"Kaspersky Lab": Proper protection of "clouds"
We continue to publish the materials of the forum “Collaborative Security of Cloud Solutions for Business” , which we conducted together with Kaspersky Lab and HUAWEI on May 31 in Moscow.
Today, when Petya and Misha are sweeping across the planet with might and main, this material is becoming especially relevant for users of virtual servers. We present the report of Vladimir Ostroverkhov, Kaspersky Lab, "Proper protection of the" clouds "."

')
Hello everyone, my name is Vladimir Ostroverhov. At the moment I am an expert in support of corporate sales of Kaspersky Lab.
Functionally, I am partly a developer, trainer, techie, training person for local teams all over the world.
Let's start with a frivolous topic. What are the requirements for a modern IT security system and why are we raising today the topic of cloud infrastructure security, virtual security, protection for virtualization, for virtual machines?
Let's start with the simplest - with the viruses that you all know about. 97th year. We had enough work. Every day, there were 20 new samples, they were really complex, interesting, we literally dismantled them with our hands, wrote “masks” and general structures of detects. And everything was fine. A year ago, I returned to Kaspersky Lab again, came to my former colleagues and asked: “Guys, how are things going now?” There were 20-30 problem viruses per day that you had to study manually. And they showed me the numbers ...

Today, more than 300,000 units of malware appear every day. Yes, these statistics are quite simple. For example, a student learned a new code in computer science lessons, wrote some program, released it on the Internet. Virus? Virus because it can spoil the data. This includes complex targeted attacks, those that are developed specifically for organizations, for certain cases, for certain situations, and they are very well able not only to break and steal data, but also very well know how to hide themselves. This all requires investigations. The volume has increased several times, thousands of times. An old and stupid question: “Kaspersky writes viruses?”, You can see them yourself, and so they write without us so much that we could get rid of ...
Second moment. The position of our company - we, of course, sell products and solutions, but the main value is the accumulated knowledge that is in our company, in fact, expressed in solutions. For this expertise and appreciate the company, it determines its reputation.
Okay, we go further about horror stories. What is good virtualization, I think everyone knows. Yes? High density, low resource consumption, everything is great, everything is beautiful, virtualization vendors usually talk about it. Why is it bad and dangerous, and why should the virtual infrastructure be further protected and we should not forget about protection? Two thirds of companies around the world, including large businesses, believe that they have invested in virtualization and no additional protection is needed. The virtual is safe by itself, everything is fine with it, no one breaks it. Not true, break and more often!

The first is that up to 80 percent of all those 300 thousand units of malware that I mentioned earlier, can live without any modifications, without any changes, inside the virtual infrastructure, inside the clouds. You do not need to edit anything, horrible, earned, started to delete, erase, spoil the data.
Hackers are also more interested in virtual infrastructure. It is much easier to hack it and access all your virtual machines and all data at once, rather than trying to hack each physical server separately. Logical and quite simple.
Thirdly, it is necessary to pay attention to the speed of propagation of viruses inside the virtual machine. Inside the virtual infrastructure, malicious code spreads with great speed. It is easy to infect 10 thousand virtual machines in 15 minutes. Somehow it must be stopped. These are epidemics of tremendous speeds and enormous proportions.
I'm not talking about the wrong protections, which are a separate level of threats that arise for all companies that use virtual environments in their work.
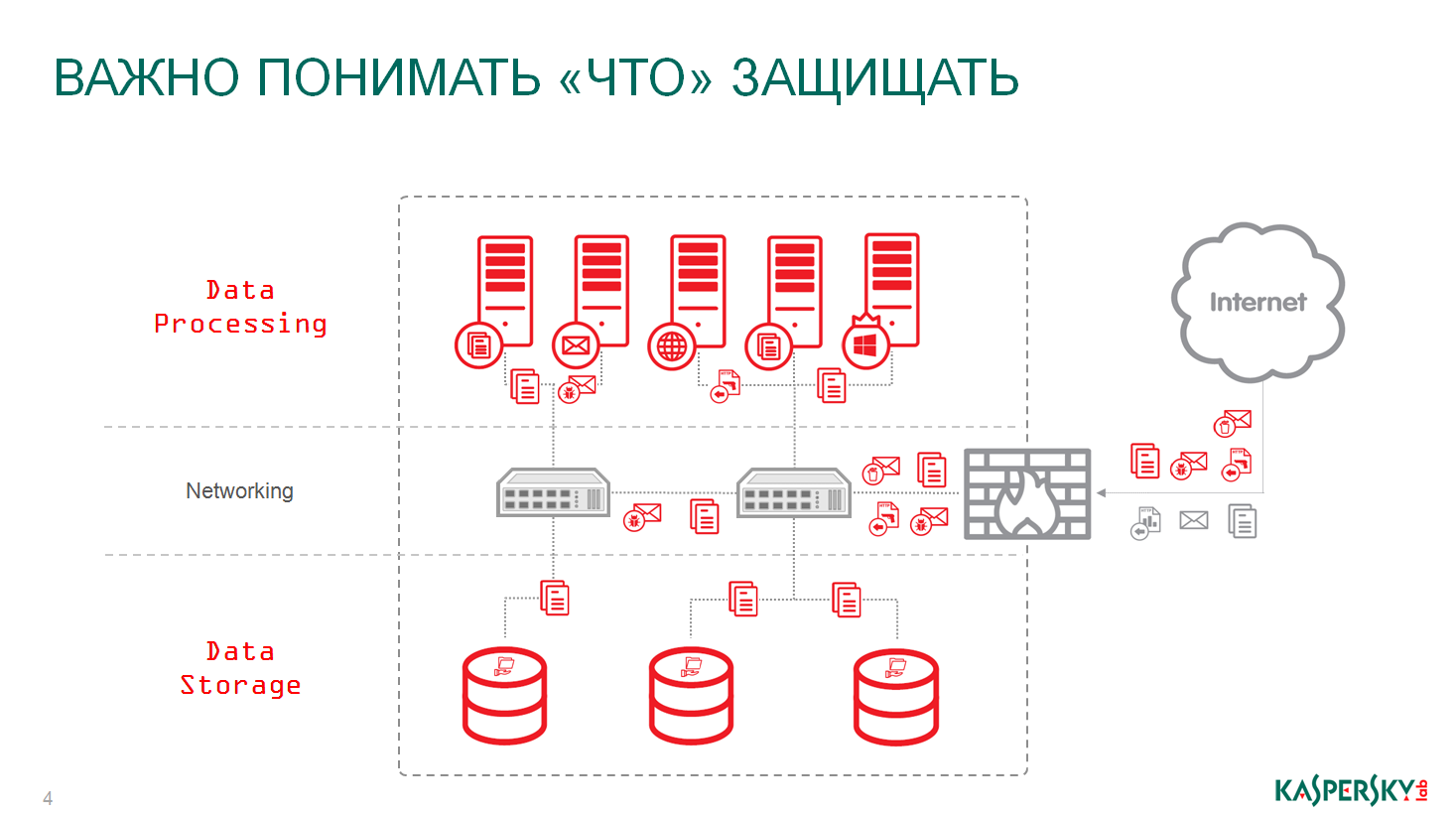
Go ahead. Clouds private, hybrid, public of themselves always represent a data center. From this you can not escape. There are servers, there is a network, there is a data storage system - this is a standard set that works, from which no one goes anywhere, it is traditional.
The main focus of malware attacks are servers and storage systems. Servers - data corruption and application operation, storage - data corruption or theft. The network is only transport.
Today I will talk about the work of the data center in terms of crypto-security and in terms of the software that you can install, and it will provide maximum protection.

And now a little scary statistics. We interviewed about five thousand companies around the world. These are large companies with at least one and a half thousand employees in 25 countries. About 75 percent of them already use virtualization, for large businesses this is a standard trend, they increasingly believe in virtualization and implement in their data centers. Statistics of virtualization vendors is shown on the slide. Another thing is interesting, about half of the companies do not use any protection for virtual machines, and the second half believes that any standard antivirus will suffice. All of these companies, on average, spend almost a million dollars on recovering from incidents: on investigation, on restoring the system, on reimbursing costs, on compensating for losses from a single hack. How is that? These are 5 thousand companies and each of them lost a million dollars last year? Statistics show "average temperature in the hospital." For example, there is a large company, a service provider, one of the largest, let it be, in Spain. A lot of clients work with her. They were the only ones hacking last year.
What will their expenses be if they compromise themselves? Direct losses for the restoration, replacement of equipment, software ... Indirect losses - reputation ... Losses for compensation for their customers, including reputation ... And incident investigation, partial replacement of infrastructure, because it has already compromised itself, it is dialogue with governments, dialogue with insurance companies, dialogue with customers who have to pay compensation.
It should be perfectly well understood that, on average, a large business loses about 800 thousand a year if improperly organized protection is a potential risk for a large company, the risk of losing about a million dollars a year. For a small company, this is about 100 thousand dollars a year. These are the statistics that we see, based on live incidents among organizations. This is really scary data, you really have to reckon with them, and you cannot get away from them. And this is found all over the world, 25 countries, I think, more or less confirm this.
Now about the protection. With terrible yet finished. There are only four approaches to building a security system. Whoever invented what, whoever said what. The first is the lack of protection, this is also a kind of protection, this is faith, religion: “prayed, crossed himself” and everything went away. I hope this is not your case.
The second is a choice in favor of traditional protection. It's about standard antivirus or traditional protection systems designed to protect non-virtual physical devices.
The third and fourth are two ways of specialized protection: agentless protection and light agent protection. This is a general trend of the entire global security market.
Now let's take a little more detail about all four approaches, we can say, strategies for building a system for protecting virtual environments.
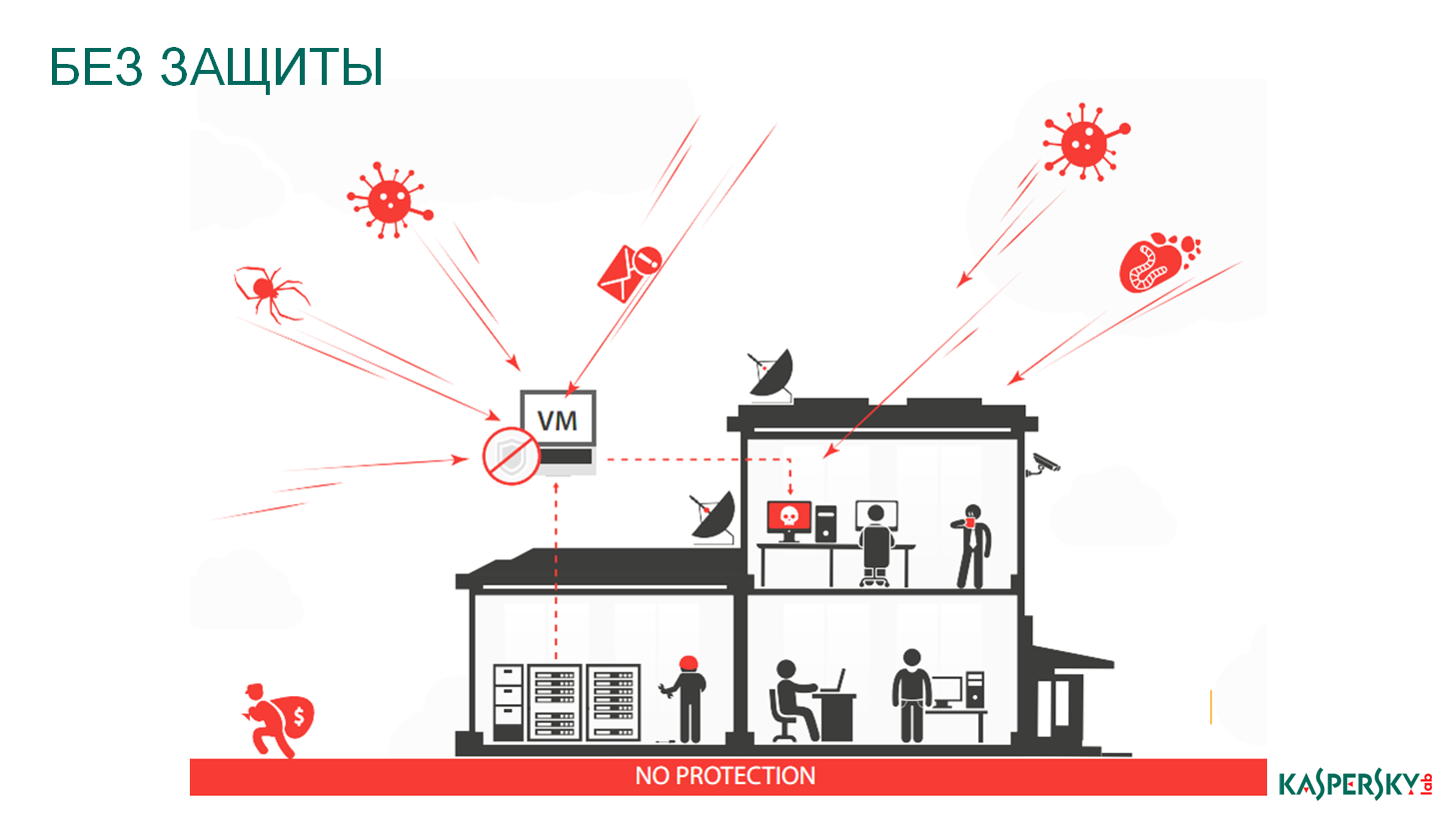
Without protection, I think, it is not necessary to tell. Everything is bad, everyone is hacked, everything is lost. Well, if someone uses this approach to building a protection system and has not yet been cracked, good luck ...

