Configuring the TheOnionBox web interface to monitor Tor's relay node
The Onion Box is an open source web interface for monitoring a relay node written in python.
He is able to display disk load, memory, network, as well as node statistics, including those received via Onionoo (protocol for monitoring status on the Tor network), and build beautiful graphics.
It looks something like this:
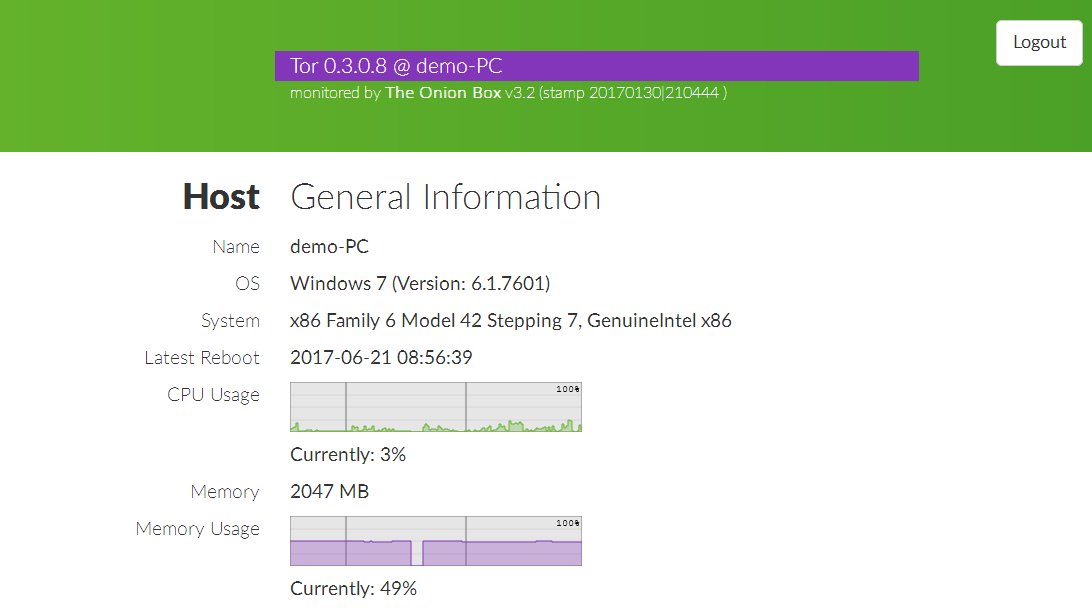
Under the cut description of the settings.
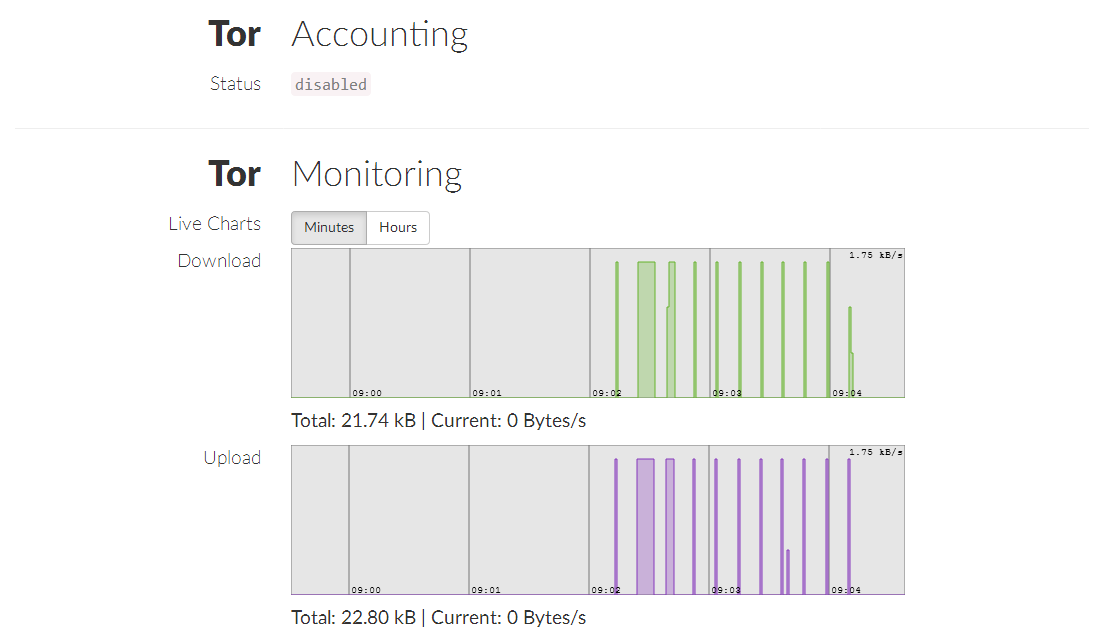
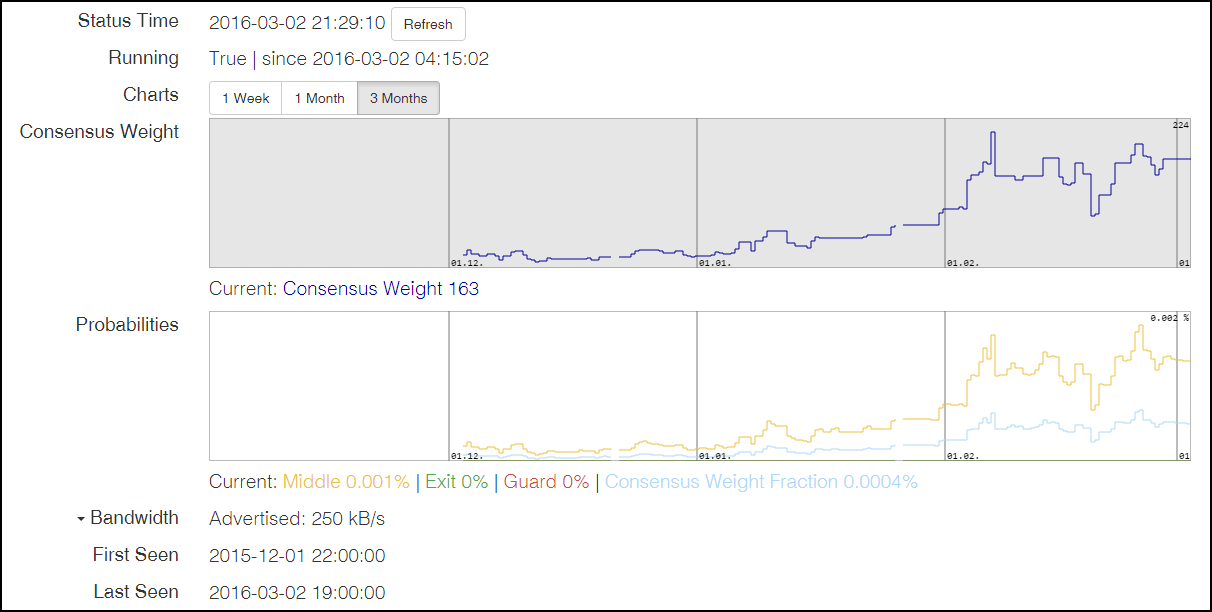
Comparing Tor-node and I2P-node ( i2pd ), in friendliness to the inexperienced user, in my opinion, Tor loses, at least in terms of quick start. I2pd has a minimal interface for monitoring and executing the simplest commands, while Tor has no interface (I know about Arm , but this is a console interface and only under Linux).
In the light of recent events, holding an exit node can be fraught with, but if you want to help the Tor network become faster, better, safer, without risking anything and with a minimum of effort, then a relay node is for you! More information about the setting can be found here . In this article I will assume that the Tor relay-node on your machine is already configured.
Tor setup
All that is needed is to enable control of the node by specifying the control port. It is also better to add a password to this admin panel (if desired, however).
To set a password, we get its hash. Go to the folder with the Tor binary, open cmd and execute:
tor --hash-password SUPER-PASSWORD > hash.txt The hast.txt file should appear in the same folder with something like this:
Jun 21 18:26:33.023 [notice] Tor v0.2.4.24 (git-a8a38e5dd1fbb67a) running on Windows 7 with Libevent 2.0.21-stable and OpenSSL 1.0.1i. Jun 21 18:26:33.025 [notice] Tor can't help you if you use it wrong! Learn how to be safe at https://www.torproject.org/download/download#warning 16:5DC1FEEC60D990AB6081B9319FD29D850CBE07545B94055C1B5490EA80 From this, we need the last line, which is our password hash: 16:5DC1FEEC60D990AB6081B9319FD29D850CBE07545B94055C1B5490EA80 .
Then open the torrc file (it usually lies in /usr/local/etc/torrc or %appData%\Roaming\tor\torrc ) and add the following lines:
