Tuning typical roles of Windows. Part One: Files and Printing

We are starting a small series of articles devoted to tuning the performance of a Windows server and its typical roles. The material will be useful both when trying to squeeze the maximum out of the old server (besides painting red), and when planning new high-load systems without buying top-end servers (as integrators advise).
General recommendations for iron
The processor is like the heart of the server, so much depends on it in terms of performance. Thanks to marketers, we know - the more cores and megahertz, the steeper. In fact, everything is not quite so:
Choose a 64-bit processor. Modern server Windows do not support 32-bit processors, and it can address the memory much more.
The number of cores is not a big deal. Not all applications and services can use multiple cores, and in the general case one core with a higher frequency will be more efficient than two with a smaller one.
Hyperthreading - Hyperthreading - when one physical core of a processor is defined as two logical ones. The processor function allows you to process two different threads on the same core, which generally improves performance. But it happens that the performance on the contrary is reduced due to the fact that the cache of the processor core is one.
CPU cache. Everything is simple: the more it is, the better, and often a larger cache gives more performance than the frequency of the processor.
No need to compare processors of different generations and manufacturers in terms of frequency: data processing speed depends on many other factors, such as cache and bus frequency.
- For Hyper-V, it is important that the processor supports SLAT (Second Level Address Translation). In Intel terminology, the capability is called Extended Page Tables (EPT), for AMD - Nested Page Tables (NPT). You can check the availability of this processor function using the systeminfo.exe utility.

Check processor under Hyper-V requirements.
With RAM, everything is quite simple: the bigger and faster it is, the better. It becomes a little more interesting if the RAM is not enough and the system needs to use the paging file. Here you can limit the following recommendations:
The paging file should be put on a separate physical disk. The faster he is, the better. If this is not possible, then it is better to place it on a disk that has fewer file reads;
- it is better not to store the paging file on a fault-tolerant array like RAID1―; it loses in speed with one disk. It’s a good idea to put a paging file on a RAID0 or several paging files on different physical disks.

Placing a paging file on the system disk is not the best option.
Now about network adapters. Of the interesting features can be noted:
Only adapters that support 64-bit systems have DMA (Direct Memory Access), a technology of direct memory access over the network. If you need a really fast network between the nodes of the cluster, you should pay attention to it.
- Multiport adapters are convenient for load balancing and fault tolerance. But 2 adapters with one port will be faster than one adapter with 2 ports. You also need to keep in mind that installing more network adapters than cores in the server is fraught with a drop in performance.

HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen7 initially has four network ports.
This concludes a small introductory and will go directly to the optimization of server roles. Let's start with the simplest - with a file server.
File server
Usually, when installing and running a file server, the performance issue is not. But only as long as databases, monstrous Excel files and the like "interesting" things start up on a regular file storage facility. I'll tell you about the parameters that can improve or degrade the performance of SMB.
Separately, I note the issue of server speed, which processes not only clients inside the local network, but also remote ones - for example, via VPN. Personally, I came across a situation when computers started to appear on the network on Windows XP \ 2003 on Windows 7 \ 2008. Then we are faced with the fact that the speed of the network of new computers leaves much to be desired when communicating with old operating systems. Having read the Internet, we performed the following script on new machines:
netsh int tcp set global autotuning=disabled netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled netsh int tcp set global rss=disabled chimney=disabled The network has earned, the script has been added to the deployed image systems.
And everything was fine until a remote segment appeared on the network with an increased demand for network speed. Files transferred via VPN are not faster than 2 Mb / s. The problem was localized: it turned out that the autotuning function was added specifically for work on LAN \ WAN networks in new operating systems. Using it, the systems determine the connection speed and agree on the TCP frame sizes for optimal performance. In order for VPN to work quickly, and the servers did not slow down when accessing Windows 2003, it was enough not to turn off autotuning , but limit it to the command:
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=highlyrestricted But let's move on to more specialized parameters.
Remember that changes to registry settings and service settings can lead to anything. Therefore, we do everything carefully.
