Why blockchain is not such a bad technology
About CryptoNote, Lightning Network, Plasma, PoS and others
The author of the article is Alexey Malanov, an expert in the development of anti-virus technologies at Kaspersky Lab.
 We recently published an article, “Six Myths about the Blockchain and Bitcoin, or Why It Is Not Such an Effective Technology . ” The article was welcomed by the Habra community and was actively discussed in the comments, which clearly indicates a great interest in this topic.
We recently published an article, “Six Myths about the Blockchain and Bitcoin, or Why It Is Not Such an Effective Technology . ” The article was welcomed by the Habra community and was actively discussed in the comments, which clearly indicates a great interest in this topic.
')
It was among the commentators and a few outraged. Someone was indignant: “Why are you writing the obvious, because this is all well known to everyone for a long time?” It is difficult to argue on this point. But there were those who wrote in the key: “All this is not true, in fact, all problems have been solved there and there”.
In the near future, we plan to release two more articles in which we analyze and criticize certain aspects related to the blockchain theme. In order not to upset blockchain-adepts and Bitcoin-optimists, we decided that, for a change, we should write an optimistic article out of turn. We will consider the same myths as last time, but only from the perspective of how these problems are solved.
Acquaintance with the original, though not necessarily, but highly desirable for a better understanding of why we chose such myths.
The last article was about Bitcoin and its blockchain. We chose a specific cryptocurrency so that the conversation would be more specific and not be full of dozens of reservations and digressions. For this we got from commentators who have heard about other cryptocurrencies.
It is important to remind that blockchain and Bitcoin technology are not the same thing. Bitcoin technology combines several others: the principle of money transfer, cryptographic principles, blockchain itself, the concept of consensus, the principle of Proof-of-Work, ad hoc network, the motivation of participants, Merkle trees for organizing transactions, principles of transparency, hashing and others.
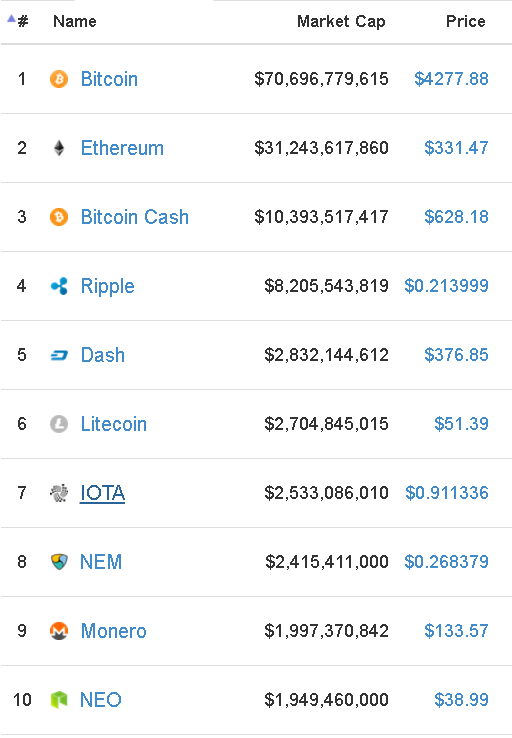
But it is also true that bitcoin-like blockchains, based on Proof-of-Work, dominate the market. The total capitalization of cryptocurrency is $ 155 billion (as of August 26, 2017). Of these, only in the first ten PoW-blockchains account for $ 120 billion. And below, many currencies are simply direct Bitcoin clones with a conceptually identical blockchain.
But the devil is in the details. This time we will go to the trick and we will not write about the blockchain, but about various add-ons and improvements to the "altcoins". We will not (almost) touch on non-monetary use of the blockchain, because otherwise the topic becomes immensely broad.
Efficiency is the ratio of useful work to the effort expended. In the case of payment systems, carrying out transactions can be considered as useful work, and it is reasonable to consider the amount of "iron" and consumed electricity as expended efforts.
Recall that the bandwidth of Bitcoin - 7 transactions per second for all participants, and the second capitalization of the Ethereum currency - 15 simple money transfers or 3-5 executions of smart contracts per second. In addition, the principle of Proof-of-Work ensures that the consumption of electricity and the amount of "iron" will grow until the mining is no longer profitable , and this increase in overhead costs will not be associated with the quality of services provided.
