnerability Scan
Imagine that you decide to hack the site with your bare hands. What will you do? First of all, try to determine the version of the used Web-server and / or CMS-system. What for? To “google” and find information about already known vulnerabilities and available exploits. So the attackers did 15 years ago, and they do the same now.
This process can be automated, as many developers of security analysis tools did: vulnerability scanners appeared. Of course, the scanners do not use Google, but are looking for information about vulnerabilities in their own database.
Vulnerability scanning allows you to quickly “shovel” IT infrastructure and find problem spots. But the scanner acts linearly and can miss interesting combinations of vulnerabilities, which together create a serious security gap.
Consider the following example. A large manufacturing company ordered security testing. On the first day of internal testing at the reception, we notice on the sticker the account password recorded by the caring hand of the secretary. We are taking a photo of it, and after five minutes with this account we launch a special utility to search for “shared” folders (now this scanner is part of the same Metasploit Framework). As a result, we find a workstation of a technical support officer responsible for “rolling” OS images onto the machines of new employees of the company.
For its and our convenience, the IT specialist “shared” a folder with prepared images for everyone. We did not fail to take advantage of such kindness and “pulled out” the password hash of the local administrator, who “unwound” overnight. Full access to all workstations of the enterprise was obtained in one day! Using a conventional scanner would allow you to find a “shared” folder, but the scanner could neither look inside nor unwind the hash.
An important intermediate conclusion: the use of vulnerability scanners speeds up testing, but in no case does not ensure its completeness.
Configuration Analysis
Any component of the IT infrastructure (OS, DBMS, active network equipment, etc.) contains a lot of settings that determine the level of security. The correct settings can be found in the vendor documentation or in the articles of experts sharing their experience. On the basis of such materials, organizations such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the Center for Internet Security have been preparing checklists for many years, allowing them to audit the configuration of various systems. There are similar closed projects within the communities of IT auditors of the Big Four companies (BIG4).
Configuration analysis can be carried out both manually and using automated tools, but in any case implies administrative access to the system being checked. This is similar to if we have a pretty girl-system administrator on our knees and show us everything. Configuration analysis is the safest security analysis option, but at the same time the longest.
Having dealt with three approaches to security testing, it's time to remember that all this should be done with a specific purpose.
Objectives of security testing
Increasingly, customers testing security voiced the following two goals: to identify the maximum number of real vulnerabilities in order to quickly close them and check the vigilance of company employees.
To achieve the goals, it is impossible to conduct a full-fledged testing, using only one of the considered approaches. We will not cover all existing vulnerabilities with a clean penetration test, limiting ourselves only to scanning for vulnerabilities, we will dig in a large number of “garbage” triggers, and errors in the settings detected during configuration analysis will not always lead to real possibility of penetration. It is necessary to combine approaches.
Comprehensive security testing
To form an integrated security testing approach, it is advisable to take a sequence of intruders' actions and add the use of effective tools that real hackers cannot afford because of their unmasking signs.
The process of testing security is divided into the following stages in accordance with the stages of real hacking:
- search for targets;
- search for vulnerabilities;
- exploitation;
- expansion of privileges and zones of influence.
Step 1. Search for targets
The only stage that the project for testing security may not be, if the customer immediately gave us a list of goals.
If testing is external, and the customer only tells us the name of the company, then at this stage we are engaged in a full-fledged Internet intelligence, the goals of which are the information resources of the customer and his staff (especially if the project involves the use of social engineering methods).
In this step, we study:
- sites related to the customer’s company, namely: we will find out domain names, email addresses, organization structure, etc .;
- job sites: carefully read who the CIO of the customer is looking for (in job descriptions, the technologies used in the company are often described in detail);
- social networks: collect data on employee users;
- IT solution / service provider sites that boast what, when and how they did for our customer;
- we make requests to the whois service and find out which networks are registered to the customer or which IP address providers it uses;
- we make queries to DNS servers and find out if the customer has resources with third level domains: vpn.ooo-romashka.ru, ftp.ooo-romashka.ru, etc. We determine which email services are used.
As a result, we form a list of IP-addresses of information resources related to the customer, lists of employees, etc.
In the case of internal security testing, an ethical hacker gains physical access to the outlet, listens for network traffic, and determines the ranges of IP networks from which he can start his work.
Step 2. Search for vulnerabilities
Knowing the goal, you can safely begin to search for vulnerabilities. Basically, we do this with the help of vulnerability scanners, but we also do not refuse to manually search for vulnerabilities, especially in the case of Web applications.
As a result, we get a list of potential vulnerabilities, which is yet to be verified.
