VMware vSAN 6.6.1 ─ one more step to perfection
In the version of vSAN 6.6.1, which was released in July of the current year, some new options were added to those that appeared several months ago in the vSAN 6.6 release. In general, the hyper-convergent infrastructure (HCI) vSAN has received several important additions and is now characterized by even lower maintenance costs.

In this article, we will look at the components of the HCI in its latest presentation ─ new processors, the updated structure of vSAN 6.6.1, the new integrated vSphere Update Manager (VUM), as well as analytics and security tools.
Intel Xeon Scalable Processors ─ new vSAN engine
')
In early July of this year, Intel officially unveiled its new Xeon Scalable processor series.
In the application plan, the company notes that “now is a great time to move from traditional distributed infrastructure to hyper-convergent computing and data storage with these processors and VMware vSAN systems.
The main goal that VMware and Intel have set for themselves with new hardware is to help companies reduce the traditional complexity and cost of the inherited IT infrastructure.
Hyper-converged IT infrastructures are faster and more cost-effective than legacy systems. They fundamentally change the approach to data storage and building network solutions, providing users with more opportunities at lower prices and better management for the most demanding enterprise applications. vSAN has also been tested with these latest Intel innovations.
When deploying HCI using new Intel Optane SSDs and new server platforms, customers can get up to 2.5 times more virtual machines (VMs) in a cluster compared to previous generations of Intel Xeon processors and vSAN systems.
These results were obtained in independent testing conducted by the Evaluator Group. They show lower prices and better return on investment (ROI). A full report can be obtained after registration here . The basics of it are below.
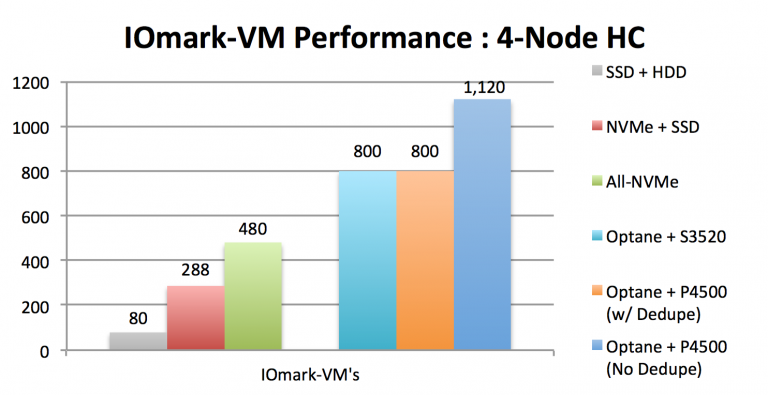
Virtual machine performance comparison in 4-node hyperconvergent infrastructure
The three left columns in the diagram refer to the previous generation of servers that used the E5-2600 v4 Intel Xeon processor. The three right-hand columns show an increase in performance during the transition to the Xeon Scalable Processors, the new generation SSD and VMware vSAN version 6.6.
The information storage systems segment is one of the fastest growing in IT today. More and more organizations are not only increasing the processing power of their servers, but also modernizing storage systems, switching to a secure hyper-convergent infrastructure.
According to VMware storage systems manager Michael Haag, in his blog on the company's website, "With the new Intel Xeon Scalable platform, this transition represents the largest update of the Intel Xeon platform in the last ten years."
New ideas from Intel provide current and future customers of vSAN systems with the following key benefits.
1. Scaling for better performance in the future.
2. Use without risk with the largest selection of HCI platforms.
3. Reducing the cost of corporate IT with a rapid return on investment. The virtual machine node now costs 2.5 times less than on previous infrastructures. It consumes less electricity with greater efficiency and can be placed on a smaller area due to the increased density of hardware.
4. Confident deployment of First Intel Select Solution. The new solution provides the fastest way to transform infrastructure, offering proven configurations to reduce complexity and investment. Intel Select Solutions are available for VMware vSAN as one of the first new generation solutions.
vSAN 6.6.1
At the end of July, VMware vSphere 6.5 Update 1 became available to clients. In vSAN 6.6.1, three new key features appeared:
- Integration with VMware vSphere Update Manager (VUM);
- Performance Diagnostics tool in vSAN Cloud Analytics;
- Expansion of Storage Device Serviceability.
In addition, new licenses have appeared, making vSAN Enterprise more accessible to IT infrastructures ROBO (Remote Office / Branch Office) and VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure).
New integrated vSphere Update Manager (VUM)
VMware vSphere administrators will welcome the new integrated vSphere Update Manager (VUM) update tool, which greatly simplifies and automates the patching and upgrading of vSphere clusters. In previous versions, administrators had to perform many operations manually.
Before upgrading the software, it was necessary to check the hardware compatibility (such as SAS, SATA I / O controllers and NVMe devices) with the new version of vSphere and vSAN. Previously, this was a manual process performed using the VMware Compatibility Guide software module.
Now VUM automatically finds and integrates information from the VMware Compatibility Guide and the vSAN Release Catalog with information about the currently installed release of the ESXi hypervisor. VUM also identifies new drivers for Dell, Fujitsu, Lenovo and Supermicro hardware.
This new VUM extension makes it easier to support newer versions of vSphere and vSAN; reduces risks by helping to ensure that every host in the cluster is working and has the same structure as the others. From an administrator’s point of view, VUM eliminates the time-consuming process of manually upgrading each host.
In fact, VMware decided to integrate VUM into vSAN for the sole purpose ─ to ensure the simplicity of the upgrade. As a result, the installation of updates for vSAN and version control not only became processes fully integrated into vSAN, but the VUM process itself was greatly simplified.