Those who convince us: “Yes, Bitcoin doesn’t need many transactions per second, it has a different purpose”, they are wrong. The topic has long been bothering experts, and this is what they came up with.
If we drop everything and leave only the essence, then the Lightning Network works like this. First, network members set up a “channel”: they deposit a deposit in the main Bitcoin network. And then they begin to exchange payments directly, in isolation from the rest of the network - at any speed.
When the channel is no longer needed, the participants write the result of “communication” to the public blockchain and take the deposit. If one of the participants in the process of communication, while no one has seen the outsider, played by the rules, the other participant has the opportunity to “present” this to the blockchain, and the offender will lose the bail.
Potentially, such a scheme allows participants to make transactions at any speed convenient to them. But there are subtleties. You need to implement everything on the basis available in Bitcoin. Including for the sake of the Lightning Network, the rules were even recently twisted (the so-called SegWit). In addition to technical problems, uncertainties remain in the field of game theory. For example, there is no certainty that all participants benefit from playing by the rules. Suddenly, someone wants to lose the bail, but get something more in return?
Anyway, according to optimistic forecasts, the Lightning Network can be launched as early as 2017, and then millions of transactions per second can be performed in the “slow blockchain”.
The blockchain is big, but it has ceased to be a problem when at least some trust has appeared on the network. The fact is that you do not need to download and check it all to make sure that you are not deceived.
First, there are web wallets and web services that do all the work. In these services you see what happens to your balance, and see how some kind of transfer flies to you. It is unlikely that the public service will deceive you, right? And if no one complains about it, then it can be considered as a reliable source of information and enjoy it.
The advantage over traditional payment systems is that if one web wallet closes, then you simply switch to another, because everyone has the same base. For comparison: if your classic bank suddenly faces a failure - the Internet bank will fall or there will be problems in processing, then you will need another bank card or cash.
And secondly, there is a more advanced way (and more reliable), which Satoshi himself wrote about in 2008. You can download and check only block headers, not the blocks themselves, as well as proof of the correctness of transactions that are directly related to you.
The fact is that transactions are packaged in an elegant structure: the Merkle tree .

To check the inclusion of the Tx3 transaction in the blockchain, you only need to know Tx3, Hash2, Hash01 and all block headers
This means that a small amount of data (Merkle's proof) helps to make sure that the transaction really exists in the blockchain. That is, the full nodes of the network considered it correct.
Further, if there are many random nodes in the network to which you connect, they report that the block headers are exactly like that, then you can assume with a large degree of confidence that everything is correct, without fakes.
Headings of all blocks now occupy only 40 MB, which is already quite compact. But you can save even more: it is not necessary to keep the headers of all transactions in the entire history - it is enough to start from a certain point.
Scalability means that by adding resources to the system, you increase its performance. So, the classic blockchain is absolutely not scalable - the increase in resources does not affect the system bandwidth.
It's also funny that the classic blockchain does not scale not only up, but also down. That is, according to the same principles, it is impossible to build a sufficiently small system to solve local problems, because it will be vulnerable to “ Attack 51% ”.
But here is what just recently suggested by Joseph Poon (the inventor of the Lightning Network from the first myth) and Vitalik Buterin (the ideological inspirer of the Ethereum network).
Plasma is a way to make blockchain blockchains. The concept is similar to the Lightning Network - someone pledges to the main Ethereum network and begins to communicate with other clients independently and independently, independently monitoring the implementation of the rules of their smart contract and the general rules of Ethereum. A smart contract is a mini-program for working with money and wallets, a key feature of Ethereum.
From time to time the results of separate communication are recorded in the main network. As in the case of the Lightning Network, all participants monitor the implementation of the rules of the smart contract and “complain” if anything happens.
Interestingly, in such a separate mini-network, “budding” can be repeated.
