Technological trends and current SDN solutions for data centers
We continue to publish materials from the “Collaborative Security of Cloud Solutions for Business” forum , which we conducted together with Kaspersky Lab and HUAWEI on May 31 in Moscow. We present the report by Sergey Aksenov from the HUAWEI company “Technological trends and current SDN solutions for the data center”

Colleagues, good afternoon. My name is Sergey Aksenov, I am a representative of Huawei and, accordingly, in Huawei I am responsible for the development of the direction of network solutions.
My topic today is related to data networks, network infrastructure. And the new trend, which was born some time ago, which finally begins to be implemented on the real infrastructure of the customer is, in fact, SDN, a software-defined infrastructure.

In fact, today's event is entirely devoted to cloud technologies and if we even looked at those conferences that were held even two or three years ago, the data network, specifically for clouds, was viewed simply as such an auxiliary element, as a kind of substrate, but in Virtualization platforms, cloud technologies have always been at the forefront. But today, SDN solutions are inherently part of the cloud. SDN solutions have become absolutely adequate in terms of their functionality, their cost and, most importantly, their capabilities. And today, those traditional solutions that have been applied over the past five to six years, they already look rudimentary, that is, they are really lagging behind. And SDN solutions are where the industry is heading, where the industry is heading. But I, too, will not talk for a long time about all the benefits of the cloud, and so on, but if you look at IDC reports, by 2020 about 50 percent of the corporate infrastructure will move completely to the cloud. Today, communicating with customers, with customers of the Enterprise market, we certainly see that the basic model is still a bimodal approach. When, accordingly, the customer already had some kind of his own infrastructure, considerable funds were invested in it and it was easy to refuse to use this infrastructure, it was wrong to transfer everything to cloud rails and, probably, it was difficult. Therefore, the bimodal approach is that those applications, those services that actually existed on the traditional infrastructure, their own, they continue to work, but some new applications that the company plans to launch or launch right now, of course already more correctly implemented using the cloud. At the same time, the data transmission network in the form in which it was, these are the traditional technologies, switching and routing, de facto, they have not changed for the last ten years, that is, they were based on some common things, of course there were minor improvements. changes and so on. But with the advent of SDN, things start to change dramatically.
')

Let's first talk about traditional networks, what they were actually bad. The traditional network implied a static and fragmented approach to network infrastructure management. That is, for example, we have a data center that consists of ten to twenty racks, each rack has a pair of top-of-rack switches for connecting servers of computing resources, and the traditional approach implied that, first, each of these devices requires special attention, requires a static configuration. At the same time, from the point of view of some kind of centralization, it was either absent, or there was just some kind of monitoring and management system that allowed assessing the status of infrastructure work, but did not give any flexibility from the point of view of centralized unified management. Again, traditional infrastructure does not comply with agile principles. The principle of agile, when we actually plan to launch some new service, some new service, respectively, we are working on it, developing it, in the course of development we see that some more changes are needed, we make them at the development stage. After that, we launch the service into the product, that is, we are testing it on our customers, and when we start it in the product, we understand that some other changes are required. That is, there is constant adaptability, the constant change of our infrastructure. Accordingly, the traditional solution in principle did not allow this to be done from the network point of view, because, for example, a trivial situation, you want to test the new 1C release in order for this to happen, you need to deploy some kind of virtual machine with certain properties, with a specific operating system. From the point of view of computing resources, everything is simple and clear, that is, we simply create this virtual machine, allocate it with the necessary properties, and everything is automated, we start working in 5-10 minutes. But from the point of view of the data transmission network, every time it is necessary to involve a network administrator, a network engineer who will manually make some specific configurations on the network equipment, on each specific port, and provide virtual machines with some configurations. Again, today, talking about the cloud infrastructure, many customers are interested in the fact that it was either a commercial cloud or its own private cloud. But at the same time it must be geographically separated, that is, this solution is active - active, in which software or hardware failures in one of the data centers, they in no way affect the operation of applications and services. Accordingly, virtual machines that fly from one data center to another data center, they also need attention. That is, if we are talking about a traditional data transfer network, then, of course, it will not allow a virtual machine that moves from one physical data center to another data center, first, to keep its addressing, to keep those security policy rules that were on it assigned with these permanent movements.

