HPE Launches New HPE ProLiant Gen10 Servers
On July 11, HPE began accepting orders for new ProLiant Gen10 servers, and in this material we want to talk about key technologies and characteristics of models in this anniversary generation.

Although the release of a new generation of servers coincided with the release of Intel Xeon Scalable Family processors, this was not the only reason for the upgrade. The prerequisites were new HPE customer challenges. Among them are: the emergence of new load classes (including those requiring processing large amounts of data in memory and high performance of the disk subsystem), improving the manageability of the hardware infrastructure (transition to management through the REST API, integration with various IT automation tools, support for templates and scripts ), new IT consumption patterns (for example, financial services and pay-as-you-go), as well as, not least, new information security threats related to the low-level vulnerability to mponentov servers (BIOS and firmware).
')
What's new in HPE ProLiant Gen10 servers in response to all these challenges. We will understand in order.
At the forefront is the increase in server performance using proprietary HPE technologies under the general name Intelligent System Tuning:
- Workload Matching is a set of server presets for various specific tasks, which in each case increase the return due to subtle changes in the configuration of memory, processors, power, disk subsystem, etc. (there are about 30 adjustable settings in total, so it may not be easy to set up a server for a specific task)

- Jitter Smoothing (smoothing jitter). With the inclusion of this technology, the server begins to track the "jitter" of the processor frequency in TurboBoost mode, and smooth out the frequency drops to eliminate delays in accessing different memory levels that occur when a sharp change in frequency. As a result, in tasks demanding for frequency and latency (for example, real-time OS and some Java applications) we get a performance boost even above the usual increase in the turbo mode. You can read more about this technology here .

- Core Boosting (acceleration cores). This technology will be available in Gen10 servers in the upcoming releases (autumn 2017 - spring 2018), for some Intel Xeon Scalable 6000 and 8000 families. It is designed to increase the frequency of active cores in Intel Xeon processors in TurboBoost mode beyond the "normal" available frequency in this mode. As a result of these settings, you can remain at the same level of performance, for example, in an Oracle database, while working on a smaller number of cores. And this is a direct saving of money on licenses.

