What is ERP system
 Many companies, as business grows, come to understand that they need some kind of ERP system. If in a small business you manage to do without this tool, then an average business uses such tools more actively every day. But in order to choose an ERP system, and even to understand whether this product is required in a business and what advantages its use will bring, it is important to correctly understand what it is.
Many companies, as business grows, come to understand that they need some kind of ERP system. If in a small business you manage to do without this tool, then an average business uses such tools more actively every day. But in order to choose an ERP system, and even to understand whether this product is required in a business and what advantages its use will bring, it is important to correctly understand what it is.In my articles, I often deal with the description of various concepts. As you know, in order to sell a service, the buyer must understand what it is and why it needs this service. It is very important to agree on the terms, only in this case, the result will meet the expectations of the client. The term ERP is one of the most difficult and controversial.
Description of the ERP system
ERP is a marketing term. To understand what is at stake, as well as to study the history of the origin of this abbreviation, you can refer to Wikipedia:
')
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning, enterprise resource planning) - an organizational strategy for integrating production and operations, human resource management, financial management and asset management, focused on continuous balancing and optimization of enterprise resources through a specialized integrated application software package that provides a common data model and processes for all spheres of activity [1] [2]. ERP-system - a specific software package that implements the strategy of ERP. Wikipedia
This definition is absolutely correct, but relatively difficult to understand, especially if a person is unfamiliar with such concepts as “balancing resources” or “data model”. It is important to understand that the term ERP is, first of all, marketing, and does not have any deep methodological basis. Therefore, I propose the following definition:
ERP is, above all, an information system that allows you to store and process most of the critical data for a company.
What is critical data? And why do I say “most”? The fact is that some ERP systems have a “Production” module, while it is a separate software product that is not connected by default to other systems and units. Others try to combine all possible processes necessary for the work of the company. Can different types of ERP be considered useful? Naturally, below I will focus on this issue in more detail. Now back to the terms.
- Critical data is a list of data, without which the work of the company is impossible. This data is the work of the sales department, and production (if the company is a manufacturer). Some companies use ERP primarily for production management, as there is no better solution for producing. Other companies are not manufacturers, for example, distributors, but also successfully apply ERP. Distribution, personnel management, sales of goods and services are becoming critically important for them.
- Most data : this is a list of processes and information that is optimal for each particular company. Of course, it would be ideal to collect all the data and information about all the processes. But this leads to higher costs of implementation. As a result, the business management, together with the implementation specialists, chooses a certain compromise solution, in which the ERP system gathers the information and processes that are necessary for operational control and management decisions, and some of the data and processes are collected in specialized systems, to which the manager addresses as needed .
The list of critical data and the part that must be processed in the ERP system are calculated empirically for each specific business. It is the analysis of these data and their correct definition that gives answers to the questions: is there a need to purchase and implement an ERP system, and will the costs for this type of business automation be justified?
What is the ERP system
All ERM-systems, regardless of who their developer, combines a common architecture, which can be described as follows:
- Platform. Basic features and environment for modules and components. Only developer can make changes to platform code. Users and implementers do not have access to this software code. The platform includes:
1. The core. The software environment in which the work will be done, for which you can write some add-ins and components.
2. Basic functionality. The list of directories and functions, without which no company can operate. This is a user directory with access rights, a customer directory, a product / service directory, etc. This functionality is built into the platform; unlike modules, it cannot be disabled. - Data management. Database, including storage and processing methods (interpretation) of data. This category includes data storage on the server, software for working with databases (SQL or any alternative), tools for interpreting and processing data and sending them to program modules.
- Modules. Components that connect to the platform as needed. All of them work with a single database and use basic functionality (as needed). Otherwise, the modules work independently of each other, they can connect seamlessly and disconnect without problems if the need for them has disappeared. Such a modular structure is an important distinguishing feature of ERP systems. Modules are divided, in turn, into several types:
1. Modules for internal use. This level - plug-ins that are used by employees of the company. These are warehouse management, production, accounting, CRM, etc. Modules can be connected, disconnected, or customized by the implementation specialists. The standard set usually includes - MRP, HR, CRM, Supply and Procurement Management.