Let's start with tuning file server clients. LanmanWorkstation is responsible for connecting to the SMB server. Most of the settings are in the following registry branch:
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters Most of the parameters are of type REG_DWORD. In modern Windows, management of some of the settings is possible via the Set-SmbClientConfiguration cmdlet . View current values — respectively, Get-SmbClientConfiguration .
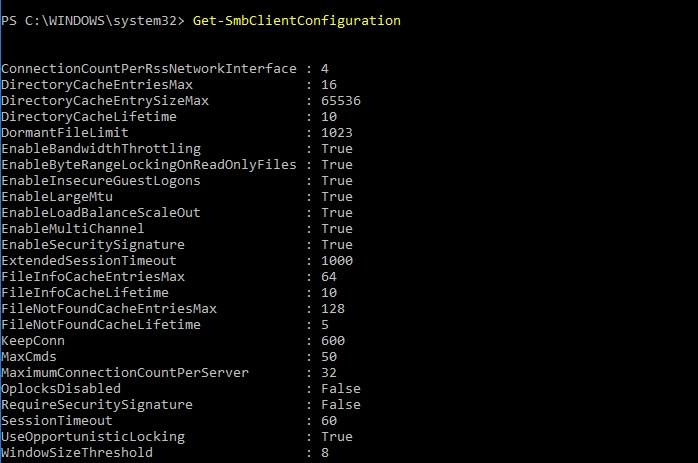
SMB client parameter values.
Parameters that should be paid attention first of all in terms of speed:
| Parameter name | Default value | Value options | What is responsible | Comment |
| DisableBandwidthThrottling | 0 | 0―1 | Enable - Disable Throttling for high latency networks | Enabling this option can increase network bandwidth with high latency (WAN) |
| FileInfoCacheEntriesMax | 64 | 1―65536 | Maximum number of values in the file metadata cache | Increasing this setting reduces traffic and increases network bandwidth when accessing a large number of files. |
| DirectoryCacheEntrySizeMax | 64 | 1―65536 | Maximum cache size for directories | Measured in kilobytes |
| FileNotFoundCacheEntriesMax | 128 | 1―65536 | Maximum number of values in the file information cache | Increasing this setting reduces traffic and increases network bandwidth when accessing a large number of files. |
| MaxCmds | 50 | 1―65536 | Maximum number of commands per session | Increasing the parameter will increase the memory consumption, but will increase the speed. Only for SMB v1 |
| DormantFileLimit | 1023 | 1―65536 | Maximum number of files that can be opened after being "released" by the application | |
| ScavengerTimeLimit | ten | 0―127 | How often does the garbageman run, clearing the file descriptor cache | Measured in seconds, relevant for Windows XP \ 2003 |
As an example of tuning, we can cite the following values:
DisableBandwidthThrottling = 1;
FileInfoCacheEntriesMax = 32768;
DirectoryCacheEntriesMax = 4096;
FileNotFoundCacheEntriesMax = 32768;
MaxCmds = 32768;
DormantFileLimit = 32768;
- ScavengerTimeLimit = 60.
Of course, specifically these values - not a panacea. Parameters must be selected individually.
