Free network security audit with Fortinet. Part 1
Relatively recently, we published a short video course and several articles on how to conduct a free network security audit using Check Point solutions. This time we would like to describe a similar procedure, but only using Fortinet solutions.
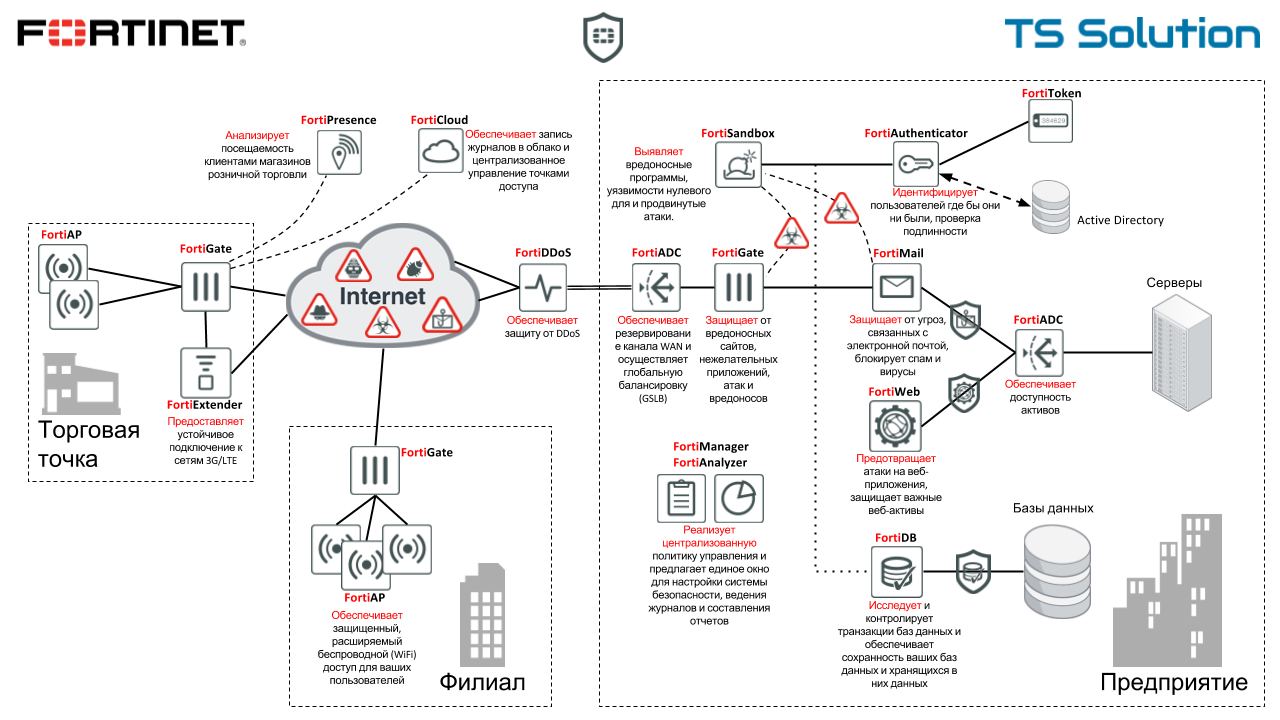
Fortinet is a prominent representative of the permanent leaders among UTM / NGFW solutions. Earlier we published the corresponding Gartner report for 2017 . Perhaps the flagship product of this company is FortiGate - the security gateway (we will consider it later). However, the company's product portfolio is much wider, as you can see from the image above. Here is a short list:
FortiGate - Next Generation Firewall (NGFW);
FortiManager - Centralized management of Fortinet devices;
FortiAnalyzer - Centralized collection of event data (logs) from all Fortinet devices;
FortiSandbox - Protection against targeted attacks (sandbox);
FortiMail - Protects against spam, malware in attachments and other email threats;
FortiWeb - Firewall for your Web applications;
FortiSIEM - System for collecting, analyzing and correlating events;
FortiSwitch - Fortinet switches;
FortiClient - Protection of users' computers;
FortiADC - Application Delivery Controller;
FortiDB - Database Protection;
FortiAuthenticator - Two-factor authentication (2FA) and SSO access;
FortiToken - Tokens for two-factor authentication (2FA);
FortiAP - Wireless Access Point;
FortiExtender - 3G / LTE signal booster;
FortiPresence - Attendance Analysis;
FortiCloud - Save logs in the cloud;
FortiDDoS - Prevent DDoS attacks.
You can read more about Fortinet solutions here , or see our previous webinar:
')
It briefly discusses modern threats, company history, product line, FortiGate models, device interface, and so on (I highly recommend this video for an express acquaintance with Fortinet).
Fortinet provides a free opportunity to conduct a network security audit using FortiGate. This program is called the Cyber Threat Assessment Program (CTAP) . The principle of auditing is quite simple - FortiGate is installed on your network, which analyzes traffic (later we will look at what is being specifically analyzed). At the same time, there are several variants of such a “pilot” project, which usually lasts from two to four weeks. Consider them.
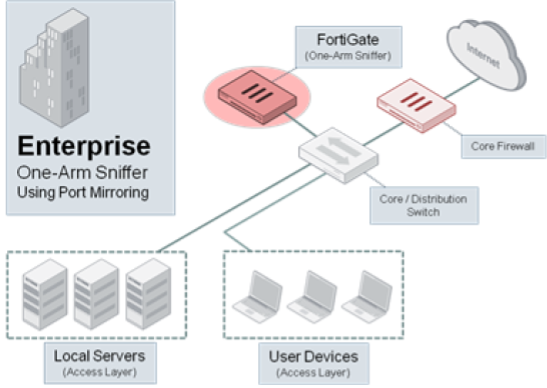
The easiest and at the same time the most popular way is to analyze traffic copies. FortiGate connects to the switch's SPAN port, which mirrors the traffic of interest. As a rule, traffic between the kernel switch and the Internet gateway is analyzed. Since FortiGate works only with a copy of the traffic, then there is no risk for your network. We will consider this method in detail.
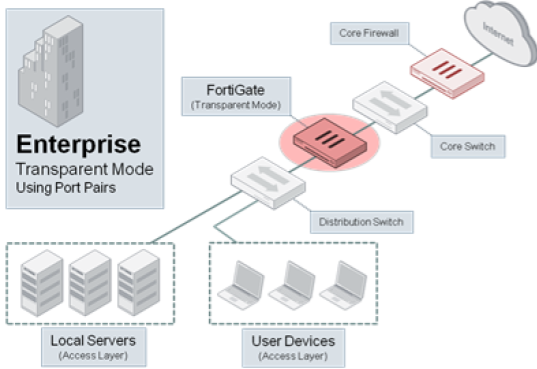
A less popular way. In this case, FortiGate is installed in bridge mode and real traffic flows through it. This method is rarely chosen, because in this case, it is necessary to change the physical topology of the network and organize the process window at the time of switching.
For auditing, you can choose two versions of FortiGate: Appliance (piece of hardware) and VM (virtual machine). Each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
"Iron" device. As a rule, several options are given to the test (depending on the volume of traffic being processed):