Important note: if you and I are acting in this step without administrative access to the systems, then do not expect any scanner to show you all the existing vulnerabilities on a particular node. To find the maximum vulnerabilities, you will have to repeat this exercise with administrative records already extracted by sweat and blood.
Step 3. Operation
After we have compiled a list of potential vulnerabilities, it would be nice to check them for exploitation and look for additional ones that cannot be found using scanners and Google. Why do you need to do this? There are several reasons for this.
First, closing any vulnerabilities is a real headache for system administrators who have a lot of other work. There is also always a chance that something will “fall off” after rolling a patch or changing settings. Therefore, it is more expedient to load our favorite system administrators with only standing problems: those vulnerabilities that are really dangerous, and this can only be established by checking the possibility of exploitation.
Secondly, there are many vulnerabilities that can only be verified during operation: for example, a weak password, the possibility of SQL injection or XSS.
At this step, we are with you:
- neatly launch exploits;
- intercept traffic using ARP-poisoning;
- we select passwords;
- “Unwind” mined password hashes;
- we check for the possibility of SQL injection / XSS and other attacks specific to Web applications;
- we do much more depending on the specific IT infrastructure of the customer.
As a result of this step, we find out which of the detected vulnerabilities are real, we find “combat” testing of new vulnerabilities and see what can be obtained if we exploit them.
If we get the desired administrative access, we can return to the previous step and find even more vulnerabilities.
Step 4. Privilege escalation
Having access to any system, we are trying to understand what we have access to and whether it can be expanded within a single system (for example, to the administrator level) or within the entire IT infrastructure.
A simple example. Having selected the user's password to one system, we check whether the given login / password pair is suitable for access to other systems.
Thus, the considered approach allows detecting the maximum number of real vulnerabilities using available tools.
Free ethical hacker toolkit
For true hacking and penetration testing, there are several hundred utilities.
Separately, I want to note that the arsenal of burglars cannot be replaced by any one, even with a commercial scanner, respectively, you need to use several tools to complete security testing.
The undisputed leader among similar tools "in one box" is the assembly of Kali Linux .
We list in one list the most useful and most frequently used free programs by ethical hackers:
- NMAP is a port scanner, it can be used as a vulnerability scanner and even a password guessing tool in the case of NSE;
- OpenVAS - vulnerability scanner;
- Metasploit Framework - a framework for penetration testing, containing both exploits and specialized modules (for example, to search for “shared” folders, to generate backdoors, to select passwords, etc.);
- Burp Suite Free Edition - local proxy / scanner for analyzing the security of Web applications;
- THC-Hydra - utility for selecting passwords for network services;
- HashCat - a utility for selecting passwords for hashes;
- Ettercap - sniffer for interception and analysis of network traffic;
- Wireshark - sniffer for intercepting and analyzing network traffic;
- Aircrack-ng is a set of utilities for testing the security of wireless networks.
There are plenty of tools that solve highly specialized tasks. A good list of such tools is included in the already mentioned Kali Linux build: https://tools.kali.org/tools-listing .
Oh, this nightmarish command line ...
The main problem faced by a specialist when working with such tools is that most of them have a non-trivial user interface, and often this is just a command line and a million incomprehensible parameters. Just this moment contributes to the cultivation of the stereotype that penetration testing is only for geeks.
At NPO Echelon, we were able to solve this problem and make a product that allows us to carry out comprehensive security testing without encountering a complicated hacker interface. In the new version of the Scanner-VS security testing complex, a convenient Web-based interface has appeared, allowing, without leaving one working space, to conduct:
- port scanning and identification of network services;
- vulnerability scanning (with and without administrative privileges);
- selection of passwords for various network services;
- search for suitable exploits;
and, of course, create a single report with the results of the audit.