We go immediately further. Traditional security solution. Not bad protects the perimeter, the physical components of the IT infrastructure, but very poorly protects the internal virtual infrastructure from an attempt at internal hacking. Therefore, it is very important to understand why traditional protection is still bad for the protection of virtual environments.
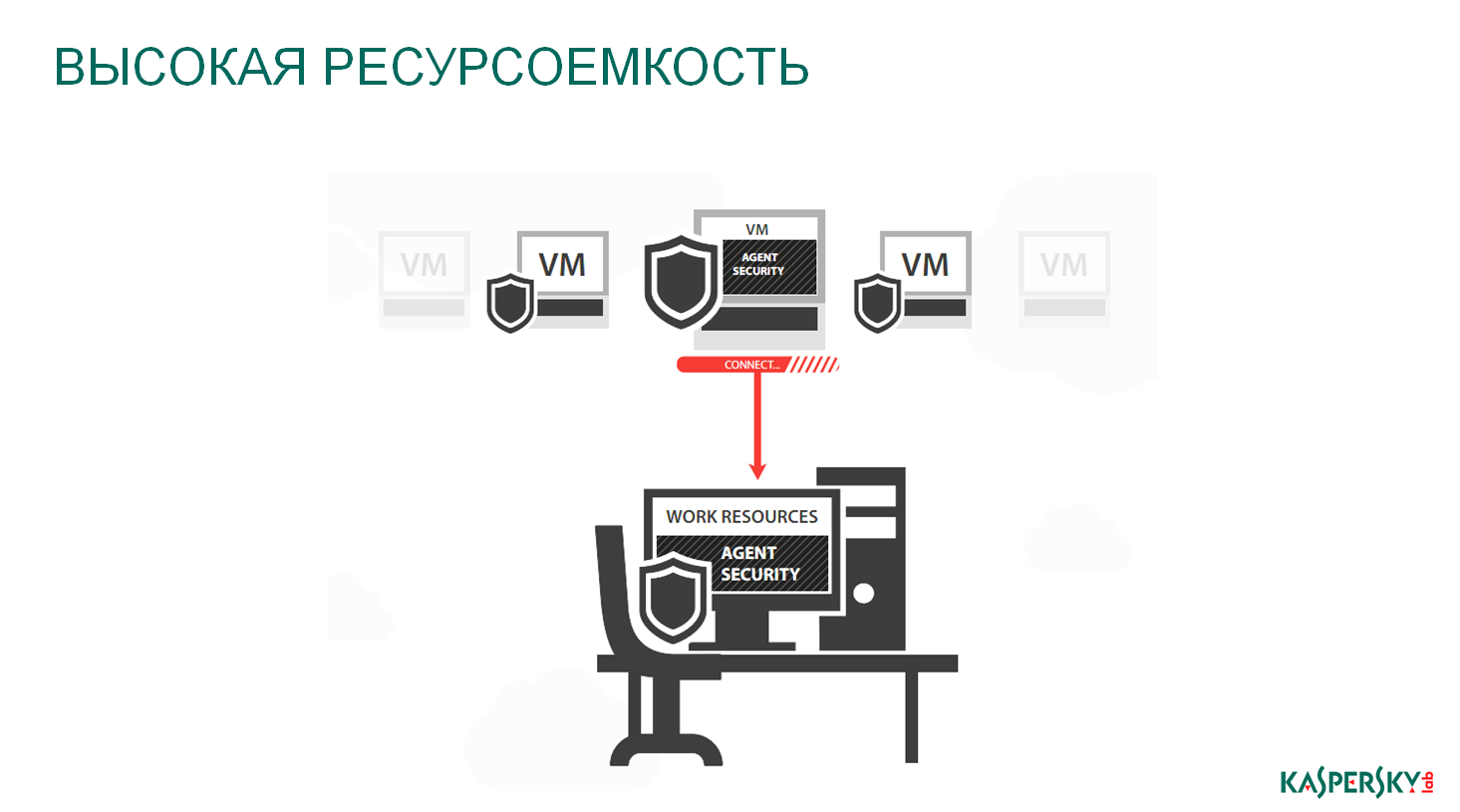
High resource intensity. Everything is simple - we put the traditional engine in each of the virtual machines. This engine begins to consume additional resources of the virtual machine, and, consequently, the entire ecosystem. Previously, before the advent and active use of virtualization, there was one physical server, there was one antivirus application on it, we did not notice it - there were plenty of resources. Now on a normal server, you can raise about 50 virtual machines, and use 50 traditional antiviruses for protection. This load is already hard to miss. And I'm not talking about VDI, where about 150-300 virtual machines can be deployed on the same physical server.
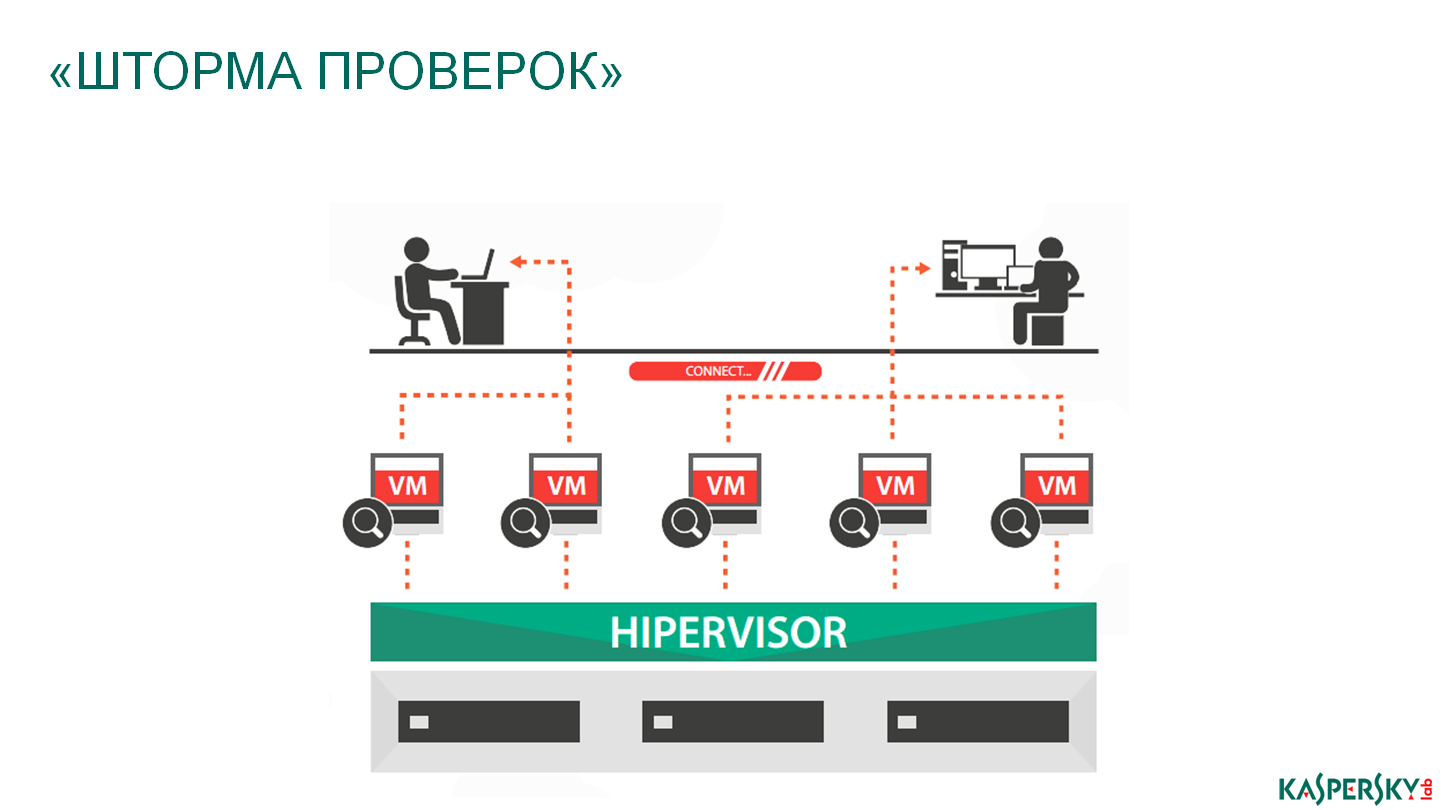
Storm checks. What it is? Some kind of virus has come to your company, it starts distributing itself across all virtual machines, throughout the ecosystem. Each virtual machine with independent security software inside, scanning the same file, begins to consume even more resources and thus slows down the process of the normal operation of the application itself, because for scanning, resources are needed for operation. The consequences are obvious ...
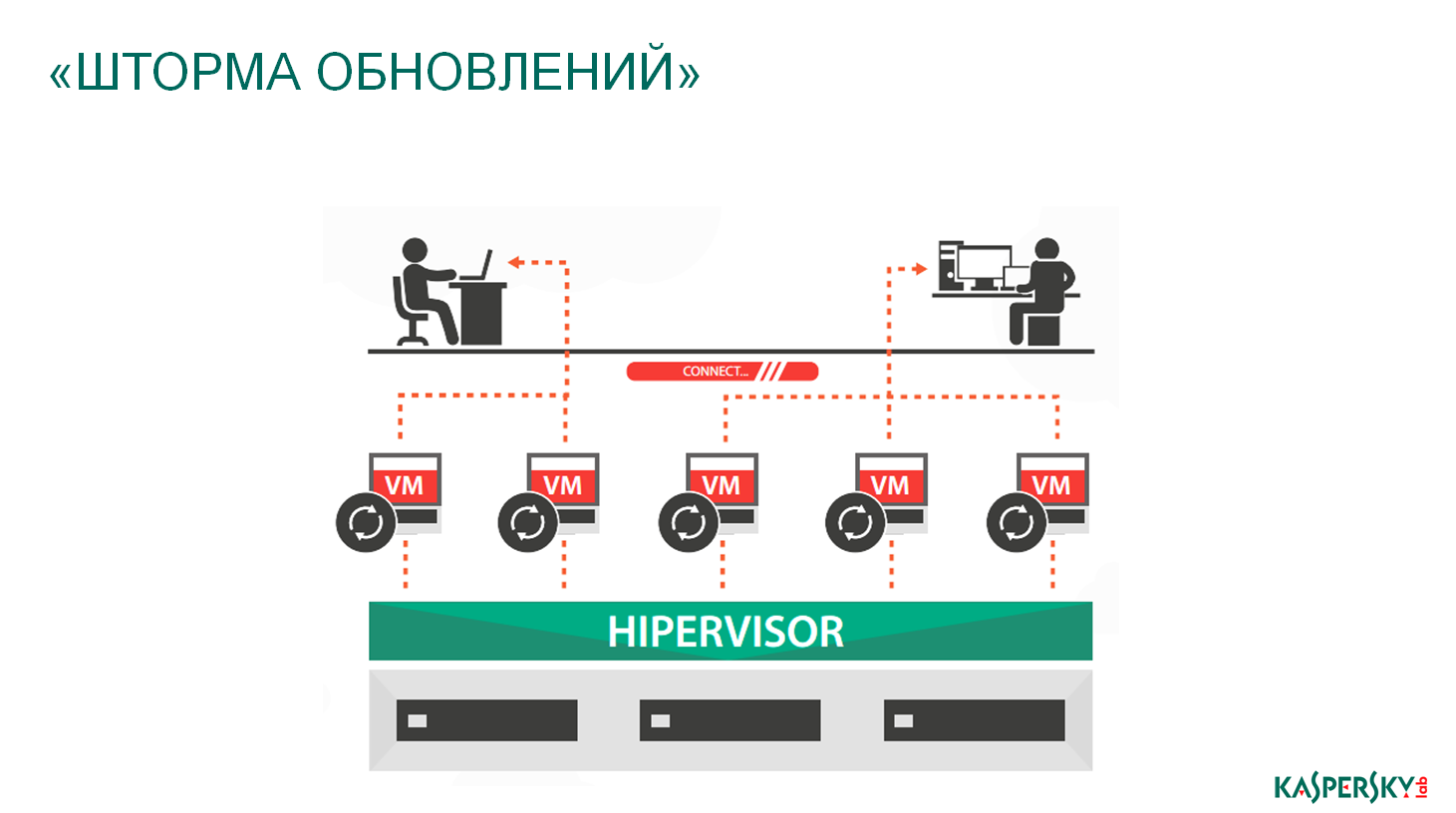
Third - storm updates. This is especially true for the infrastructure of large companies, especially service providers, where virtual machines are actually measured in tens of thousands. When the anti-virus database is updated, it may be 1-2-5 megabytes, but all virtual machines in one second, in one nanosecond, start downloading this 1-5 megabytes. Well, if there are duplicate channels. If there are no duplicate channels, as we have seen more than once, then these companies often drawdown over the network. And it is total, it may happen within some 20-30 seconds, but my colleague from the banking sector says that nanoseconds are now counted. 20-30 seconds is the loss of the channel, this is really a big drawdown, this is really bad, that in these 20-30 seconds the whole world could not reach this data center. Why is it bad? This is a traditional approach. And it is not a question of the fact that someone has wrongly designed traditional solutions, it is the use of a traditional solution not for the intended purpose, not for the physical, but for the virtual infrastructure. Standard solutions in specific conditions. These are not bad IT security solution designs, but bad security solution designs for virtual environments.
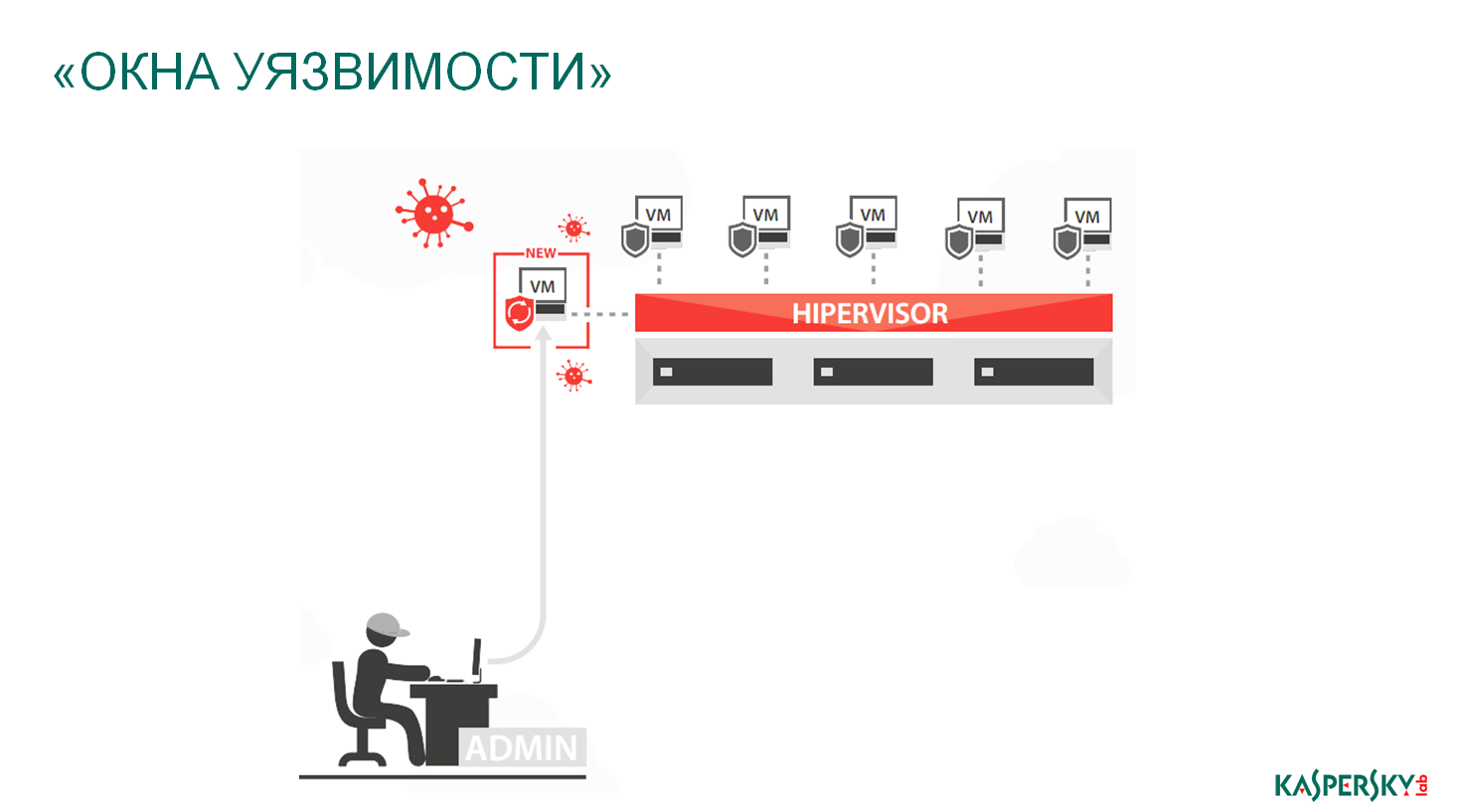
Windows vulnerability. Traditional antivirus, standing inside each virtual machine, it is very difficult to understand how the communication between virtual machines. He basically does not see this, he sees the perimeter from within his virtual machine and everything, and that’s where his area of responsibility ends. And how many attacks, how much activity, how many vulnerabilities exist and exist within the communications between the hypervisor and the virtual machine, between physics and the virtual machine, and so on, does not see the usual solution.
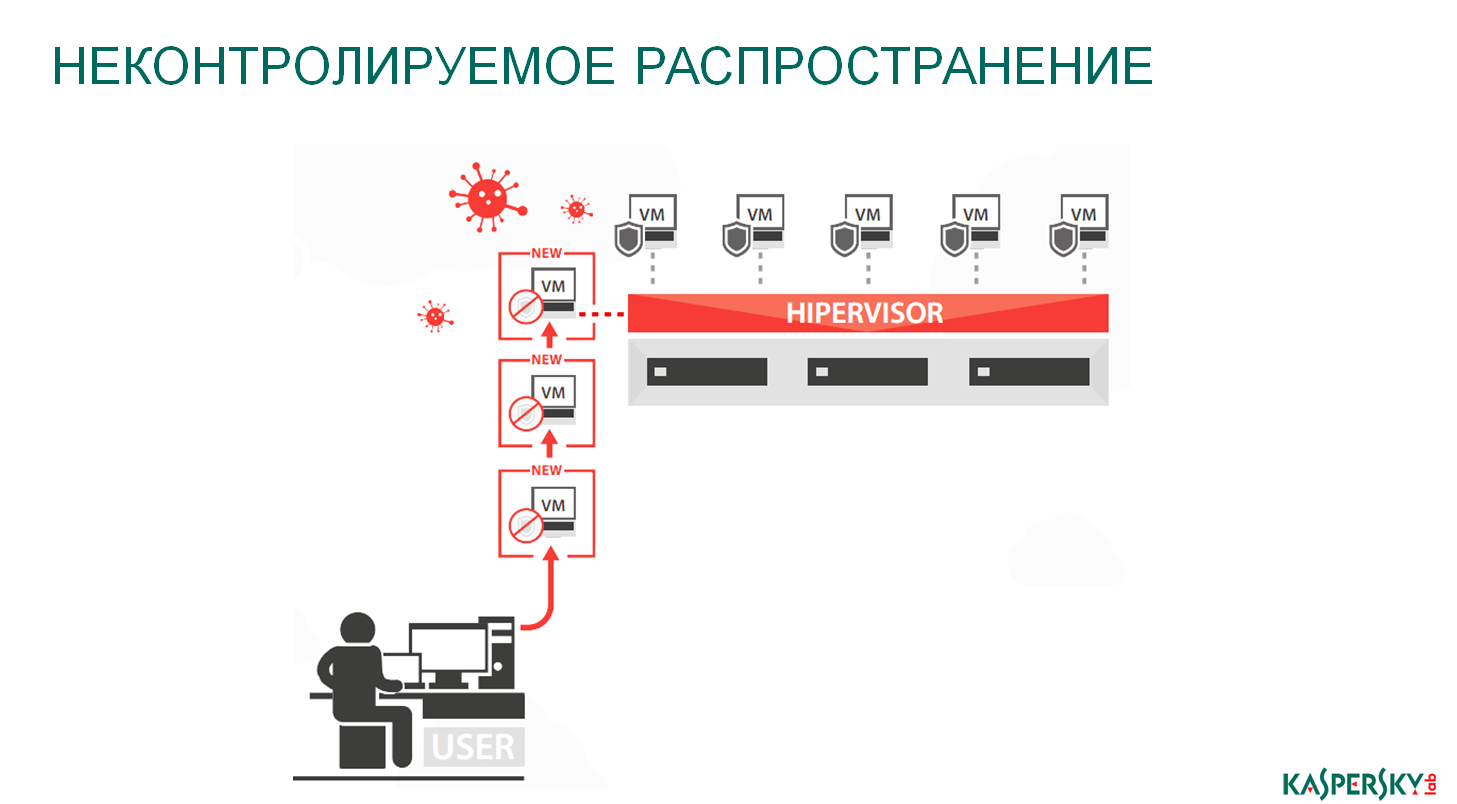
