When will there be enough IP addresses for everyone?
The number of IP addresses for devices available in the global network via the IPv4 protocol has reached about 4.3 billion and is almost exhausted due to the IP address length of 32 bits. 128 bits are involved in the IPv6 address space, which makes the number of addressable devices almost infinite. IPv4 and IPv6 do not have direct and simple compatibility with each other. It is because of this quick and cheap transition to IPv6 only will not. Fearfully? Well no. You just need to embark on this road - and sooner or later we will enter the era of "clean" IPv6. Is it good or bad?

Recently, MTS subscribers in the Central Federal District have had the opportunity to try out Internet access using IPv6. For one session of this protocol, the subscriber is issued addressing in two standards at once: IPv4 and IPv6. This mode is called Dual-Stack. In order for your device to work with IPv6, you need to connect the free service "Access to IPv6", as well as make some settings on the subscriber terminal. In this post, our expert Oleg Ermakov, his nickname on Khabrhab - eov, will tell you more about the new service. Give him the word.
')
Hello! My story will consist of two parts. The first describes the user settings and ways to control that everything is going according to plan. The second one already gives a brief insight into the technology: as it is done on the cellular operator’s network in the 3GPP-access field. The non-3GPP segment will not be affected. This is a topic for a separate article.
Part I
As a result of switching to a new protocol, the subscriber has the following:
1. Services that work with IPv6 addressing will receive and transmit traffic WITHOUT using NAT . I don’t know if everyone has come across the fact that the search query on Google sometimes needs to enter the Captcha code, or Google refuses to search at all. The reason is that Google believes that there are too many requests from one public IP, and this is perceived by it as a robotic survey.
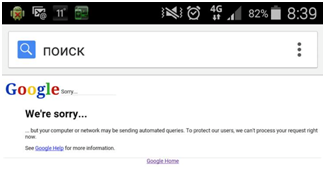
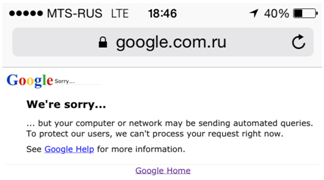
2. The subscriber will receive a public IPv6 address, and “incoming” traffic from the Internet will be available to it. Now, due to the use of NAT, this is not easy.
3. The subscriber who "distributes" the Internet will get the opportunity for each device that is located behind the "distributor" to have its IPv6 address. I propose to discuss the pros and cons of this in the comments ...
I don’t hide the fact that we (the operator) also gain from the transition to IPv6: the more subscribers switch to IPv6, the less IPv4 addresses will be required for NAT / PAT broadcasts. I am sure that 99% of subscribers do not think that as a result, they will incur the financial costs of purchasing additional IPv4 space.
I foresee the question: “When will this service become available to subscribers throughout the country”? I answer. We are working on it and will try to launch access to most of the network by the end of this summer.
On our site there is a setup instruction , general terms are written there. Additionally I want to clarify a few points:
1. While Dual-Stack works only on devices with Android OS, Windows and on some routers. In the near future, IPv6 can be enabled on Apple mobile devices. However, to be able to work with iOS devices, we need to pass a series of additional tests. Please treat this with understanding and be patient. For now, you can get IPv6 on Apple devices by connecting to a “mobile access point” with a working IPv6 service via Wi-Fi.
2. At the current stage, the service is primarily focused on advanced users who understand what they are doing and why. You join high technology, and we study your customer experience, which is extremely important at this stage. We expect to receive feedback from users, refine and improve the service. In the future, we plan to simplify the connection and abandon the “service” as such, and make the IPv6 functionality available in the default phone settings “out of the box”. Ideally, the transition to IPv6 in MTS mobile networks is planned to be seamless.