Another problem that we see with customers, there is always some kind of maintenance service that supports IT infrastructure. At the same time, this operation service is always divided into two camps. The first camp is the network engineers who are fully responsible for the transfer of data and the second camp is the people who are responsible for the so-called IT resources, the computing infrastructure, the data storage system. Between them there is such a hard watershed, respectively, we get independent control of components and in case of any problems, in case of any failures. Troubling, identification of the root of the problem, its elimination takes a considerable amount of time and at the same time it is sometimes very difficult to understand on which side the problem arose and who should fix it. Here we come to a situation where the data network is really a rudiment, it is a substrate, which, nevertheless, does not allow us to quickly introduce new services on the fly, does not allow us to move to a full-fledged agile approach.
If you look at the solutions and the problems that exist in the SDN market today, then absolutely all network vendors are large, Huawei, our competitors, offer a ready-made SDN concept. That is, it is a vertically built infrastructure that allows you to make and centralized management, allows you to do automation, allows you to make tight integration with computing resources. But if you look at the end customer, then the end customer is very unhappy with the current situation for the simple reason that each vendor offers his own proprietary solution, that is, buy my switches, buy my SDN controller, it can work only in this configuration, it can Only with such a hypervisor. In this case, from the point of view of an ICT customer, the infrastructure, IT infrastructure must be diversified, that is, built on several vendors, and the controller or network equipment, servers, storage systems may be from different manufacturers. That is, this is the model that goes almost every customer today. Therefore, this problem really exists today and the company Huawei, nevertheless, if you look at the strategy, trying to release the SDN solution more open.
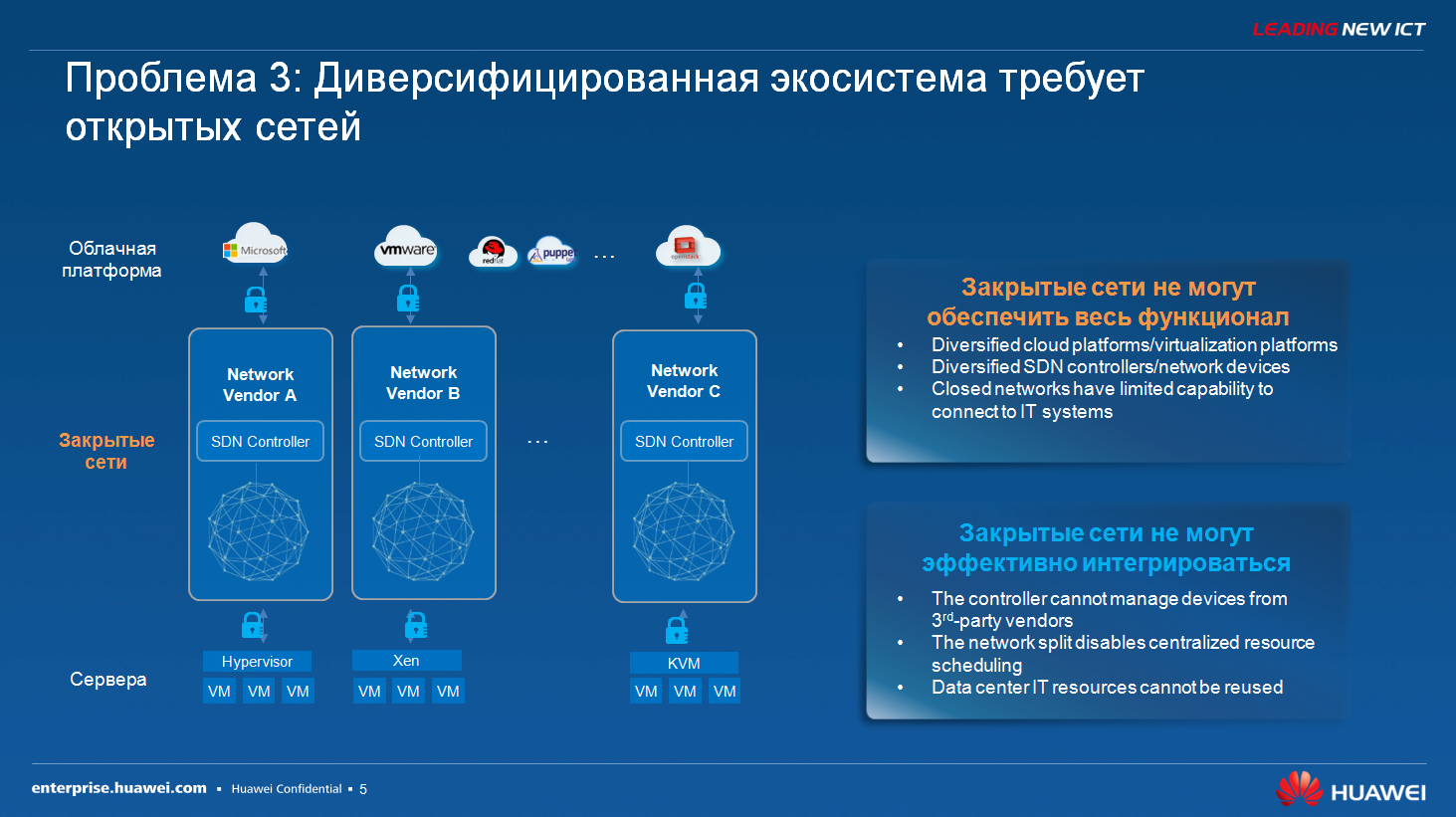
I’ll continue to show here, we have an ecosystem of partners, these are the largest developers of virtualization platforms and network equipment, respectively, we follow the ideology of an open infrastructure, that is, open software interfaces that do not tie the customer to using only our equipment using the solution SDN.
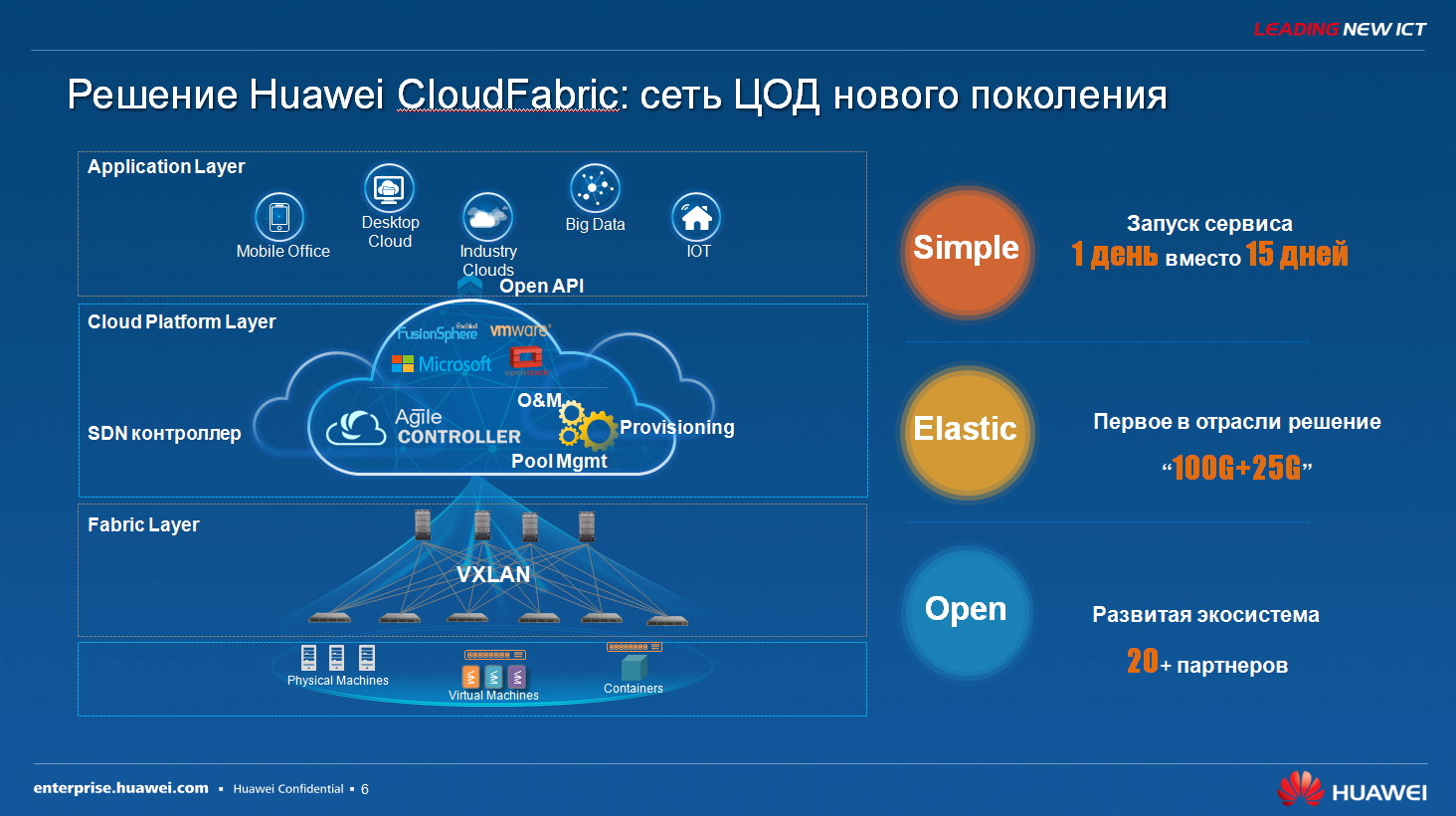
The solution Huawei offers is called Huawei Cloud Fabric, a cloud factory or a programmable factory. From the point of view of architecture, the picture shows, in principle, everything is quite simple, understandable and, probably, logical. On the one hand, we have data transmission networks - these are some physical devices, some ports to which we connect hardware servers, we still have these our servers, while on top we have an application layer, there is a cloud platform. Here a key element appears, which is called the SDN controller, in terms of Huawei it is an agile controller. This is the orchestrator that has, on the one hand, southern interfaces for communicating with virtualization platforms, and on the other hand, it has northern interfaces for communicating with virtualization platforms and