How to monitor the state of a corporate wireless network with Extreme NSight
Today in retail without a wireless LAN - nowhere. However, it is important to monitor it in time to troubleshoot problems and problems. Talk about how to do it effectively.
In recent years, wireless LAN has become one of the most important keys to success in retail, providing the necessary data in real time. This simplifies day-to-day business processes, improves customer service, and reduces the number of possible mistakes that can lead to lower profitability, higher lost sales and, ultimately, to the loss of customers.
In order to achieve a high level of reliability of a wireless network, we need to know about its state and understand what is happening in it at any time. It is imperative to timely collect and receive information for troubleshooting and problems. This data can also be used for budget planning in the case of network scaling and analytics of an organization’s business processes.
In the corporate segment, solutions of Cisco, Aruba Networks, Extreme Networks companies are used for these tasks. Taking into account the experience of "Pilot" in the deployment of wireless networks , we analyze how to effectively monitor their condition in real time using the example of the popular Extreme NSight software for Extreme Networks equipment. This is, in fact, a software add-on that expands the functionality of the WiNG5 infrastructure with the help of additional capabilities for managing and controlling a wireless domain. So, the key features and functionality of NSight:
')
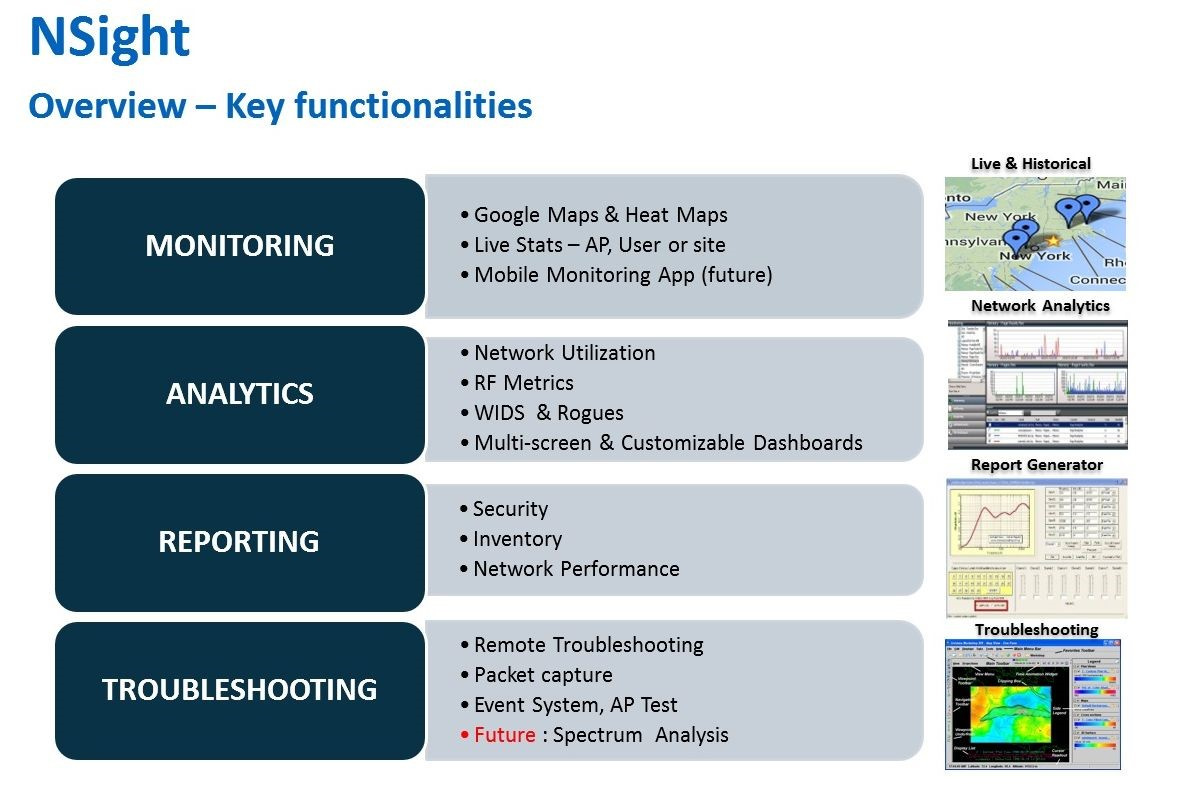
Monitoring NSight allows you to track the status of an enterprise's wireless domain. The program body (customizable dashboard) can import the corporate network site tree directly from WING5 infrastructure (from NX or VX, RFDM controllers). You can import maps from Google Maps with geo-coordinates linked to sites, create and monitor floor plans with placed access points and a heat map. Information and visualization of the network tree are structured: from a specific point or user on the site to summarized information on the entire wireless domain. Customizable Dashboard NSight is an interactive, multi-user and multi-window program that allows you to easily navigate the structure tree to the levels of interest for analysis and troubleshooting. It is possible to display the operational status of wireless domain network devices, the number of users, network load, bandwidth. All information can be ranked and provided to users with different levels of access and role of impact. This is very convenient if the control over the network is of a nature distributed over the zones of responsibility.