Parameters configured via powershell and registry:
| Parameter name | Default value | Value options | What is responsible | Comment |
| ConnectionCountPerNetworkInterface | one | 1―16 | Maximum number of connections to the server with non-RSS interface | MS does not recommend changing the default value. |
| ConnectionCountPerRssNetworkInterface | four | 1―16 | Maximum number of connections to the server with RSS interface | |
| ConnectionCountPerRdmaNetworkInterface | 2 | 1―16 | Maximum number of connections to the server with an interface with RDMA support | |
| MaximumConnectionCountPerServer | 32 | 1―64 | Maximum number of connections to one server | |
| DormantDirectoryTimeout | 600 | Maximum amount of directory processing time | Measured in seconds | |
| FileInfoCacheLifetime | ten | Cache information storage time | ||
| DirectoryCacheLifetime | ten | Time to store directory metadata in cache | ||
| FileNotFoundCacheLifetime | five | Cache retention time for files not found | ||
| Cachefiletime | ten | Cache storage time for a file after the file is “released” by the application | ||
| DisableLargeMtu | 0 (win8) | 0―1 | Enable ― disable large MTU | With the enabled option, the request size is limited to 64 KB, with the enabled option - 1 MB. |
| RequireSecuritySignature | 0 | 0―1 | Enable ― Disable SMB Signature Mandatory | Enabling this option slows down the speed of operation, but increases protection against the MITM attack. |
| DirectoryCacheEntriesMax | sixteen | 1―4096 | Maximum number of values in the directory information cache | Increasing this setting reduces traffic and increases network bandwidth when accessing large directories. |
| Maxcredits | 128 | Maximum number of commands per session | Same as MaxCmds, but for SMB v2 |
Parameters configured via powershell:
| EnableMultiChannel | one | 0―1 | Enable ― disable the use of multiple physical adapters | |
| EnableByteRangeLockingOnReadOnlyFiles | True | True \ False | Enable ― Disable Read-Only File Locking | |
| EnableInsecureGuestLogons | True | True \ False | Enable ― disable guest login to resource | Disconnection will not allow accessing folders on a non-home server (NAS) without authorization to the shared folders for all. |
| EnableLoadBalanceScaleOut | True | True \ False | Enable — Disable support for load sharing when connecting to a cluster. | |
| EnableSecuritySignature | True | True \ False | Enable ― Disable SMB Signature Capability | |
| ExtendedSessionTimeout | 1000 | Server timeout | Measured in seconds | |
| Keepconn | 600 | Time to close inactive session | Measured in seconds, applicable only to SMB v1 | |
| OplocksDisabled | False | True \ False | Switched automatically depending on the value of the parameter UseOpportunisticLocking | |
| Sessiontimeout | 60 | Time to close inactive session | Measured in seconds | |
| UseOpportunisticLocking | True | True \ False | Enable ― disable flexible locking (oplock) of files with their buffering | The included mechanism greatly increases the speed, but on unreliable networks can damage files |
| Windowseize threshold | 1 for server systems, 8 for client systems | Minimum window size before Multichannel mode |
If we speak directly about the file server, here are some general recommendations:
For better performance, do not use unnecessary functions like file system mini-filters, IPSec, NTFS encryption and compression, SMB encryption, and others. The inclusion of an antivirus can significantly spoil the speed, and if the network perimeter is protected, it is better not to install it.
You should regularly check the relevance of drivers, especially on network cards. There were situations when, due to driver curves, the network card worked stably only when forcing one hundred megabits. And only with the release of fresh drivers managed to squeeze a full gigabit.
- Copying files is a fairly regular operation for a file server. When copying over the network, it is preferable to use the utility robocopy.exe with the / mt key, which includes multithreading for a large number of small files. A bit of speed will be added by the lack of output to the console - the / log key for robocopy and / q for xcopy.
To assess the performance of the SMB protocol, you can use performance counters that exist for both the server and the client.
The perfmon.exe utility will help here. After launch, it is convenient to switch the display to the “report” mode:
Then you need to add the necessary performance counters. For example, add the “SMB Server Shares” counter by clicking on the green plus, choosing the counter and share we need:
And enjoy the result:

I recommend reading the Microsoft blog more fully with the procedure for using performance counters, collecting and analyzing results.
We turn to tuning. The Lanmanserver service is responsible for the operation of the SMB server, so part of the parameters can be changed in the corresponding registry branch:
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters. It is more convenient, of course, to use the Set-SmbServerConfiguration cmdlet .