southern for communicating with the network layer, that is, with ordinary network switches. This is the traditional openflow protocol, which is used to program network devices. And here are the three main whales, the three main directions of this solution are the simple - simple, elastic - flexible, and open - open infrastructure. What is the plus.
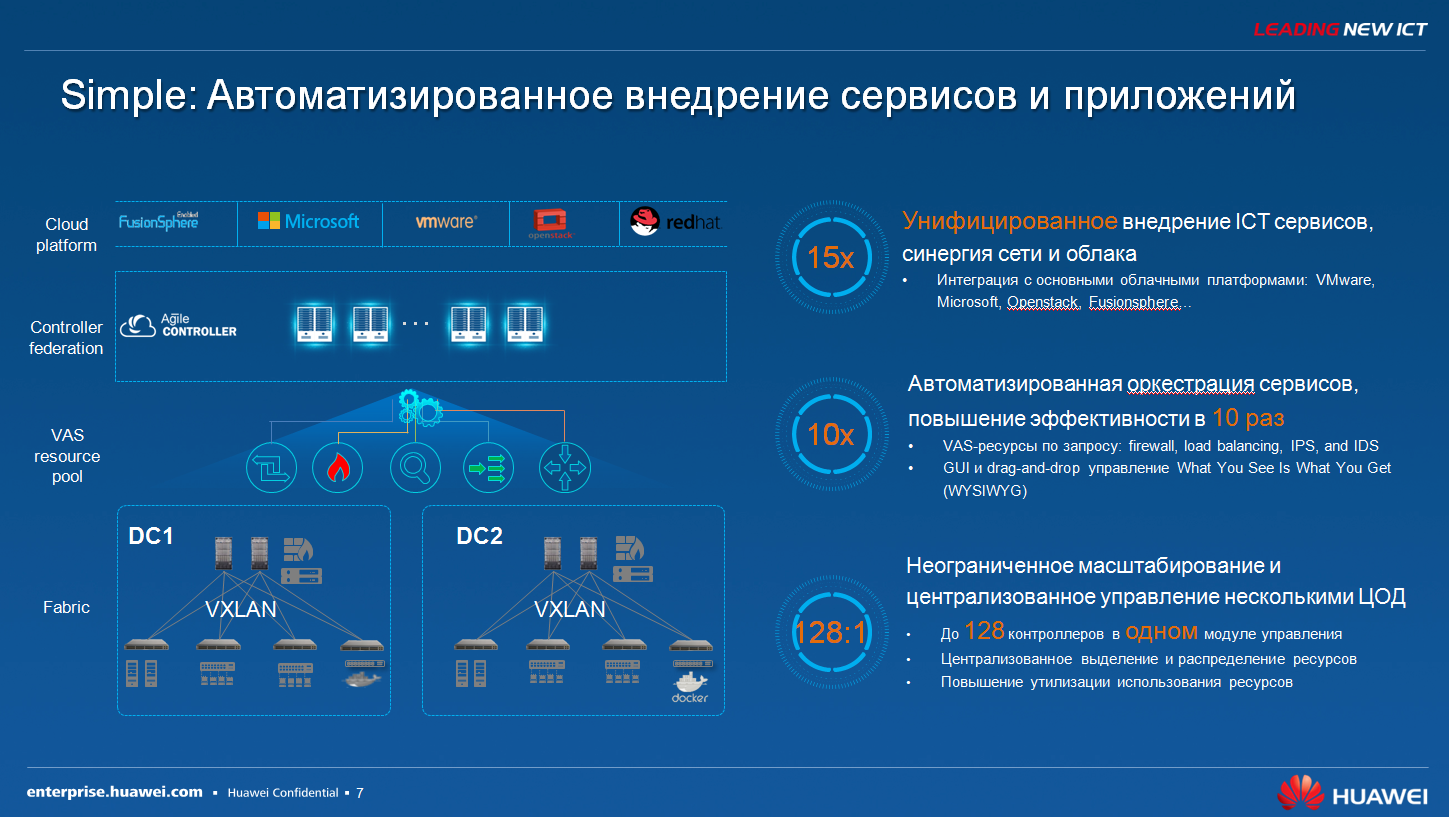
The main advantage is that when we talked about this simplest scenario, we need to test a new release of 1C, we cannot immediately launch it into production, we need to deploy some kind of test environment, we create a virtual machine, we endow it with then the properties using the graphical interface, which is in the agile controller and then all the configurations that need to happen from the point of view of the network, they are completely automated. That is, we do not need to go to a particular switch of some kind for this virtual machine, to set up rules for security policy and quality of service policy there. We create, relatively speaking, in the graphical interface, the icon for this virtual machine, we endow it with certain properties, and these properties are automatically automatically installed.
The key theme of today's event is safety. And here they talked about security in terms of data compromise, external attacks and other threats. But another threat that lurks is the threat of lack of professionalism of the personnel involved in the operation. That is, due to some wrong actions, from the point of view of a data transmission network or virtualization, a business can also suffer, that is, we will shut down some kind of virtual machine that is necessary to support business processes.