Conducting security tests using the "Scanner-VS"
To demonstrate the implementation of comprehensive security testing, we will review the process of analyzing the Metasploitable virtual machine 2
Download "Scanner-VS" from USB-drive and the main window opens:
')
We create a project within which tasks are already associated with the corresponding phases of security testing. We consistently scan ports, vulnerabilities, passwords and exploits, and get the big picture:
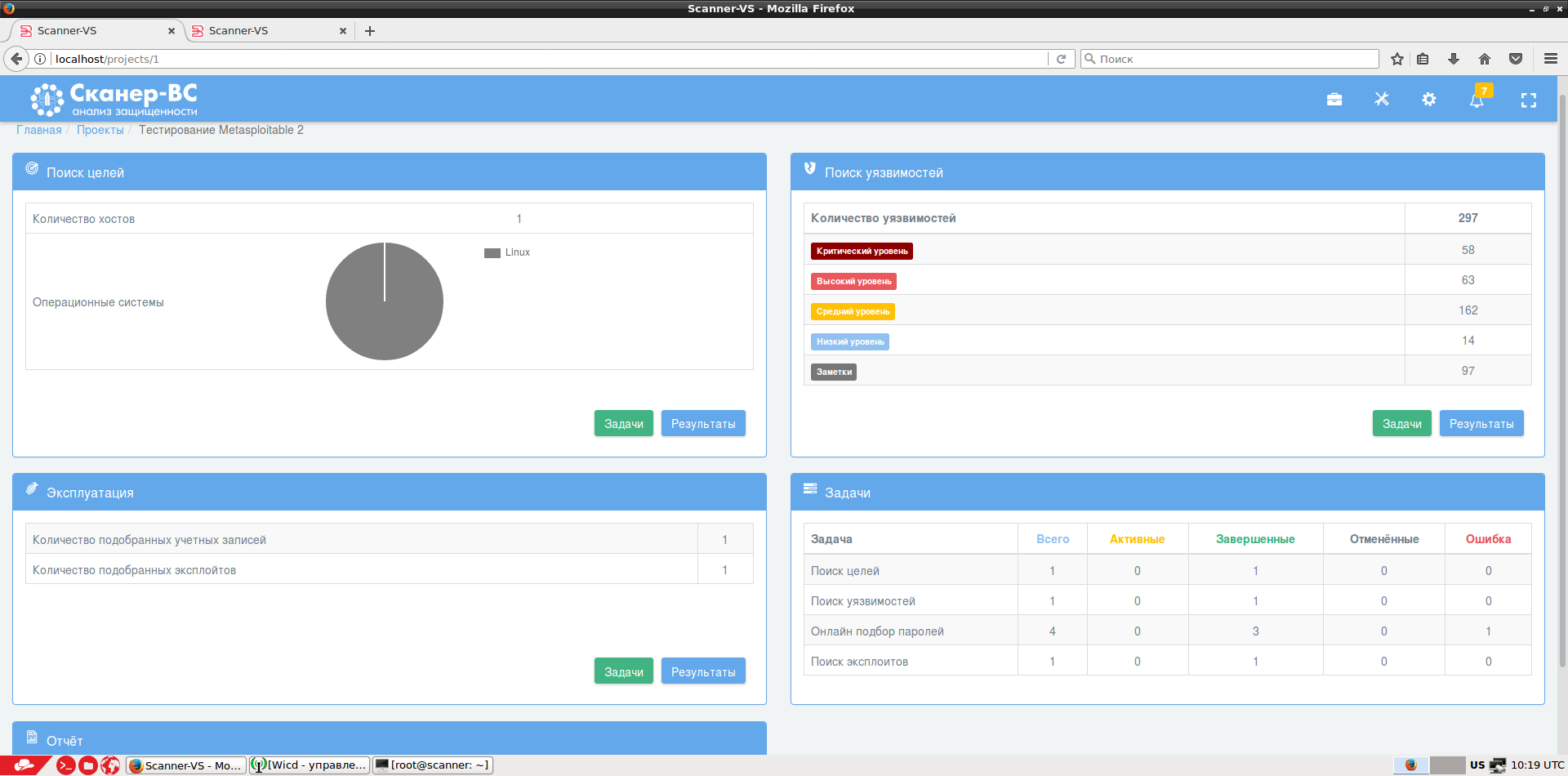
Corresponding results are available within each phase.