A device for a test can be obtained only upon request to Fortinet partners.
Pros:
In addition, not every city has a partner who can provide you with equipment for a test. With virtual machines everything is easier ...
FortiGate virtual machine. Supported Hypervisors - VMware ESXi, KVM, Hyper-V,
XenServer .

Not only FortiGate is available as virtual machines, as can be seen from the figure above.
Advantages of using FortiGate VM:
In general, this is not such a big problem, because for a medium-sized network (100-200 computers), a virtual machine with the parameters of 2-4 cores and 2-4 GB of RAM is sufficient. Virtual machine features:

Next, we will consider this particular way of auditing - using the FortiGate VM virtual machine.
FortiGate itself, when analyzing traffic, generates a huge number of logs. Example:

Logs, though interesting (show the applications used, traffic volumes, visited sites, malicious activity, etc.), but do not provide a complete picture of the network security. Complex reports are much more interesting, which can be generated in different ways:
We will consider the third option, where together with the virtual FortiGate we will deploy the virtual FortiAnalyzer . In addition, for a virtual solution there is no possibility to send logs to the cloud for analysis.
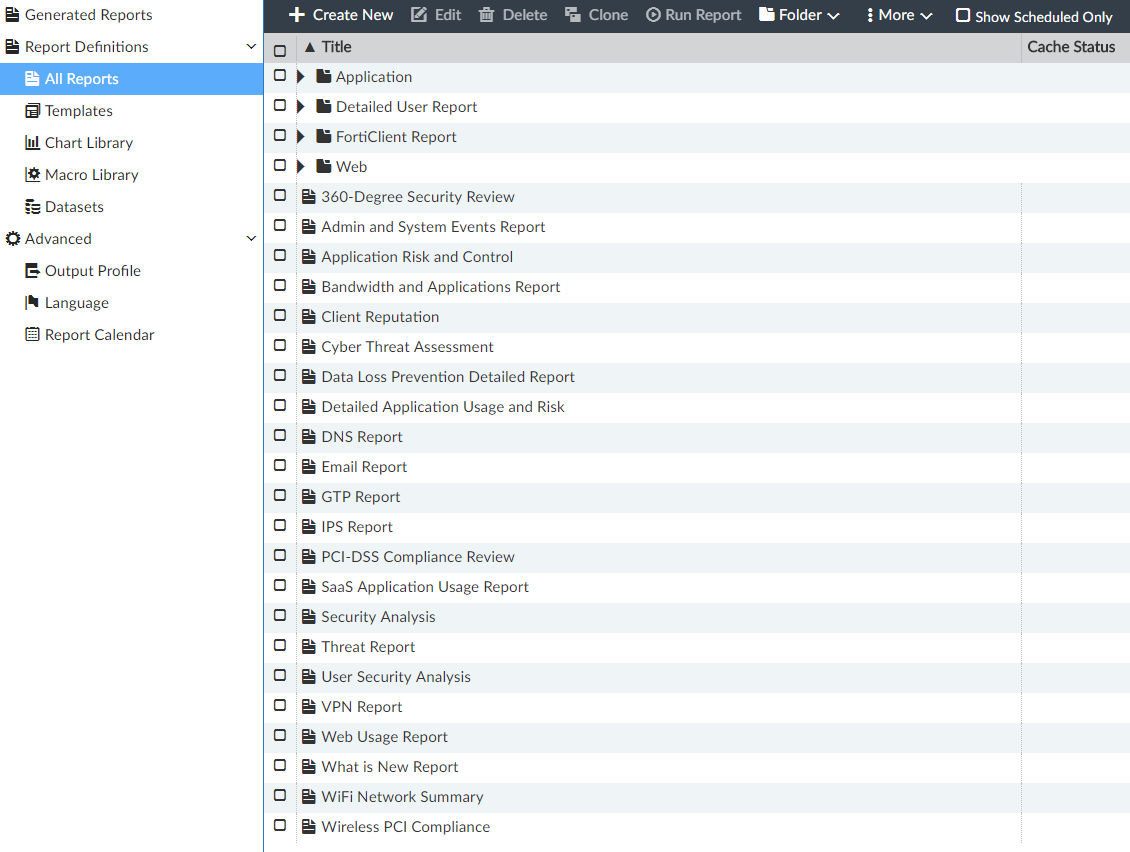
In the case of using local FortiAnalyzer , a large number of types of reports are available to us:
Since we do a comprehensive analysis of network security, then we will be more interested in the Cyber Threat Assessment report. This report contains a large amount of information on the network status:
On the first page you will see a general summary, something like:

Then you can see the statistics on “dangerous” applications:

Vulnerabilities found:

Statistics on downloaded viruses:

The volume of traffic for specific applications:

Categories used sites:

And much more. Sample report can be downloaded here .
In general, this audit option provides fairly detailed statistics on your network, which will be useful for any company. Based on the results of testing, it will be possible to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of existing remedies, threats that exist, or just about the quality of Fortinet solutions. If you are interested in a similar test, you can feel free to contact .
The first part ends here. In the second part, we will look at the process of setting up and generating a report.
Fortinet