SDN is also good because, first, we have the possibility of centralized unified management, we have a full-fledged dashboard for analytics, for a full understanding of how our infrastructure works. And if at some point we made some kind of mistake, some kind of problem in terms of configuration, then all this can be easily and quickly eliminated. In this case, due to the fact that we have automated configurations, then there is manual labor, that is, some kind of really work from the command line, it is minimized, that is, the possibility of the occurrence of an incorrect configuration of this error is reduced to a minimum.
Another plus of modern network solutions, be it cloud solutions, be it just a corporate infrastructure, is that there are completely new network processors, which Huawei calls ENP - Ethernet Processor. These are fully programmable solutions, which, firstly, provide a significantly larger increase in performance relative to traditional asiki, on the other hand they are fully programmable. That is, to date, the SDN, unfortunately, has not yet been standardized to the end, that is, there have been some RFCs, some IE standards have appeared, according to which vendors and manufacturers are trying to produce solutions, but, nevertheless, some final version of standardization has not yet been achieved. appeared. Therefore, these ENP processors are also good because, today buying equipment with such processors, you as an end customer receive investment protection. That is, it is enough just to change the firmware of this network processor, and it will be able on the fly to support new types of protocols, new types of technologies that will appear. Traditional ASICs, traditional network processors did not allow this in principle.
A big plus of SDN is that when we talk about centralized and unified management, we, as an additional benefit, as an additional plus, have the ability to collect analytics and forecasting. That is, in one way or another, we have a certain central point, a certain intellect, which controls the traffic transmission routes and understands what is happening in each segment of our infrastructure. Thanks to this, we can accumulate statistics on what happens to us with the network infrastructure, and when at some point an external attack occurs or some non-standard pattern traffic appears in the case of DDoS or some internal exploit, the SDN controller about it also notify. He has a central security module as one of the modules, this is the Big Data module, which actually stores the login for all traffic passing inside the network factory, that is, each switchboard acts as some kind of agent that collects this information. And then we can control at the network level what happens in the end from a security point of view.
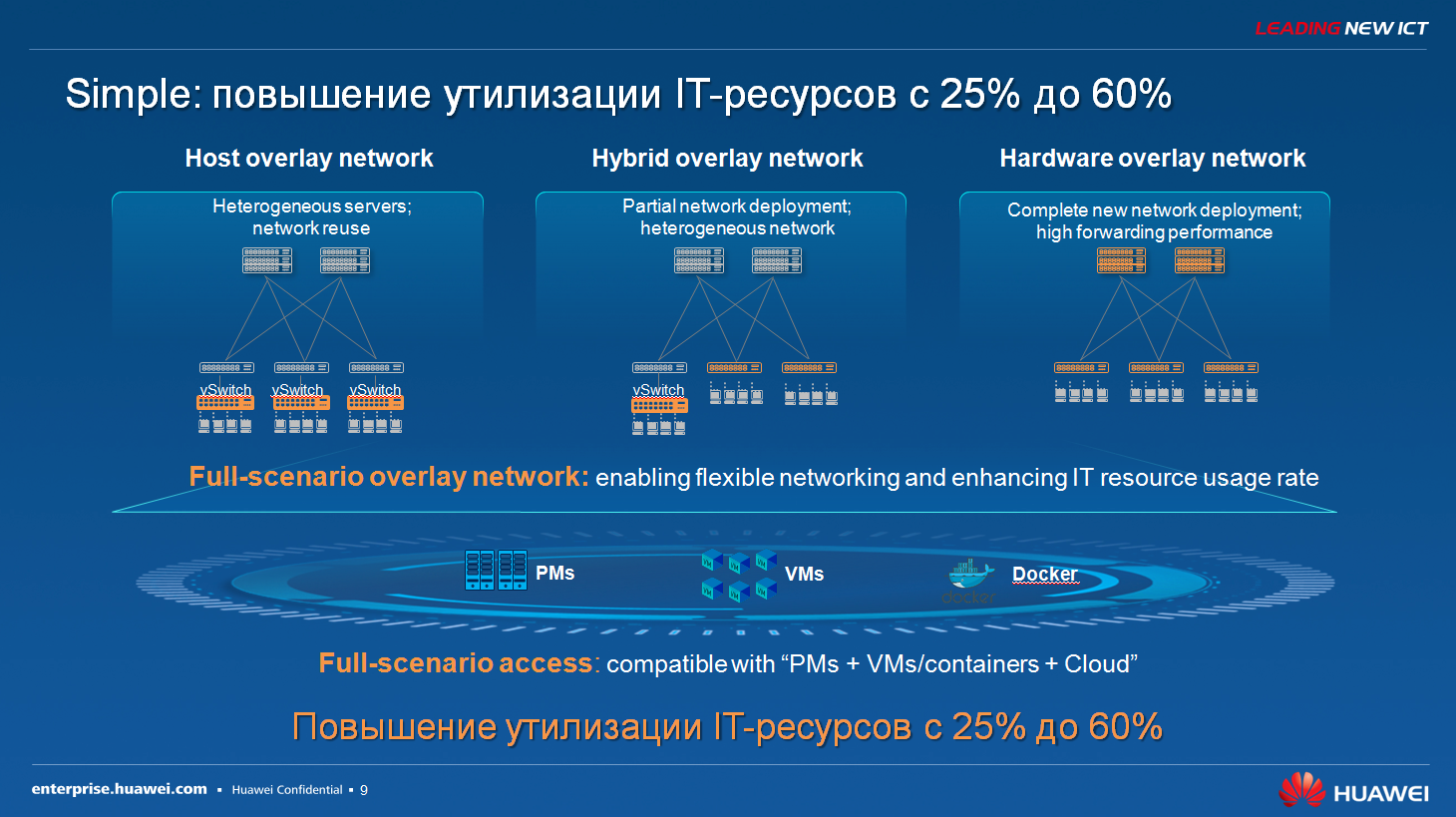
If you look at existing SDN solutions, they can be divided, probably, into three types of architecture, on which SDN is built today. The first option is the one that is most widely, probably, used today in the infrastructure of many customers. Some time ago, for example, the data center was built, that is, substantial funds were invested in the network infrastructure, in the computing infrastructure, and now such a customer comes to understand that the network is indeed the brake that prevents it from managing the infrastructure more flexibly and new applications and services. Accordingly, he understands that he needs SDN, he needs programmability, he needs centralized management, but he does not want to change the network, that is, funds have been invested in it, the network equipment is up and running, and why change it. Here, the only way out is to build an overlay network, that is, on top of that traditional data network, which is, an overlay data network is created and this superimposed network is created using software. That is, either with the help of virtual candles, which can be created in the hypervisor, or with the help of simply superimposed software that runs from inside the virtual machine. That is, we are on top of the traditional network that simply provides connectivity, we create a logical network that provides us with automatic configurations and automatic provisioning.
The second option, which is offered, is an option that Huawei and other network vendors actually offer. This solution consists in the fact that we also install hardware switches, which now support full programmability, that is, it is not necessary, as I said, to configure each piece of hardware separately. We put just a new generation of programmable switches that work with a centralized controller.
And the third option is such a hybrid version. We put and new switches that can support this programmability, while in existing data centers we put virtual switches that spin on the server in the same place, conditionally speaking, and thus we get such a complete solution.