Uncontrolled distribution. Here we are talking about the so-called golden images. How often does the gold image of virtual machines update inside the company? In fact, once every 3-5 months. Because they created, they did beautifully, they did it optimally, so let's leave it. But virtual machines are copied using copies of this image, very often. If updates of anti-virus databases are released, they will not automatically fall into the golden image created and configured earlier, and copies of virtual machines continue to appear using an un-updated golden image. See the threat?
And there is the problem of the fact that with this traditional antivirus we create, deploy a virtual machine that spends its time updating the security component, and at this point attacks occur. Or very often we find situations, including on the Russian market, when previously unknown malicious software was located inside the golden image, and the administrator, copying this golden image, distributed it throughout the network. In general, everything is fine, hello, botnet is a network, everything works as it should - just not for you, but for the hacker.
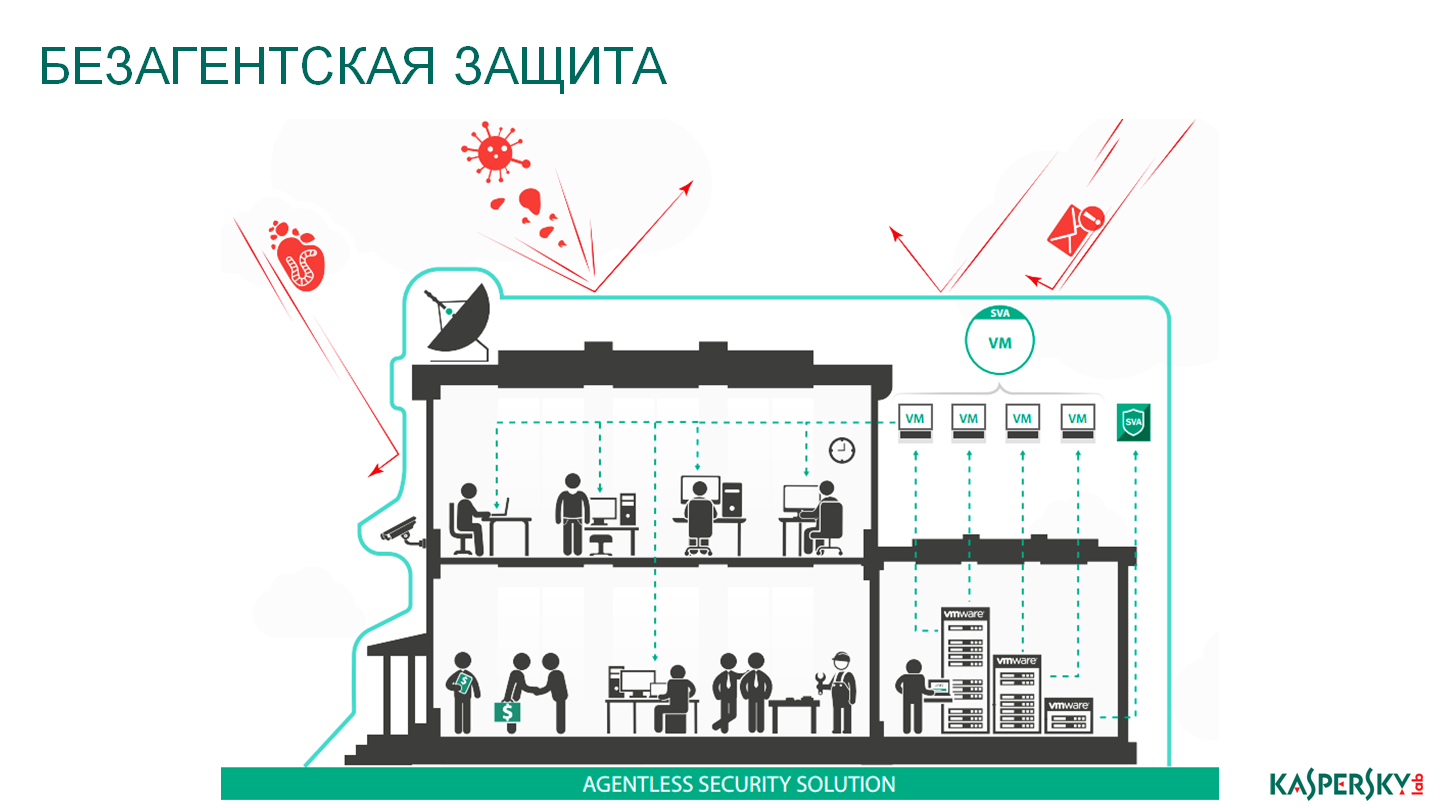
We go further, now a little bit about specialized protection. There are two types of security solutions for virtual environments: agentless and light agent protection. I should note that agentless protection is currently possible exclusively on VMware solutions, because only VMware has provided its API so that all the information security companies in the world can develop agentless protection.
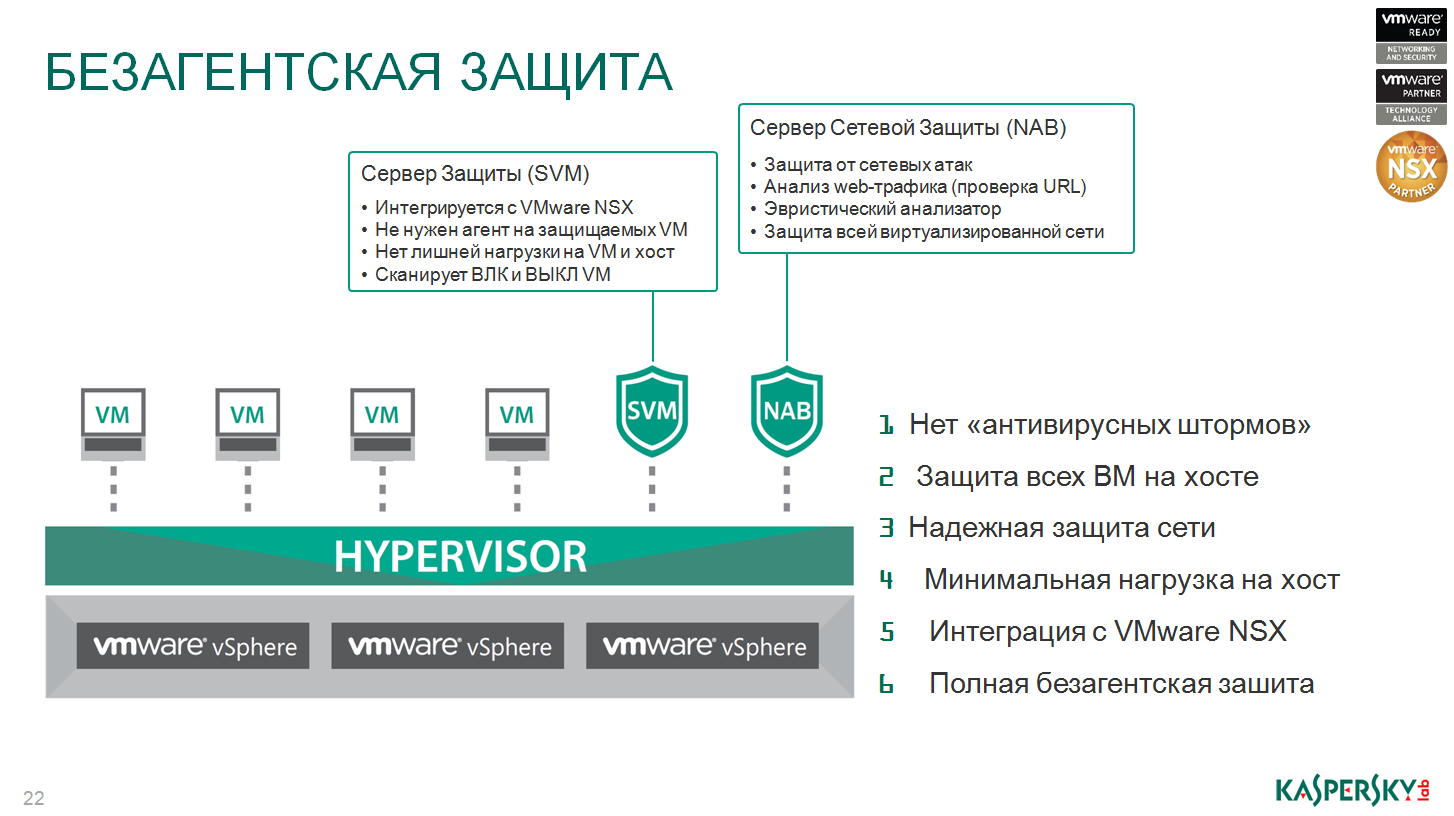
The principle of operation is very simple. On the physical server, where your virtual machines are located, two additional virtual machines are deployed, nothing is put inside each virtual machine. In one of these virtual machines (SVM on the slide) there is an anti-virus kernel and that's it. In the network machine protection network attack blocker, this component is responsible specifically for testing communications between virtual machines and what is happening in the ecosystem. He is also responsible for communication with the NSX technology, but about this separately, perhaps, at another time or during the question and answer session. How is the test? Here, under this SVM, this is its jurisdiction, everything.
Everything that has migrated and arrived at this physical server falls within the area of responsibility of this SVM. She is involved in checking and monitoring software. If you need to scan for virtual protection, this one and only one SVM will do. If necessary, it is much easier to increase the power and speed of this virtual machine, for it we can easily expand the parameters of RAM, processor capacity, and so on. We do not load the virtual machines in any way and do not slow down the security task. There are no anti-virus storms, because SVM deals with checking all the traffic, it takes on this task, and the malware breaks no longer inside each virtual machine.
And now an interesting technology - a pool of verdicts that are inside each data center created on this technology. All security virtual machines share a common verdict cache. If it happened that some kind of attack happened on your first server, some kind of malware was detected that was detected, then the record that this file is malicious will be put into the verdict pool. The next security virtual machine on another server will first contact this verdict pool, it will not scan the system, it will not consume resources if it simply compares the file with the verdict list and blocks it automatically in case it finds out that the verdict is malware ... It greatly accelerated the work of the entire ecosystem. This greatly reduced the consumption of resources, because one SVM worked, it checked and checked, the other virtual machines are not loaded, they just watch the general list of verdicts.
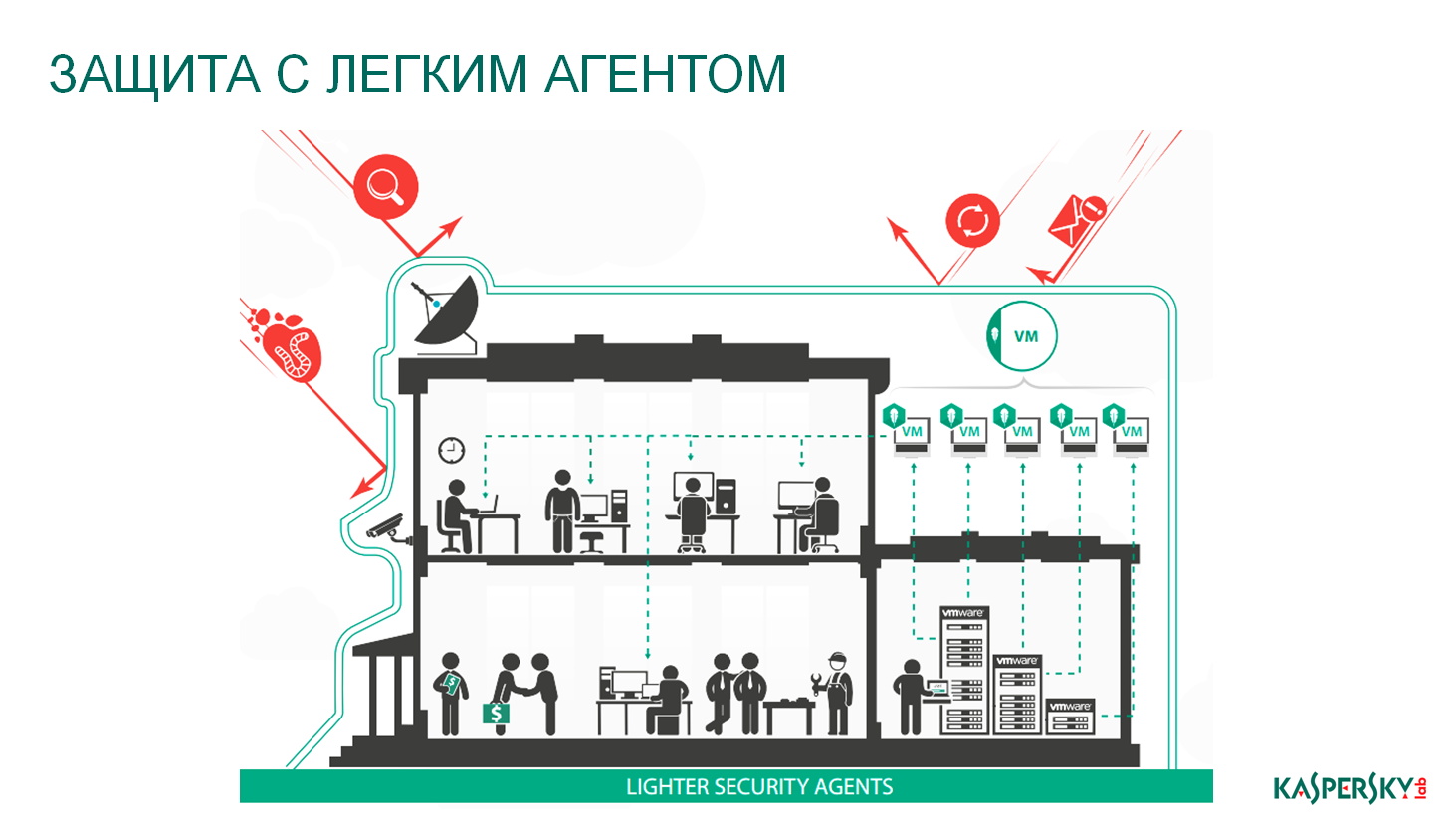