Analysis. With the help of pre-installed and easily mounted widgets, you can summarize the information received from the domain’s wireless infrastructure into different groups and levels:
- access points;
- used channels;
- the number of users and their type, the type of their operating systems;
- used applications;
- wireless network protocols;
- enemy points, attacks;
- events of different significance level.
This information is collected during the monitoring of the wireless domain and is archived into a database with a customized retention period.
Report generation Extreme NSight implements report generation functionality. Two report creation modes: on demand and on schedule. There are ready-made sets of reports on the type of key metrics for analysis - an inventory of wireless equipment, the state of the network and its components, security, compliance with the standards of industry regulators, the dynamics and direction (trend) of network utilization, its load. It is also possible to customize reports with the selection of information of interest to us and the method of its extraction from the system.
Trashshuting NSight's interactive interface makes it easy to access the data we need to analyze and fix wireless network problems. There is no need to go to any specific access point to obtain information, everything is available through the program interface. Instead, we can create our own dashboard and on the fly collect and track data metrics from remote access points and their clients on any particular site or their entirety. There are three built-in mechanisms for obtaining and analyzing information:
- Packet Capture;
- Wireless Debug Log access;
- Event Log Browser.
Packet Capture allows you to capture wireless and wired traffic with filtering by types and protocols of network communication. This data can be saved to a file for further analysis.
Wireless Debug Log makes it easy to get detailed information about 802.11 protocol errors at the level of access errors and authentication that may occur during operation of the wireless network.
The Event Log Browser organizes access to the event log via the Extreme NSight interface to view events for a specific period of time that occurred with an access point or mobile wireless clients.
Composition, requirements, licensing, deployment models
Extreme NSight - lines of software code that are included in the core of the WiNG5, which is part of the normal distribution for the NX, VX and RFS controllers. Available starting with version WiNG5 - 5.8.2. The functionality is enabled only in the WiNG5 command line with just a couple of commands:
• An NSight Policy is created for the NOC controller

• Assign the NS of the NOC controller

Another group of settings relates to NSight clients — infrastructure and database.
NSight is an application of the Client-Server type with a database, where the role of the server on which all collected information is stored and maintained is usually the NOC controller (VX or NX controller), and the client that collects this data on each site and provides them to the server, performs either RFDM on AP, or RFDM on RFS or on NX controllers. Accordingly, they also create policies in which the ip address of the NSight server (or cluster of servers) will be specified. User access to the application itself is via the https protocol:

where as fdqn or ip is the address of the NSight server (domain controller). A general view of the interface NSight is presented below:
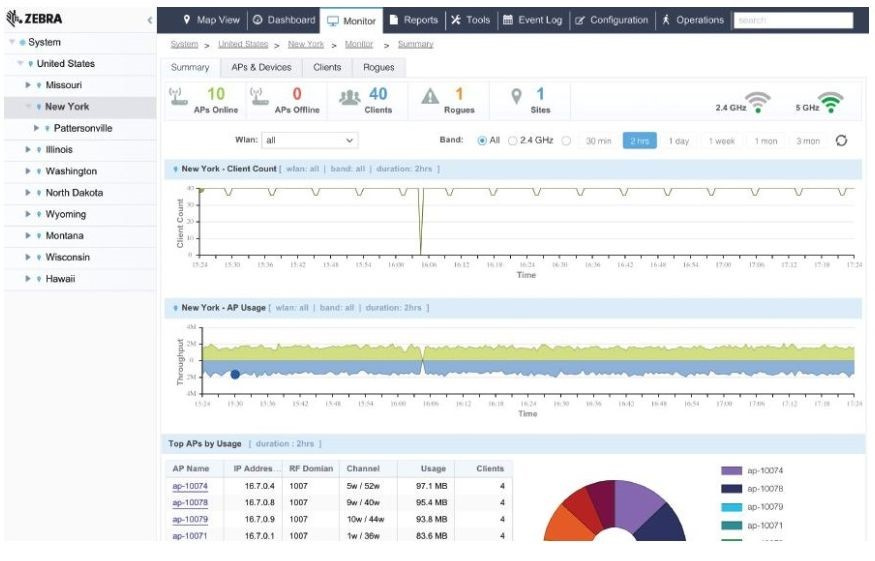
Learn more about NSight components.