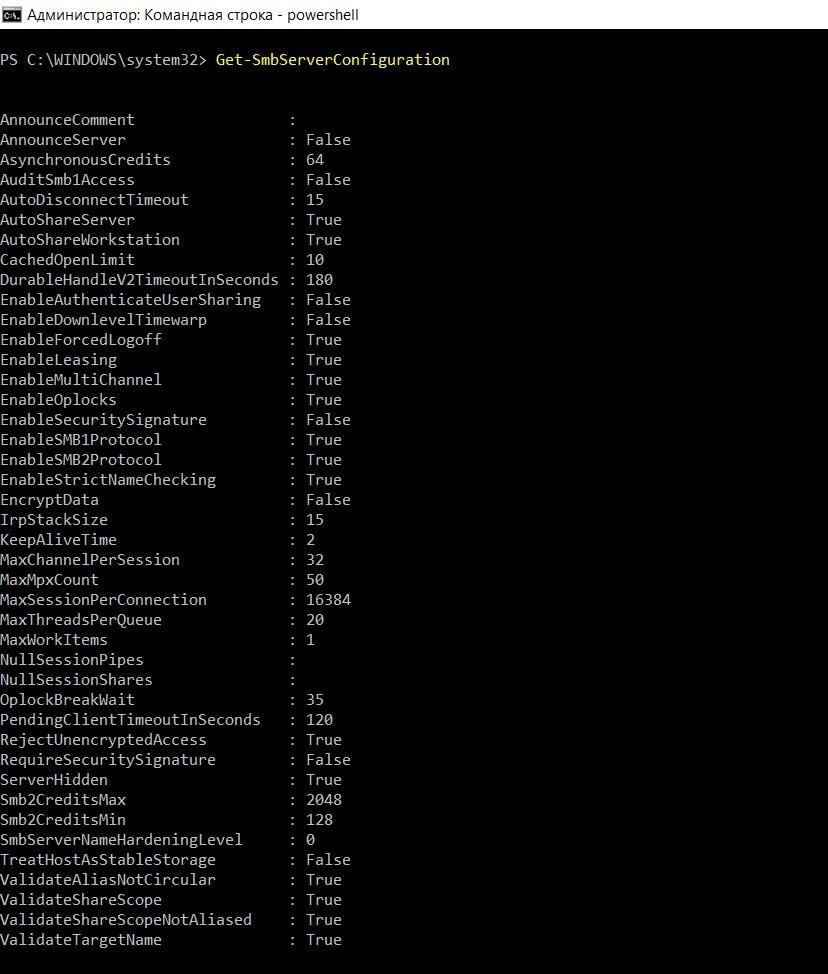
Displaying parameter values using the Get-SmbServerConfiguration cmdlet.
Parameters that should be paid attention first of all:
| Parameter name | Default value | Parameter type | What is responsible | Comment |
| Smb2CreditsMax | 8192 | uint32 | Maximum number of SMB v2 commands | These two parameters allow you to dynamically distribute the load. Sometimes when using high-speed channels with high latency (WAN), changing these parameters will increase the speed. To see if there are any problems, help the performance counter “SMB Client Total Resources - Credit Delays / c” |
| Smb2CreditsMin | 512 | uint32 | Minimum number of SMB v2 commands | |
| MaxThreadsPerQueue | 20 | unit32 | Maximum number of server threads when processing simultaneous requests | Increasing the parameter affects the hardware boot, but increases performance. The indicator to change a parameter can be the value of the performance counter “Server Work Queues - Queue Length - SMB2 NonBlocking” becomes more than 100. |
| Asynchronouscredits | 512 | uint32 | Maximum number of simultaneous asynchronous commands in one session | In some cases, for example, when using a loaded web server, increasing the value of the parameter increases performance |
| MaxMpxCt | 50 | uint32 | Maximum number of outstanding client requests for each client | Affects only SMB v1 clients |
There is another registry entry that is not controlled by the powershell cmdlet:
path: HKLM \ System \ CurrentControlSet \ Control \ Session Manager \ Executive;
parameter: REG_DWORD with the name AdditionalCriticalWorkerThreads;
- default value is 0.
This parameter is responsible for additional workflows responsible for writing and reading in the system cache of the file system. By default, there are no additional processes, and changing this parameter can significantly speed up the operation of the file server. Especially in the presence of multi-core processors and productive disk system. You can think about increasing this parameter while the “Cache -“ Dirty ”page performance counter grows.
An example of tuning is the following parameter values:
AdditionalCriticalWorkerThreads = 64;
MaxThreadsPerQueue = 64;
- MaxMpxCt = 32768.