To enable Jitter Smoothing and Core Boosting, an iLO Advanced or higher license must be activated on the server. Core Boosting, in addition, will not work on all processors and server configurations. Briefly about all three technologies - here .
The mechanisms for ensuring fault tolerance of memory were also improved. In modern systems, where the amount of memory in the hundreds of gigabytes, the probability of errors in some memory chips is very high. Therefore, the use of tools to ensure the reliability of memory (RAS) is becoming increasingly reasonable. With the Gen10 generation, HPE introduced another such tool - SmartMemory Fast Fault Tolerance (FFT) technology. Proactive algorithms in HPE servers constantly analyze the state of memory chips. And, in the event of a risk for data in a certain area of memory in a chip, the FFT assigns it “spare” areas of comparable volume on the same memory channel. As a result, writing and reading data in the protected area comes with integrity monitoring, and throughput and total volume only fall for this small area.
What is the difference between this technology, for example, from the mechanism of Lockstep with Intel's DDDC, which is used in Xeon E7 processors now? In that with thin control of HPE Advanced Error Detection and Fast Fault Tolerance, we reduce performance only when there is a probability of data loss and only for a small memory area, unlike Lockstep, where performance is reduced throughout the system from a few to 50% . With FFT, bandwidth per server drops on average by no more than 1%. This technology is also unique to HPE and will not appear in servers from other manufacturers for another 2 years under a licensing agreement with Intel . In general, the use of modern RAS technologies in HPE servers, according to HPE statistics, reduces the number of system crashes per year (Annual Crash Rate) by 85%. Another answer to the question why the memory from HPE is called Smart Memory.
A video about this technology can be viewed below, and a detailed technical document will be released soon.
Another set of innovations in working with memory is the two technologies of non-volatile RAM, HPE NVDIMM and HPE Scalable Persistent Memory . The first is the memory modules existing for more than two years combined with a non-volatile USB flash drive (on the same module) with battery power in the server. Such modules are visible to the usual OS (Windows and Linux) as a very fast block device - see the experiments here . And for some applications (for example, Microsoft SQL Server 2016 ), such a module is visible as a special device with byte-by-addressing (as in RAM), but with power-off resistance. When placed on such modules, the tail of the transaction log (MS SQL Server), we see a performance increase of the database up to 4 times compared to placing the tail of the log on the SSD. New HPE NVDIMM modules now have a capacity of 8 and 16 GB, while for SQL databases of a few hundred gigabytes in most cases, 1 NVDIMM module is enough to accommodate the tail of the transaction log.
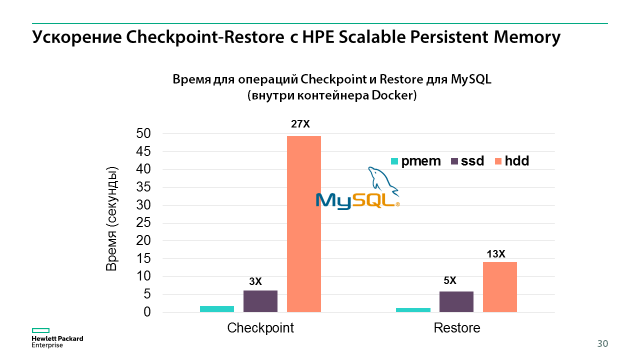
HPE Scalable Persistent Memory are complex devices based on HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 servers, conventional DDR4 memory modules and a special RAM protection mechanism against power loss using NVMe drives and a backup power supply unit with an internal UPS in the server itself. With this device, you can store up to 1 TB of data in memory without the risk of losing it when a power outage occurs, and thus speed up many applications many times. For example, in internal tests with MySQL, Checkpoint operations (saving database data from memory to non-volatile media) on HPE Scalable Persistent Memory were performed 27 times faster than on the HDD and 3 times faster than on the SSD. And Restore (the inverse operation - returning data to memory after a failure) occurred 13 and 5 times faster, respectively. And besides, with such a system almost any database can be turned into in-memory, repeatedly increasing its performance.
The use of NVMe-drives also received a very deep development. Now you can install several times more NVMe drives in each server (up to 20 in DL380 Gen10, for example), and you can install both NVMe and SAS / SATA disks in the same disk cage in the server (regular recycle bins without support NVMe if you don’t need it). Plus, there is support for a new format of drives - uFF (micro-Form Factor), which places 2 in place of one SFF-drive (volumes 120 and 340 GB, SATA). uFF-SSD can be used as bootable or cache disks for a variety of tasks, and save server space for more capacious drives for productive data.
Updated and line of controllers . Now they are faster (up to 1.6 million IOPS from the controller) and can work simultaneously in HBA and RAID mode (some disks on the controller in one mode, some in the other). The full line of controllers in Gen10 at the moment looks like this:

One of the most powerful innovations of the Gen10 generation is the advanced HPE iLO 5 remote control system. In addition to the faster iLO chip, which speeds up operations with a remote console and virtual drives, a number of new features have appeared:
HPE Silicon Root Trust is the iLO firmware check for malicious code or damage by checking the checksum with a hardware chip inside the iLO system. When the iLO firmware is checked, this management tool itself checks the firmware of all other server components, including the BIOS, for intruders or other integrity problems. If a problem is detected, iLO can automatically or, on command, restore a specific firmware to the latest operating state from the protected firmware repository, return the server to factory settings or not respond.
 Why this technology? First, component firmware can be damaged during the update process manually or simply due to a failure in the chip. Secondly, analysts of information security threats every year discover more and more vulnerabilities in firmware and other low-level server code. The latest loud example is a vulnerability found in patches for SuperMicro server firmware that Apple has bought for itself ( link ). This level is almost not controlled by the usual antivirus, and therefore the threat there is significant.
Why this technology? First, component firmware can be damaged during the update process manually or simply due to a failure in the chip. Secondly, analysts of information security threats every year discover more and more vulnerabilities in firmware and other low-level server code. The latest loud example is a vulnerability found in patches for SuperMicro server firmware that Apple has bought for itself ( link ). This level is almost not controlled by the usual antivirus, and therefore the threat there is significant.
The uniqueness of the HPE approach here: a) complete control over the production of firmware components; All components under the HPE brand are specially designed, or tested and supplied only through the HPE channel firmware and, starting with the Gen10 generation, are supplied with the HPE digital signature. And b) only HPE develops and manufactures its own iLO management system, from software to microchips, thanks to which it can integrate a firmware signature verification tool into it.
Another small but useful security improvement is the server case opening sensor, which, if triggered, can iLO block the server operation until the causes of the incident are determined.
Functional improvements in iLO 5 - now a server configuration tool, including RAID settings, called Intelligent Provisioning, can be launched directly from the iLO console, and not just when the server is booted by pressing F10. This allows you to avoid unnecessary server restarts.
The loading procedure itself began to run faster when using the UEFI BIOS mode — on average, booting is 3 times faster . The RBSU BIOS configuration interface has changed and become more convenient, and it can also be launched from Intelligent Provisioning (and from iLO).
A big plus for users of various automation tools, including in multi-vendor environments - iLO now supports most Open IPMI instructions. And besides, HPE continues to lead in filling the standard of management with hardware through the REST API (read here ). Now HPE's REST API is fully compliant with the DMTF Redfish standard, except for part of managing the RAID controllers (there’s own REST API for now). To manage through the REST API, there is both a proprietary tool and a lot of tools (for example, for Python and PowerShell ).
Another innovation - this time in the diagnosis of faults. If earlier, the Active Health System Log (recording of the “flight recorder” of the server) could only be unloaded via iLO and sent to the HPE Support Center for analysis, now it can be downloaded to a USB flash drive via a special USB port on the front of the server and analyzed by yourself free service Active Health System Viewer . The service shows and offers a solution for 25% of possible vulnerabilities, and for the rest, it just makes it much easier to contact support, reducing the time for analyzing the malfunction.

The second part of our review is about the models that are already available to order today. This is how the entire main portfolio of HPE servers will look like (here we are not talking about Apollo, Integrity and some other lines):
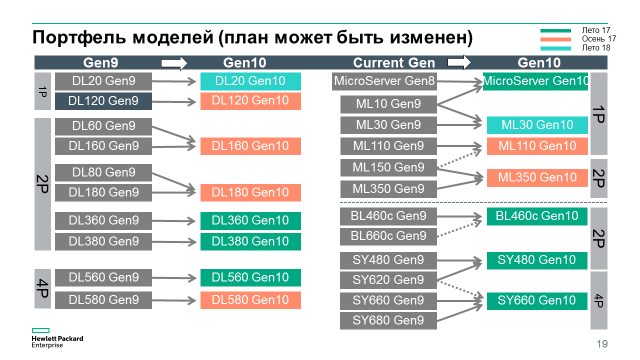
Green highlighted those models that can be ordered now. Overview of models in pictures:
ProLiant DL360 Gen10



ProLiant DL380 Gen10



ProLiant DL560 Gen10


ProLiant BL460c Gen10 - yes, we continue to release blades in the current chassis!