There are still many open questions. For example, is the owner of the main branch responsible for the implementation of the rules by those who branched off from him? And vice versa? These are all interesting problems from game theory. So far the proposal is only a draft, but one thing is clear: if the conceived concept can be implemented, the blockchain's scalability problem will remain a thing of the past.
Proof-of-Work is by far the most popular principle of consensus among cryptocurrencies. In it, a new block is created after lengthy calculations — this is necessary solely so that you cannot quickly rewrite the financial history. Miners of PoW networks burn electricity, and the number of burned megawatts is not governed by considerations of security or common sense, but only by economics: power is increased as long as it is still profitable at the current price of cryptocurrency.
But there is an alternative approach to the allocation of the right to create blocks - Proof-of-Stake. In this concept, the probability to create a block, and therefore the right to receive a reward (in the form of commissions or emitted currency) does not depend on how much effort you put on (burned electricity), but on how much currency you have in this system.
If you have a third of all coins, then a pseudo-random algorithm with a probability of one third will contact you with a request to form a block. This principle also motivates participants to behave according to the rules, because the more currency you have, the more interested you are for the network to function properly.
But there are thin places. For example, imagine that you are buying now empty wallets for a pittance, on which just a year ago the lion's share of all the money was in total. After that, you can rewrite the financial history from the time when you supposedly were rich. And in this story, you will remain rich, and all other participants will accept your version, because your story is supported by a larger capital than the conventional one.

Pavel Ivanovich Chichikov warmly approves Proof-of-Stake without additional measures of protection
Different implementations solve the described problem in different ways. For example, you can regularly sign with the developer key the correct blocks so that the story cannot be rewritten too deep.
It is important that technical difficulties can be solved. It is nice to see that the most modern and advanced cryptocurrencies abandon the principle of Proof-of-Work.
But there is a more radical method. Allow only trusted participants to create blocks. For example, 10 hospitals can write in the blockchain epidemiological situation in the city. Each hospital has its own key for signing, we trust hospitals. At the same time, openness will remain - an important property of the blockchain.
Although justice for the sake of PoA most of all destroys the original idea, because in this case the network is essentially centralized and can do without distribution.
At another time, we’ll tell you about networks that perform useful work within the Proof-of-Work: looking for prime numbers of a special type (PrimeCoin), calculating a tertiary protein structure (FoldingCoin), or performing another scientific task related to computing (GridCoin). And the reward for "mining" stimulates to invest more resources in science.
It is not so easy to make changes to the decentralized network protocol. If you are a developer and control the source code, then one of two things: either you can upgrade all clients forcibly, but such a network cannot be considered truly decentralized; or you make changes to the code and must persuade all participants to accept these changes. If a significant part remains against it, then there is a great chance that the community will split, the block chain will be divided into two incompatible ones, and there will already be two currencies.
Sometimes persuasion is painful, because different participants, depending on their role, have different interests. For example, miners are interested in the growth of awards and commissions; users, on the contrary, want to pay less for transfers; Fans don't care about commissions, they want cryptocurrency to become more popular, and tech geeks want technology to add useful innovations.
Splits have already occurred with Bitcoin - they did not agree on a strategy to increase the block size (to get more transactions), and Ethereum did not agree on whether it would be fair to “cancel” the hacking of one investment fund and return the money to depositors. As a result, four of the two currencies.
Usually a vote on the proposals goes like this:

The voting results of various miners on the three proposals for the development of the Bitcoin network. A source
It turns out that only the opinion of miners is taken into account, and the greater the power of the pool, the more votes it has.
At the very least, according to this principle, the protocol is amended.
But it is preparing to release Tezos cryptocurrency, which simplifies the process of amending the protocol, because it is embedded in the currency architecturally. Wherein:
It is assumed that this approach will significantly reduce the intensity of passions and the need for hard forks.
There is a very real possibility that by such changes at some point the majority shareholders will deprive minority shareholders of the right to vote. In a simple way - the rich will rule. The developers themselves believe that this should have a negative impact on the price of the currency and therefore is unlikely to happen. Well, we'll see.
Imagine that you are WikiLeaks and collect donations in bitcoins. Everyone knows your address, they know how much money you have collected, and when you try to exchange this money on the stock exchange for dollars, law enforcement will also know your dollar bill. In other words, there is a problem.