3. In the connection settings in the MANDATORY order, you need to specify the APN internet.mts.ru and the type of IPv4v6 protocol (this is IMPORTANT). The main sign of the correct indication of the APN is that the subscriber is issued an IPv4 address from the range 10.0.0.0/8 RFC1918 , and not from the range 100.64.0.0/10 RFC6598 . If IPv4 or IPv6 is selected in the phone settings, the network will display exactly what was requested (IPv4 OR IPv6). In the first case, everything will work on IPv4, and in the second - most of the Internet resources will become unavailable simply because not all have switched to IPv6. If everything is done correctly, then two IPv4 and IPv6 (Dual-Stack) addresses will be issued. We do not intentionally plan to extend the solution to the “wrong settings” (with the wrong APN). In doing so, we proceed from the principle of "do no harm."
4. To access Internet resources in IPv6 addressing, it is necessary that the DNS system also works as expected. For subscriber sessions with IPv4v6 issued and IPv6 DNS server. The presence of IPv6 DNS servers is not necessary, because IPv4 servers successfully reolve AAAA records. When connecting to the network, we issue both servers solely to ensure that everything is “feng shui”.
5. Pay special attention to the fact that the subscriber is given a public IPv6 address (actually a block of / 64 addresses), which is accessible from the Internet! Do not neglect the elementary security measures. It is highly desirable to install antivirus and firewall.
Thus, subscribers have an IPv4 and IPv6 address. Rezolving of Internet resources is performed on both IPv4 and IPv6. The case for applications. In our experience, the Google Chrome browser primarily uses the IPv6 protocol for resources that have the ability to work on IPv6. For example, such popular resources as Yandex and Google have long been working on IPv6.
For verification, you can use the test-ipv6.com resource. If everything is configured correctly, the test will show a score of 10 out of 10.
If this is not the case, then you need to make sure that traffic optimizers are turned off in the browser settings.

Part II
Here we dive into the professional field. Those who prefer to restrict the applied part of the story, please comment or write in a personal question. I will say right away that I cannot help everyone, but I am ready to consider particularly interesting cases. Thank you for understanding.
IPv6 as such appeared in 1998 and is described in RFC2460 , support for IPv6 in mobile networks appeared in the recommendations of 3GPP Rel99 (2000). Widespread technology has not received. Probably then, few in the world knew what IPv6 is, and there was no shortage of IPv4 addresses. After 10 years, there was no urgent need, so we conducted internal testing, but did not implement it.
Beginning with 3GPP Rel8 for LTE networks, the Dual-Stack era is emerging. The benefits are obvious. Dual-Stack makes technologies such as NAT64 and DNS64 unnecessary , while maintaining “backward compatibility” with networks on IPv4, in effect, making a smooth transition between technologies.
It became better, and it could already be used. Unfortunately, when establishing a connection, the network raises two PDP contexts and inefficiently uses network resources.
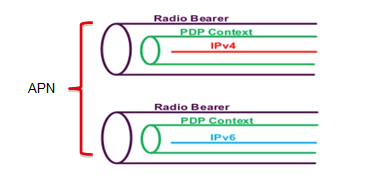
Dual-Stack further developed in 3GPP Rel9. It has added support for 2G / 3G networks and it has the opportunity to issue an IPv4 and IPv6 address within the same PDP context (bearer-a). This technology is used on the MTS network.
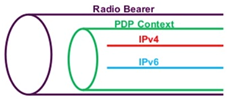
If you look a little deeper, you can say that 3GPP Rel10 describes DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation technology (DHCPv6-PD) . Now the need for its use in the mobile network is not obvious. If there are specific proposals - write in the comments or in a personal.
In order for the technology to work, support for the necessary functionality on the HLR / HSS, SGSN / MME, GGSN / PGW, PCRF, OCS, CDR collector network elements, and, of course, on the transport network was included.