VUM High Level Architecture
Now vSAN versions 6.6.1 and later provides an automated "seamless" update process, while ensuring that the vSAN cluster is updated with the most recent software. The first step uses the vSAN Build Recommendation Engine. After a successful login, vSAN will produce a core group of recommended updates for each vSAN cluster.
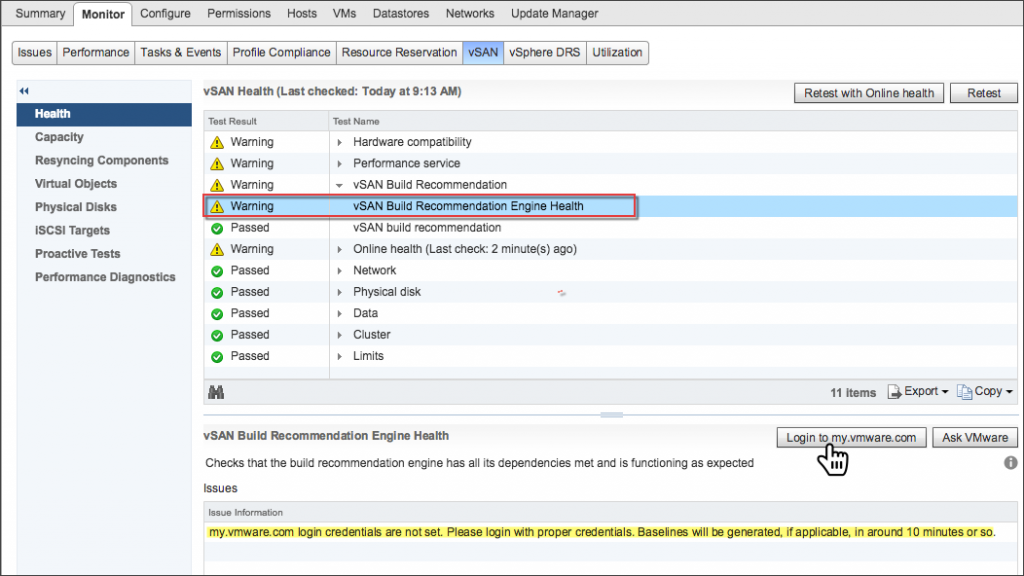
Recommendation for vSAN operation
After checking the VMware Compatibility Guide and vSAN Release Catalog, the Update Manager will find an available recommended update.