And alone, "launder" the money, which is being monitored, in Bitcoin is impossible. Attempting to scatter money on 10 wallets only leads to the fact that now 10 wallets are associated with you.
In the last article we talked about "mixers". These are anonymous services, which for a fee mix a large amount of money, and it becomes unclear where whose. But using them is inconvenient for a variety of reasons.
First, they came up with a mixer right in the currency. This is how Dash (the former Darkcoin) appeared with the PrivateSend function. It works as follows:
It is not difficult to see that if someone (for example, law enforcement agencies) controls a significant part of the master session, he will be able to track the transfer. Although it is unlikely.
In addition, mixing dirty money with clean money makes all money gray, that is, suspicious. It turns out that gray money should become white, money should be mixed all and always.
And a more reliable approach was invented. You can rightly say that Monero is anonymous.
First, it uses ring signatures to anonymize. A ring signature is an electronic signature that allows one of the group members (called a ring) to sign some message on behalf of the entire group, and it will not be known for certain which of the group members executed the signing. This property allows the sender to cover their own tracks. At the same time, the protocol will still protect against double spending.
Secondly, at the wallet address you cannot see the transaction history and balance, because in Monero you have not only spend spend private to spend money, but also an additional private view key to view receipts to your address.
Well and thirdly, for different senders it is worth generating disposable addresses. For example, money from the mother, "dirty" money and money from the exchange should not be taken at the same address. But this rule has long been recommended even in Bitcoin.
For the sake of justice, we also mention the currency Zcash, anonymity in which is based on other, but no less advanced principles.
Well, a brief overview of the shortcomings turned by talented people into advantages has been completed. But this is not all, because we almost did not write about Ethereum smart contracts, Ripple prospects in the banking sector or cryptocurrency without the IOTA blockchain.
Strictly speaking, the title of this article contained a lie: after all, we were not talking about the blockchain, but about its add-ins. But the advantage of the blockchain is that it inspires people to look for ways to excellence.
The author of the article is Alexey Malanov, an expert in the development of anti-virus technologies at Kaspersky Lab.
 We recently published an article, “Six Myths about the Blockchain and Bitcoin, or Why It Is Not Such an Effective Technology . ” The article was welcomed by the Habra community and was actively discussed in the comments, which clearly indicates a great interest in this topic.
We recently published an article, “Six Myths about the Blockchain and Bitcoin, or Why It Is Not Such an Effective Technology . ” The article was welcomed by the Habra community and was actively discussed in the comments, which clearly indicates a great interest in this topic.')
It was among the commentators and a few outraged. Someone was indignant: “Why are you writing the obvious, because this is all well known to everyone for a long time?” It is difficult to argue on this point. But there were those who wrote in the key: “All this is not true, in fact, all problems have been solved there and there”.
In the near future, we plan to release two more articles in which we analyze and criticize certain aspects related to the blockchain theme. In order not to upset blockchain-adepts and Bitcoin-optimists, we decided that, for a change, we should write an optimistic article out of turn. We will consider the same myths as last time, but only from the perspective of how these problems are solved.
Acquaintance with the original, though not necessarily, but highly desirable for a better understanding of why we chose such myths.
Not about bitcoin
The last article was about Bitcoin and its blockchain. We chose a specific cryptocurrency so that the conversation would be more specific and not be full of dozens of reservations and digressions. For this we got from commentators who have heard about other cryptocurrencies.
It is important to remind that blockchain and Bitcoin technology are not the same thing. Bitcoin technology combines several others: the principle of money transfer, cryptographic principles, blockchain itself, the concept of consensus, the principle of Proof-of-Work, ad hoc network, the motivation of participants, Merkle trees for organizing transactions, principles of transparency, hashing and others.
But it is also true that bitcoin-like blockchains, based on Proof-of-Work, dominate the market. The total capitalization of cryptocurrency is $ 155 billion (as of August 26, 2017). Of these, only in the first ten PoW-blockchains account for $ 120 billion. And below, many currencies are simply direct Bitcoin clones with a conceptually identical blockchain.