Values must also be selected individually.
| Parameter name | Default value | Parameter type | What is responsible | Comment |
| AnnounceComment | null | string | Server view | |
| AnnounceServer | False | boolean | Enable - Disable Server View | |
| AuditSmb1Access | False | boolean | Enable - Disable SMB Access Audit v1 | The parameter appeared only in Windows 10 \ 2016 |
| AutoDisconnectTimeout | 15 | uint32 | The time after which the inactive session is disconnected | |
| Autoshareserver | True | boolean | Enable - disable default server network resources | |
| AutoShareWorkstation | True | boolean | Enable — Disables the network resources of the default workstation. | |
| CachedOpenLimit | ten | uint3 | Maximum number of open files in cache | |
| DurableHandleV2TimeoutInSeconds | 180 | uint32 | Disable inactive handle timeout | |
| EnableAuthenticateUserSharing | False | boolean | Enable — Disable Connection Sharing | |
| EnableDownlevelTimewarp | False | boolean | Enable - Disable Low Level Time Distortion | |
| EnableForcedLogoff | True | boolean | Enable - Disable forced exit | |
| EnableLeasing | True | boolean | Enable - Disable Rent | |
| EnableMultiChannel | True | boolean | Enable — Disable the use of multiple physical adapters. | |
| EnableOplocks | True | boolean | Enable - Disable flexible locks (oplock) | |
| EnableSecuritySignature | False | boolean | Enable - Disable SMB Signature Capability | |
| EnableSMB1Protocol | True | boolean | Enable - Disable SMB v1 protocol | |
| EnableSMB2Protocol | True | boolean | Enable - Disable SMB v2 + Protocol | |
| EnableStrictNameChecking | True | boolean | Enable - Disable incoming connection check | |
| EncryptData | False | boolean | Enable — Disable data encryption support. | |
| IrpStackSize | 15 | unit32 | The size of the stack IRP (I / O requests) | |
| KeepAliveTime | 2 | unit32 | TCP keepalive request rate for SMB connection | |
| MaxChannelPerSession | 32 | unit32 | The number of channels in one session | |
| MaxMpxCount | 50 | unit32 | Maximum number of commands per session | The parameter must be configured the same way as the MaxCmds client parameter |
| MaxSessionPerConnection | 16384 | unit32 | Maximum number of sessions in one connection | |
| MaxWorkItems | one | uint32 | Maximum number of work items | This parameter affects SMB v1 only. |
| NullSessionPipes | null | string | Channels available in zero session | |
| NullSessionShares | null | string | Network resources available in zero session | |
| OplockBreakWait | 35 | uint32 | Timeout before interruption of the lock | |
| PendingClientTimeoutInSeconds | 120 | uint32 | Client waiting time | |
| RejectUnencryptedAccess | True | boolean | Enable — Disable unencrypted access requests. | |
| RequireSecuritySignature | False | boolean | Enable — Disable SMB Signature Mandatory | Enabling this option slows down the speed of operation, but increases protection against the MITM attack. |
| ServerHidden | True | boolean | Enable - Disable Server View | By default, the server does not present itself. |
| SmbServerNameHardeningLevel | 0 | uint32 | Server Name Simplification Level | |
| TreatHostAsStableStorage | False | boolean | Enable — Disable Trusted Disk Storage | Enabling this option tells the server about the reliability of disk storage, it is worth including it when working with a disk with a non-volatile write cache. Then the server will not wait for confirmation to write to the disk, which will speed up performance. |
| ValidateAliasNotCircular | True | boolean | Enabling - disabling the use of aliases | |
| ValidateShareScope | True | boolean | Enable — Disable resource name checking when creating a new resource. | |
| ValidateShareScopeNotAliased | True | boolean | Enabling - disabling the checking of resource aliases when creating a new resource | |
| ValidateTargetName | True | boolean | Enable - disable checking the name of the target resource when creating an alias |
I repeat: changing the parameters can lead to server malfunction. Therefore, it is better to first "practice on cats." Or at least make backups.
I turn to the next, seemingly simple role - the print server.
Print server
In addition to the recommendations of the "faster, higher, stronger" in terms of hardware, you need to note several other interesting points.