Example: vSAN Baseline identified the ESXi host as not matching the profile.
To update the vSAN cluster, simply use one of the Update Manager features. The corresponding "wizard" offers several options for configuring the update.
- you can select specific hosts and clusters;
- You can perform the update immediately or set a time;
- You can specify the support mode (Specify Maintenance Mode) ─ assign parameters for virtual machines, media processing and ESXi.
After selecting the desired options, Update Manager automatically updates each host.
Thus, vSAN 6.6.1 with VUM integration greatly simplifies the process of managing updates and patches for a cluster of vSAN groups.
For the first time, IT specialists can manage the entire information center, ─ including storage, ─ using a software-defined approach, where changes are achieved through the user interface, and not changes in hardware configuration.
Performance Diagnostics has been added to vSAN Cloud Analytics
The latest release extends the capabilities of vSAN Cloud Analytics, which appeared earlier in vSAN 6.6. First of all, it concerns the new Performance Diagnostics, which analyzes the performance of a given vSAN cluster as compared to the previous benchmarks.
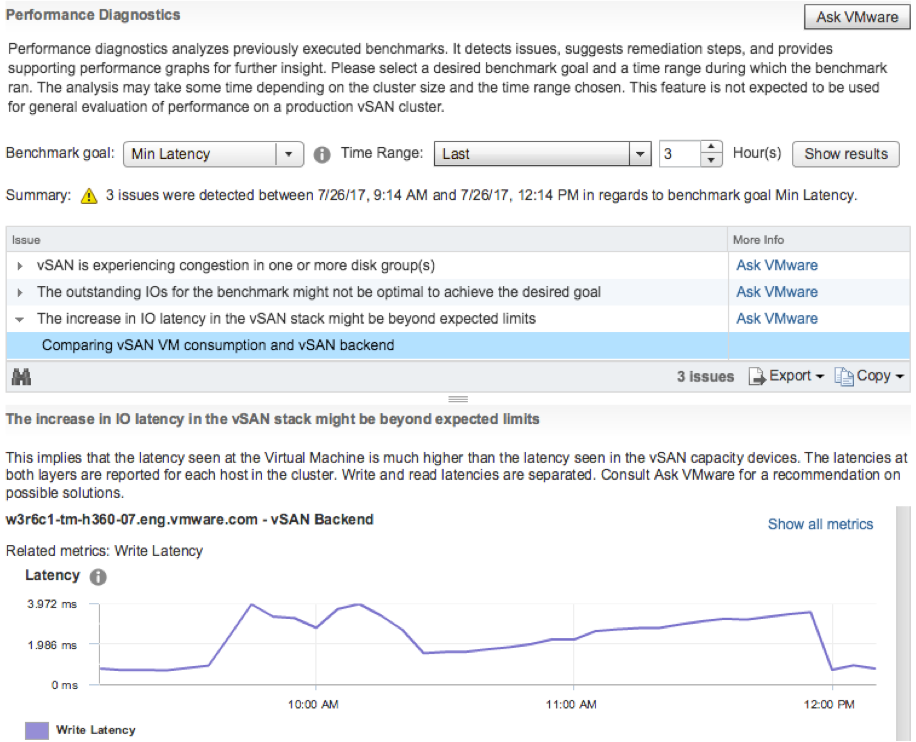
Performance Diagnostic Tool
Administrators can select the desired option — for example, maximum bandwidth or minimum latency, as well as set a specific range of comparison times. However, this feature requires the user to join the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) and vSAN Performance Service.
After that, administrators can manage the HCIBench assessment tests and view detailed test results in Performance Diagnostics, where the relevant diagrams are supported.
The accompanying VMware Ask tool provides access to relevant VMware Knowledge Base articles that contain additional information. These guidelines help administrators optimize cluster performance, understand the impact of a particular choice of hardware, and perform faster troubleshooting if performance problems occur.
HCI Security in software-defined repositories
In her blog on the VMware website, Anita Kibunguchy gives the following examples.
A certain financial company recently reported that it has been experiencing up to 10 thousand attempts at unauthorized access to its systems on a daily basis. Hospitals talk about the need to respect the safety of individual patient data. Another company said it physically destroys the hard-drives that have been used to ensure that unencrypted data will not be inadvertently missed.
The security domain was not previously closely related to hyperconvergent infrastructures. However, 39% of respondents in the ESG survey believe that security problems will appear here in 2017 and will make them pay attention. In the new release, VMware vSAN software implements encryption, which makes HCI well suited for building a secure IT environment.
According to the Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain (a company's own structure for identifying and preventing cyber attacks), many attacks are directed at endpoints, then moving through the organization's IT infrastructure to servers in order to gain access to corporate data.
This poses a serious risk of information security in HCI systems, creating the need to encrypt data in the system core for maximum security. There are a number of advantages to encrypting data directly in their source.
- An additional level of security for distributed organizations that typically work with third companies instead of maintaining their own staff.
- Simplified storage of media data ─ there is no need for their physical destruction.
- No need to waste time reformatting data, since all their types can be encrypted
The easiest way to achieve static data encryption in existing HCI solutions is to use Self-Encrypting Drive (SED). However, there are some limitations.
- First of all, it is their high cost and low payback.
- Implementation of SED can be problematic due to the need to comply with a number of requirements of compatibility with the law.
- Certain risks ─ the entire disk has to be replaced if one of its sections fails. In addition, the principles of building SED make it difficult to study.
- Practical management of SED is relatively difficult.
VMware vSAN has no SED restrictions. This is a software-defined infrastructure. Within its framework, in a single solution on the industrial standard of x86 systems, computing, data storage, network, and information services are easily combined.
ESG notes that VMware solutions are operationally efficient, less complicated than traditional system types, and easier to manage. According to the ESG study, the benefits of deploying a hyperconvergent solution are as follows:
- 22% of organizations reported lower TCO values as the main benefit of deploying such a solution.
- 26% noted less deployment time
- 24% reported improved service and support, as well as scalability.
- 23% as a benefit, noted the simplification of IT infrastructure management as a benefit
VMware vSAN offers native encryption for both virtual machines and physical hardware. No need for sed. The solution can be deployed on existing or new storage devices.
Security is built into the core of the system, at the level of the hypervisor, and not within the VM or hardware. This maximizes protection. Management is also simplified, since it is carried out at the host level.
ESG analysts also noted that vSAN ─ "a clear solution, for organizations that are looking for safer, faster, and more easily managed information centers, should explore the capabilities of VMware vSAN."
For many customers, VMware vSAN is the first hyperconvergent solution in their IT history. At the same time, native encryption is one of the main elements to consider, ─ both in terms of the cost of HCI and the manageability of the entire corporate IT infrastructure.
Storage Reliability
To help simplify hardware maintenance, vSphere includes plug-ins that provide enhanced control and information about physical storage devices connected to local controllers on the server.
As practice shows, this feature is especially useful for vSAN infrastructure. For example, through these plugins, the local location of the required drive in the server chassis can be shown to simplify its administration and maintenance.
vSAN 6.6.1 further expands this option, not only determining the location of a particular drive, but also making its indicator blink to help find its physical location. As a result, the administrator visually identifies the device to which attention must be paid and appropriate measures taken.