Go ahead. The most interesting and the most delicious for us is the use of protection of virtual environments through a light agent. The principle of operation is very similar. There is the same SVM, there is the same antivirus engine, exactly the same as in your traditional antivirus software, but unlike the previous case, where VMware limited our ability to check, here our solution is given complete freedom of action.
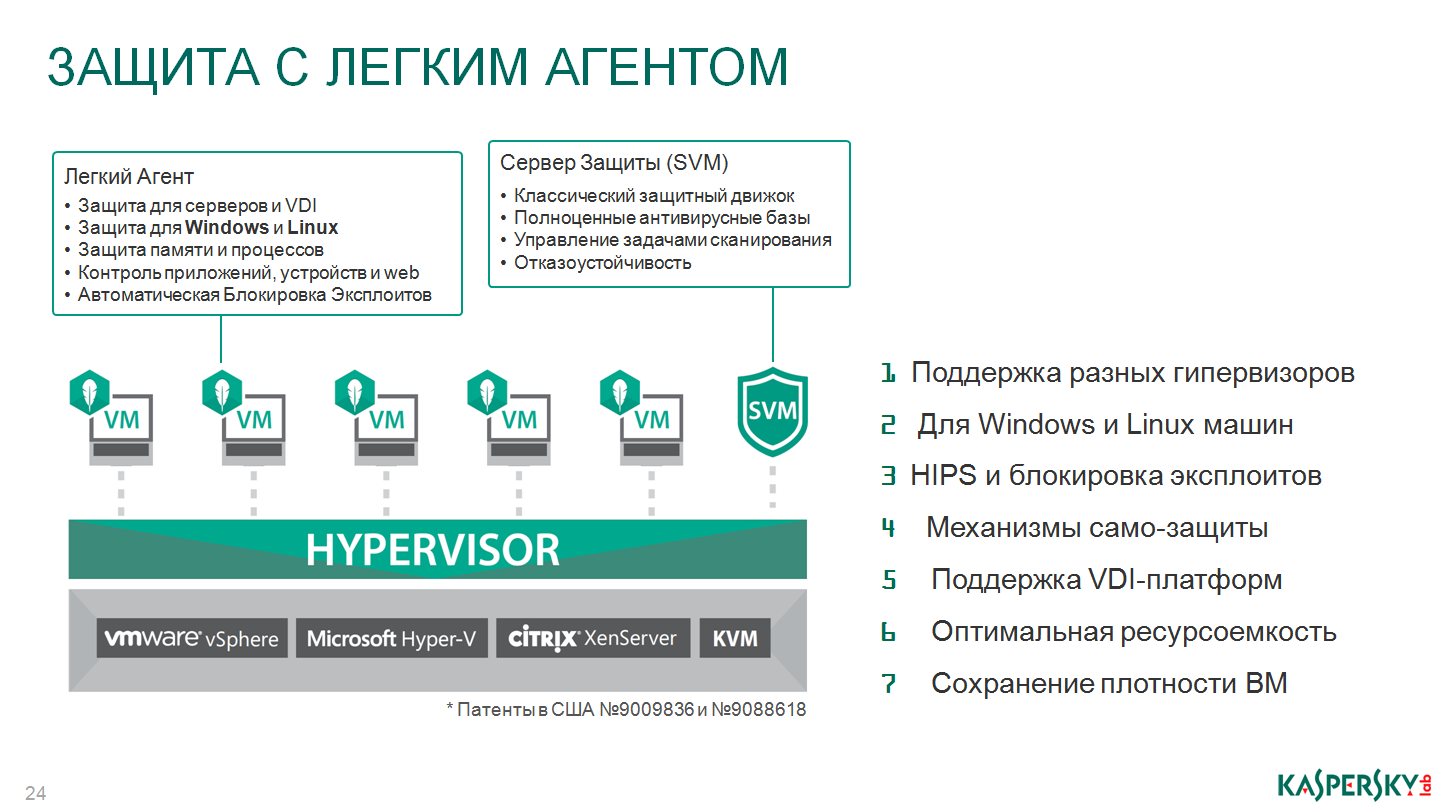
Here we provide our solution, our small, patented lightweight agent, which we install inside each virtual machine. He is really very small, does not perform any checks, he is engaged only in monitoring what is happening inside this virtual machine, and then he returns the result of his work back to this virtual machine of protection in the SVM. How do we expand the functionality with this approach, and why is it so tasty, and why is it so interesting? Because the security level here is not lower than in the traditional anti-virus engine, and taking into account the single pool of verdicts and taking into account a number of additional technologies, it turns out to be much higher than in the traditional anti-virus engine. Plus, if before we had to allocate 2 gigabytes of RAM inside each virtual machine for protection (with the traditional approach), for some additional processor core, here we allocate one virtual protection machine and that's it.
When people ask me: “How can I count, convince my director that we really need this?” And everything is simple.
Suppose you come to the conclusion that your data center or data center of your cloud provider is faced with the fact that you can no longer allocate resources, there is a pool of a thousand virtual machines that you deployed, ten physical servers are required for this pool . Everything. Physically, more than ten servers do not fit into the room. If you are told that you will have to cut these resources twice, give twice the same number of servers, find another room, add cooling again, add software again to all these additional 20 servers, then let's calculate it all . And then the cost of licenses will be completely different when using protection with a light agent, it will be quite small, relatively advantageous.
Let's talk now about technology. This is a pressing issue, because using the example of the latest Wannacry epidemic, no one understood how it happened, but all Kaspersky Lab clients were protected. By the way, I have a question for the audience, I just flew in from another country, asked the same question there. Who suffered from wannacry? Raise your hands, please. Somehow? if not yourself, then maybe a relative, mom, dad, grandmother, children? Who was hurt by the Wannacry epidemic? No, no one? There is? A number of customers, yes? Super. Why ask? Not just out of idle curiosity. And now this question: are there in the hall those who suffered and he at the same time established the decision of Kaspersky Lab? Not.
No other country has told me the opposite. Ok, but in fact the world statistics, I will show it at the end, it is really very scary. Look, I will quickly go over the most delicious technologies that answer the question why the protection developed by Kaspersky Lab's experts worked so well. The question is relevant, because everyone is shouting now “NextGen antivirus”, “NextGen firewall”. No NextGen concept. This is a marketing hyip, which all companies have raised, and which is very cool, like surfing, rolling on the wave. All these technologies, which I will talk about now, are partly our competitors have. The oldest of them is 12 years old already. And now this is all collected now in the so-called NextGen antivirus. Just because they decided under a different sauce to submit technology.