2. Modules of work with external users. This layer contains the modules necessary for interaction with external users, potential and real customers of the company, partners, product users, suppliers and customers. This may be an online store, personal offices for suppliers and customers on the corporate website and similar solutions. Some ERP-systems contain ready-made CMS-systems for creating an online store or corporate site from scratch, others offer only separate tools to the "add-in" to the site and / or client applications (for mobile and tablets).
3. Connectors - ready-made solutions for communication with third-party applications. Most often use API from a kernel of a platform. They allow you to integrate telephony, set up data exchange with the site or any software products and systems. Connectors are intended only for data exchange and are usually used for data exchange with EDI,
CMS, CAD, BI, OLAP, etc. That is, with those systems that are not included in the EPR, but are used in the company.
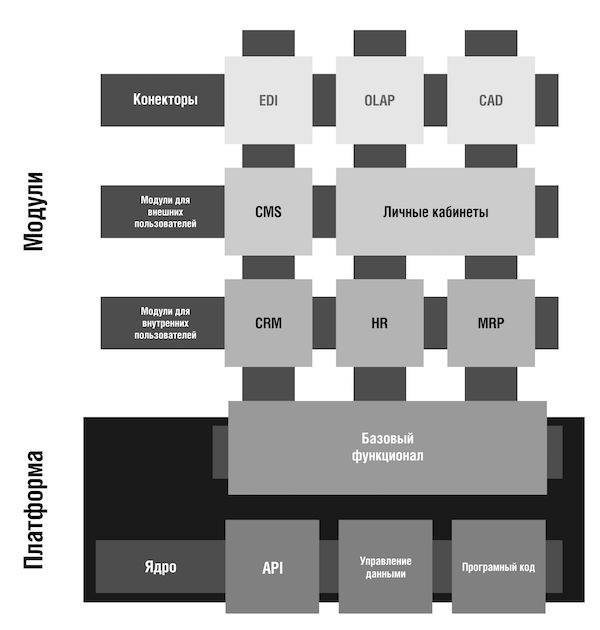
The structure described above is typical for ERP from a logical point of view. Some systems do not have pronounced modularity, they are all already built into the program, but they can be used separately from each other as needed. Others refer to disconnectable modules as subsystems. And part of the ERP-systems allocate all the modules really in separate products. And they propose to buy a core, and to it - a list of modules to choose from. With the ability to buy and add features in the future as needed.
Benefits of an ERP modular structure
An important advantage of ERP systems is the ability to connect and use any of the modules (internal or external) in a short time. Moreover, the possibilities that are thus connected to ERP are added to the system absolutely seamlessly. This is an important difference between ERP from the integration of several software products among themselves or from a system that has grown from a specialized one due to numerous improvements and add-ons by own or invited IT specialists.
- Each of the ERP-system modules works independently of the others, it can be connected or disconnected at any time, it can simply not be used, while other modules can continue to work. And to connect a particular module, there is no need to make changes to the program code of the kernel and other modules.
- When using an ERP system to expand the capabilities and connect a new unit, there is no need to add program code, create a new part of the program from scratch, or engage in complex and, sometimes, not very convenient integration of different programs. Simply select the desired module, connect and configure it to the needs of the business. In ERP systems, almost everything that may be required in business automation has already been implemented. Recorded improvements are required in isolated cases.
For example, you can use a CRM module, but abandon the personnel management module. As the company grows and develops, any of the modules is easily connected, configured and the software product continues to work with new functions.
Often I hear from customers the phrase "we have developed our ERP-system." In fact, in this case, not ERP is used, but some kind of similarity that has grown out of some specialized system. For example, we started working in CRM, then we added a module for the warehouse to it, set up data exchange with accounting programs, etc. Or they started with an accounting system and a website, and also - they were integrating, adding modules, all this was somehow “docked” with each other.
All this is not an ERP system. The main difference between ERP from any similar programs is that ERP is initially created as a constructor from the platform and modules that can be connected as needed. There are already provided a variety of possibilities.
ERP is a product that was originally created, on the one hand, for scalability, and on the other - to ensure maximum opportunities.
In the ERP system, the boundaries of the modules are very clearly separated. And disabling any of them (except for some basic reference books and features) will not affect the work of the rest. In samopisnyh systems that grow out of specialized, as a rule, this architecture is not provided. And if you disable features, for example, accounting, most likely, the program will stop working or will not work correctly. Programmer intervention and significant improvements will be required. Such software products, as a rule, use common documents and the components in them are closely intertwined. The ERP architecture is truly modular. And it is very important to understand.
