IBM has created a new generation of carbon nanotube transistors
Not so long ago we published an article on the creation of a 5nm process technology, which allows us to create more productive and efficient processors. Today, IBM publishes another important news - the fact is that specialists of the corporation, using materials of a new type, created transistors that are smaller than all other transistors in size and at the same time faster.
The new material is carbon nanotubes, rolled sheets of carbon atoms with a thickness of 1 nanometer. The existence of this material has been known for a long time, but it was difficult to create something from it because of a number of its features. Existing technologies allowed making transistors from carbon nanotubes, but in this case the size of the elements would be even larger than the size of existing silicon transistors.
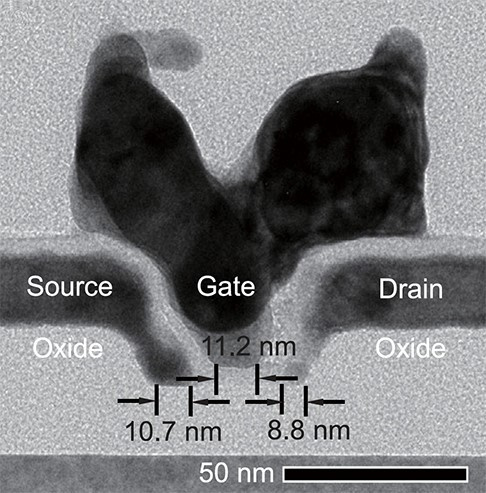
In order to achieve the desired and reduce the size of nanocarbon transistors, scientists used a new type of contact circuitry that allows current to pass through the nanotubes. The new method provides the ability to create contacts of molybdenum, which are associated with the ends of the nanotubes, making them smaller. Cobalt is also added to enable the entire system to operate at a lower temperature. This, in turn, has reduced the distance between the contacts.
')
The basis of this technology is the development of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), which allows separating semiconducting nanotubes from metal with high accuracy - up to 99.9%. Experts from IBM, in turn, have created their own technology for placing nanotubes that float in solution at certain places using a special kind of polymers.
Now, in order to conduct current from one contact to another, you need no more than a few nanocarbon tubes. In each transistor, the company's specialists added several parallel tubes, which are located close to each other. As a result, the total size of the transistor was only 40 nanometers. The performance of such transistors is higher than the performance of ordinary ones.
As a result, the basic form of the processor, created by the new technology, turned out. But, unfortunately, this is only a prototype, which can not be used. As a result, it was decided to create separate transistors, and this was justified. Each of the 192 transistors turned out to be working. After that, scientists have developed an experimental circuit of the ring generator, which earned. It turned out 55 ring generators with a total capacity of 2.8 GHz. True, not all the generators turned out to be workers, since a total of about 160 attempts were made.
But after several years of active work, the technology can be brought to the possibility of its practical use.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/333000/
All Articles