Another big plus of SDN is that now we can more efficiently utilize data transfer channels.
Speaking about these active-active solutions, disaster recovery solutions, when all of our computing resources are not within the same data center, but we make such geographical separation, here the cost of links between data centers is also important, these links are very, very expensive. When we talked about traditional solutions, there it was difficult for us to evaluate, to get some kind of comprehensive assessment about how data channels are used, how loaded they are. When we come to the SDN model, we somehow have a controller that sees, that is, receives information on the workload of data transmission channels. This allows us to load and utilize them more effectively, allows us to do load balancing, that is, load balancing. And thus we can distribute it more evenly, the load on communication channels, and in some cases we understand that we can even give up such wide channels that we have today, and simply use more efficiently those channels that we previously had .
From the point of view of hardware resources, Huawei offers here a whole line of switches, about 120 modifications of switches today.

This line is called CloudEngine. Here the main trend that is observed is the trend of transition to 25-gigabit connections, that is, if you look at absolutely all manufacturers of server equipment on the roadmap, then they all say that 10 gigabits is not enough, 40 gigabits is very, very expensive, therefore 25 gigabit is the golden mean. In fact, it is. If you look at the cost of a 25-gigabit port, then today it is fully on par with the cost of a 10-gigabit interface. Therefore, today, a modern data center is access, that is, connecting servers of 25 gigabits and actually connecting top-of-rack switches to the network core of 100 gigabits, that is, 25 plus 100. This is the formula by which all modern data centers are built .
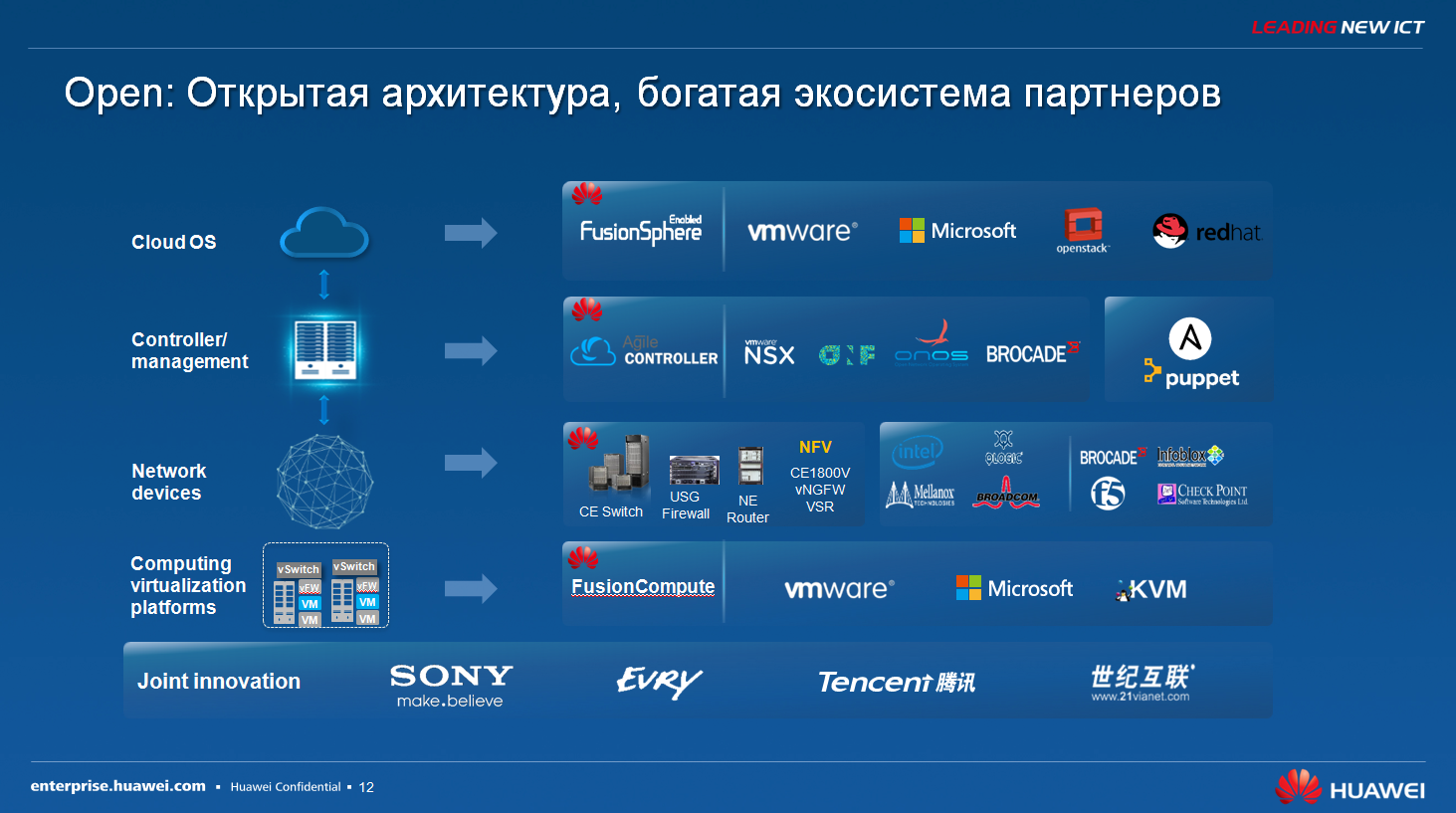
Speaking of the ecosystem. As I said, for Huawei, one of the key areas of the SDN strategy is to build an open infrastructure. When we offer a non-proprietary solution and tell the customer, buy only our equipment, throw away everything that you have, but in fact it’s really an open infrastructure.
Here here are our partners in different areas. If we talk about cloud platforms, virtualization platforms, here we are certified by vmware and microsoft, we are working perfectly with openstack, and there is our own hypervisor, the fusion sphere, with which our SDN controller also interacts perfectly.

