Six Myths about Big Data
Natalya Garakhanova, marketing director at Black Engine agency and a graduate student in the course “ Product Management ”, debunks the myths in the field of Big Data.
Big Data has recently become a trend. But what it is, is not clear to everyone.
Many people think that big data is either just a huge array of data or a simple and cheap way to store it.
')
Big data is not at all a subject, but a set of approaches, tools and methods for processing structured and unstructured data of huge volumes. These are technologies that help to solve important tasks for business and science. Due to a misunderstanding of the essence of technology, myths arose that I tried to debunk in this article.

The myth is based on statistics, which says that about 80% of work tasks can be automated. This is a big problem from the point of view of education: a huge number of personnel will have to relearn for other professions. In some ways this myth is right. Many people will have to abandon their current activities. But there will be no fundamental unemployment.
For example, if we design an effective targeted advertising system using Big Data, we need a specialist in a new field of knowledge at the intersection of mathematics and marketing. That he will monitor the operation of the system and the health of the mechanism. Now the market is already beginning to appear such people in the position of "Data Management Platform Operator".
Do not be afraid that people will remain without work. Other professions will appear, as has happened many times in the history of mankind. After all, the printing press once changed the history of typography and made the census of books unnecessary.
The need for learning algorithms leads to the fact that there are companies and services that aggregate data in one place. This can cause problems with security and access to user information.
The aggregation of data for learning artificial intelligence, algorithms and machines has ceased to be as important as before. Now corporations like Google and Apple are actively working to make their devices part of a distributed network of machine learning.
Google on their devices has one network that works simultaneously. Apple follows in its footsteps in the field of big data based technology. For example, in Google's “Federated Learning” patent, everything is based on distributed learning. Data from the phone does not flow away to a certain Data Center, but a model arrives, learns and starts communicating with other models of mobile phones or through a common hub. Thus, privacy is preserved.
A model is an algorithm that can be complex or simple, but the output will be answered to the question of interest to us. It can be given mathematically by formulas or words. In principle, even our legal laws are a model that allows us to classify a person’s actions into acceptable (unpunishable) and unacceptable (punishable).
A model can be a set of formulas for describing a physical phenomenon, or there can be rules of language dividing the diversity of words and phrases into correct (literate) and incorrect (illiterate). If we generalize, without resorting to rigorous mathematical formulations, the model is a formalizable criterion, which we obtain from training on the available data.
There are areas of knowledge where you have to deal with a lot of data to process. But Big Data does not always give a tangible result.
Gartner has conducted research on which cases are most popular in various industries. All data was presented in the form of a heat map of cases implemented in business. The redder the square (the higher the percentage), the more of the surveyed companies implemented cases based on Big Data in their business.
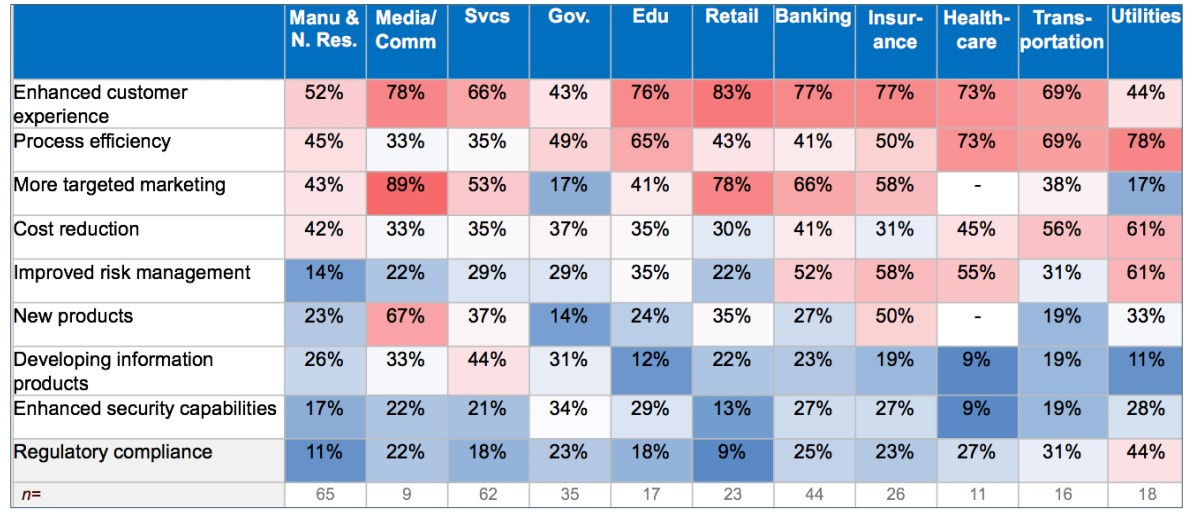
As can be seen from the study, most cases are implemented in the field of marketing, targeting and customer experience. That is, in the most relevant area of client analytics and customer service, in the b2c sales area. Least of all cases implemented in the public sector, but the area of process efficiency for this sector is most relevant. The scope of new products is still not significant for this sector.