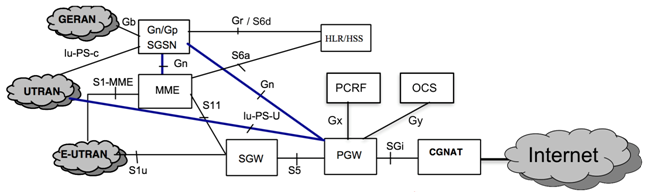
HLR / HSS
Connecting a service causes the protocol type in the APN settings from IPv4 to IPv4v6 (or both) to be changed in the HLR and in the HSS. The specification of TS 29.272 (Rel9) literally states the following:
As you may have guessed, we use option 2.
SGSN / MME
Configuring these devices for IPv6 support is simple; it is essentially limited to activating the appropriate license and enabling dual-address-pdp support for SGSN and MME services, as well as in the RNC settings connected to the SGSN.
PGW / GGSN
All is not so simple. Upgrades are:
- interfaces in the direction of the transport network (address-family ipv6 rises), and IP routing is prescribed;
- prescribed ip-pool, from which subscribers are given addresses;
- IPv6 support on APN is activated;
- prescribes IPv6 DNS, which will be issued to the subscriber when connected.
PCRF / OCS
PGW is exchanged with PCRF and OCS using the Diameter protocol (Gx and Gy interfaces, respectively). The peculiarity of IPv6 activation is that AVP Framed-IPv6-Prefix appears in this signaling exchange and one more AVP PDP-Address with IPv6 address is added. Accordingly, PCRF and OCS must accept and take them into account (save).
CDR collector
It is expected that the format of the CDR records has changed. The subscriber’s IPv4 address moved to the servedPPPPDNAddressExt field, and the IPv6 address will be recorded in the servedPDPPDNAddress (this field initially supported both IPv4 and IPv6).
Transportation network
Address-family ipv6 rises and routing is written.
In conclusion, I want to ask you a question.

Recently, MTS subscribers in the Central Federal District have had the opportunity to try out Internet access using IPv6. For one session of this protocol, the subscriber is issued addressing in two standards at once: IPv4 and IPv6. This mode is called Dual-Stack. In order for your device to work with IPv6, you need to connect the free service "Access to IPv6", as well as make some settings on the subscriber terminal. In this post, our expert Oleg Ermakov, his nickname on Khabrhab - eov, will tell you more about the new service. Give him the word.
')
Hello! My story will consist of two parts. The first describes the user settings and ways to control that everything is going according to plan. The second one already gives a brief insight into the technology: as it is done on the cellular operator’s network in the 3GPP-access field. The non-3GPP segment will not be affected. This is a topic for a separate article.
Part I
As a result of switching to a new protocol, the subscriber has the following:
1. Services that work with IPv6 addressing will receive and transmit traffic WITHOUT using NAT . I don’t know if everyone has come across the fact that the search query on Google sometimes needs to enter the Captcha code, or Google refuses to search at all. The reason is that Google believes that there are too many requests from one public IP, and this is perceived by it as a robotic survey.


2. The subscriber will receive a public IPv6 address, and “incoming” traffic from the Internet will be available to it. Now, due to the use of NAT, this is not easy.
3. The subscriber who "distributes" the Internet will get the opportunity for each device that is located behind the "distributor" to have its IPv6 address. I propose to discuss the pros and cons of this in the comments ...
I don’t hide the fact that we (the operator) also gain from the transition to IPv6: the more subscribers switch to IPv6, the less IPv4 addresses will be required for NAT / PAT broadcasts. I am sure that 99% of subscribers do not think that as a result, they will incur the financial costs of purchasing additional IPv4 space.
I foresee the question: “When will this service become available to subscribers throughout the country”? I answer. We are working on it and will try to launch access to most of the network by the end of this summer.
On our site there is a setup instruction , general terms are written there. Additionally I want to clarify a few points:
1. While Dual-Stack works only on devices with Android OS, Windows and on some routers. In the near future, IPv6 can be enabled on Apple mobile devices. However, to be able to work with iOS devices, we need to pass a series of additional tests. Please treat this with understanding and be patient. For now, you can get IPv6 on Apple devices by connecting to a “mobile access point” with a working IPv6 service via Wi-Fi.