There are some other open source solutions, for example, Puppet, which allows you to get complete freedom in terms of programmability, but it requires a higher qualification of your network engineers, in fact, they should be for the most part even programmers now. This decision is for quite a guru. For the average customer, the recommended solution is to use our controller with a clear graphical interface, in which you use icons to control your entire network infrastructure using templates. That is, you don’t even have to go into the console, to the command line of some network equipment, and set something up there.

Well, speaking about the prospects of SDN, today, as I said at the beginning, SDN has already become a really working solution from such a long-playing topic, which began almost 7-8 years ago. If you look at the forecasts that give IDC, then by 2020 about 95 percent of large commercial data centers will be built using SDN technology. Huawei feels very comfortable in this market, that is, we are growing year to year by almost 70 percent in the supply of network equipment for data centers. And there are shown examples in different countries, what could we do.
A little bit about Russia if we talk, here our largest implementation of SDN is Sberbank, in fact it is one of the data centers, which is used directly by developers. And there they just need on the fly to create some new virtual infrastructure as quickly as possible and test their new developments. The second SDN project that we have, which is implemented, is NSPK, the national payment card system. If you know, these are MIR payment cards, which are now distributed to all state employees. Actually, these are two data centers operating in active-active mode, that is, virtual machines can move seamlessly, seamlessly, between these data centers. Here, the entire infrastructure is also built on Huawei equipment using our CloudEngine lines.
Colleagues, on this I complete my excursion on the program-defined networks “What is happening today?” I finish.
Data Center MIR cards they are in our territory?
Sure, of course. This is completely our infrastructure. The Central Bank oversees this topic, that is, everything is with us, yes, in the Moscow region.
But in principle, virtualization services, cloud solutions are in China?
No, look, those solutions that Huawei offers, controllers, it’s all sold as a finished product, and it’s all put in the local data center. Huawei itself does not provide any cloud resources, we work with our partner RUVDS, in fact, all the services from a partner.
Is it possible to connect an SDN, agile controller, controller to something that will enrich the data of agents that supply switches?
Good question really. Today, agile controller, SDN is on the path of development, when it is centralized to control, firstly, equipment, on the other hand, it is automation, provisioning configurations and tighter integration with computing resources. The next step is really Big Data, this is when we can integrate with various external sources, for example, attacks, antiviruses and other things, and from there control everything. Today we are not in the framework of the agile controller, but we have our separate firewalls, Next Generation devices that integrate with the agile controller. This allows the bundle to provide such a hardware and software solution.
That is, the SDN controller pushes some rules to these firewalls, or can it receive data from there?
He is pushing rules there for now only. That is, for example, you want to say that virtual machine A should interact with virtual machine B, passing the DPI, a deep analysis from the point of view, what is behind the traffic is spinning, and the agile controller just spreads this policy to network security devices, and there is this analyst.
Thanks for attention!

Colleagues, good afternoon. My name is Sergey Aksenov, I am a representative of Huawei and, accordingly, in Huawei I am responsible for the development of the direction of network solutions.
My topic today is related to data networks, network infrastructure. And the new trend, which was born some time ago, which finally begins to be implemented on the real infrastructure of the customer is, in fact, SDN, a software-defined infrastructure.

In fact, today's event is entirely devoted to cloud technologies and if we even looked at those conferences that were held even two or three years ago, the data network, specifically for clouds, was viewed simply as such an auxiliary element, as a kind of substrate, but in Virtualization platforms, cloud technologies have always been at the forefront. But today, SDN solutions are inherently part of the cloud. SDN solutions have become absolutely adequate in terms of their functionality, their cost and, most importantly, their capabilities. And today, those traditional solutions that have been applied over the past five to six years, they already look rudimentary, that is, they are really lagging behind. And SDN solutions are where the industry is heading, where the industry is heading. But I, too, will not talk for a long time about all the benefits of the cloud, and so on, but if you look at IDC reports, by 2020 about 50 percent of the corporate infrastructure will move completely to the cloud. Today, communicating with customers, with customers of the Enterprise market, we certainly see that the basic model is still a bimodal approach. When, accordingly, the customer already had some kind of his own infrastructure, considerable funds were invested in it and it was easy to refuse to use this infrastructure, it was wrong to transfer everything to cloud rails and, probably, it was difficult. Therefore, the bimodal approach is that those applications, those services that actually existed on the traditional infrastructure, their own, they continue to work, but some new applications that the company plans to launch or launch right now, of course already more correctly implemented using the cloud. At the same time, the data transmission network in the form in which it was, these are the traditional technologies, switching and routing, de facto, they have not changed for the last ten years, that is, they were based on some common things, of course there were minor improvements. changes and so on. But with the advent of SDN, things start to change dramatically.
')

Let's first talk about traditional networks, what they were actually bad. The traditional network implied a static and fragmented approach to network infrastructure management. That is, for example, we have a data center that consists of ten to twenty racks, each rack has a pair of top-of-rack switches for connecting servers of computing resources, and the traditional approach implied that, first, each of these devices requires special attention, requires a static configuration. At the same time, from the point of view of some kind of centralization, it was either absent, or there was just some kind of monitoring and management system that allowed assessing the status of infrastructure work, but did not give any flexibility from the point of view of centralized unified management. Again, traditional infrastructure does not comply with agile principles. The principle of agile, when we actually plan to launch some new service, some new service, respectively, we are working on it, developing it, in the course of development we see that some more changes are needed, we make them at the development stage. After that, we launch the service into the product, that is, we are testing it on our customers, and when we start it in the product, we understand that some other changes are required. That is, there is constant adaptability, the constant change of our infrastructure. Accordingly, the traditional solution in principle did not allow this to be done from the network point of view, because, for example, a trivial situation, you want to test the new 1C release in order for this to happen, you need to deploy some kind of virtual machine with certain properties, with a specific operating system. From the point of view of computing resources, everything is simple and clear, that is, we simply create this virtual machine, allocate it with the necessary properties, and everything is automated, we start working in 5-10 minutes. But from the point of view of the data transmission network, every time it is necessary to involve a network administrator, a network engineer who will manually make some specific configurations on the network equipment, on each specific port, and provide virtual machines with some configurations. Again, today, talking about the cloud infrastructure, many customers are interested in the fact that it was either a commercial cloud or its own private cloud. But at the same time it must be geographically separated, that is, this solution is active - active, in which software or hardware failures in one of the data centers, they in no way affect the operation of applications and services. Accordingly, virtual machines that fly from one data center to another data center, they also need attention. That is, if we are talking about a traditional data transfer network, then, of course, it will not allow a virtual machine that moves from one physical data center to another data center, first, to keep its addressing, to keep those security policy rules that were on it assigned with these permanent movements.