But this survey was conducted by Tech Pro Research:
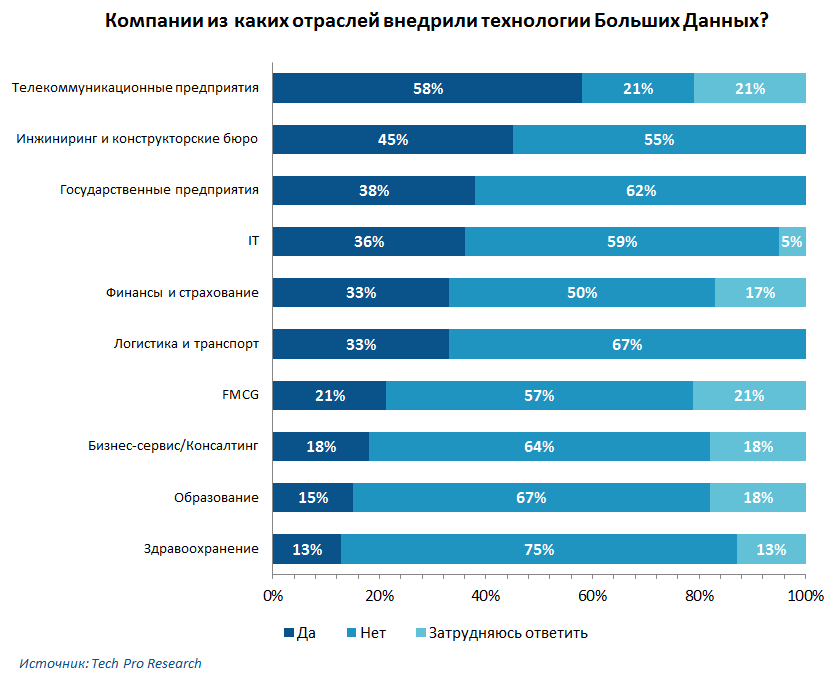
Interestingly, in the areas of education and health, big data was not so popular. But financial and government structures, engineering and IT are actively using these methods. And telecom is the most popular area for implementing Big Data technologies.
Big Data is not needed if your company:
Another myth, successfully debunked by exponential successful cases. It is based on the fact that in the sphere of medium or small business the data collection itself can become a problem.
Systems such as Google Analytics or Yandex.Metrica are used solely to estimate the attendance of a resource, and no additional reports are generated with their help. Many companies still keep their data in good old Excel, and it is clear that in this case it’s too early to talk about using Big Data methods. In Russian IT, basically everyone refers to the same Google Analytics, the simplest system using big data, but effective for collecting and organizing data. Some have successfully used Retail Rocket, a platform for multi-channel personalization of online stores based on Big Data.
Also for those who want to try high technology, there are data exchanges where even small companies can afford to acquire data around which you can build a business or improve organizational and marketing processes.
In the West, this topic is more actively discussed. The examples are the services Followerwonk, YouTube Analytics and Tweriod. Some representatives of small and medium business successfully use cloud solutions, for example, the Amazon platform, built specifically for computing based on Big Data.
There are companies that go even further and build their own infrastructures, for example, Hadoop, an open source project that serves as a repository of petabytes of data and is used for reliable, scalable and distributed computing.
If small and medium businesses want to expand the scope of tasks for research and production purposes, the use of Big Data will not only systematize the data, but also increase the speed of their processing.
This myth is often found when it is necessary to build a model from a distributed file system. Solution providers claim that "all data must be processed." Here lies the contradiction. There is no relationship between the amount of information processed and the result of the work. The increase in the volume of processed data does not affect the increase in the accuracy of the final model.
The well-known theory, built on mathematical calculus, showed that we get the best results when we build models from small segments, specially selected for the purpose of the model.
From the point of view of mathematics, each sample object has an equal probability of falling into a random subsample for training a model. And its accuracy will depend not on the number of elements, but on the quality of the sample. From several thousand answers to a certain survey, it turns out to build a very accurate forecast for the entire result.
