PETYA malware. Recovery is possible

On June 27, messages began to appear on the network about the rapid spread of a malicious program, the Petya encryptor, which encrypts data on the victim's computer. Large corporations of Russia, Ukraine, the EU, the USA and a number of other countries were attacked. Specialists of the company BiZone conducted a detailed analysis of the malware. Below are the results of the study, as well as recommendations for its removal from the victim's computer and data recovery.
Spread
It is distributed initially in several ways, including as an email attachment (phishing mailing).
For subsequent distribution within the network uses:
- Vulnerability MS17-10, as well as WannaCry;
- Remote access to the WMI console (Windows Management Instrumentation), commands like
wmic.exe /node:"<hostname>" /user:"<username>" /password:"<password> process call create "C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe \"C:\Windows\perfc.dat\" #1 - Microsoft's PSEXEC utility (usernames and passwords are collected on an infected machine using a utility similar in functionality to the Mimikatz utility; passwords in open form are obtained by reading the lsass.exe process memory.
Encryption
To make the subsequent analysis difficult, Petya clears the event logs and the file system log with the command:
wevtutil cl Setup & wevtutil cl System & wevtutil cl Security & wevtutil cl Application & fsutil usn deletejournal /D %c: The entries in the event logs are not deleted; only a note is made in the header of the log stating that it is cleared, it is possible to restore the entries.
System encryption can be done in two different ways:
')
1. Encryption of the $ MFT file allocation table (NotPetya)
The malicious file writes its code in the MBR and the next several sectors (the original MBR is saved in the 34th sector in encrypted form (xor 0x07)). Next, the system is rebooted (using the “schtasks” and “at” commands) and the next time the system is turned on, the screen about the operation of the CHKDSK utility is displayed. In fact, at this moment $ MFT is encrypted using the Salsa20 cryptographically strong cipher (code c is similar to the original Petya). The peculiarity of this method is that file records are encrypted, and not the contents of the files themselves. Data recovery is possible.
Ways to recover data:
- Manually. You can search for files on the disk by signatures, but this method works only for unfragmented files, and the file name is not restored. The next applicable method is to search for file records by the “FILE” signature, retrieving the list of clusters belonging to the file, thus restoring the contents and file name. Also, in the course of our research, a method was developed for restoring sample files by restoring a non-resident list of sectors belonging to a file (Data Runs). This method is based on the following concept: it searches for a cluster containing the beginning of the file (the search is performed by signature), then this cluster number is used to search for a non-resident list of sectors belonging to the file. With the help of the described methods, you can recover large files that can not be restored by signature search and automatic tools.
- Automatic: R-Studio , GetDataBack , etc.
- You can restore the MBR with the “bootrec / FixMbr” command before the system is rebooted (Vista +, in the case of Windows XP, you can use the “fixmbr” command).
- Recover MBR after reboot, but before encryption. It is necessary to extract the original MBR from 34 sectors (0x4400 disk offset, size 0x200) to decipher (xor 0x07) and write to the beginning of the disk.
2. File Encryption (Misha)
When it is impossible to obtain privileges in the system for rewriting the MBR, files are encrypted without rebooting. List of encrypted file extensions:
3ds, 7z, accdb, ai, asp, aspx, avhd, back, bak, c, cfg, conf, cpp, cs, ctl, dbf, disk, djvu, doc, docx, dwg, eml, fdb, gz, h, hdd, kdbx, mail, mdb, msg, nrg, ora, ost, ova, ovf, pdf, php, pmf, ppt, pptx, pst, pvi, py, pyc, rar, rtf, sln, sql, tar, vbox, vbs, vcb, vdi, vfd, vmc, vmdk, vmsd, vmx, vsdx, vsv, work, xls, xlsx, xvd, zip. Decryption methods are currently unknown, perhaps only restore from backup copies, for example, from Volume Shadow Copy, Restore points, File History.
Paying a ransom is not recommended, since the attacker's mailbox has been blocked. Currently, the technical possibility of decrypting the data is in doubt, and there are no confirmed cases of successful decryption.
Why is data recovery possible?
NotPetya encrypts only the file table, but not the files themselves, so it is possible to recover files after this cryptographer. Before encryption, the file system structure is as follows:
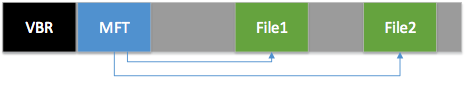
At the beginning of the section is the main file table (MFT), in which the file names and their location are indicated. After encryption, all references to files in the MFT are encrypted, but the contents of the files remain unchanged:

Thus, all data recovery methods based on carving (Carving) continue to work. Also identical MFT records are stored in different parts of the file system. They can get into the hiberfil.sys file, into the directories and MFTmirr files, etc. Therefore, it is possible to recover even fragmented files by collecting all the complete MFT records.
Indicators
When infecting a system using PSEXEC software, the following files may be present in the Windows directory:
«C:\Windows\perfc.dat» «C:\Windows\dllhost.dat» Recommendations
Also, to stop the spread of this malware, it is necessary to block the launch of the “PSEXEC.EXE” software using local or group security policy on potentially vulnerable machines, and, if possible, block or disable remote access to WMI.
In the course of the study, a feature was identified that prevents infection through PsExec and WMI. To do this, simply create an empty file “C: \ Windows \ perfc”.
UPD: NotPetya and Misha can act together, the launch of Misha does not depend on the success of the MBR infection. However, in many cases, Misha does not have time to encrypt all files with the listed extensions on the disk.
When using GPT instead of MBR on an infected computer, NotPetya writes random data to the place of the first ten sectors, and the partition table in this case will be lost forever. However, in this case, the main file table is not encrypted, and the partition offset can be found by the signature of the NTFS partition (R-Studio automatically performs this task).
Creating a perfc file only helps prevent infection if the original Petya executable file was called “perfc.dat”. In the cases studied by us, this is true, but changing this name is not difficult, so this method may lose its effectiveness in the next wave of phishing messages.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/331854/
All Articles