2. At the current stage, the service is primarily focused on advanced users who understand what they are doing and why. You join high technology, and we study your customer experience, which is extremely important at this stage. We expect to receive feedback from users, refine and improve the service. In the future, we plan to simplify the connection and abandon the “service” as such, and make the IPv6 functionality available in the default phone settings “out of the box”. Ideally, the transition to IPv6 in MTS mobile networks is planned to be seamless.
3. In the connection settings in the MANDATORY order, you need to specify the APN internet.mts.ru and the type of IPv4v6 protocol (this is IMPORTANT). The main sign of the correct indication of the APN is that the subscriber is issued an IPv4 address from the range 10.0.0.0/8 RFC1918 , and not from the range 100.64.0.0/10 RFC6598 . If IPv4 or IPv6 is selected in the phone settings, the network will display exactly what was requested (IPv4 OR IPv6). In the first case, everything will work on IPv4, and in the second - most of the Internet resources will become unavailable simply because not all have switched to IPv6. If everything is done correctly, then two IPv4 and IPv6 (Dual-Stack) addresses will be issued. We do not intentionally plan to extend the solution to the “wrong settings” (with the wrong APN). In doing so, we proceed from the principle of "do no harm."
4. To access Internet resources in IPv6 addressing, it is necessary that the DNS system also works as expected. For subscriber sessions with IPv4v6 issued and IPv6 DNS server. The presence of IPv6 DNS servers is not necessary, because IPv4 servers successfully reolve AAAA records. When connecting to the network, we issue both servers solely to ensure that everything is “feng shui”.
5. Pay special attention to the fact that the subscriber is given a public IPv6 address (actually a block of / 64 addresses), which is accessible from the Internet! Do not neglect the elementary security measures. It is highly desirable to install antivirus and firewall.
Thus, subscribers have an IPv4 and IPv6 address. Rezolving of Internet resources is performed on both IPv4 and IPv6. The case for applications. In our experience, the Google Chrome browser primarily uses the IPv6 protocol for resources that have the ability to work on IPv6. For example, such popular resources as Yandex and Google have long been working on IPv6.
For verification, you can use the test-ipv6.com resource. If everything is configured correctly, the test will show a score of 10 out of 10.
If this is not the case, then you need to make sure that traffic optimizers are turned off in the browser settings.

Part II
Here we dive into the professional field. Those who prefer to restrict the applied part of the story, please comment or write in a personal question. I will say right away that I cannot help everyone, but I am ready to consider particularly interesting cases. Thank you for understanding.
IPv6 as such appeared in 1998 and is described in RFC2460 , support for IPv6 in mobile networks appeared in the recommendations of 3GPP Rel99 (2000). Widespread technology has not received. Probably then, few in the world knew what IPv6 is, and there was no shortage of IPv4 addresses. After 10 years, there was no urgent need, so we conducted internal testing, but did not implement it.
Beginning with 3GPP Rel8 for LTE networks, the Dual-Stack era is emerging. The benefits are obvious. Dual-Stack makes technologies such as NAT64 and DNS64 unnecessary , while maintaining “backward compatibility” with networks on IPv4, in effect, making a smooth transition between technologies.
It became better, and it could already be used. Unfortunately, when establishing a connection, the network raises two PDP contexts and inefficiently uses network resources.

Dual-Stack further developed in 3GPP Rel9. It has added support for 2G / 3G networks and it has the opportunity to issue an IPv4 and IPv6 address within the same PDP context (bearer-a). This technology is used on the MTS network.

If you look a little deeper, you can say that 3GPP Rel10 describes DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation technology (DHCPv6-PD) . Now the need for its use in the mobile network is not obvious. If there are specific proposals - write in the comments or in a personal.
In order for the technology to work, support for the necessary functionality on the HLR / HSS, SGSN / MME, GGSN / PGW, PCRF, OCS, CDR collector network elements, and, of course, on the transport network was included.