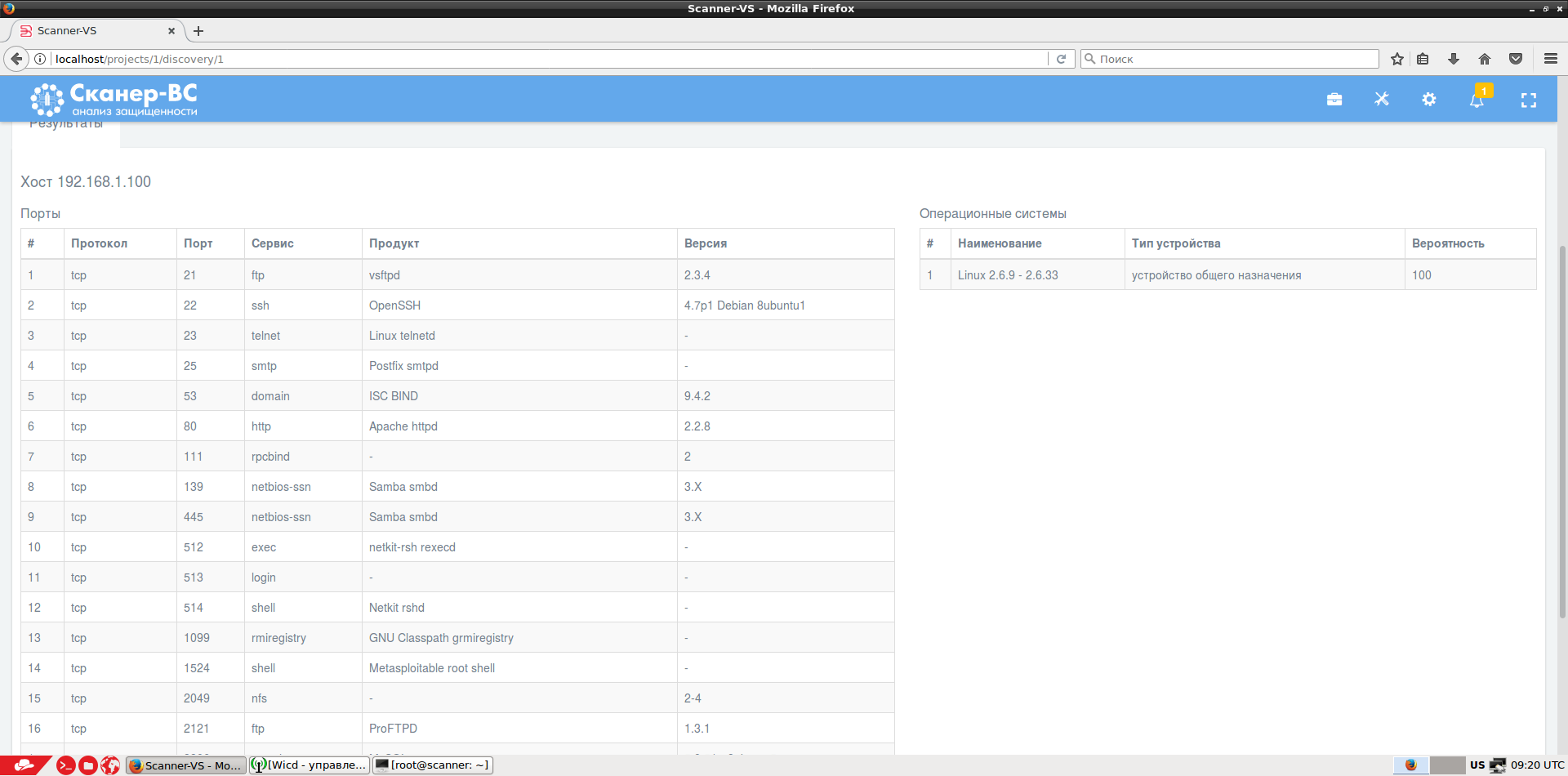
Port scan:
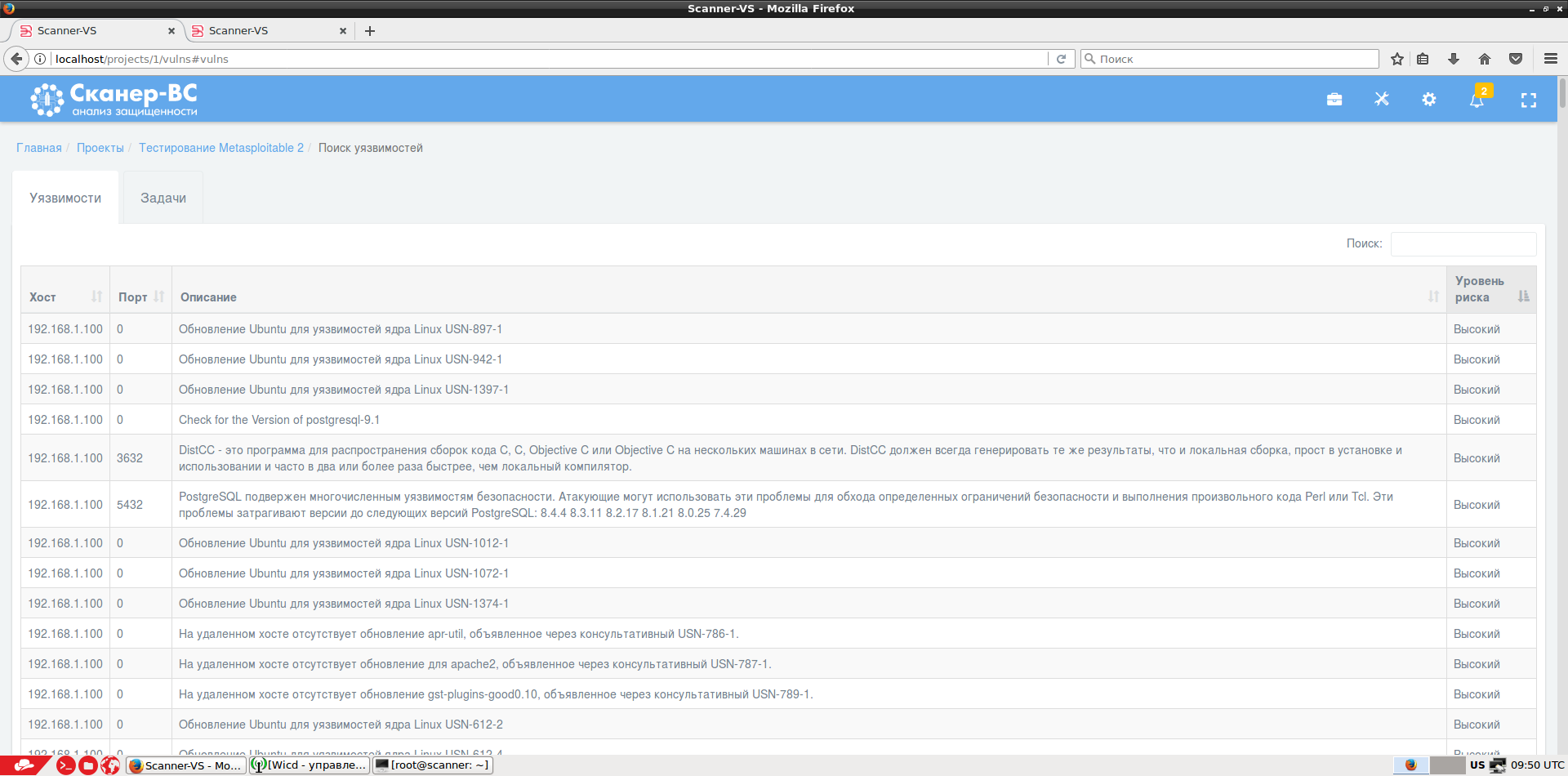
Vulnerability scanning using ready-made policies or your own. It is worth noting that the vulnerability database is updated weekly and contains plug-ins to identify vulnerabilities in domestic GIS. We also support the Threat Data Bank of the FSTEC of Russia .