But the devil is in the details. This time we will go to the trick and we will not write about the blockchain, but about various add-ons and improvements to the "altcoins". We will not (almost) touch on non-monetary use of the blockchain, because otherwise the topic becomes immensely broad.
Myth 1: The blockchain is slow and inefficient.
Efficiency is the ratio of useful work to the effort expended. In the case of payment systems, carrying out transactions can be considered as useful work, and it is reasonable to consider the amount of "iron" and consumed electricity as expended efforts.
Recall that the bandwidth of Bitcoin - 7 transactions per second for all participants, and the second capitalization of the Ethereum currency - 15 simple money transfers or 3-5 executions of smart contracts per second. In addition, the principle of Proof-of-Work ensures that the consumption of electricity and the amount of "iron" will grow until the mining is no longer profitable , and this increase in overhead costs will not be associated with the quality of services provided.
Lightning network
Those who convince us: “Yes, Bitcoin doesn’t need many transactions per second, it has a different purpose”, they are wrong. The topic has long been bothering experts, and this is what they came up with.
If we drop everything and leave only the essence, then the Lightning Network works like this. First, network members set up a “channel”: they deposit a deposit in the main Bitcoin network. And then they begin to exchange payments directly, in isolation from the rest of the network - at any speed.
When the channel is no longer needed, the participants write the result of “communication” to the public blockchain and take the deposit. If one of the participants in the process of communication, while no one has seen the outsider, played by the rules, the other participant has the opportunity to “present” this to the blockchain, and the offender will lose the bail.
Potentially, such a scheme allows participants to make transactions at any speed convenient to them. But there are subtleties. You need to implement everything on the basis available in Bitcoin. Including for the sake of the Lightning Network, the rules were even recently twisted (the so-called SegWit). In addition to technical problems, uncertainties remain in the field of game theory. For example, there is no certainty that all participants benefit from playing by the rules. Suddenly, someone wants to lose the bail, but get something more in return?
Anyway, according to optimistic forecasts, the Lightning Network can be launched as early as 2017, and then millions of transactions per second can be performed in the “slow blockchain”.
Myth 2: The blockchain is bulky
The blockchain is big, but it has ceased to be a problem when at least some trust has appeared on the network. The fact is that you do not need to download and check it all to make sure that you are not deceived.
Web Wallets
First, there are web wallets and web services that do all the work. In these services you see what happens to your balance, and see how some kind of transfer flies to you. It is unlikely that the public service will deceive you, right? And if no one complains about it, then it can be considered as a reliable source of information and enjoy it.
The advantage over traditional payment systems is that if one web wallet closes, then you simply switch to another, because everyone has the same base. For comparison: if your classic bank suddenly faces a failure - the Internet bank will fall or there will be problems in processing, then you will need another bank card or cash.
Thin wallets
And secondly, there is a more advanced way (and more reliable), which Satoshi himself wrote about in 2008. You can download and check only block headers, not the blocks themselves, as well as proof of the correctness of transactions that are directly related to you.
The fact is that transactions are packaged in an elegant structure: the Merkle tree .

To check the inclusion of the Tx3 transaction in the blockchain, you only need to know Tx3, Hash2, Hash01 and all block headers
This means that a small amount of data (Merkle's proof) helps to make sure that the transaction really exists in the blockchain. That is, the full nodes of the network considered it correct.
Further, if there are many random nodes in the network to which you connect, they report that the block headers are exactly like that, then you can assume with a large degree of confidence that everything is correct, without fakes.
Headings of all blocks now occupy only 40 MB, which is already quite compact. But you can save even more: it is not necessary to keep the headers of all transactions in the entire history - it is enough to start from a certain point.
Myth 3: Blockchain is not scalable
Scalability means that by adding resources to the system, you increase its performance. So, the classic blockchain is absolutely not scalable - the increase in resources does not affect the system bandwidth.
It's also funny that the classic blockchain does not scale not only up, but also down. That is, according to the same principles, it is impossible to build a sufficiently small system to solve local problems, because it will be vulnerable to “ Attack 51% ”.