MicroServer Gen10


In addition, new servers for the Synergy platform — the SY480 Gen10 and SY660 Gen10 — are now available, and the Synergy platform itself has received 25/50 GbE support from the Mellanox factory, powerful graphics options and an expansion of the configuration options for the internal disk shelves.
Plus, the product line for high-performance computing (LDCs) has been significantly updated. A new flagship supercomputer world - HPE SGI 8600 system with liquid (water) cooling. Responding to the rapid progress in the LDC world and the needs of HPE customers, the 6000 series is completely redesigned - a new highly integrated HPE Apollo 6000 Gen10 system (XL230k Gen10 nodes and k6000 chassis) is introduced. To solve a wide range of tasks in the field of artificial intelligence and some other loads, a new HPE Apollo 10-series node family was introduced, supporting the most advanced computing acceleration technologies Intel Xeon Phi 7000 and NVIDIA Tesla P100 on the NVLink bus.
This concludes this article, and we are waiting for your wishes - what technologies, applications, and server models will we touch on in our upcoming reviews and webinars? We have planned 4 webinars for October - it's up to you what they will be about. Please reply in the comments.
In the meantime, many great Gen10 videos can be viewed here .

Although the release of a new generation of servers coincided with the release of Intel Xeon Scalable Family processors, this was not the only reason for the upgrade. The prerequisites were new HPE customer challenges. Among them are: the emergence of new load classes (including those requiring processing large amounts of data in memory and high performance of the disk subsystem), improving the manageability of the hardware infrastructure (transition to management through the REST API, integration with various IT automation tools, support for templates and scripts ), new IT consumption patterns (for example, financial services and pay-as-you-go), as well as, not least, new information security threats related to the low-level vulnerability to mponentov servers (BIOS and firmware).
')
What's new in HPE ProLiant Gen10 servers in response to all these challenges. We will understand in order.
Processors
At the forefront is the increase in server performance using proprietary HPE technologies under the general name Intelligent System Tuning:
- Workload Matching is a set of server presets for various specific tasks, which in each case increase the return due to subtle changes in the configuration of memory, processors, power, disk subsystem, etc. (there are about 30 adjustable settings in total, so it may not be easy to set up a server for a specific task)

- Jitter Smoothing (smoothing jitter). With the inclusion of this technology, the server begins to track the "jitter" of the processor frequency in TurboBoost mode, and smooth out the frequency drops to eliminate delays in accessing different memory levels that occur when a sharp change in frequency. As a result, in tasks demanding for frequency and latency (for example, real-time OS and some Java applications) we get a performance boost even above the usual increase in the turbo mode. You can read more about this technology here .

- Core Boosting (acceleration cores). This technology will be available in Gen10 servers in the upcoming releases (autumn 2017 - spring 2018), for some Intel Xeon Scalable 6000 and 8000 families. It is designed to increase the frequency of active cores in Intel Xeon processors in TurboBoost mode beyond the "normal" available frequency in this mode. As a result of these settings, you can remain at the same level of performance, for example, in an Oracle database, while working on a smaller number of cores. And this is a direct saving of money on licenses.