This feature seems to be a small service supplement, but it significantly reduces the maintenance time of storage devices and the risk of human error. The feature also works in RAID arrays, and is currently supported on generic HPE DL and ML servers with a Gen 9 controller.
New vSAN licensing for ROBO and VDI
New licensing options concern ROBO (Remote Office / Branch Office) and one of the environments for Horizon VDI. vSAN Enterprise for ROBO includes the use of its own encryption tools and stretched clusters in the “per virtual machine” pricing model in small deployments. These extensions are a supplement to the VMware HCI Kit, which was released earlier this year. It includes simple configuration, vSphere and vSAN licenses.
Summing up this brief review, it is worth emphasizing two aspects once again. vSAN 6.6.1 further simplifies the lifecycle management of hardware and software for the hyper-converged IT infrastructure. New features further reduce operating costs.

In this article, we will look at the components of the HCI in its latest presentation ─ new processors, the updated structure of vSAN 6.6.1, the new integrated vSphere Update Manager (VUM), as well as analytics and security tools.
Intel Xeon Scalable Processors ─ new vSAN engine
')
In early July of this year, Intel officially unveiled its new Xeon Scalable processor series.
In the application plan, the company notes that “now is a great time to move from traditional distributed infrastructure to hyper-convergent computing and data storage with these processors and VMware vSAN systems.
The main goal that VMware and Intel have set for themselves with new hardware is to help companies reduce the traditional complexity and cost of the inherited IT infrastructure.
Hyper-converged IT infrastructures are faster and more cost-effective than legacy systems. They fundamentally change the approach to data storage and building network solutions, providing users with more opportunities at lower prices and better management for the most demanding enterprise applications. vSAN has also been tested with these latest Intel innovations.
When deploying HCI using new Intel Optane SSDs and new server platforms, customers can get up to 2.5 times more virtual machines (VMs) in a cluster compared to previous generations of Intel Xeon processors and vSAN systems.
These results were obtained in independent testing conducted by the Evaluator Group. They show lower prices and better return on investment (ROI). A full report can be obtained after registration here . The basics of it are below.