The most delicious thing is monitoring system performance. This is what everyone likes to call self-learning networks. When a technology remembers the correct sequence of applications and when it is confronted with the fact that the sequence of actions of the application inside the virtual machine is wrong, it blocks it. This technology, first of all, stopped the crypto activity of Wannacry. She noticed the beginning of a suspicious activity (file changes by the encrypter), noted who made these changes and how, placed the files in the backup storage in a timely manner and stopped the continuation of this action. However, if the administrator for some reason incorrectly configured or turned off this protection technology, then the actions of malware, of course, spread further.
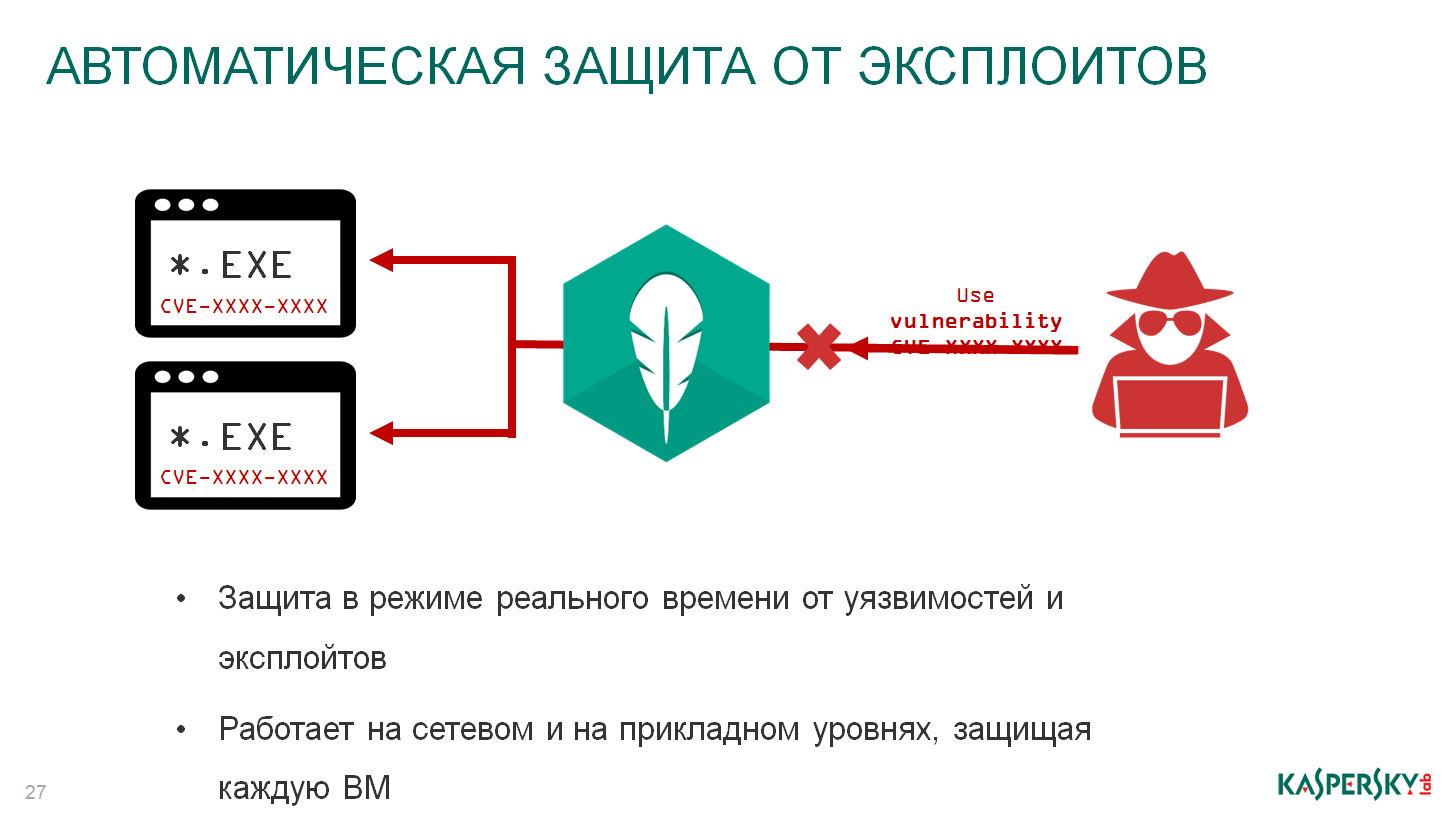
Automatic protection against exploits. About the vulnerability through which Wannacry spread, Microsoft had already known February of this year, but the patch was released only in March-April. In our solutions there is an automatic protection against exploits, namely, exploits and used Wannacry. Partially, this technology is carried out through a network security machine, through a network attack blocker. In defense with a light agent through just the same light agent. We monitor those vulnerabilities that are known to us, monitor application attempts to use non-standard propagation paths. When such attempts are required, alerts will be sent to the administration console, these attempts will be stopped, they will be prohibited until they are physically resolved by the hands of the administrator or information security officer, if required.