Server. This is a web application. It interacts with WiNG5 and performs the following functions:
- automatically saves configuration updates coming from the WiNG Management module;
- periodically stores updates of statistical data from all RFDM wireless domains of the corporation;
- saves information about the adaptation process for access points, coming from the NOC and the site of the controllers;
- manages and maintains API requests from third-party applications.
Customer. Client functions are assigned to each site's RFDM. The RFDM can be a dynamically selected access point or local site controller. The client collects statistics from all access points of this site and sends them to the server every 60 seconds (by default). Sends the following data:
- AP statistics;
- client (mobile) statistics;
- wired statistics;
- event history;
- adoption information.
Database. NSight Server stores a database of all wireless clients, access points and controllers:
- all devices are identified by their unique MAC address;
- all information about the device is stored: Mac, IP, hostname, location, etc;
- information on the SMART-RF neighbor from each access point;
- enemy access points detected in the network coverage area;
- statistics about clients and from access points;
- event history for each device.
Extreme NSight is supported on NX 95XX, 96XX and VX9000 platforms in two deployment modes - standalone server and integrated WING5 + NSigt mode. The standalone mode is when only NSight functionality is launched on the controller (NX or VX), and integrated is when the controller simultaneously performs the functions of WiNG management and NSight.
The following table lists the system requirements for VX9000 appliances, depending on the scale of the network being served:

To transfer data from the NSight client to the NSight server, no more than 1 kbps per point is required, which belongs to the site from which the information goes to the NSight server.
Extreme NSight - licensed functionality. The license includes two key components: the number of devices and the expiration date.
The number of devices is the sum of the access points and controllers that make up the organization's wireless domain. The number of licenses must be equal to or greater than it.
Validity - two options are available - for 1 and 3 years. If the number of licenses is not enough and the validity period expires, then NSight displays a warning message 60 days before the program is blocked. If the program is blocked, the user interface is no longer available. At the same time, the system continues to collect statistics and write it to the database. As soon as the license is installed, the system will open access to the user interface and database.
If we use the integrated deployment model (WING + NSight), then only one license is required, which is installed on the NOC controller and shared by all cluster members (if any). When implementing a standalone scheme, only one license is also required, which is installed on the primary replica set. It is also shared among all members of the replica set topology. If, for example, we launched the NSight server on the VX9000 in standalone mode, then we will not need a license for the VX platform as such. Only license for NSight.
What is replica set
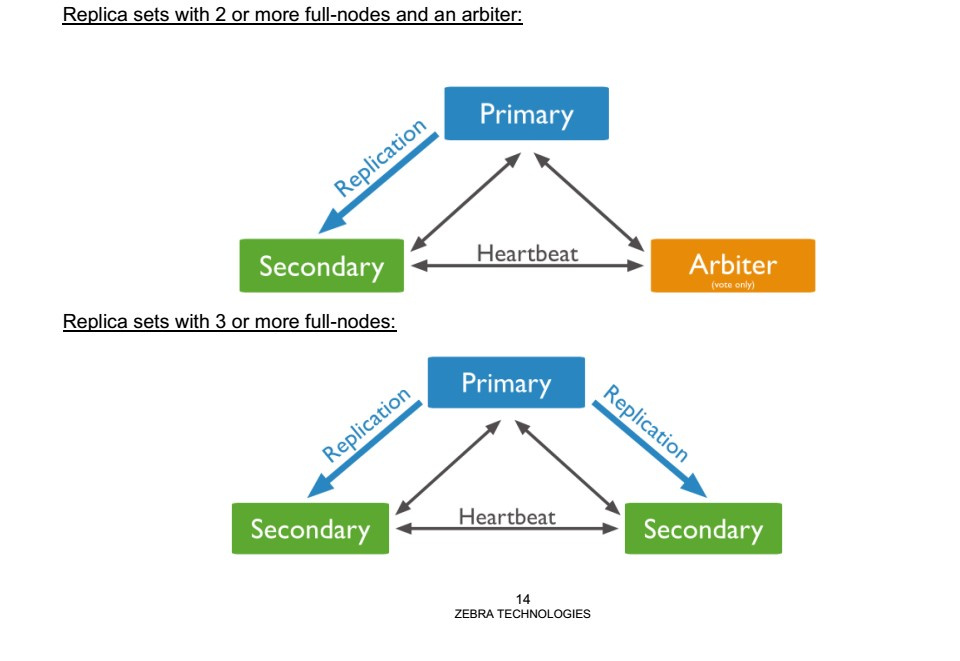
The created and stored NSight database must have a high degree of availability and reliability of data storage in the event of failure of any of the elements of the NSight topology. For this, a three-node database storage and maintenance model was recommended. Here two aspects are important:
- the database storage topology should always consist of an odd number of storage and processing nodes (for example, 3);
- Database backup is a process independent of the clustering process of the WING topology.