Plasma
But here is what just recently suggested by Joseph Poon (the inventor of the Lightning Network from the first myth) and Vitalik Buterin (the ideological inspirer of the Ethereum network).
Plasma is a way to make blockchain blockchains. The concept is similar to the Lightning Network - someone pledges to the main Ethereum network and begins to communicate with other clients independently and independently, independently monitoring the implementation of the rules of their smart contract and the general rules of Ethereum. A smart contract is a mini-program for working with money and wallets, a key feature of Ethereum.
From time to time the results of separate communication are recorded in the main network. As in the case of the Lightning Network, all participants monitor the implementation of the rules of the smart contract and “complain” if anything happens.
Interestingly, in such a separate mini-network, “budding” can be repeated.
There are still many open questions. For example, is the owner of the main branch responsible for the implementation of the rules by those who branched off from him? And vice versa? These are all interesting problems from game theory. So far the proposal is only a draft, but one thing is clear: if the conceived concept can be implemented, the blockchain's scalability problem will remain a thing of the past.
Myth 4: Miners burn planet resources
Proof-of-Work is by far the most popular principle of consensus among cryptocurrencies. In it, a new block is created after lengthy calculations — this is necessary solely so that you cannot quickly rewrite the financial history. Miners of PoW networks burn electricity, and the number of burned megawatts is not governed by considerations of security or common sense, but only by economics: power is increased as long as it is still profitable at the current price of cryptocurrency.
Proof-of-stake
But there is an alternative approach to the allocation of the right to create blocks - Proof-of-Stake. In this concept, the probability to create a block, and therefore the right to receive a reward (in the form of commissions or emitted currency) does not depend on how much effort you put on (burned electricity), but on how much currency you have in this system.
If you have a third of all coins, then a pseudo-random algorithm with a probability of one third will contact you with a request to form a block. This principle also motivates participants to behave according to the rules, because the more currency you have, the more interested you are for the network to function properly.
But there are thin places. For example, imagine that you are buying now empty wallets for a pittance, on which just a year ago the lion's share of all the money was in total. After that, you can rewrite the financial history from the time when you supposedly were rich. And in this story, you will remain rich, and all other participants will accept your version, because your story is supported by a larger capital than the conventional one.

Pavel Ivanovich Chichikov warmly approves Proof-of-Stake without additional measures of protection
Different implementations solve the described problem in different ways. For example, you can regularly sign with the developer key the correct blocks so that the story cannot be rewritten too deep.
It is important that technical difficulties can be solved. It is nice to see that the most modern and advanced cryptocurrencies abandon the principle of Proof-of-Work.
Proof-of-authority
But there is a more radical method. Allow only trusted participants to create blocks. For example, 10 hospitals can write in the blockchain epidemiological situation in the city. Each hospital has its own key for signing, we trust hospitals. At the same time, openness will remain - an important property of the blockchain.
Although justice for the sake of PoA most of all destroys the original idea, because in this case the network is essentially centralized and can do without distribution.
Resources can be wasted
At another time, we’ll tell you about networks that perform useful work within the Proof-of-Work: looking for prime numbers of a special type (PrimeCoin), calculating a tertiary protein structure (FoldingCoin), or performing another scientific task related to computing (GridCoin). And the reward for "mining" stimulates to invest more resources in science.
Myth 5: Blockchain is decentralized and therefore does not develop
It is not so easy to make changes to the decentralized network protocol. If you are a developer and control the source code, then one of two things: either you can upgrade all clients forcibly, but such a network cannot be considered truly decentralized; or you make changes to the code and must persuade all participants to accept these changes. If a significant part remains against it, then there is a great chance that the community will split, the block chain will be divided into two incompatible ones, and there will already be two currencies.
Sometimes persuasion is painful, because different participants, depending on their role, have different interests. For example, miners are interested in the growth of awards and commissions; users, on the contrary, want to pay less for transfers; Fans don't care about commissions, they want cryptocurrency to become more popular, and tech geeks want technology to add useful innovations.