Further, white and black lists. This is super technology. We add only what should be launched to the white list. Anything that does not fall into the white list does not start automatically. Very simple, very effective. We now have the technology to protect ATMs, there are technologies to protect the banking systems of the financial sector, there, in general, the same technology is used. Only the operating system and only one application should work there. Anything else that will try to run on these virtual machines in this environment will be prohibited by the machine.
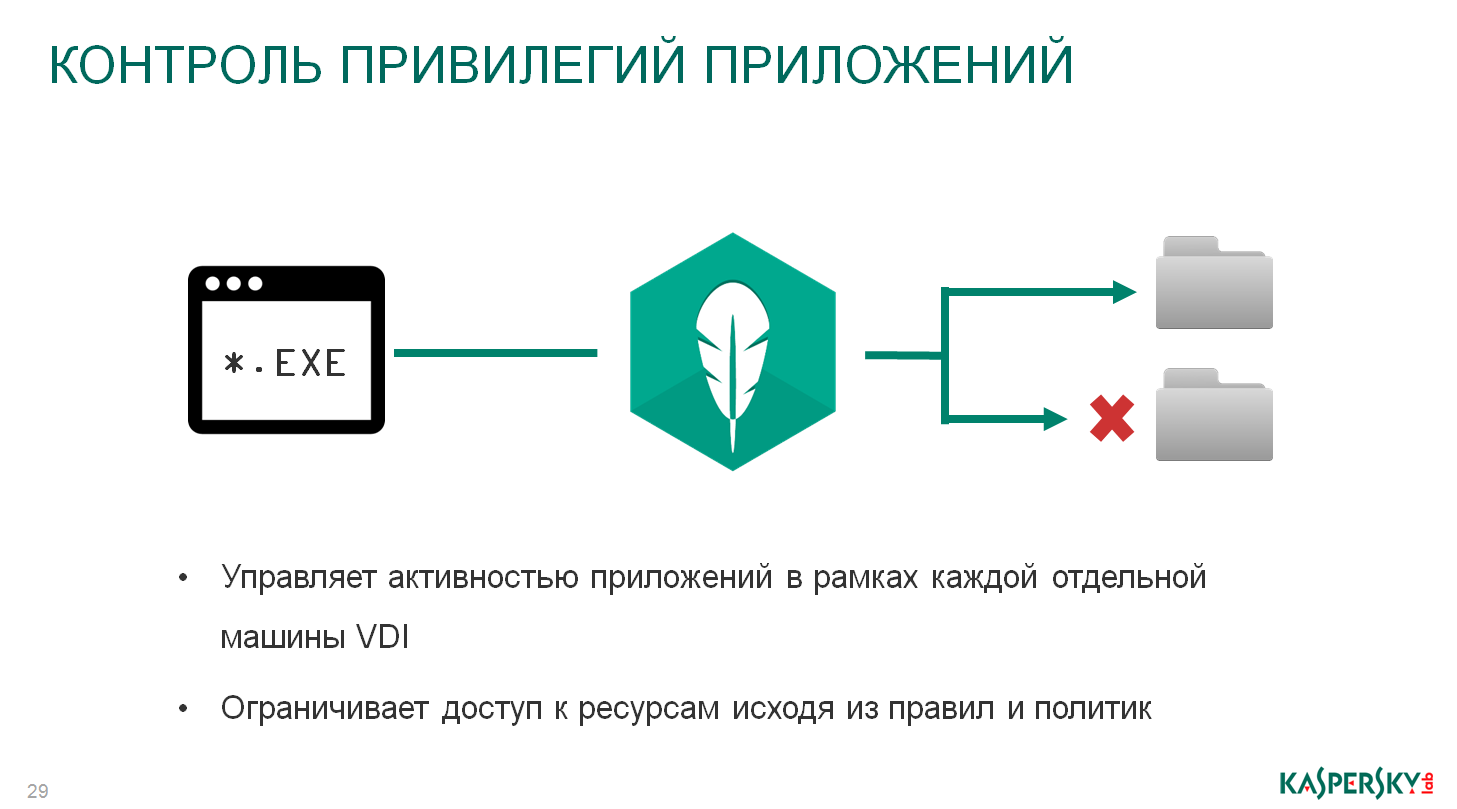
There is a black list - where we are adding specifically the software that should never, under any circumstances, run, everything else is allowed, but this is variability. You can configure application privileges, which software, when, from which virtual machine it is allowed to access a specific resource, with what rights (for example, read only, read and write, etc.).
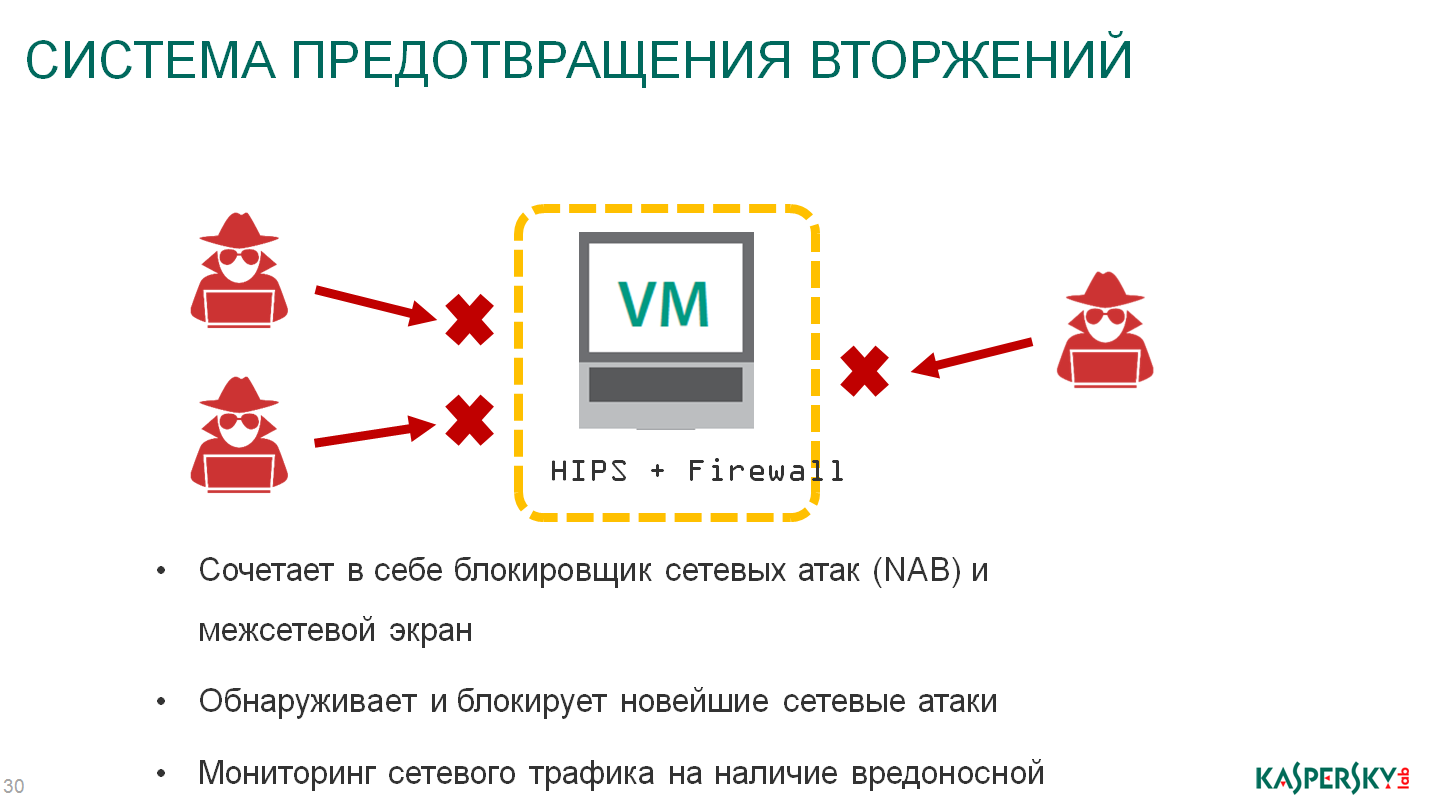
The next technology is an intrusion prevention system. Here is the combination of the network protection machine (SVM) and the very ordinary firewall that is. It was this technology that stopped the spread of Wannacry in virtual networks. Monitoring of systems stopped the activity of the cryptographer, stopped the spread, the main trump card of Wannacry.
Automatic blocking of exploits stopped the spread and infection of the virtual machine. This is what makes the Wannacry epidemic stop among our customers.
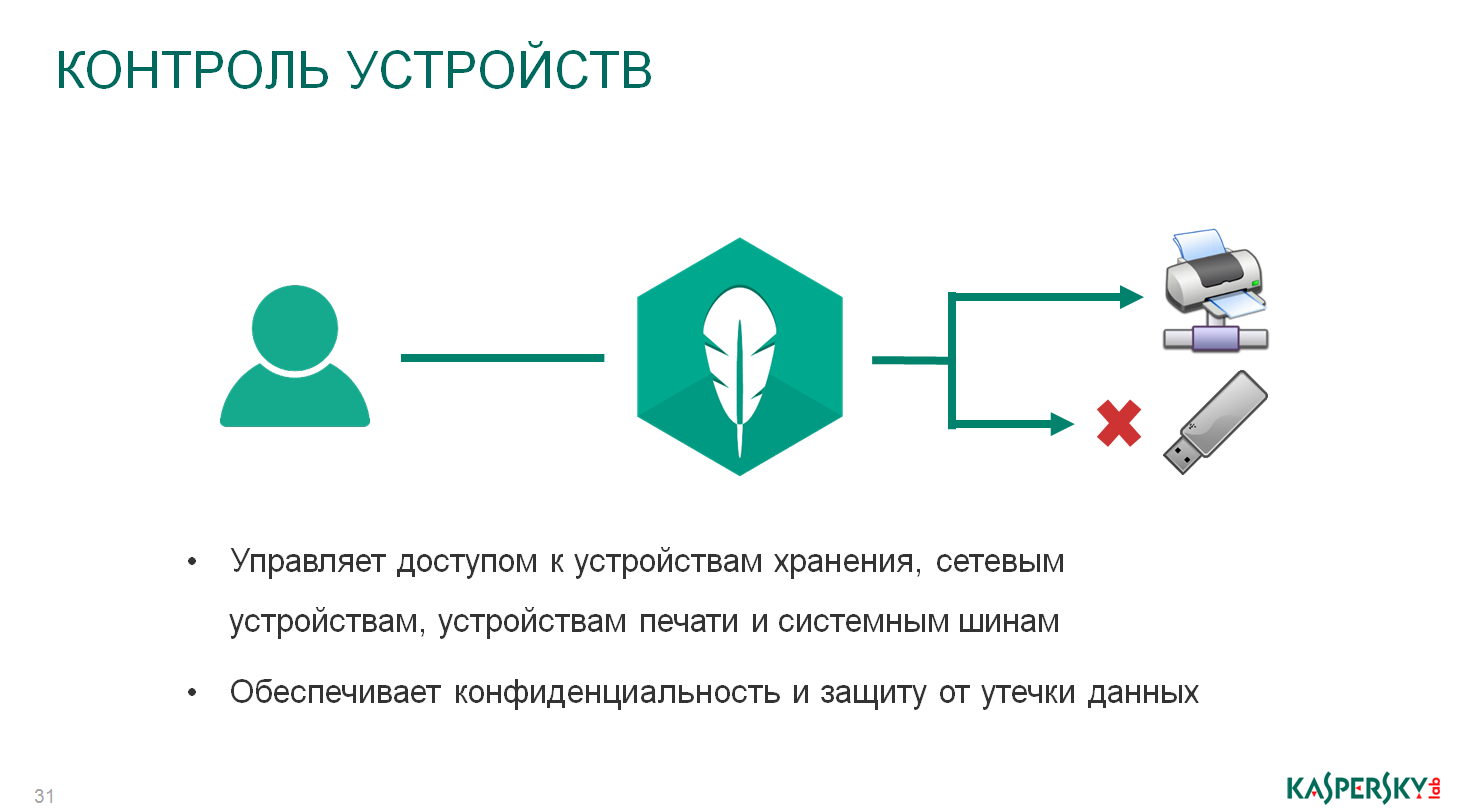
Device control is responsible for the use of external media pilits. Which virtual machines can be accessed using usb devices, with what rights, which devices — all of this is controlled by this technology.
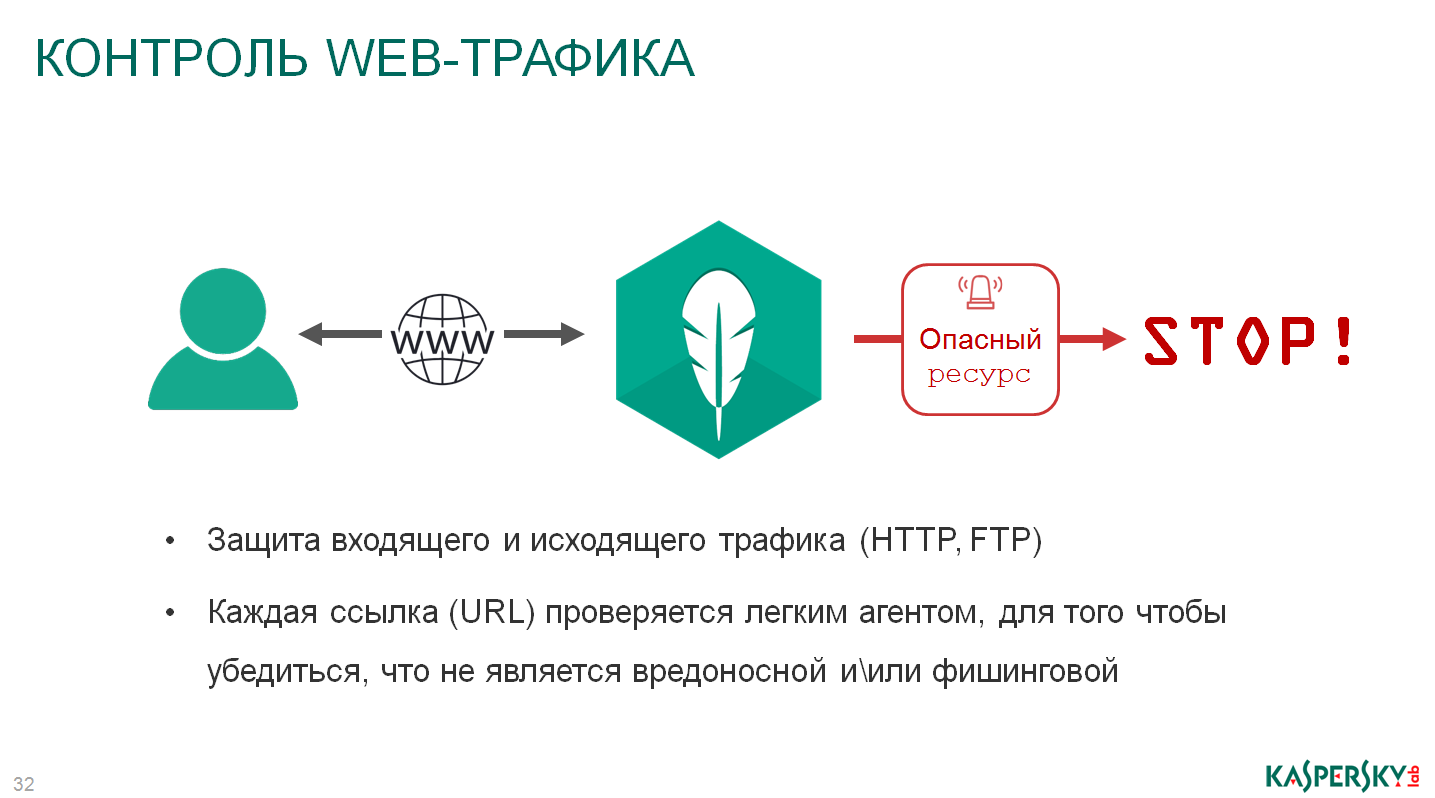
Web traffic is pretty simple too. The technology checks the URLs, what I said, remember how the legitimate facebook-page passes inside our company, everyone misses it, all the firewalls have missed, it’s normal, it’s the most common, real and honest Facebook page, but it’s some link. Here our technology will go through this nested link, see what will happen there, and if there is malicious activity there, it will block the virus that sat on the link and this link that was presented inside this page. You will get your page anyway, but clicking on the link will give you a message that, you know, it is dangerous, we do not recommend switching, or it will be blocked if the administrator decides that it requires blocking, it will be blocked as well.
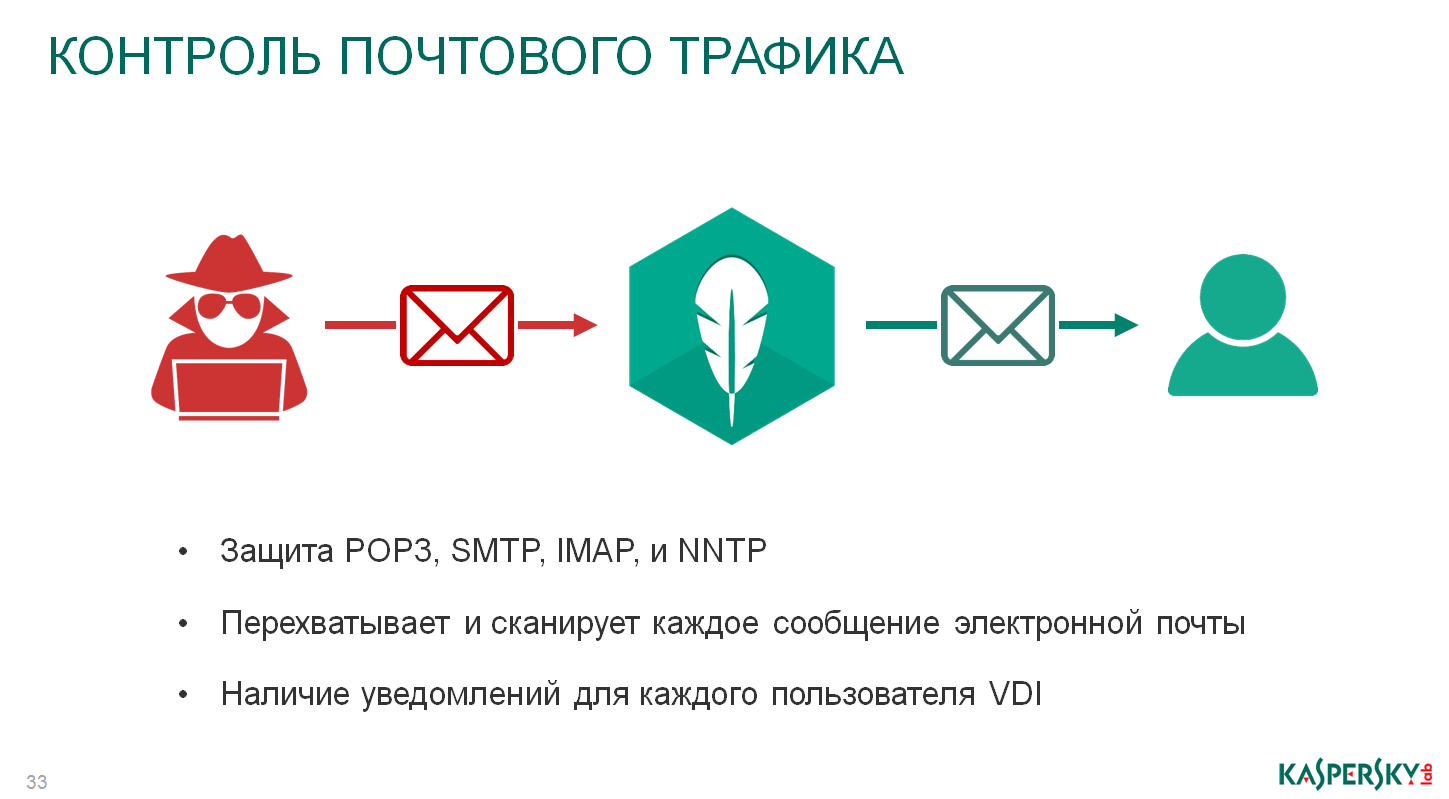
Control mail traffic. Currently, the spread of viruses always uses people as a target (social engineering, sending spam, sending out some suspicious letters of unknown content). And here I’ll get a little away from the topic, because I am still responsible, including for the direction of work with targeted attacks, with investigations of targeted attacks, everything is always interesting, everything is deeply and cunningly brewed.
Do you know how long a targeted attack lasts on average today? About 300 days. That is, out of these 300 days, 100 days, attackers will gather information on some of your employee, through whom an infection will occur. Days 50, maybe 70, will be very slow, very quiet, very calm (God forbid, somewhere some of the systems will give an allert) infection of the entire ecosystem, without negative destructive activity. Attackers do not need it. After these, on average, 200 days, when organizations realize that everything is infected, the attackers have infiltrated the company, there is a data leakage or compromising data is added, or someone quietly quietly steals a part.
We had a case when we investigated the incident in one of the banks, the hacker team employees were introduced into the process of microtransaction. And with each transaction began to take one nanocent, because he was the ninth decimal place. This is a miserable money, but in the banking accounting system then only eight decimal places were counted. And the system simply rounded this ninth sign, and on this rounding up in three months of work, the hackers earned huge money, they really earned billions. Just because the ninth decimal place was rounded, and the system did not take it into account. No financial analysis reports even saw him. Then, deeply analyzing the code and having caught this hacker campaign, we were able to figure it out, we could understand that it was the ninth sign. And it was a standard propagating attack. In the case of targeted attacks, one of the most difficult and terrible moments is the fact that intruders after their destructive activities sweep traces very well. Hiding in two ways, they really disguise their activity completely, and the second - they often attack those companies that are very frightened to come to someone and say that they have been hacked.Because the impact on their reputation and financial response from all this will be much higher than the consequences of hacking. Therefore, hackers choose victims very correctly. They really own a phenomenal fantasy, a phenomenal approach, and it turns into art.
, , , , , . . , . . . , , . — , , , . — , , .
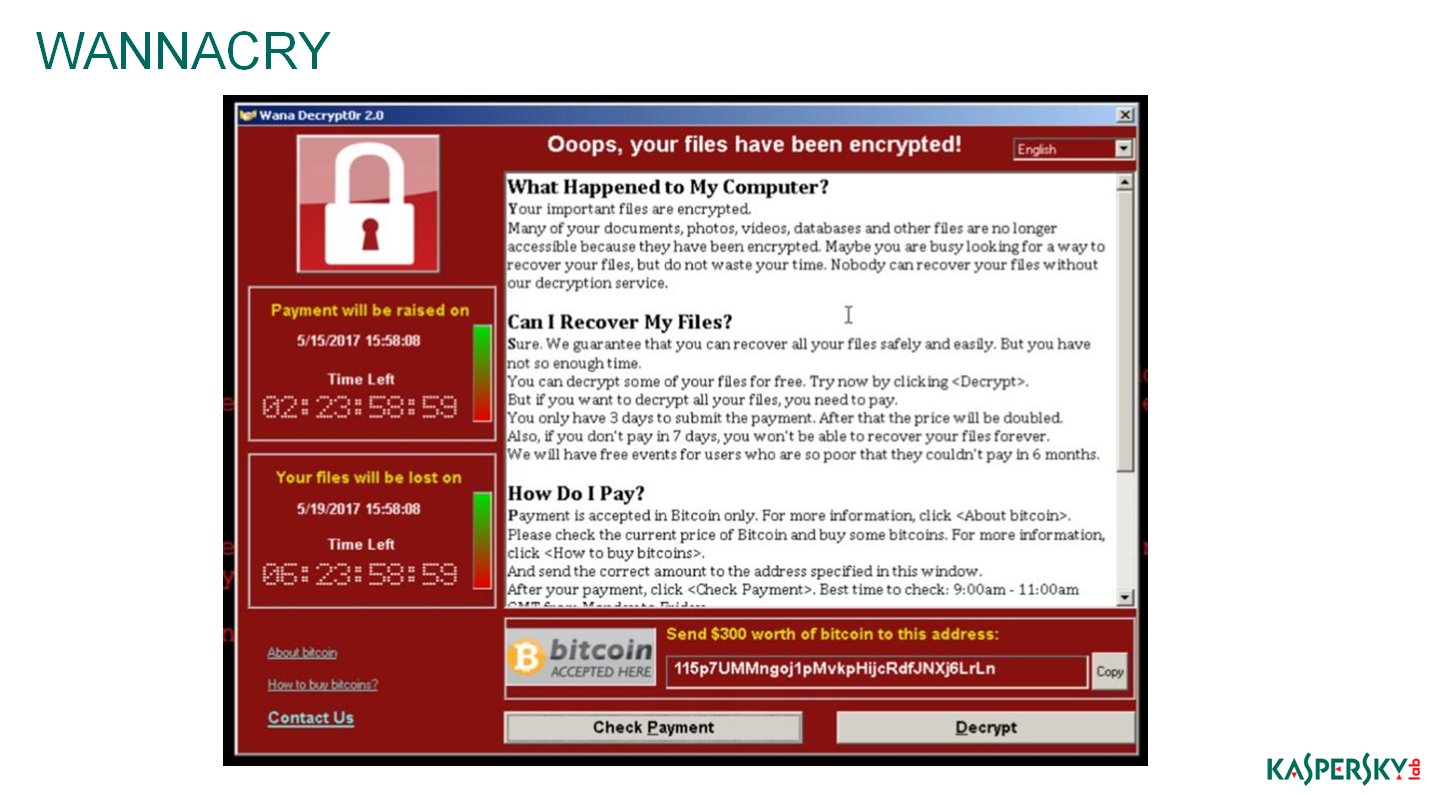
Now about sore, about Wannacry. This is what everyone saw. Here it appeared on the scoreboard of many airports. I saw it at the airport when I was waiting for a transfer, and it was sadly because I understood that the airport had been hacked and the data (including passenger registration data) was lost, and what if my ticket got there? This is the reality that the world has encountered. Here is such a straight and beautiful, now known to the whole world kartinochka. This is the first crypto worm. For cryptographers self-propagation is not peculiar. Encryption in the standard environment is peculiar to the fact that the user himself initiates the process :, opened an incomprehensible letter, clicked on an unfamiliar link, and the data encryption process started further.