Directly replica set - a group of database processes (servers) that support the same data set. Replica sets provide redundancy, high availability and are the basis for all deployment models. In essence, this is a distributed group of servers that are synchronized with each other, store and maintain a common database, and also ensure its reliability and availability in the event of the failure of any topology nodes. Full-node is a member of the replica set topology with a full copy of the database. Arbiter is a process (server) that does not store any data, but participates in the generation of synchronization signals and in the selection of the primary database.
Some Extreme NSight infrastructure deployment models:
1. Integrated WiNG5 + NSight model on one controller in the NOC center
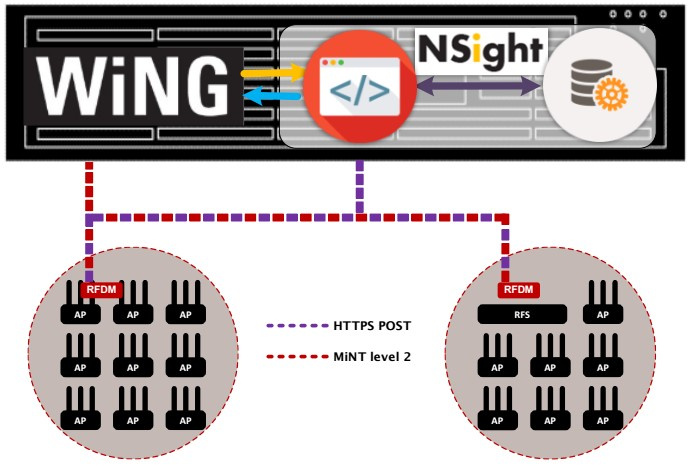
NSight components operate with WiNG5 within the same physical controller (VX, NX). NSight receives data from the RFDM (AP or controller) of each individual site via websocket. And the data exchange between the elements of the WiNG5 infrastructure is carried out using the MINT protocol (level2).
2. Model standalone (NSight only)
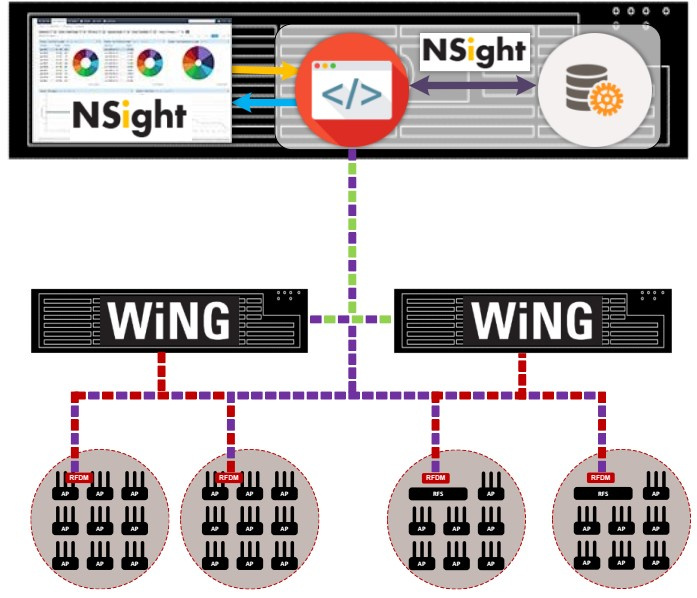
In it, the Extreme NSight server runs on a standalone VX or NX9XXX platform without any WiNG5 control functions. The Extreme NSight module only receives statistical data and configuration information from remote sites. In addition, each WiNG5 controller of the NOC-center transmits information about the structure of the site tree configuration. The standalone Nsight server does not interact with the WING5 module on the same controller and does not report any statistics about itself to the Nsight base. Data exchange and statistics collection also takes place via websocket for NSight and via MINT for WiNG5.