Selection of suitable exploits from Metasploit Framework. Possible as a rigorous search for the service version, and lax for its type.
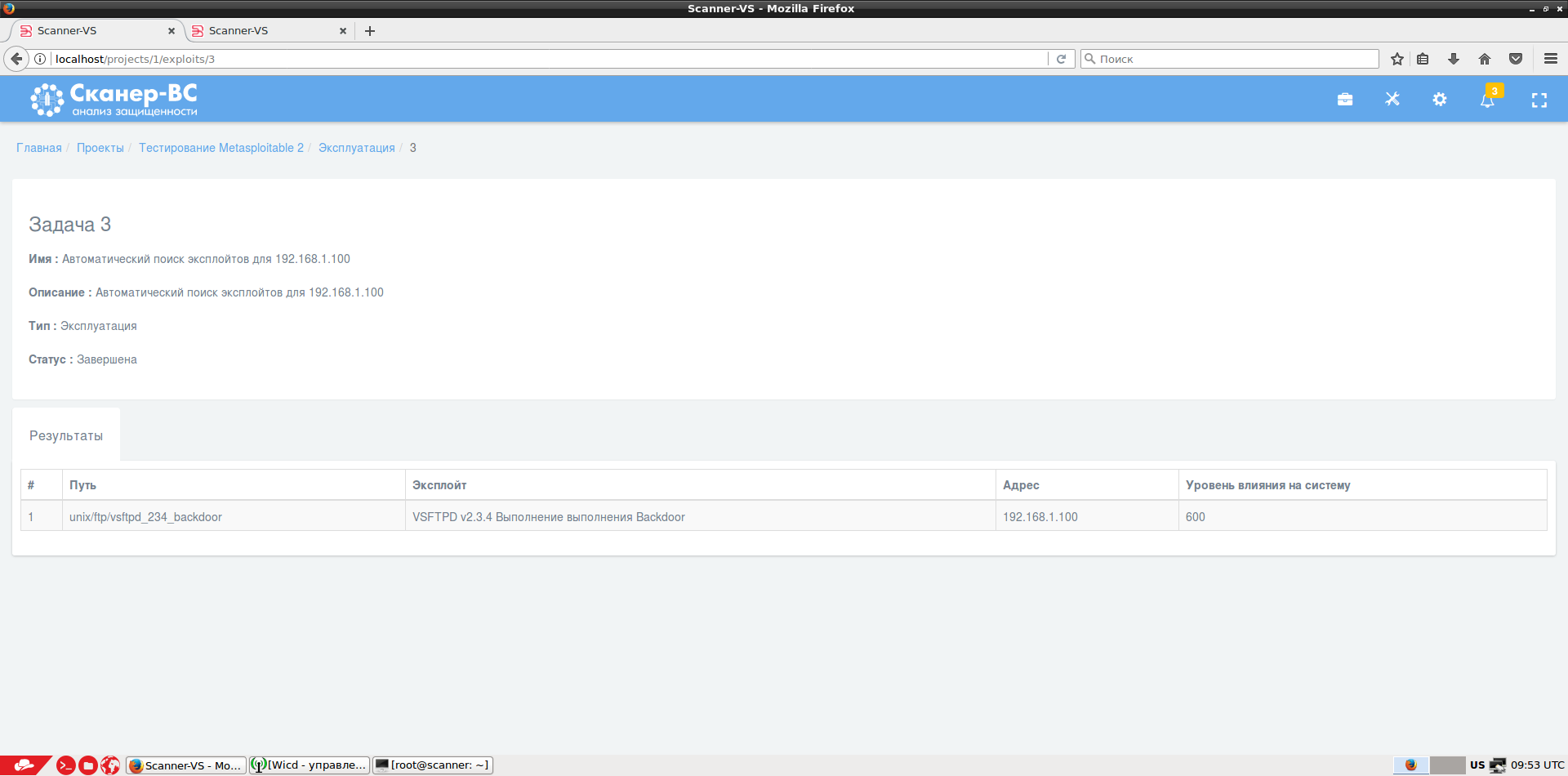
Selection of passwords is carried out to various network services. In this case, you can use both your own user / password sets, and built-in lists containing the most common options.