Transferring a print queue to a non-system disk will greatly increase server performance. This is done in the properties of the print server, in the "advanced settings" tab.
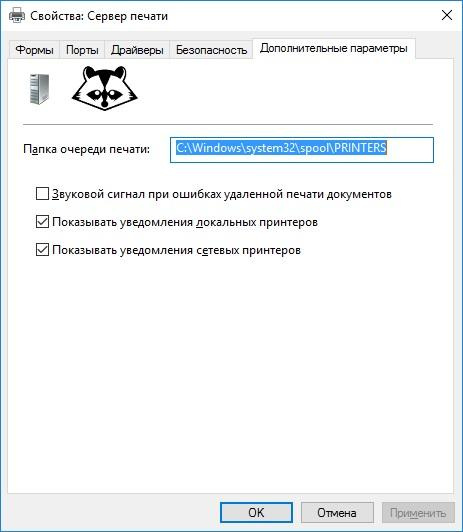
Setting the location of the print queue.
Whenever possible it is better to draw tasks on the client . In this case, the client will translate the document into a special format for printing (PDL). The server will not waste resources on this conversion.
By default, this feature is already enabled; you can turn it on ― by using Group Policy for all printers. Printers can be individually configured using the command
printui /Xs /n "printer" ClientSideRender disabled It makes sense to turn off rendering on the client with a sufficient margin of print server performance to offload clients.
Printers with XPS (OpenXPS) support put less pressure on the server than printers without it. Printers with PCL 6 and Postscript support are a bit less efficient because of the vector format. Therefore, when choosing a printer is better to choose with support for XPS, and install the appropriate driver.
With the release of Windows 8 \ 2012, there is support for print drivers v4 . The 4th version drivers are more productive, but Windows 7 will print on the fourth type driver, drawing tasks on the client. Therefore, if there are still old Windows on the network, it is worthwhile to install third type drivers. You can look at the driver type in the print server properties on the Drivers tab:

Installation window for additional drivers.
If we talk about the capabilities of drivers of the fourth type, then these include:
use of graphics card for drawing print tasks. Yes, now, to improve performance when drawing tasks on the server, you can install a video card in the print server;
- simplified system for connecting a “shared” printer: now you don’t need to install drivers for different processor architectures.
Branch Office technology also deserves attention . With its help, the client works with the printer directly, bypassing any processing on the print server. True, you will need printers with support for TCP \ IP or WSD. You can learn more about the technology on the Microsoft website, and you can enable or disable it for a specific printer using the powershell cmdlet:
Set―Printer ―name <printername> ―ComputerName <computername> ―RenderingMode BranchOffice The technology does not work if print processing is used on the server.
To diagnose bottlenecks when printing, pay attention to three processes:
Spoolsv.exe;
Printfilterpipelinesvc.exe;
- Printisolationhost.exe;
And also look at the expense of these processes of memory, processor and hard disk load. For a more subtle search for bottlenecks, special performance counters will help.

A set of typical print subsystem performance counters.
| Title | Description |
| Total jobs printed | Number of jobs printed |
| Total pages printed | Number of pages printed |
| Call Add Network Printer | Number of connections to the shared printer since the last restart of the service |
| Tasks | Number of jobs printed since the last service restart |
| Jobs Handled by the Print Manager | The current number of jobs in the print service |
| Maximum jobs processed by the dispatcher | Maximum number of jobs in print service |
| Maximum links | The maximum number of accesses to the print queue |
| Task errors | Number of job errors |
| Errors "Missing Paper" | The number of errors caused by the lack of paper |
| Errors "The printer is not ready" | Number of printer errors |
| Printable bytes / c | The speed of the current printing in bytes, allows you to approximately estimate the time the printer is busy |
| Links | The current number of accesses to the print queue |
In general, selecting parameters for a specific situation can improve the performance of these simple roles up to 50%. A refurbished server will still give light to modern monsters with the default settings.
Tell us in the comments about the performance improvement of any Windows roles you would be interested to read. Have you ever been involved in tuning roles and services? What results have been achieved?
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/332600/
All Articles