This is the first crypto worm that spread itself, climbed into the system itself, encrypted it itself. He exploited vulnerabilities, he worked on a specific port, and he spread very quickly. The more he encrypted, the more he spread further into the system. This is an avalanche activity. How many attacks have been prevented? I can say that this time we stopped the epidemic of encrypters, so far, this particular world has stopped this one.

74 countries were touched, they tried to spread wherever possible. The attackers did not choose something concrete, it was not a controlled epidemic, it was chaotic, it was completely free. Where has spread, where climbed, there and climbed, who was not protected, those hurt. See how badly Europe hurt. In Russia, it is clear that we have not touched on the outback, there are still not very many computers there, but this is more of a painful than a pleasant information. Nevertheless, a lot of financial centers, a lot of large companies have suffered precisely from this action.

Encrypted files, among them you can find standard jpeg, txt-files, exel, video, music, everything. Almost everything that has value to the user has been encrypted. Encrypted and exhibited such a Wannacry tag, that's why it got its name.

Now, about how to escape from this malware. Patch, patch, patch. This is the first. You know, we have a very interesting trend, I recently reviewed the global analytics of the use of VDI-infrastructures. How often on your home physical computers do you switch to a new operating system? For example, I’ve got a dozen, for example, but it’s worth a year, I haven’t thought about any Redstone yet, everything works for me. Usually the trend is 1-4 years, people understand that their own is outdated, you need to put something new. Here in VDI-infrastructures, in virtual machines, an update to a new operating system on average in the world occurs two to three weeks after the release of a new operating system, often faster on average. Therefore, it was much easier with them, because they were all patched.Therefore, VDI in the first place it is virtualization is not affected. There is a very high tendency to update the operating systems, there is a very high tendency to try, because when something does not work in the operating system on our computer, we have to take it all down, reinstall it, look for new errors in the system. When we talk about a virtual machine, but recreated, deleted, raised from backup, in general, everything is fast, everything is cool, admins are happy, satisfied, everything is fine.all is well.all is well.
Be sure to install some critical security updates. Again, I repeat, the attack was directed specifically at one vulnerability, about which Microsoft had known since at least February, but did not close it. I will not ask why, but did not close. The consequences we see everything. Now quickly released a patch, quickly closed. For myself, I found such an interesting balance. I always have a virtual machine at home, on which I put a new operating system, and I use it there. If after a couple of months I get used to it, then I put this operating system to myself, having migrated all the applications inside this virtual machine from the beginning, and roll this image. Great work. Ask your admins to do the same.
Very simple indeed. A second virtual machine is being created (you can ask the service provider to create a virtual machine with a new operating system) and applications are slowly migrating. Sit, get used, update, move to a new operating system. Will be more protected.
As I said KSN, this is Kaspersky Security Network. All people who use Kaspersky Lab products are asked if they want to participate in the KSN program, Kaspersky Security Network.
What it is?This is a global global community, where records of all incidents are recorded, data is stored in the cloud network. Employees of our company, as well as our automated systems, constantly analyze this data, are always looking for something new, put new masks. But in fact it is 400 million people who every second tell the whole world about new incidents requiring blocking.
And a lot of automatic systems respond to this in our company. For example, our employee was attacked by the Wannacry virus in Brazil, the virus was investigated right there, and Wannacry was stopped there on the spot. Because the virus did not pass the system watcher, a record of virus activity appeared, did not pass the technology of automatic protection against exploits, did not pass the encryption technology, did not pass the monitoring of network activity. All of these links, all of these activities have been marked as dangerous. And these verdicts went to KSN. Any other employee who at that moment was on the Internet in any other part of the world and was connected to the KSN network, automatically received information that if this file came to him, then he was angry, he should be stopped. This stopped the entire Wannacry epidemic.
Next, the network attack blocker, which forbade the use of exploits inside virtual machines, has already worked. Next, the automatic protection against exploits worked, which did not allow intrusion into the virtual machine, monitoring systems, which did not allow encryption and application launch control, which in general did not allow something illegal to start inside the system.
Thank you for your attention.
Answers to the questions:
You talked about this latest virus, what did you know about the vulnerability in February, about the possibility, the bug "Microsoft" in fact, why couldn’t your software close the hole in advance?
Our software is closed. Just one thing when you close it on your own, another thing when it is closed at the operating system level. And our task in cooperation with Microsoft, we, if we find something in their code, we inform them about it. Not everyone uses Kaspersky Lab products, they also want to be protected.
Do you find a vulnerability, and it is immediately closed by your forces, your software? At the level where it actually works?
, , , , system watcher automatic exploit prevention 0-day , , , . , .
Today, when Petya and Misha are sweeping across the planet with might and main, this material is becoming especially relevant for users of virtual servers. We present the report of Vladimir Ostroverkhov, Kaspersky Lab, "Proper protection of the" clouds "."
')
Hello everyone, my name is Vladimir Ostroverhov. At the moment I am an expert in support of corporate sales of Kaspersky Lab.
Functionally, I am partly a developer, trainer, techie, training person for local teams all over the world.
Let's start with a frivolous topic. What are the requirements for a modern IT security system and why are we raising today the topic of cloud infrastructure security, virtual security, protection for virtualization, for virtual machines?
Let's start with the simplest - with the viruses that you all know about. 97th year. We had enough work. Every day, there were 20 new samples, they were really complex, interesting, we literally dismantled them with our hands, wrote “masks” and general structures of detects. And everything was fine. A year ago, I returned to Kaspersky Lab again, came to my former colleagues and asked: “Guys, how are things going now?” There were 20-30 problem viruses per day that you had to study manually. And they showed me the numbers ...
Today, more than 300,000 units of malware appear every day. Yes, these statistics are quite simple. For example, a student learned a new code in computer science lessons, wrote some program, released it on the Internet. Virus? Virus because it can spoil the data. This includes complex targeted attacks, those that are developed specifically for organizations, for certain cases, for certain situations, and they are very well able not only to break and steal data, but also very well know how to hide themselves. This all requires investigations. The volume has increased several times, thousands of times. An old and stupid question: “Kaspersky writes viruses?”, You can see them yourself, and so they write without us so much that we could get rid of ...
Second moment. The position of our company - we, of course, sell products and solutions, but the main value is the accumulated knowledge that is in our company, in fact, expressed in solutions. For this expertise and appreciate the company, it determines its reputation.
Okay, we go further about horror stories. What is good virtualization, I think everyone knows. Yes? High density, low resource consumption, everything is great, everything is beautiful, virtualization vendors usually talk about it. Why is it bad and dangerous, and why should the virtual infrastructure be further protected and we should not forget about protection? Two thirds of companies around the world, including large businesses, believe that they have invested in virtualization and no additional protection is needed. The virtual is safe by itself, everything is fine with it, no one breaks it. Not true, break and more often!
The first is that up to 80 percent of all those 300 thousand units of malware that I mentioned earlier, can live without any modifications, without any changes, inside the virtual infrastructure, inside the clouds. You do not need to edit anything, horrible, earned, started to delete, erase, spoil the data.
Hackers are also more interested in virtual infrastructure. It is much easier to hack it and access all your virtual machines and all data at once, rather than trying to hack each physical server separately. Logical and quite simple.
Thirdly, it is necessary to pay attention to the speed of propagation of viruses inside the virtual machine. Inside the virtual infrastructure, malicious code spreads with great speed. It is easy to infect 10 thousand virtual machines in 15 minutes. Somehow it must be stopped. These are epidemics of tremendous speeds and enormous proportions.
I'm not talking about the wrong protections, which are a separate level of threats that arise for all companies that use virtual environments in their work.
Go ahead. Clouds private, hybrid, public of themselves always represent a data center. From this you can not escape. There are servers, there is a network, there is a data storage system - this is a standard set that works, from which no one goes anywhere, it is traditional.
The main focus of malware attacks are servers and storage systems. Servers - data corruption and application operation, storage - data corruption or theft. The network is only transport.
Today I will talk about the work of the data center in terms of crypto-security and in terms of the software that you can install, and it will provide maximum protection.
And now a little scary statistics. We interviewed about five thousand companies around the world. These are large companies with at least one and a half thousand employees in 25 countries. About 75 percent of them already use virtualization, for large businesses this is a standard trend, they increasingly believe in virtualization and implement in their data centers. Statistics of virtualization vendors is shown on the slide. Another thing is interesting, about half of the companies do not use any protection for virtual machines, and the second half believes that any standard antivirus will suffice. All of these companies, on average, spend almost a million dollars on recovering from incidents: on investigation, on restoring the system, on reimbursing costs, on compensating for losses from a single hack. How is that? These are 5 thousand companies and each of them lost a million dollars last year? Statistics show "average temperature in the hospital." For example, there is a large company, a service provider, one of the largest, let it be, in Spain. A lot of clients work with her. They were the only ones hacking last year.
What will their expenses be if they compromise themselves? Direct losses for the restoration, replacement of equipment, software ... Indirect losses - reputation ... Losses for compensation for their customers, including reputation ... And incident investigation, partial replacement of infrastructure, because it has already compromised itself, it is dialogue with governments, dialogue with insurance companies, dialogue with customers who have to pay compensation.
It should be perfectly well understood that, on average, a large business loses about 800 thousand a year if improperly organized protection is a potential risk for a large company, the risk of losing about a million dollars a year. For a small company, this is about 100 thousand dollars a year. These are the statistics that we see, based on live incidents among organizations. This is really scary data, you really have to reckon with them, and you cannot get away from them. And this is found all over the world, 25 countries, I think, more or less confirm this.
Now about the protection. With terrible yet finished. There are only four approaches to building a security system. Whoever invented what, whoever said what. The first is the lack of protection, this is also a kind of protection, this is faith, religion: “prayed, crossed himself” and everything went away. I hope this is not your case.
The second is a choice in favor of traditional protection. It's about standard antivirus or traditional protection systems designed to protect non-virtual physical devices.
The third and fourth are two ways of specialized protection: agentless protection and light agent protection. This is a general trend of the entire global security market.
Now let's take a little more detail about all four approaches, we can say, strategies for building a system for protecting virtual environments.
Without protection, I think, it is not necessary to tell. Everything is bad, everyone is hacked, everything is lost. Well, if someone uses this approach to building a protection system and has not yet been cracked, good luck ...
We go immediately further. Traditional security solution. Not bad protects the perimeter, the physical components of the IT infrastructure, but very poorly protects the internal virtual infrastructure from an attempt at internal hacking. Therefore, it is very important to understand why traditional protection is still bad for the protection of virtual environments.
High resource intensity. Everything is simple - we put the traditional engine in each of the virtual machines. This engine begins to consume additional resources of the virtual machine, and, consequently, the entire ecosystem. Previously, before the advent and active use of virtualization, there was one physical server, there was one antivirus application on it, we did not notice it - there were plenty of resources. Now on a normal server, you can raise about 50 virtual machines, and use 50 traditional antiviruses for protection. This load is already hard to miss. And I'm not talking about VDI, where about 150-300 virtual machines can be deployed on the same physical server.
Storm checks. What it is? Some kind of virus has come to your company, it starts distributing itself across all virtual machines, throughout the ecosystem. Each virtual machine with independent security software inside, scanning the same file, begins to consume even more resources and thus slows down the process of the normal operation of the application itself, because for scanning, resources are needed for operation. The consequences are obvious ...
Third - storm updates. This is especially true for the infrastructure of large companies, especially service providers, where virtual machines are actually measured in tens of thousands. When the anti-virus database is updated, it may be 1-2-5 megabytes, but all virtual machines in one second, in one nanosecond, start downloading this 1-5 megabytes. Well, if there are duplicate channels. If there are no duplicate channels, as we have seen more than once, then these companies often drawdown over the network. And it is total, it may happen within some 20-30 seconds, but my colleague from the banking sector says that nanoseconds are now counted. 20-30 seconds is the loss of the channel, this is really a big drawdown, this is really bad, that in these 20-30 seconds the whole world could not reach this data center. Why is it bad? This is a traditional approach. And it is not a question of the fact that someone has wrongly designed traditional solutions, it is the use of a traditional solution not for the intended purpose, not for the physical, but for the virtual infrastructure. Standard solutions in specific conditions. These are not bad IT security solution designs, but bad security solution designs for virtual environments.
Windows vulnerability. Traditional antivirus, standing inside each virtual machine, it is very difficult to understand how the communication between virtual machines. He basically does not see this, he sees the perimeter from within his virtual machine and everything, and that’s where his area of responsibility ends. And how many attacks, how much activity, how many vulnerabilities exist and exist within the communications between the hypervisor and the virtual machine, between physics and the virtual machine, and so on, does not see the usual solution.
Uncontrolled distribution. Here we are talking about the so-called golden images. How often does the gold image of virtual machines update inside the company? In fact, once every 3-5 months. Because they created, they did beautifully, they did it optimally, so let's leave it. But virtual machines are copied using copies of this image, very often. If updates of anti-virus databases are released, they will not automatically fall into the golden image created and configured earlier, and copies of virtual machines continue to appear using an un-updated golden image. See the threat?
And there is the problem of the fact that with this traditional antivirus we create, deploy a virtual machine that spends its time updating the security component, and at this point attacks occur. Or very often we find situations, including on the Russian market, when previously unknown malicious software was located inside the golden image, and the administrator, copying this golden image, distributed it throughout the network. In general, everything is fine, hello, botnet is a network, everything works as it should - just not for you, but for the hacker.
We go further, now a little bit about specialized protection. There are two types of security solutions for virtual environments: agentless and light agent protection. I should note that agentless protection is currently possible exclusively on VMware solutions, because only VMware has provided its API so that all the information security companies in the world can develop agentless protection.
The principle of operation is very simple. On the physical server, where your virtual machines are located, two additional virtual machines are deployed, nothing is put inside each virtual machine. In one of these virtual machines (SVM on the slide) there is an anti-virus kernel and that's it. In the network machine protection network attack blocker, this component is responsible specifically for testing communications between virtual machines and what is happening in the ecosystem. He is also responsible for communication with the NSX technology, but about this separately, perhaps, at another time or during the question and answer session. How is the test? Here, under this SVM, this is its jurisdiction, everything.
Everything that has migrated and arrived at this physical server falls within the area of responsibility of this SVM. She is involved in checking and monitoring software. If you need to scan for virtual protection, this one and only one SVM will do. If necessary, it is much easier to increase the power and speed of this virtual machine, for it we can easily expand the parameters of RAM, processor capacity, and so on. We do not load the virtual machines in any way and do not slow down the security task. There are no anti-virus storms, because SVM deals with checking all the traffic, it takes on this task, and the malware breaks no longer inside each virtual machine.
And now an interesting technology - a pool of verdicts that are inside each data center created on this technology. All security virtual machines share a common verdict cache. If it happened that some kind of attack happened on your first server, some kind of malware was detected that was detected, then the record that this file is malicious will be put into the verdict pool. The next security virtual machine on another server will first contact this verdict pool, it will not scan the system, it will not consume resources if it simply compares the file with the verdict list and blocks it automatically in case it finds out that the verdict is malware ... It greatly accelerated the work of the entire ecosystem. This greatly reduced the consumption of resources, because one SVM worked, it checked and checked, the other virtual machines are not loaded, they just watch the general list of verdicts.
Go ahead. The most interesting and the most delicious for us is the use of protection of virtual environments through a light agent. The principle of operation is very similar. There is the same SVM, there is the same antivirus engine, exactly the same as in your traditional antivirus software, but unlike the previous case, where VMware limited our ability to check, here our solution is given complete freedom of action.
Here we provide our solution, our small, patented lightweight agent, which we install inside each virtual machine. He is really very small, does not perform any checks, he is engaged only in monitoring what is happening inside this virtual machine, and then he returns the result of his work back to this virtual machine of protection in the SVM. How do we expand the functionality with this approach, and why is it so tasty, and why is it so interesting? Because the security level here is not lower than in the traditional anti-virus engine, and taking into account the single pool of verdicts and taking into account a number of additional technologies, it turns out to be much higher than in the traditional anti-virus engine. Plus, if before we had to allocate 2 gigabytes of RAM inside each virtual machine for protection (with the traditional approach), for some additional processor core, here we allocate one virtual protection machine and that's it.
When people ask me: “How can I count, convince my director that we really need this?” And everything is simple.
Suppose you come to the conclusion that your data center or data center of your cloud provider is faced with the fact that you can no longer allocate resources, there is a pool of a thousand virtual machines that you deployed, ten physical servers are required for this pool . Everything. Physically, more than ten servers do not fit into the room. If you are told that you will have to cut these resources twice, give twice the same number of servers, find another room, add cooling again, add software again to all these additional 20 servers, then let's calculate it all . And then the cost of licenses will be completely different when using protection with a light agent, it will be quite small, relatively advantageous.
Let's talk now about technology. This is a pressing issue, because using the example of the latest Wannacry epidemic, no one understood how it happened, but all Kaspersky Lab clients were protected. By the way, I have a question for the audience, I just flew in from another country, asked the same question there. Who suffered from wannacry? Raise your hands, please. Somehow? if not yourself, then maybe a relative, mom, dad, grandmother, children? Who was hurt by the Wannacry epidemic? No, no one? There is? A number of customers, yes? Super. Why ask? Not just out of idle curiosity. And now this question: are there in the hall those who suffered and he at the same time established the decision of Kaspersky Lab? Not.
No other country has told me the opposite. Ok, but in fact the world statistics, I will show it at the end, it is really very scary. Look, I will quickly go over the most delicious technologies that answer the question why the protection developed by Kaspersky Lab's experts worked so well. The question is relevant, because everyone is shouting now “NextGen antivirus”, “NextGen firewall”. No NextGen concept. This is a marketing hyip, which all companies have raised, and which is very cool, like surfing, rolling on the wave. All these technologies, which I will talk about now, are partly our competitors have. The oldest of them is 12 years old already. And now this is all collected now in the so-called NextGen antivirus. Just because they decided under a different sauce to submit technology.
The most delicious thing is monitoring system performance. This is what everyone likes to call self-learning networks. When a technology remembers the correct sequence of applications and when it is confronted with the fact that the sequence of actions of the application inside the virtual machine is wrong, it blocks it. This technology, first of all, stopped the crypto activity of Wannacry. She noticed the beginning of a suspicious activity (file changes by the encrypter), noted who made these changes and how, placed the files in the backup storage in a timely manner and stopped the continuation of this action. However, if the administrator for some reason incorrectly configured or turned off this protection technology, then the actions of malware, of course, spread further.
Automatic protection against exploits. About the vulnerability through which Wannacry spread, Microsoft had already known February of this year, but the patch was released only in March-April. In our solutions there is an automatic protection against exploits, namely, exploits and used Wannacry. Partially, this technology is carried out through a network security machine, through a network attack blocker. In defense with a light agent through just the same light agent. We monitor those vulnerabilities that are known to us, monitor application attempts to use non-standard propagation paths. When such attempts are required, alerts will be sent to the administration console, these attempts will be stopped, they will be prohibited until they are physically resolved by the hands of the administrator or information security officer, if required.
Further, white and black lists. This is super technology. We add only what should be launched to the white list. Anything that does not fall into the white list does not start automatically. Very simple, very effective. We now have the technology to protect ATMs, there are technologies to protect the banking systems of the financial sector, there, in general, the same technology is used. Only the operating system and only one application should work there. Anything else that will try to run on these virtual machines in this environment will be prohibited by the machine.
There is a black list - where we are adding specifically the software that should never, under any circumstances, run, everything else is allowed, but this is variability. You can configure application privileges, which software, when, from which virtual machine it is allowed to access a specific resource, with what rights (for example, read only, read and write, etc.).
The next technology is an intrusion prevention system. Here is the combination of the network protection machine (SVM) and the very ordinary firewall that is. It was this technology that stopped the spread of Wannacry in virtual networks. Monitoring of systems stopped the activity of the cryptographer, stopped the spread, the main trump card of Wannacry.
Automatic blocking of exploits stopped the spread and infection of the virtual machine. This is what makes the Wannacry epidemic stop among our customers.
Device control is responsible for the use of external media pilits. Which virtual machines can be accessed using usb devices, with what rights, which devices — all of this is controlled by this technology.
Web traffic is pretty simple too. The technology checks the URLs, what I said, remember how the legitimate facebook-page passes inside our company, everyone misses it, all the firewalls have missed, it’s normal, it’s the most common, real and honest Facebook page, but it’s some link. Here our technology will go through this nested link, see what will happen there, and if there is malicious activity there, it will block the virus that sat on the link and this link that was presented inside this page. You will get your page anyway, but clicking on the link will give you a message that, you know, it is dangerous, we do not recommend switching, or it will be blocked if the administrator decides that it requires blocking, it will be blocked as well.
Control mail traffic. Currently, the spread of viruses always uses people as a target (social engineering, sending spam, sending out some suspicious letters of unknown content). And here I’ll get a little away from the topic, because I am still responsible, including for the direction of work with targeted attacks, with investigations of targeted attacks, everything is always interesting, everything is deeply and cunningly brewed.
Do you know how long a targeted attack lasts on average today? About 300 days. That is, out of these 300 days, 100 days, attackers will gather information on some of your employee, through whom an infection will occur. Days 50, maybe 70, will be very slow, very quiet, very calm (God forbid, somewhere some of the systems will give an allert) infection of the entire ecosystem, without negative destructive activity. Attackers do not need it. After these, on average, 200 days, when organizations realize that everything is infected, the attackers have infiltrated the company, there is a data leakage or compromising data is added, or someone quietly quietly steals a part.
We had a case when we investigated the incident in one of the banks, the hacker team employees were introduced into the process of microtransaction. And with each transaction began to take one nanocent, because he was the ninth decimal place. This is a miserable money, but in the banking accounting system then only eight decimal places were counted. And the system simply rounded this ninth sign, and on this rounding up in three months of work, the hackers earned huge money, they really earned billions. Just because the ninth decimal place was rounded, and the system did not take it into account. No financial analysis reports even saw him. Then, deeply analyzing the code and having caught this hacker campaign, we were able to figure it out, we could understand that it was the ninth sign. And it was a standard propagating attack. In the case of targeted attacks, one of the most difficult and terrible moments is the fact that intruders after their destructive activities sweep traces very well. Hiding in two ways, they really disguise their activity completely, and the second - they often attack those companies that are very frightened to come to someone and say that they have been hacked.Because the impact on their reputation and financial response from all this will be much higher than the consequences of hacking. Therefore, hackers choose victims very correctly. They really own a phenomenal fantasy, a phenomenal approach, and it turns into art.
, , , , , . . , . . . , , . — , , , . — , , .
Now about sore, about Wannacry. This is what everyone saw. Here it appeared on the scoreboard of many airports. I saw it at the airport when I was waiting for a transfer, and it was sadly because I understood that the airport had been hacked and the data (including passenger registration data) was lost, and what if my ticket got there? This is the reality that the world has encountered. Here is such a straight and beautiful, now known to the whole world kartinochka. This is the first crypto worm. For cryptographers self-propagation is not peculiar. Encryption in the standard environment is peculiar to the fact that the user himself initiates the process :, opened an incomprehensible letter, clicked on an unfamiliar link, and the data encryption process started further.

