Why mobile apps take up more space
More recently, several interesting infographics have appeared on the Internet, indicating that popular mobile phone applications have increased by a factor of 12 in a couple of years. This post attempts to clarify some non-obvious reasons for the growing size of mobile apps.
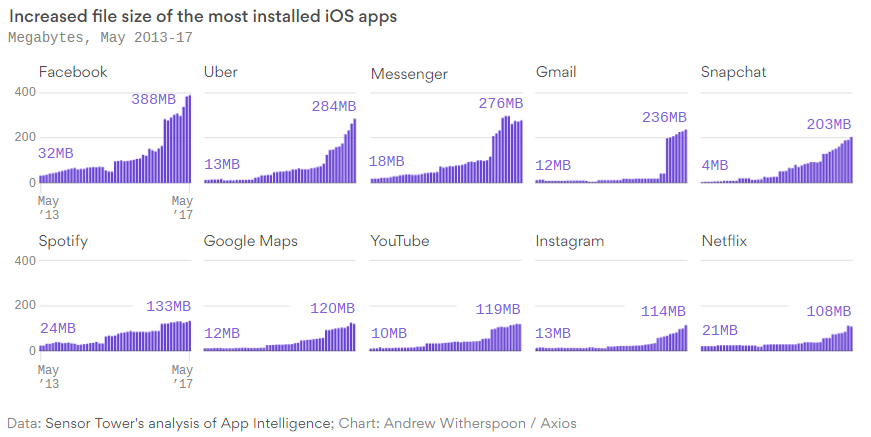
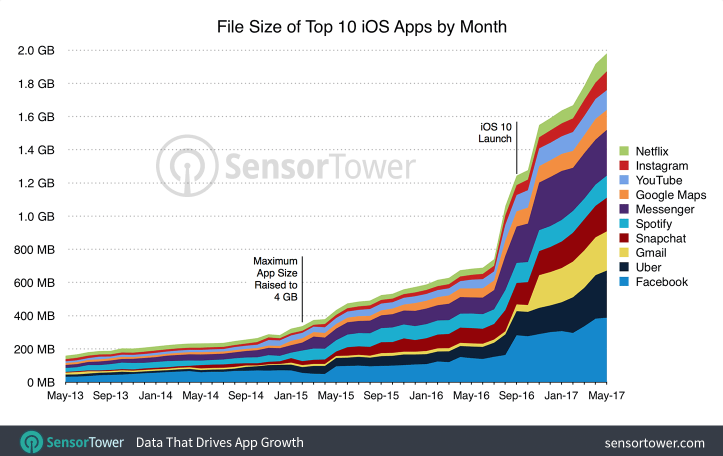
The authors of infographics in the original articles identify two reasons for this growth:
- increase the maximum allowable size of the AppStore application
- Equipping phones with more memory
In my opinion, these theses are only prerequisites and do not fully answer the question " why do applications become larger?".
Of course, the first thing is to add new features. Development of application functionality requires a larger size.

That's just the size of applications, in contrast to their functionality, is growing tenfold, and usually this growth has completely different reasons. Further, on the basis of different sources with specific examples, I will try to systematize different reasons:
Extra copies of resources in the application
No matter how trite it sounds, applications often store the same internal resources (pictures, libraries, and so on) for several copies. This is due to the fact that large applications are developed by several teams of developers responsible for their specific program functionality. It so happens that the team drags for its module the same resources as the other, causing zadvoenie.
In one of the articles, the author decided to analyze in detail the internal structure of the Facebook application for iOS after it had increased in six months from 165 to 253 megabytes. He found that the application contained over 40 megabytes of redundant duplicate data. These were mostly pictures, but there were also absolutely identical internal program files. Thus, simply removing duplicates could reduce the size of the application by 15% percent. Which, by the way, Facebook subsequently did .
A / B testing and implementation of new features
A common practice when developing an application is to add new functionality and disable it by default. This allows you to gradually turn it on for test or pilot groups and, if necessary, adjust it or turn it off again. But even after a long time, as a rule, the ability to disable the new functionality and restore the old one is not removed and still remains in the application just in case and to save time.
Transition to more comfortable programming languages
In the case of iOS applications, switching from Objective-C to Swift can increase the size of compiled application code by a factor of 3-4 . This is due to the fact that for the sake of convenience and speed of development, new languages can:
- use large default data types that take up more space
- enter additional tests and checks in the code when compiling
- use a large standard library of functions
This also includes the transition of applications to new frameworks that drag with them a lot of the files they need.
The inclusion in the program of its own functions, replacing the standard operating system
One of the trends of mobile development for several platforms is the desire to minimize dependence on a specific operating system. This approach has its advantages. First, it allows not to rewrite a lot of code when changing external system libraries. Secondly, it allows you to keep the user in your application and provide a more consistent user experience (although it often happens that its implementation is visually indistinguishable from the standard one).
Among the most popular "bikes", replacing the standard OS tools, you can highlight:
- Browsers
- Work with the camera
- Text input and gesture processing
- Spellchecking
Increased application requirements
As telephones evolve, ecosystem owners (Apple, Google) are beginning to place new demands on software systems to support the emerging phone capabilities that require more space:
- After the appearance of Retina, developers were obliged to add images with more detail and size accordingly.
- The transition of iOS from 32 to 64 bits subsequently forced all developers to release exactly 64-bit applications.
By the way, in the AppStore to combat the growing size of applications for such requirements, App thinning technologies were later introduced, according to which an adapted version of the application is downloaded to a specific phone without redundant resources for other versions of phones.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/332602/
All Articles