Those. If you choose an ERP system, you get a single system for automating the various departments of your company plus a wide range of opportunities for development. You will not need to change the software product for a very long time, it will be enough to call specialists who will help you select and connect ready-made modular solutions. And there are a huge number of them for a variety of business areas and job features.
What is ERP system used for?
The introduction of any ERP-system allows you to get certain advantages and features. About who and why the need for the implementation of ERP, let's see more.
The principle of a single database: control, management, accuracy and efficiency
To understand this principle, let's imagine the company before and after the implementation of ERP. Suppose an organization has its own production. Most likely, accounting for production is conducted in Excel spreadsheets or in a specialized program. Warehouse accounting works in its own accounting system, accounting - in accounting software. Data transfer from department to department is made in the form of paper documents, and sometimes even verbally, after which it is manually entered into the necessary accounting system.
Such an approach very much depends on the human factor, as a result, the information comes with delays, often significant. There are frequent distortions and errors, and in some cases, some data do not enter the system at all due to human factors, which leads to malfunctions, the need for regular reconciliations, etc. Moreover, any mistake and subsequent correction can lead to significant losses. For example, an error in the code or size when transferring data from the design department to production ends very sadly, since the result is not what was ordered and designed. There are downtime, the cancellation of a marriage or an excess of goods in a warehouse, the failure of terms under the contract with the client, etc.
In the case of implementing the ERP system, a single database is created into which all the information used by different departments is collected. In this case, the percentage of errors is significantly reduced, since the data is entered into the system once by a specialist, and then read automatically by all departments in the required format and encoding.
In addition, the data transfer rate when using a single database becomes instantaneous. Those. Immediately after the designers or sales specialists have placed an order in the database, they see it in the design department or in production. Also, the payment mark appears on the order immediately after the accounting department received information from the bank. The number of errors related to the human factor decreases, and those that do occur are eliminated much faster.
And because the ERP system is necessary for companies for which the speed and accuracy of data transfer between departments is a critical factor.
Flexibility in the company with regard to market changes
If the company aims to maximize compliance with the ever-changing market conditions and customer needs, it just needs prompt data exchange between departments and prompt management decisions.
A small company in the case of receipt of atypical orders or changes in the volume of purchases of certain goods, of course, can do without the ERP-system. When all employees work in one small office, you can always coordinate actions among themselves, and create an order on the basis of data from orders even in Excel-tables.
In conditions of medium-sized businesses, where there are several divisions, branches, it is possible that their production, a single database and the rapid exchange of data in the context of the changing needs of customers become critical. It is important that all information be collected in a short time, timely purchases are made, and operational changes are made to the production and supply plan. Here, without a single system with a common database is indispensable.
Complex business processes: integration no longer helps
Another case where the ERP-system is indispensable is companies in which, as they grow and develop, complex processes appear that require significant amounts of data exchange. At a certain stage, the integration between several software systems becomes complex, cumbersome and unprofitable. ERP system becomes a solution to this problem.
What does a business get from ERP implementation?
ERP is, first of all, the ability to combine all business processes in one powerful and convenient system, and therefore the advantages of the solution can be listed for a long time. Below I have highlighted only a few, which I consider to be the most significant:
- Data availability Once the entered data becomes available within the whole system, no reconciliations, additional approvals and checks are required.
- Data consistency. The use of a common database avoids the stages of reconciliation and harmonization of data. For example, if the design department has submitted and approved a project, the procurement department can use the data from this project immediately, without an additional confirmation step.
- Monitoring the work of employees. In the case when one of the divisions enters data, for example, about the expenditure (movement) of the goods, the other division immediately receives information about it, and after actually receiving the listed items, puts it on the parish. The discrepancy in numbers in this case is almost impossible, the general database eliminates the possibility of many abuses, and the manager in real time can identify any discrepancies and their causes.
- A significant reduction in the number of errors associated with human factors . The unified system will not allow the goods to be written off from the wrong warehouse, as the general database will indicate that the goods are not there. Information about payments will be transferred to the accounting department and the sales department automatically based on data from the bank or cash register, which also eliminates errors. Technical parameters and project data will also be transferred automatically, without distortion, etc.