The results of each task are stored in a database, and a final report is generated on their basis.
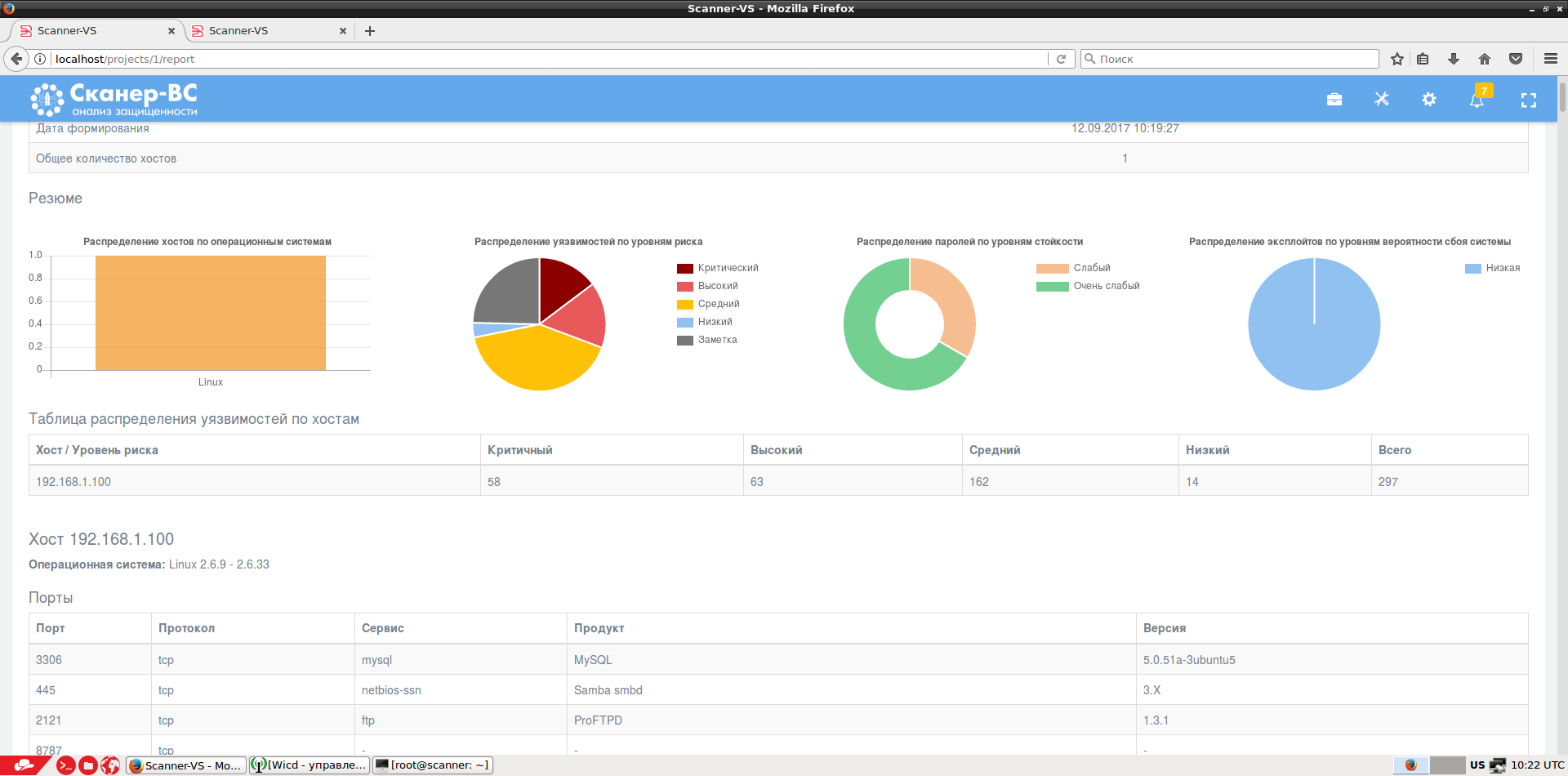
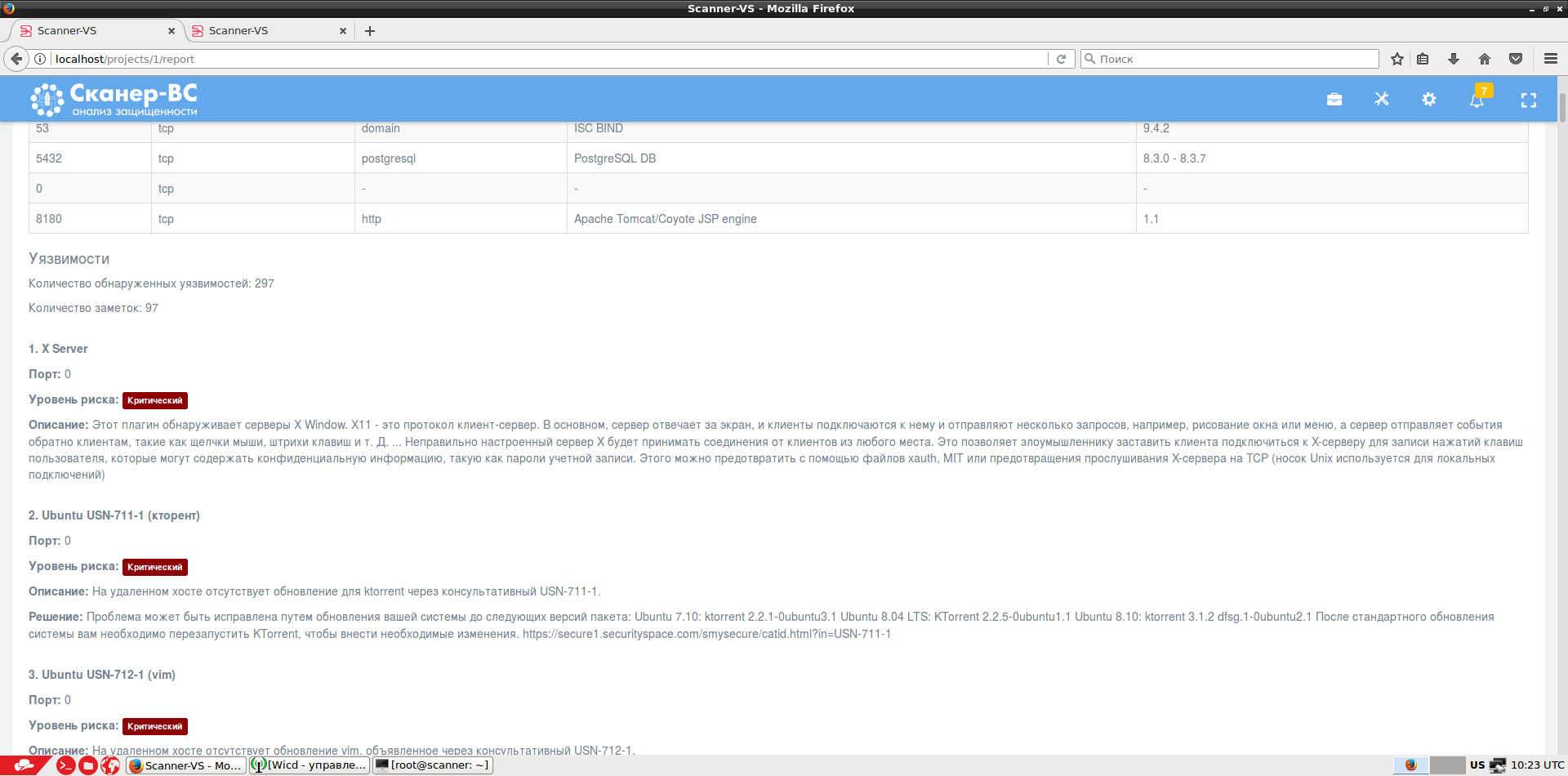
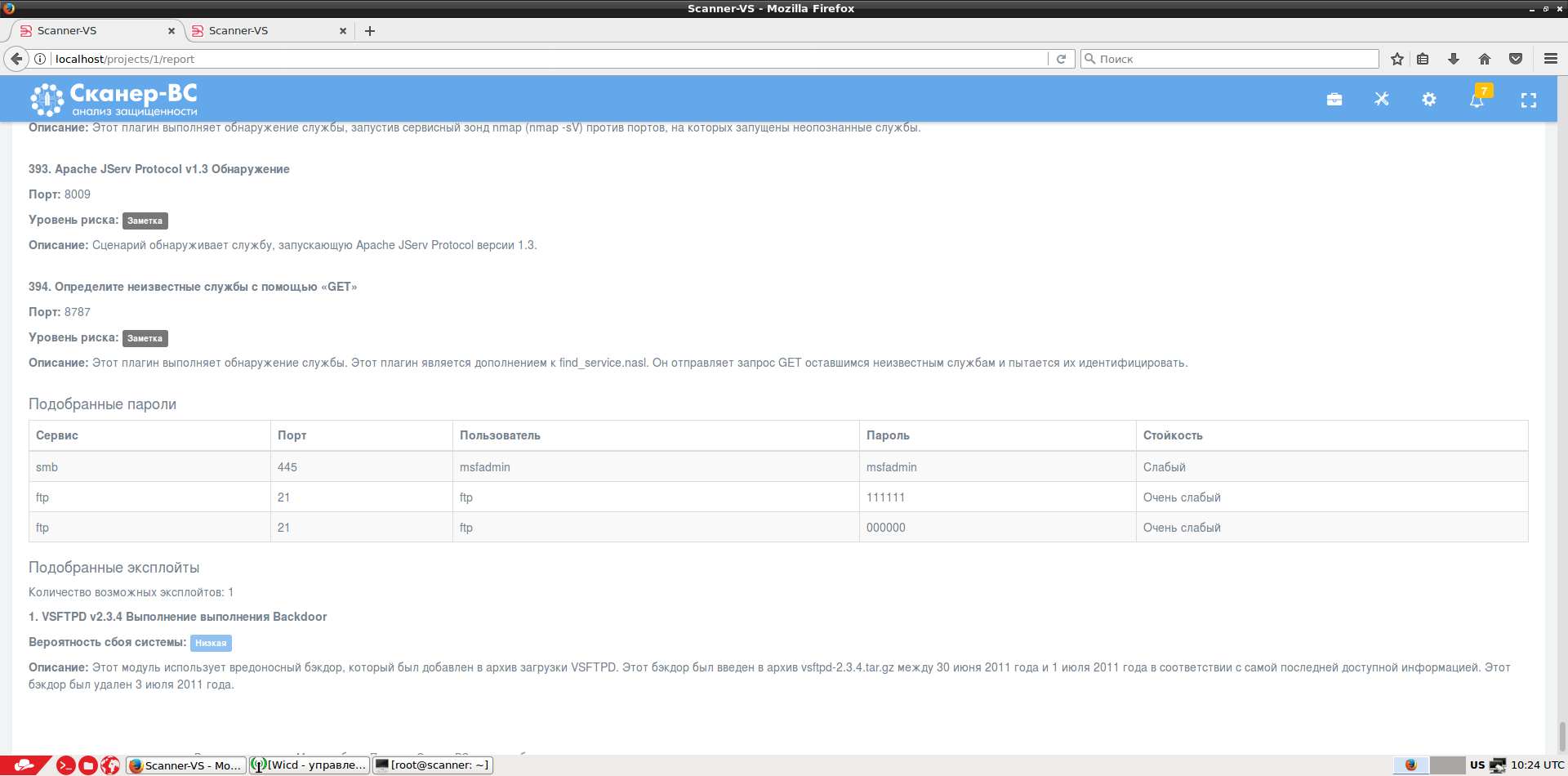
Since Scanner-VS is built on the basis of Kali Linux, all standard utilities from this assembly of hacking tools are available to the user. The following tools were also used to evaluate the effectiveness of information security tools:
- security analysis of Astra Linux configuration;
- Windows update level analysis
- check summation;
- search for residual information;
- analysis of used software and hardware;
- guaranteed destruction of information on the disk.
In order not to further slide into direct advertising of our development, all those who are interested, try our solution in action, we invite you to visit the site http://scaner-vs.ru and download the latest version of the solution for testing .
Literature and useful sources of information
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/337776/
All Articles