Virtual machine performance comparison in 4-node hyperconvergent infrastructure
The three left columns in the diagram refer to the previous generation of servers that used the E5-2600 v4 Intel Xeon processor. The three right-hand columns show an increase in performance during the transition to the Xeon Scalable Processors, the new generation SSD and VMware vSAN version 6.6.
The information storage systems segment is one of the fastest growing in IT today. More and more organizations are not only increasing the processing power of their servers, but also modernizing storage systems, switching to a secure hyper-convergent infrastructure.
According to VMware storage systems manager Michael Haag, in his blog on the company's website, "With the new Intel Xeon Scalable platform, this transition represents the largest update of the Intel Xeon platform in the last ten years."
New ideas from Intel provide current and future customers of vSAN systems with the following key benefits.
1. Scaling for better performance in the future.
2. Use without risk with the largest selection of HCI platforms.
3. Reducing the cost of corporate IT with a rapid return on investment. The virtual machine node now costs 2.5 times less than on previous infrastructures. It consumes less electricity with greater efficiency and can be placed on a smaller area due to the increased density of hardware.
4. Confident deployment of First Intel Select Solution. The new solution provides the fastest way to transform infrastructure, offering proven configurations to reduce complexity and investment. Intel Select Solutions are available for VMware vSAN as one of the first new generation solutions.
vSAN 6.6.1
At the end of July, VMware vSphere 6.5 Update 1 became available to clients. In vSAN 6.6.1, three new key features appeared:
- Integration with VMware vSphere Update Manager (VUM);
- Performance Diagnostics tool in vSAN Cloud Analytics;
- Expansion of Storage Device Serviceability.
In addition, new licenses have appeared, making vSAN Enterprise more accessible to IT infrastructures ROBO (Remote Office / Branch Office) and VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure).
New integrated vSphere Update Manager (VUM)
VMware vSphere administrators will welcome the new integrated vSphere Update Manager (VUM) update tool, which greatly simplifies and automates the patching and upgrading of vSphere clusters. In previous versions, administrators had to perform many operations manually.
Before upgrading the software, it was necessary to check the hardware compatibility (such as SAS, SATA I / O controllers and NVMe devices) with the new version of vSphere and vSAN. Previously, this was a manual process performed using the VMware Compatibility Guide software module.
Now VUM automatically finds and integrates information from the VMware Compatibility Guide and the vSAN Release Catalog with information about the currently installed release of the ESXi hypervisor. VUM also identifies new drivers for Dell, Fujitsu, Lenovo and Supermicro hardware.
This new VUM extension makes it easier to support newer versions of vSphere and vSAN; reduces risks by helping to ensure that every host in the cluster is working and has the same structure as the others. From an administrator’s point of view, VUM eliminates the time-consuming process of manually upgrading each host.
In fact, VMware decided to integrate VUM into vSAN for the sole purpose ─ to ensure the simplicity of the upgrade. As a result, the installation of updates for vSAN and version control not only became processes fully integrated into vSAN, but the VUM process itself was greatly simplified.

VUM High Level Architecture
Now vSAN versions 6.6.1 and later provides an automated "seamless" update process, while ensuring that the vSAN cluster is updated with the most recent software. The first step uses the vSAN Build Recommendation Engine. After a successful login, vSAN will produce a core group of recommended updates for each vSAN cluster.

Recommendation for vSAN operation
After checking the VMware Compatibility Guide and vSAN Release Catalog, the Update Manager will find an available recommended update.

Example: vSAN Baseline identified the ESXi host as not matching the profile.
To update the vSAN cluster, simply use one of the Update Manager features. The corresponding "wizard" offers several options for configuring the update.
- you can select specific hosts and clusters;
- You can perform the update immediately or set a time;
- You can specify the support mode (Specify Maintenance Mode) ─ assign parameters for virtual machines, media processing and ESXi.
After selecting the desired options, Update Manager automatically updates each host.
Thus, vSAN 6.6.1 with VUM integration greatly simplifies the process of managing updates and patches for a cluster of vSAN groups.
For the first time, IT specialists can manage the entire information center, ─ including storage, ─ using a software-defined approach, where changes are achieved through the user interface, and not changes in hardware configuration.
Performance Diagnostics has been added to vSAN Cloud Analytics
The latest release extends the capabilities of vSAN Cloud Analytics, which appeared earlier in vSAN 6.6. First of all, it concerns the new Performance Diagnostics, which analyzes the performance of a given vSAN cluster as compared to the previous benchmarks.