Fortinet is a prominent representative of the permanent leaders among UTM / NGFW solutions. Earlier we published the corresponding Gartner report for 2017 . Perhaps the flagship product of this company is FortiGate - the security gateway (we will consider it later). However, the company's product portfolio is much wider, as you can see from the image above. Here is a short list:
FortiGate - Next Generation Firewall (NGFW);
FortiManager - Centralized management of Fortinet devices;
FortiAnalyzer - Centralized collection of event data (logs) from all Fortinet devices;
FortiSandbox - Protection against targeted attacks (sandbox);
FortiMail - Protects against spam, malware in attachments and other email threats;
FortiWeb - Firewall for your Web applications;
FortiSIEM - System for collecting, analyzing and correlating events;
FortiSwitch - Fortinet switches;
FortiClient - Protection of users' computers;
FortiADC - Application Delivery Controller;
FortiDB - Database Protection;
FortiAuthenticator - Two-factor authentication (2FA) and SSO access;
FortiToken - Tokens for two-factor authentication (2FA);
FortiAP - Wireless Access Point;
FortiExtender - 3G / LTE signal booster;
FortiPresence - Attendance Analysis;
FortiCloud - Save logs in the cloud;
FortiDDoS - Prevent DDoS attacks.
You can read more about Fortinet solutions here , or see our previous webinar:
')
It briefly discusses modern threats, company history, product line, FortiGate models, device interface, and so on (I highly recommend this video for an express acquaintance with Fortinet).
Cyber Threat Assessment Program (CTAP)
Fortinet provides a free opportunity to conduct a network security audit using FortiGate. This program is called the Cyber Threat Assessment Program (CTAP) . The principle of auditing is quite simple - FortiGate is installed on your network, which analyzes traffic (later we will look at what is being specifically analyzed). At the same time, there are several variants of such a “pilot” project, which usually lasts from two to four weeks. Consider them.
1) Traffic copy (One-Arm Sniffer)
The easiest and at the same time the most popular way is to analyze traffic copies. FortiGate connects to the switch's SPAN port, which mirrors the traffic of interest. As a rule, traffic between the kernel switch and the Internet gateway is analyzed. Since FortiGate works only with a copy of the traffic, then there is no risk for your network. We will consider this method in detail.