HLR / HSS
Connecting a service causes the protocol type in the APN settings from IPv4 to IPv4v6 (or both) to be changed in the HLR and in the HSS. The specification of TS 29.272 (Rel9) literally states the following:
7.3.62 PDN-Type ...
7.3.62 PDN-Type
The PDN-Type AVP is a type of enumerated and indicates the address type of PDN. The following values are defined:
IPv4 (0)
This can be accessed only in
IPv4 mode.
IPv6 (1)
This value can be accessed only in IPv6 mode.
IPv4v6 (2)
It can be accessed both by the IPS4 and by the UEs supporting dualstack IPv4v6.
IPv4_OR_IPv6 (3)
This is a case of supporting dualstack IPv4v6. It would be noted that the PDN Types, ie, IPv4 only, IPv6 only or IPv4v6 (or dualstack). This is not the case for the APN subscription context of the authorization mechanism between HSS and MME.
The PDN-Type AVP is a type of enumerated and indicates the address type of PDN. The following values are defined:
IPv4 (0)
This can be accessed only in
IPv4 mode.
IPv6 (1)
This value can be accessed only in IPv6 mode.
IPv4v6 (2)
It can be accessed both by the IPS4 and by the UEs supporting dualstack IPv4v6.
IPv4_OR_IPv6 (3)
This is a case of supporting dualstack IPv4v6. It would be noted that the PDN Types, ie, IPv4 only, IPv6 only or IPv4v6 (or dualstack). This is not the case for the APN subscription context of the authorization mechanism between HSS and MME.
As you may have guessed, we use option 2.
SGSN / MME
Configuring these devices for IPv6 support is simple; it is essentially limited to activating the appropriate license and enabling dual-address-pdp support for SGSN and MME services, as well as in the RNC settings connected to the SGSN.
PGW / GGSN
All is not so simple. Upgrades are:
- interfaces in the direction of the transport network (address-family ipv6 rises), and IP routing is prescribed;
- prescribed ip-pool, from which subscribers are given addresses;
- IPv6 support on APN is activated;
- prescribes IPv6 DNS, which will be issued to the subscriber when connected.
PCRF / OCS
PGW is exchanged with PCRF and OCS using the Diameter protocol (Gx and Gy interfaces, respectively). The peculiarity of IPv6 activation is that AVP Framed-IPv6-Prefix appears in this signaling exchange and one more AVP PDP-Address with IPv6 address is added. Accordingly, PCRF and OCS must accept and take them into account (save).
CDR collector
It is expected that the format of the CDR records has changed. The subscriber’s IPv4 address moved to the servedPPPPDNAddressExt field, and the IPv6 address will be recorded in the servedPDPPDNAddress (this field initially supported both IPv4 and IPv6).
recordType ...
recordType PGWRECORD
servedIMSI 25001 **********
p-GWAddress 213.87.xx
chargingID 15934348563
servingNodeAddress 213.87.xx
accessPointNameNI internet.mts.ru
pdpPDNType IPV4 + IPV6
servedPDPPDNAddress 2a00: 1fa0: 800 :: 5c: 7ef: 201
servedPDPPDNAddressExt 10.21.12.11
servinggNodePLMNIdentifier 250, 01
servedIMEISV 35915 ***********
rATType eUTRAN
mSTimeZone + 03:00,
servedIMSI 25001 **********
p-GWAddress 213.87.xx
chargingID 15934348563
servingNodeAddress 213.87.xx
accessPointNameNI internet.mts.ru
pdpPDNType IPV4 + IPV6
servedPDPPDNAddress 2a00: 1fa0: 800 :: 5c: 7ef: 201
servedPDPPDNAddressExt 10.21.12.11
servinggNodePLMNIdentifier 250, 01
servedIMEISV 35915 ***********
rATType eUTRAN
mSTimeZone + 03:00,
Transportation network
Address-family ipv6 rises and routing is written.
Useful links to our topic
In conclusion, I want to ask you a question.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/334610/
All Articles