Performance Diagnostic Tool
Administrators can select the desired option — for example, maximum bandwidth or minimum latency, as well as set a specific range of comparison times. However, this feature requires the user to join the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) and vSAN Performance Service.
After that, administrators can manage the HCIBench assessment tests and view detailed test results in Performance Diagnostics, where the relevant diagrams are supported.
The accompanying VMware Ask tool provides access to relevant VMware Knowledge Base articles that contain additional information. These guidelines help administrators optimize cluster performance, understand the impact of a particular choice of hardware, and perform faster troubleshooting if performance problems occur.
HCI Security in software-defined repositories
In her blog on the VMware website, Anita Kibunguchy gives the following examples.
A certain financial company recently reported that it has been experiencing up to 10 thousand attempts at unauthorized access to its systems on a daily basis. Hospitals talk about the need to respect the safety of individual patient data. Another company said it physically destroys the hard-drives that have been used to ensure that unencrypted data will not be inadvertently missed.
The security domain was not previously closely related to hyperconvergent infrastructures. However, 39% of respondents in the ESG survey believe that security problems will appear here in 2017 and will make them pay attention. In the new release, VMware vSAN software implements encryption, which makes HCI well suited for building a secure IT environment.
According to the Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain (a company's own structure for identifying and preventing cyber attacks), many attacks are directed at endpoints, then moving through the organization's IT infrastructure to servers in order to gain access to corporate data.
This poses a serious risk of information security in HCI systems, creating the need to encrypt data in the system core for maximum security. There are a number of advantages to encrypting data directly in their source.
- An additional level of security for distributed organizations that typically work with third companies instead of maintaining their own staff.
- Simplified storage of media data ─ there is no need for their physical destruction.
- No need to waste time reformatting data, since all their types can be encrypted
The easiest way to achieve static data encryption in existing HCI solutions is to use Self-Encrypting Drive (SED). However, there are some limitations.
- First of all, it is their high cost and low payback.
- Implementation of SED can be problematic due to the need to comply with a number of requirements of compatibility with the law.
- Certain risks ─ the entire disk has to be replaced if one of its sections fails. In addition, the principles of building SED make it difficult to study.
- Practical management of SED is relatively difficult.
VMware vSAN has no SED restrictions. This is a software-defined infrastructure. Within its framework, in a single solution on the industrial standard of x86 systems, computing, data storage, network, and information services are easily combined.
ESG notes that VMware solutions are operationally efficient, less complicated than traditional system types, and easier to manage. According to the ESG study, the benefits of deploying a hyperconvergent solution are as follows:
- 22% of organizations reported lower TCO values as the main benefit of deploying such a solution.
- 26% noted less deployment time
- 24% reported improved service and support, as well as scalability.
- 23% as a benefit, noted the simplification of IT infrastructure management as a benefit
VMware vSAN offers native encryption for both virtual machines and physical hardware. No need for sed. The solution can be deployed on existing or new storage devices.
Security is built into the core of the system, at the level of the hypervisor, and not within the VM or hardware. This maximizes protection. Management is also simplified, since it is carried out at the host level.
ESG analysts also noted that vSAN ─ "a clear solution, for organizations that are looking for safer, faster, and more easily managed information centers, should explore the capabilities of VMware vSAN."
For many customers, VMware vSAN is the first hyperconvergent solution in their IT history. At the same time, native encryption is one of the main elements to consider, ─ both in terms of the cost of HCI and the manageability of the entire corporate IT infrastructure.
Storage Reliability
To help simplify hardware maintenance, vSphere includes plug-ins that provide enhanced control and information about physical storage devices connected to local controllers on the server.
As practice shows, this feature is especially useful for vSAN infrastructure. For example, through these plugins, the local location of the required drive in the server chassis can be shown to simplify its administration and maintenance.
vSAN 6.6.1 further expands this option, not only determining the location of a particular drive, but also making its indicator blink to help find its physical location. As a result, the administrator visually identifies the device to which attention must be paid and appropriate measures taken.

This feature seems to be a small service supplement, but it significantly reduces the maintenance time of storage devices and the risk of human error. The feature also works in RAID arrays, and is currently supported on generic HPE DL and ML servers with a Gen 9 controller.
New vSAN licensing for ROBO and VDI
New licensing options concern ROBO (Remote Office / Branch Office) and one of the environments for Horizon VDI. vSAN Enterprise for ROBO includes the use of its own encryption tools and stretched clusters in the “per virtual machine” pricing model in small deployments. These extensions are a supplement to the VMware HCI Kit, which was released earlier this year. It includes simple configuration, vSphere and vSAN licenses.
Summing up this brief review, it is worth emphasizing two aspects once again. vSAN 6.6.1 further simplifies the lifecycle management of hardware and software for the hyper-converged IT infrastructure. New features further reduce operating costs.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/336760/
All Articles