- Ready set of interconnected tools. For example, if the sales department creates an invoice, then it is the basis for the automatic creation of accounting documents, and after payment - the expense documents from the warehouse.
A significant number of tools that may be needed in the future. Almost all ERP-systems are very powerful and versatile. They have the potential to implement a huge number of processes. Almost always, when implementing is used only part of these features. And as the company grows and develops, modules are being connected or purchased that allow to introduce new solutions, to connect new divisions of the company to work. And all this - with minimal expenditure of finance and time.
What is important to know when choosing an ERP system
One of the first questions that arise when choosing any software is to choose between Saas or Stand-Alone, i.e. pay for access to the system located in the "clouds" or buy a "box solution". In detail about this choice, I told in the article What are CRM-systems and how to choose them correctly?
In the case of ERP-systems, there is exactly the same choice as in the implementation of CRM-systems. You can also look at SAAS solutions or buy and implement a “box”. But there is one nuance that is very important to consider. The fact is that ERP is a large system in itself, including a large number of possibilities. In fact, it combines all the data on the work of the company. And in the case of the use of the “cloud” it will be extremely difficult to change the service if the need arises. Unlike CRM-systems, which are very popular just in the SAAS variant, the data array in ERP is bulky and cumbersome, and in the case of switching from one software product to another, the question arises as to what to do with them.
And so it makes sense to focus on the purchase of a software product "in the box" and its subsequent installation on its own or rented servers. So, what you need to first pay attention to:
- Choosing a team or implementation specialist. If some software products, for example, CRM-systems for a small company, with a strong desire to actually implement even without a specialist or with his minimum participation, the ERP-system without an experienced specialist will remain the next "unclaimed box". The complexity of the software products of this family is due to the complexity of the tasks that are put before them. A single database, integration with other programs, many other nuances of work can not be configured without the participation of a professional.
- ERP system is not the key to all doors and not a Swiss knife. Just like the rest of the system, they can have specificity and industry affiliation. That is, if you are selling, not manufacturing, then ERP should be taken primarily for sales. The same goes for modules.
- Understanding of business processes. It is very important that the implementation specialist deeply understands not only the features of the software product, but also has a fairly wide range of knowledge in the field of business, as it is necessary to understand how the accountant works with what is needed to tune the work of the accounting department. To implement ERP in stock, knowledge of stock accounting is required. That is why the level of knowledge and understanding of the company's business processes is especially important for the project manager who will set the tasks for the technical specialists and control their execution.
- Budget. ERP-system as a software product is relatively expensive, regardless of the developer. But for successful implementation will require cooperation with experienced professionals. And if the budget is only enough to pay for the program, then as a result the “box” is unclaimed, i.e. the company is wasting a significant amount. Calculate your possibilities in advance.
The disadvantages of ERP-systems
The disadvantages of this type of software products are the result of their advantages. A single database and a single system give rise to a significant number of links, the high complexity of the system itself, and high demands on the hardware (server) part. And because for the organization of the ERP-system, you need powerful equipment, which entails the corresponding costs.
Another problem that often arises when implementing an ERP system is ensuring data security. Since the system employs all divisions and employees of the company, then the access rights must be configured for each of their own. And if, when using separate specialized programs, it is usually necessary to create several levels of access (an ordinary employee, head of department, manager), then the system of access rights in ERP is difficult. Here you need to configure and access to the modules for different departments, and within each department configure the hierarchy. Such a complex setup often leads to errors and requires additional time for testing and debugging.
In addition, the use of a single system with a single database with all its advantages also contains a certain problem. If, for one reason or another, the ERP system stops working (electricity is turned off or other problems occur on the server), the entire company stops working. Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to ensuring the reliability of the server part and timely maintenance.
Also ERP-system inherent flaws that are typical for all complex systems, namely - a high level of entry and, consequently, a high level of implementation costs.
Summary
In this article, I tried as simple as possible and without unnecessary technical details to talk about what the ERP-system and how they can bring business. I hope that I managed to give a basic knowledge of why such a system may be needed, in what cases it is needed, and where the costs of its implementation most likely will not pay off. And understanding what the ERP systems can do, and also what you want to get from their implementation, will help you make the right choice among software products of this class.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/333018/
All Articles