This is the first crypto worm that spread itself, climbed into the system itself, encrypted it itself. He exploited vulnerabilities, he worked on a specific port, and he spread very quickly. The more he encrypted, the more he spread further into the system. This is an avalanche activity. How many attacks have been prevented? I can say that this time we stopped the epidemic of encrypters, so far, this particular world has stopped this one.

74 countries were touched, they tried to spread wherever possible. The attackers did not choose something concrete, it was not a controlled epidemic, it was chaotic, it was completely free. Where has spread, where climbed, there and climbed, who was not protected, those hurt. See how badly Europe hurt. In Russia, it is clear that we have not touched on the outback, there are still not very many computers there, but this is more of a painful than a pleasant information. Nevertheless, a lot of financial centers, a lot of large companies have suffered precisely from this action.

Encrypted files, among them you can find standard jpeg, txt-files, exel, video, music, everything. Almost everything that has value to the user has been encrypted. Encrypted and exhibited such a Wannacry tag, that's why it got its name.

Now, about how to escape from this malware. Patch, patch, patch. This is the first. You know, we have a very interesting trend, I recently reviewed the global analytics of the use of VDI-infrastructures. How often on your home physical computers do you switch to a new operating system? For example, I’ve got a dozen, for example, but it’s worth a year, I haven’t thought about any Redstone yet, everything works for me. Usually the trend is 1-4 years, people understand that their own is outdated, you need to put something new. Here in VDI-infrastructures, in virtual machines, an update to a new operating system on average in the world occurs two to three weeks after the release of a new operating system, often faster on average. Therefore, it was much easier with them, because they were all patched.Therefore, VDI in the first place it is virtualization is not affected. There is a very high tendency to update the operating systems, there is a very high tendency to try, because when something does not work in the operating system on our computer, we have to take it all down, reinstall it, look for new errors in the system. When we talk about a virtual machine, but recreated, deleted, raised from backup, in general, everything is fast, everything is cool, admins are happy, satisfied, everything is fine.all is well.all is well.
Be sure to install some critical security updates. Again, I repeat, the attack was directed specifically at one vulnerability, about which Microsoft had known since at least February, but did not close it. I will not ask why, but did not close. The consequences we see everything. Now quickly released a patch, quickly closed. For myself, I found such an interesting balance. I always have a virtual machine at home, on which I put a new operating system, and I use it there. If after a couple of months I get used to it, then I put this operating system to myself, having migrated all the applications inside this virtual machine from the beginning, and roll this image. Great work. Ask your admins to do the same.
Very simple indeed. A second virtual machine is being created (you can ask the service provider to create a virtual machine with a new operating system) and applications are slowly migrating. Sit, get used, update, move to a new operating system. Will be more protected.
As I said KSN, this is Kaspersky Security Network. All people who use Kaspersky Lab products are asked if they want to participate in the KSN program, Kaspersky Security Network.
What it is?This is a global global community, where records of all incidents are recorded, data is stored in the cloud network. Employees of our company, as well as our automated systems, constantly analyze this data, are always looking for something new, put new masks. But in fact it is 400 million people who every second tell the whole world about new incidents requiring blocking.
And a lot of automatic systems respond to this in our company. For example, our employee was attacked by the Wannacry virus in Brazil, the virus was investigated right there, and Wannacry was stopped there on the spot. Because the virus did not pass the system watcher, a record of virus activity appeared, did not pass the technology of automatic protection against exploits, did not pass the encryption technology, did not pass the monitoring of network activity. All of these links, all of these activities have been marked as dangerous. And these verdicts went to KSN. Any other employee who at that moment was on the Internet in any other part of the world and was connected to the KSN network, automatically received information that if this file came to him, then he was angry, he should be stopped. This stopped the entire Wannacry epidemic.
Next, the network attack blocker, which forbade the use of exploits inside virtual machines, has already worked. Next, the automatic protection against exploits worked, which did not allow intrusion into the virtual machine, monitoring systems, which did not allow encryption and application launch control, which in general did not allow something illegal to start inside the system.
Thank you for your attention.
Answers to the questions:
You talked about this latest virus, what did you know about the vulnerability in February, about the possibility, the bug "Microsoft" in fact, why couldn’t your software close the hole in advance?
Our software is closed. Just one thing when you close it on your own, another thing when it is closed at the operating system level. And our task in cooperation with Microsoft, we, if we find something in their code, we inform them about it. Not everyone uses Kaspersky Lab products, they also want to be protected.
Do you find a vulnerability, and it is immediately closed by your forces, your software? At the level where it actually works?
, , , , system watcher automatic exploit prevention 0-day , , , . , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/331830/
All Articles