To enable Jitter Smoothing and Core Boosting, an iLO Advanced or higher license must be activated on the server. Core Boosting, in addition, will not work on all processors and server configurations. Briefly about all three technologies - here .
Memory
The mechanisms for ensuring fault tolerance of memory were also improved. In modern systems, where the amount of memory in the hundreds of gigabytes, the probability of errors in some memory chips is very high. Therefore, the use of tools to ensure the reliability of memory (RAS) is becoming increasingly reasonable. With the Gen10 generation, HPE introduced another such tool - SmartMemory Fast Fault Tolerance (FFT) technology. Proactive algorithms in HPE servers constantly analyze the state of memory chips. And, in the event of a risk for data in a certain area of memory in a chip, the FFT assigns it “spare” areas of comparable volume on the same memory channel. As a result, writing and reading data in the protected area comes with integrity monitoring, and throughput and total volume only fall for this small area.
What is the difference between this technology, for example, from the mechanism of Lockstep with Intel's DDDC, which is used in Xeon E7 processors now? In that with thin control of HPE Advanced Error Detection and Fast Fault Tolerance, we reduce performance only when there is a probability of data loss and only for a small memory area, unlike Lockstep, where performance is reduced throughout the system from a few to 50% . With FFT, bandwidth per server drops on average by no more than 1%. This technology is also unique to HPE and will not appear in servers from other manufacturers for another 2 years under a licensing agreement with Intel . In general, the use of modern RAS technologies in HPE servers, according to HPE statistics, reduces the number of system crashes per year (Annual Crash Rate) by 85%. Another answer to the question why the memory from HPE is called Smart Memory.
A video about this technology can be viewed below, and a detailed technical document will be released soon.
Another set of innovations in working with memory is the two technologies of non-volatile RAM, HPE NVDIMM and HPE Scalable Persistent Memory . The first is the memory modules existing for more than two years combined with a non-volatile USB flash drive (on the same module) with battery power in the server. Such modules are visible to the usual OS (Windows and Linux) as a very fast block device - see the experiments here . And for some applications (for example, Microsoft SQL Server 2016 ), such a module is visible as a special device with byte-by-addressing (as in RAM), but with power-off resistance. When placed on such modules, the tail of the transaction log (MS SQL Server), we see a performance increase of the database up to 4 times compared to placing the tail of the log on the SSD. New HPE NVDIMM modules now have a capacity of 8 and 16 GB, while for SQL databases of a few hundred gigabytes in most cases, 1 NVDIMM module is enough to accommodate the tail of the transaction log.
HPE Scalable Persistent Memory are complex devices based on HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 servers, conventional DDR4 memory modules and a special RAM protection mechanism against power loss using NVMe drives and a backup power supply unit with an internal UPS in the server itself. With this device, you can store up to 1 TB of data in memory without the risk of losing it when a power outage occurs, and thus speed up many applications many times. For example, in internal tests with MySQL, Checkpoint operations (saving database data from memory to non-volatile media) on HPE Scalable Persistent Memory were performed 27 times faster than on the HDD and 3 times faster than on the SSD. And Restore (the inverse operation - returning data to memory after a failure) occurred 13 and 5 times faster, respectively. And besides, with such a system almost any database can be turned into in-memory, repeatedly increasing its performance.

The use of NVMe-drives also received a very deep development. Now you can install several times more NVMe drives in each server (up to 20 in DL380 Gen10, for example), and you can install both NVMe and SAS / SATA disks in the same disk cage in the server (regular recycle bins without support NVMe if you don’t need it). Plus, there is support for a new format of drives - uFF (micro-Form Factor), which places 2 in place of one SFF-drive (volumes 120 and 340 GB, SATA). uFF-SSD can be used as bootable or cache disks for a variety of tasks, and save server space for more capacious drives for productive data.
Updated and line of controllers . Now they are faster (up to 1.6 million IOPS from the controller) and can work simultaneously in HBA and RAID mode (some disks on the controller in one mode, some in the other). The full line of controllers in Gen10 at the moment looks like this:

iLO 5
One of the most powerful innovations of the Gen10 generation is the advanced HPE iLO 5 remote control system. In addition to the faster iLO chip, which speeds up operations with a remote console and virtual drives, a number of new features have appeared:

HPE Silicon Root Trust is the iLO firmware check for malicious code or damage by checking the checksum with a hardware chip inside the iLO system. When the iLO firmware is checked, this management tool itself checks the firmware of all other server components, including the BIOS, for intruders or other integrity problems. If a problem is detected, iLO can automatically or, on command, restore a specific firmware to the latest operating state from the protected firmware repository, return the server to factory settings or not respond.
 Why this technology? First, component firmware can be damaged during the update process manually or simply due to a failure in the chip. Secondly, analysts of information security threats every year discover more and more vulnerabilities in firmware and other low-level server code. The latest loud example is a vulnerability found in patches for SuperMicro server firmware that Apple has bought for itself ( link ). This level is almost not controlled by the usual antivirus, and therefore the threat there is significant.
Why this technology? First, component firmware can be damaged during the update process manually or simply due to a failure in the chip. Secondly, analysts of information security threats every year discover more and more vulnerabilities in firmware and other low-level server code. The latest loud example is a vulnerability found in patches for SuperMicro server firmware that Apple has bought for itself ( link ). This level is almost not controlled by the usual antivirus, and therefore the threat there is significant.The uniqueness of the HPE approach here: a) complete control over the production of firmware components; All components under the HPE brand are specially designed, or tested and supplied only through the HPE channel firmware and, starting with the Gen10 generation, are supplied with the HPE digital signature. And b) only HPE develops and manufactures its own iLO management system, from software to microchips, thanks to which it can integrate a firmware signature verification tool into it.
Another small but useful security improvement is the server case opening sensor, which, if triggered, can iLO block the server operation until the causes of the incident are determined.
Functional improvements in iLO 5 - now a server configuration tool, including RAID settings, called Intelligent Provisioning, can be launched directly from the iLO console, and not just when the server is booted by pressing F10. This allows you to avoid unnecessary server restarts.
The loading procedure itself began to run faster when using the UEFI BIOS mode — on average, booting is 3 times faster . The RBSU BIOS configuration interface has changed and become more convenient, and it can also be launched from Intelligent Provisioning (and from iLO).
A big plus for users of various automation tools, including in multi-vendor environments - iLO now supports most Open IPMI instructions. And besides, HPE continues to lead in filling the standard of management with hardware through the REST API (read here ). Now HPE's REST API is fully compliant with the DMTF Redfish standard, except for part of managing the RAID controllers (there’s own REST API for now). To manage through the REST API, there is both a proprietary tool and a lot of tools (for example, for Python and PowerShell ).
Another innovation - this time in the diagnosis of faults. If earlier, the Active Health System Log (recording of the “flight recorder” of the server) could only be unloaded via iLO and sent to the HPE Support Center for analysis, now it can be downloaded to a USB flash drive via a special USB port on the front of the server and analyzed by yourself free service Active Health System Viewer . The service shows and offers a solution for 25% of possible vulnerabilities, and for the rest, it just makes it much easier to contact support, reducing the time for analyzing the malfunction.

New HPE ProLiant Gen10 models
The second part of our review is about the models that are already available to order today. This is how the entire main portfolio of HPE servers will look like (here we are not talking about Apollo, Integrity and some other lines):

Green highlighted those models that can be ordered now. Overview of models in pictures:
ProLiant DL360 Gen10



ProLiant DL380 Gen10



ProLiant DL560 Gen10


ProLiant BL460c Gen10 - yes, we continue to release blades in the current chassis!


MicroServer Gen10


In addition, new servers for the Synergy platform — the SY480 Gen10 and SY660 Gen10 — are now available, and the Synergy platform itself has received 25/50 GbE support from the Mellanox factory, powerful graphics options and an expansion of the configuration options for the internal disk shelves.
Plus, the product line for high-performance computing (LDCs) has been significantly updated. A new flagship supercomputer world - HPE SGI 8600 system with liquid (water) cooling. Responding to the rapid progress in the LDC world and the needs of HPE customers, the 6000 series is completely redesigned - a new highly integrated HPE Apollo 6000 Gen10 system (XL230k Gen10 nodes and k6000 chassis) is introduced. To solve a wide range of tasks in the field of artificial intelligence and some other loads, a new HPE Apollo 10-series node family was introduced, supporting the most advanced computing acceleration technologies Intel Xeon Phi 7000 and NVIDIA Tesla P100 on the NVLink bus.
This concludes this article, and we are waiting for your wishes - what technologies, applications, and server models will we touch on in our upcoming reviews and webinars? We have planned 4 webinars for October - it's up to you what they will be about. Please reply in the comments.
In the meantime, many great Gen10 videos can be viewed here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/333800/
All Articles