The real significance of Big Data is not to process as much data as possible, but to ensure that the entire amount of data is segmented and divided into clusters, and in building a large number of models for small clusters.
This myth is common in companies that are just starting to use big data. It is not enough just to calculate a recommendation, for example, which product should be targeted at whom, or which product with which one should be supplied. It is important to be able to do the placement itself. At this step, many projects stop.
Big Data needs a lot of work. This involves creating a complex project, collecting data, creating an infrastructure, designing a model, and then finding the necessary data to help improve processes.
This is just a small part of the superstitions and misconceptions about big data. Big Data is not a magic wand. This is a tool that, in the hands of a skilled analyst, will help to build your business processes correctly.
Netology is recruiting for Big Data courses:
For whom: engineers, programmers, analysts, marketers - everyone who is just beginning to delve into the technology of Big Data.
Training format: online.
Details by reference → http://netolo.gy/dAZ
For whom: professionals working or intending to work with Big Data, as well as those who are planning to build a career in Data Science. For training, you must have at least one of the programming languages (preferably Python) and remember the program in high school math (and better university).
Course topics:
Format of studies: offline, Moscow, Digital October center. Experts from Yandex Data Factory, Rostelecom, Sberbank-Technologies, Microsoft, OWOX, Clever DATA, MTS.
Details on the link → netolo.gy/dA0
Big Data has recently become a trend. But what it is, is not clear to everyone.
Many people think that big data is either just a huge array of data or a simple and cheap way to store it.
')
Big data is not at all a subject, but a set of approaches, tools and methods for processing structured and unstructured data of huge volumes. These are technologies that help to solve important tasks for business and science. Due to a misunderstanding of the essence of technology, myths arose that I tried to debunk in this article.

Myth 1. Big Data based machines will replace people
The myth is based on statistics, which says that about 80% of work tasks can be automated. This is a big problem from the point of view of education: a huge number of personnel will have to relearn for other professions. In some ways this myth is right. Many people will have to abandon their current activities. But there will be no fundamental unemployment.
New areas of knowledge give rise to new professions.
For example, if we design an effective targeted advertising system using Big Data, we need a specialist in a new field of knowledge at the intersection of mathematics and marketing. That he will monitor the operation of the system and the health of the mechanism. Now the market is already beginning to appear such people in the position of "Data Management Platform Operator".
Man must always control and monitor processes.
Do not be afraid that people will remain without work. Other professions will appear, as has happened many times in the history of mankind. After all, the printing press once changed the history of typography and made the census of books unnecessary.
Myth 2. Data needs to be collected in one place.
The need for learning algorithms leads to the fact that there are companies and services that aggregate data in one place. This can cause problems with security and access to user information.
The aggregation of data for learning artificial intelligence, algorithms and machines has ceased to be as important as before. Now corporations like Google and Apple are actively working to make their devices part of a distributed network of machine learning.
Google on their devices has one network that works simultaneously. Apple follows in its footsteps in the field of big data based technology. For example, in Google's “Federated Learning” patent, everything is based on distributed learning. Data from the phone does not flow away to a certain Data Center, but a model arrives, learns and starts communicating with other models of mobile phones or through a common hub. Thus, privacy is preserved.
A model is an algorithm that can be complex or simple, but the output will be answered to the question of interest to us. It can be given mathematically by formulas or words. In principle, even our legal laws are a model that allows us to classify a person’s actions into acceptable (unpunishable) and unacceptable (punishable).
A model can be a set of formulas for describing a physical phenomenon, or there can be rules of language dividing the diversity of words and phrases into correct (literate) and incorrect (illiterate). If we generalize, without resorting to rigorous mathematical formulations, the model is a formalizable criterion, which we obtain from training on the available data.
Myth 3. Big Data is needed by everyone
There are areas of knowledge where you have to deal with a lot of data to process. But Big Data does not always give a tangible result.
Gartner has conducted research on which cases are most popular in various industries. All data was presented in the form of a heat map of cases implemented in business. The redder the square (the higher the percentage), the more of the surveyed companies implemented cases based on Big Data in their business.

As can be seen from the study, most cases are implemented in the field of marketing, targeting and customer experience. That is, in the most relevant area of client analytics and customer service, in the b2c sales area. Least of all cases implemented in the public sector, but the area of process efficiency for this sector is most relevant. The scope of new products is still not significant for this sector.
But this survey was conducted by Tech Pro Research:

Interestingly, in the areas of education and health, big data was not so popular. But financial and government structures, engineering and IT are actively using these methods. And telecom is the most popular area for implementing Big Data technologies.