2) In bridge mode (Transparent mode)
A less popular way. In this case, FortiGate is installed in bridge mode and real traffic flows through it. This method is rarely chosen, because in this case, it is necessary to change the physical topology of the network and organize the process window at the time of switching.

FortiGate Appliance vs FortiGate VM
For auditing, you can choose two versions of FortiGate: Appliance (piece of hardware) and VM (virtual machine). Each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
1) FortiGate Appliance
"Iron" device. As a rule, several options are given to the test (depending on the volume of traffic being processed):

A device for a test can be obtained only upon request to Fortinet partners.
Pros:
- No allocation of virtual resources (which is often lacking) is required;
- High performance;
- You are testing a real device and can evaluate its performance (if you look at FortiGate, then most often they buy the “iron” solution).
- Waiting for the Appliance (there is almost always a shortage of hardware, everything is on tests).
In addition, not every city has a partner who can provide you with equipment for a test. With virtual machines everything is easier ...
2) FortiGate VM
FortiGate virtual machine. Supported Hypervisors - VMware ESXi, KVM, Hyper-V,
XenServer .
Not only FortiGate is available as virtual machines, as can be seen from the figure above.
Advantages of using FortiGate VM:
- Ease of deployment (imported via ovf);
- Deployment speed (get a virtual machine from partners much faster than the “iron” solution).
- It is necessary to allocate virtual power.
In general, this is not such a big problem, because for a medium-sized network (100-200 computers), a virtual machine with the parameters of 2-4 cores and 2-4 GB of RAM is sufficient. Virtual machine features:
Next, we will consider this particular way of auditing - using the FortiGate VM virtual machine.
Report generation
FortiGate itself, when analyzing traffic, generates a huge number of logs. Example:
Logs, though interesting (show the applications used, traffic volumes, visited sites, malicious activity, etc.), but do not provide a complete picture of the network security. Complex reports are much more interesting, which can be generated in different ways:
- Send logs to the Fortinet cloud for further analysis . This feature is only available for hardware. Perhaps this is the easiest option. At the end of the audit, the partner provides a detailed security report on your network. There is one BUT - not everyone is ready to send their logs to the outside world (even to the Fortinet cloud). In this case, there are tradeoffs.
- Collect logs locally on the device, and then transfer them to the partner for analysis in one archive . There is a limit of 100 MB. This option is used very rarely.
- Send logs to the local FortiAnalyzer . In this case, all the logs are stored with you and you can generate reports at least every hour, and not just at the end of the pilot project. The only thing - will have to additionally deploy FortiAnalyzer (it is not difficult).
We will consider the third option, where together with the virtual FortiGate we will deploy the virtual FortiAnalyzer . In addition, for a virtual solution there is no possibility to send logs to the cloud for analysis.
The composition of the report
In the case of using local FortiAnalyzer , a large number of types of reports are available to us:
Since we do a comprehensive analysis of network security, then we will be more interested in the Cyber Threat Assessment report. This report contains a large amount of information on the network status:
The composition of the report
On the first page you will see a general summary, something like:
Then you can see the statistics on “dangerous” applications:
Vulnerabilities found:
Statistics on downloaded viruses:
The volume of traffic for specific applications:
Categories used sites:
And much more. Sample report can be downloaded here .
Conclusion
In general, this audit option provides fairly detailed statistics on your network, which will be useful for any company. Based on the results of testing, it will be possible to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of existing remedies, threats that exist, or just about the quality of Fortinet solutions. If you are interested in a similar test, you can feel free to contact .
The first part ends here. In the second part, we will look at the process of setting up and generating a report.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/335184/
All Articles