ontrolPort 9051 HashedControlPassword 16:5DC1FEEC60D990AB6081B9319FD29D850CBE07545B94055C1B5490EA80 CookieAuthentication 1 And restart the node so that the config is applied.
Install and configure OnionBox
To run OnionBox, you need a python. Any version (works with both 2.7 and 3.x).
Under Linux, everything is trivial, and under Windows, after installation, you need to make a logoff-login (or execute a script ) for the changes to the PATH to apply.
Check that the python is ready, open cmd and write: python -V
The installed version should be displayed.
If it did not work, you need to add to PATH the path where the python is installed, for example, C:\Python3.6 and C:\Python3.6\Scripts .
Download the latest release from github , at the time of writing this article is 3.2.1. We unpack into a folder, for example, C:\Tor\UI .
If you installed another control port (not 9051 ) in the 9051 , open the config ( config\theonionbox.cfg ), find the line tor_control_port = 9051 and write the same port as in the Tor configuration.
After that, you need to install the necessary dependencies for OnionBox.
Open cmd and first of all put pip (package manager for python), if it is not already installed.
- Download https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
- execute:
python get-pip.py - check:
pip -V
Next, we put the necessary modules:
pip install psutil stem bottle apscheduler requests For Python 2.7, you need to additionally install the configparser module.
And we start the service itself:
python theonionbox.py If everything is in order, you can open the admin panel in the browser ( http://127.0.0.1:8080 ) and enjoy.
Tips & Tricks
Also, for convenience, you can demonize this service. Under Windows, in particular, this can be done through NSSM . To do this, go to the folder with the binary nssm, run cmd, execute:
nssm install TorUI "path-to-python\python.exe" "path-to-onionbox\theonionbox.py" We start service and it is ready!
Links
→ Habrastia for setting up a relay node
→ The official man of Tor
→ TheOnionBox on github
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/331358/
All Articles