Big Data is not needed if your company:
- employees are able to process and automate customer data using conventional CRM systems;
- planning, accounting and control of business processes can be fully implemented using ERP-systems;
- previously they combined data from various sources of information, processed them, evaluated the result obtained using BI systems and did not experience any difficulties with all of the above.
Myth 4. Big Data is only suitable for big companies.
Another myth, successfully debunked by exponential successful cases. It is based on the fact that in the sphere of medium or small business the data collection itself can become a problem.
Systems such as Google Analytics or Yandex.Metrica are used solely to estimate the attendance of a resource, and no additional reports are generated with their help. Many companies still keep their data in good old Excel, and it is clear that in this case it’s too early to talk about using Big Data methods. In Russian IT, basically everyone refers to the same Google Analytics, the simplest system using big data, but effective for collecting and organizing data. Some have successfully used Retail Rocket, a platform for multi-channel personalization of online stores based on Big Data.
Also for those who want to try high technology, there are data exchanges where even small companies can afford to acquire data around which you can build a business or improve organizational and marketing processes.
In the West, this topic is more actively discussed. The examples are the services Followerwonk, YouTube Analytics and Tweriod. Some representatives of small and medium business successfully use cloud solutions, for example, the Amazon platform, built specifically for computing based on Big Data.
There are companies that go even further and build their own infrastructures, for example, Hadoop, an open source project that serves as a repository of petabytes of data and is used for reliable, scalable and distributed computing.
If small and medium businesses want to expand the scope of tasks for research and production purposes, the use of Big Data will not only systematize the data, but also increase the speed of their processing.
Myth 5. All data must be processed
This myth is often found when it is necessary to build a model from a distributed file system. Solution providers claim that "all data must be processed." Here lies the contradiction. There is no relationship between the amount of information processed and the result of the work. The increase in the volume of processed data does not affect the increase in the accuracy of the final model.
The well-known theory, built on mathematical calculus, showed that we get the best results when we build models from small segments, specially selected for the purpose of the model.
From the point of view of mathematics, each sample object has an equal probability of falling into a random subsample for training a model. And its accuracy will depend not on the number of elements, but on the quality of the sample. From several thousand answers to a certain survey, it turns out to build a very accurate forecast for the entire result.
No longer means better.
The real significance of Big Data is not to process as much data as possible, but to ensure that the entire amount of data is segmented and divided into clusters, and in building a large number of models for small clusters.
Myth 6. Big Data gives instant and magical results.
This myth is common in companies that are just starting to use big data. It is not enough just to calculate a recommendation, for example, which product should be targeted at whom, or which product with which one should be supplied. It is important to be able to do the placement itself. At this step, many projects stop.
Big Data needs a lot of work. This involves creating a complex project, collecting data, creating an infrastructure, designing a model, and then finding the necessary data to help improve processes.
The main task is to integrate the models into the business processes in production and profitably use the solutions found.
This is just a small part of the superstitions and misconceptions about big data. Big Data is not a magic wand. This is a tool that, in the hands of a skilled analyst, will help to build your business processes correctly.
From the editors of Netology
Netology is recruiting for Big Data courses:
1. The program “ Big Data: Basics of working with large data arrays ”
For whom: engineers, programmers, analysts, marketers - everyone who is just beginning to delve into the technology of Big Data.
- introduction to the history and basics of technology;
- ways to collect big data;
- data types;
- basic and advanced methods for analyzing big data;
- Basics of programming, storage and processing architecture for working with large data sets.
Training format: online.
Details by reference → http://netolo.gy/dAZ
2. The program "Data Scientist"
For whom: professionals working or intending to work with Big Data, as well as those who are planning to build a career in Data Science. For training, you must have at least one of the programming languages (preferably Python) and remember the program in high school math (and better university).
Course topics:
- express training for basic tools, Hadoop, cluster computing;
- decision trees, k-nearest-neighbor method, logistic regression, clustering;
- data dimension reduction, decomposition methods, straightening spaces;
- introduction to recommendation systems;
- image recognition, machine vision, neural networks;
- word processing, distributive semantics, chatbot;
- time series, ARMA / ARIMA models, complex prediction models.
Format of studies: offline, Moscow, Digital October center. Experts from Yandex Data Factory, Rostelecom, Sberbank-Technologies, Microsoft, OWOX, Clever DATA, MTS.
Details on the link → netolo.gy/dA0
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/332184/
All Articles