Splits have already occurred with Bitcoin - they did not agree on a strategy to increase the block size (to get more transactions), and Ethereum did not agree on whether it would be fair to “cancel” the hacking of one investment fund and return the money to depositors. As a result, four of the two currencies.
Voting
Usually a vote on the proposals goes like this:
- Developers suggest something to change in the rules of the network.
- The miner who creates the block, in a special place of the block, puts the checkbox "I agree / disagree with the proposal X".
- After a certain time measurements are taken, who voted for what.
- Then the miners manually integrate the new rules.

The voting results of various miners on the three proposals for the development of the Bitcoin network. A source
It turns out that only the opinion of miners is taken into account, and the greater the power of the pool, the more votes it has.
At the very least, according to this principle, the protocol is amended.
Tezos
But it is preparing to release Tezos cryptocurrency, which simplifies the process of amending the protocol, because it is embedded in the currency architecturally. Wherein:
- For the new rules do not vote mining capacity, and capital.
- Your voice can be delegated to someone who understands better.
- Developers have the right to veto the entire first year after launch, and if necessary, can extend it.
- The initial quorum is 80%, but it will change over time, adapting to the actual activity of the “holders”.
It is assumed that this approach will significantly reduce the intensity of passions and the need for hard forks.
There is a very real possibility that by such changes at some point the majority shareholders will deprive minority shareholders of the right to vote. In a simple way - the rich will rule. The developers themselves believe that this should have a negative impact on the price of the currency and therefore is unlikely to happen. Well, we'll see.
Myth 6: The blockchain is too transparent
Imagine that you are WikiLeaks and collect donations in bitcoins. Everyone knows your address, they know how much money you have collected, and when you try to exchange this money on the stock exchange for dollars, law enforcement will also know your dollar bill. In other words, there is a problem.
And alone, "launder" the money, which is being monitored, in Bitcoin is impossible. Attempting to scatter money on 10 wallets only leads to the fact that now 10 wallets are associated with you.
In the last article we talked about "mixers". These are anonymous services, which for a fee mix a large amount of money, and it becomes unclear where whose. But using them is inconvenient for a variety of reasons.
Coinjoin
First, they came up with a mixer right in the currency. This is how Dash (the former Darkcoin) appeared with the PrivateSend function. It works as follows:
- First, the payment is divided into pieces of 100, 10, 1, 0.1, etc., so that it cannot be traced by size.
- Then the same parts from different transactions are mixed.
- Mixing consists of several stages, at each stage a new mixing master number is selected. Masternodes are managed by volunteers and receive a commission.
- After mixing, the amount is returned to the owner at new anonymous addresses and can be used when needed (there is no need to wait for mixing).
It is not difficult to see that if someone (for example, law enforcement agencies) controls a significant part of the master session, he will be able to track the transfer. Although it is unlikely.
In addition, mixing dirty money with clean money makes all money gray, that is, suspicious. It turns out that gray money should become white, money should be mixed all and always.
Cryptonote
And a more reliable approach was invented. You can rightly say that Monero is anonymous.
First, it uses ring signatures to anonymize. A ring signature is an electronic signature that allows one of the group members (called a ring) to sign some message on behalf of the entire group, and it will not be known for certain which of the group members executed the signing. This property allows the sender to cover their own tracks. At the same time, the protocol will still protect against double spending.
Secondly, at the wallet address you cannot see the transaction history and balance, because in Monero you have not only spend spend private to spend money, but also an additional private view key to view receipts to your address.
Well and thirdly, for different senders it is worth generating disposable addresses. For example, money from the mother, "dirty" money and money from the exchange should not be taken at the same address. But this rule has long been recommended even in Bitcoin.
For the sake of justice, we also mention the currency Zcash, anonymity in which is based on other, but no less advanced principles.
Conclusion
Well, a brief overview of the shortcomings turned by talented people into advantages has been completed. But this is not all, because we almost did not write about Ethereum smart contracts, Ripple prospects in the banking sector or cryptocurrency without the IOTA blockchain.
Strictly speaking, the title of this article contained a lie: after all, we were not talking about the blockchain, but about its add-ins. But the advantage of the blockchain is that it inspires people to look for ways to excellence.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/336674/
All Articles