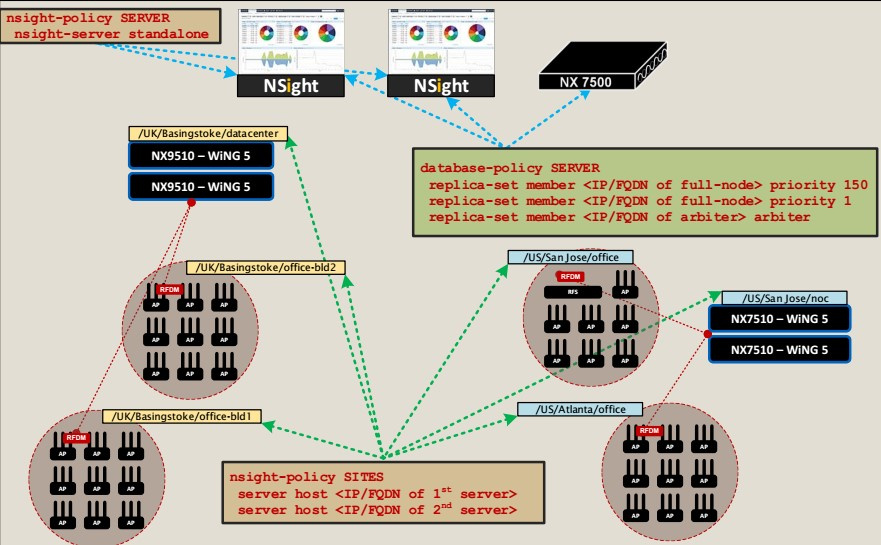
In both of the above examples, NSight is deployed within the same physical device. If we need high availability and reliability of the NSight functional and its database, then the replica set topology, mentioned earlier, is implemented. A scheme consisting of three nodes, one in each data center. The third node does not necessarily require a separate data center, as long as it is located in a separate location with reliable and uninterrupted power and access to the corporate network. If this server performs the role of Arbiter, then it is not necessary to purchase an expensive IBM (HP) server. Quite enough ordinary computer that can work with VMware.
The pictures below show two schemes of the three replica set topology nodes. The first consists of two full-node nodes plus an arbiter. It should be noted that full-node nodes should be placed on the same type of device - for example, VX9000-VX9000 or NX9500 - NX9500.
The second model: all three nodes are full-node servers. Notice how the database policy is configured — by setting the priority for each specific device.
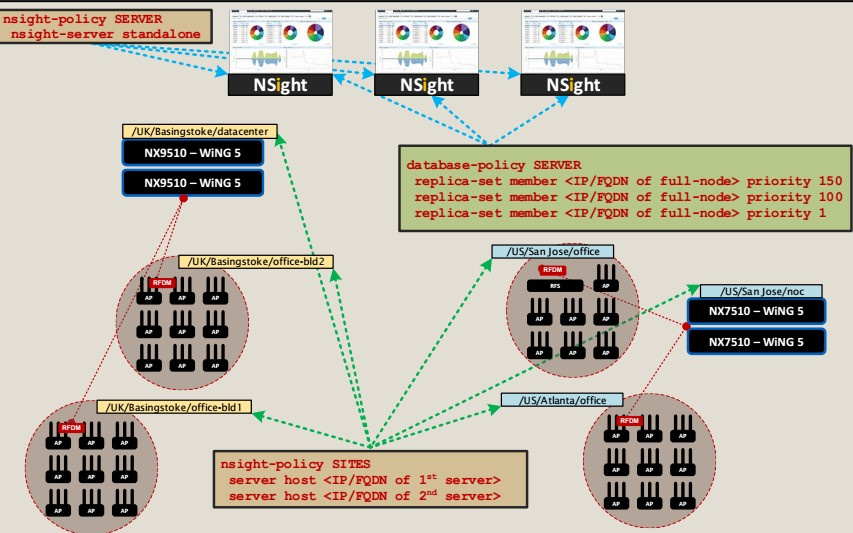
In both of these examples, the replica set topology is applied to the stand-alone NSight infrastructure model. But other options are possible.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/334646/
All Articles