Another problem that we see with customers, there is always some kind of maintenance service that supports IT infrastructure. At the same time, this operation service is always divided into two camps. The first camp is the network engineers who are fully responsible for the transfer of data and the second camp is the people who are responsible for the so-called IT resources, the computing infrastructure, the data storage system. Between them there is such a hard watershed, respectively, we get independent control of components and in case of any problems, in case of any failures. Troubling, identification of the root of the problem, its elimination takes a considerable amount of time and at the same time it is sometimes very difficult to understand on which side the problem arose and who should fix it. Here we come to a situation where the data network is really a rudiment, it is a substrate, which, nevertheless, does not allow us to quickly introduce new services on the fly, does not allow us to move to a full-fledged agile approach.
If you look at the solutions and the problems that exist in the SDN market today, then absolutely all network vendors are large, Huawei, our competitors, offer a ready-made SDN concept. That is, it is a vertically built infrastructure that allows you to make and centralized management, allows you to do automation, allows you to make tight integration with computing resources. But if you look at the end customer, then the end customer is very unhappy with the current situation for the simple reason that each vendor offers his own proprietary solution, that is, buy my switches, buy my SDN controller, it can work only in this configuration, it can Only with such a hypervisor. In this case, from the point of view of an ICT customer, the infrastructure, IT infrastructure must be diversified, that is, built on several vendors, and the controller or network equipment, servers, storage systems may be from different manufacturers. That is, this is the model that goes almost every customer today. Therefore, this problem really exists today and the company Huawei, nevertheless, if you look at the strategy, trying to release the SDN solution more open.

I’ll continue to show here, we have an ecosystem of partners, these are the largest developers of virtualization platforms and network equipment, respectively, we follow the ideology of an open infrastructure, that is, open software interfaces that do not tie the customer to using only our equipment using the solution SDN.

The solution Huawei offers is called Huawei Cloud Fabric, a cloud factory or a programmable factory. From the point of view of architecture, the picture shows, in principle, everything is quite simple, understandable and, probably, logical. On the one hand, we have data transmission networks - these are some physical devices, some ports to which we connect hardware servers, we still have these our servers, while on top we have an application layer, there is a cloud platform. Here a key element appears, which is called the SDN controller, in terms of Huawei it is an agile controller. This is the orchestrator that has, on the one hand, southern interfaces for communicating with virtualization platforms, and on the other hand, it has northern interfaces for communicating with virtualization platforms and southern for communicating with the network layer, that is, with ordinary network switches. This is the traditional openflow protocol, which is used to program network devices. And here are the three main whales, the three main directions of this solution are the simple - simple, elastic - flexible, and open - open infrastructure. What is the plus.

The main advantage is that when we talked about this simplest scenario, we need to test a new release of 1C, we cannot immediately launch it into production, we need to deploy some kind of test environment, we create a virtual machine, we endow it with then the properties using the graphical interface, which is in the agile controller and then all the configurations that need to happen from the point of view of the network, they are completely automated. That is, we do not need to go to a particular switch of some kind for this virtual machine, to set up rules for security policy and quality of service policy there. We create, relatively speaking, in the graphical interface, the icon for this virtual machine, we endow it with certain properties, and these properties are automatically automatically installed.
The key theme of today's event is safety. And here they talked about security in terms of data compromise, external attacks and other threats. But another threat that lurks is the threat of lack of professionalism of the personnel involved in the operation. That is, due to some wrong actions, from the point of view of a data transmission network or virtualization, a business can also suffer, that is, we will shut down some kind of virtual machine that is necessary to support business processes.

SDN is also good because, first, we have the possibility of centralized unified management, we have a full-fledged dashboard for analytics, for a full understanding of how our infrastructure works. And if at some point we made some kind of mistake, some kind of problem in terms of configuration, then all this can be easily and quickly eliminated. In this case, due to the fact that we have automated configurations, then there is manual labor, that is, some kind of really work from the command line, it is minimized, that is, the possibility of the occurrence of an incorrect configuration of this error is reduced to a minimum.
Another plus of modern network solutions, be it cloud solutions, be it just a corporate infrastructure, is that there are completely new network processors, which Huawei calls ENP - Ethernet Processor. These are fully programmable solutions, which, firstly, provide a significantly larger increase in performance relative to traditional asiki, on the other hand they are fully programmable. That is, to date, the SDN, unfortunately, has not yet been standardized to the end, that is, there have been some RFCs, some IE standards have appeared, according to which vendors and manufacturers are trying to produce solutions, but, nevertheless, some final version of standardization has not yet been achieved. appeared. Therefore, these ENP processors are also good because, today buying equipment with such processors, you as an end customer receive investment protection. That is, it is enough just to change the firmware of this network processor, and it will be able on the fly to support new types of protocols, new types of technologies that will appear. Traditional ASICs, traditional network processors did not allow this in principle.
A big plus of SDN is that when we talk about centralized and unified management, we, as an additional benefit, as an additional plus, have the ability to collect analytics and forecasting. That is, in one way or another, we have a certain central point, a certain intellect, which controls the traffic transmission routes and understands what is happening in each segment of our infrastructure. Thanks to this, we can accumulate statistics on what happens to us with the network infrastructure, and when at some point an external attack occurs or some non-standard pattern traffic appears in the case of DDoS or some internal exploit, the SDN controller about it also notify. He has a central security module as one of the modules, this is the Big Data module, which actually stores the login for all traffic passing inside the network factory, that is, each switchboard acts as some kind of agent that collects this information. And then we can control at the network level what happens in the end from a security point of view.

If you look at existing SDN solutions, they can be divided, probably, into three types of architecture, on which SDN is built today. The first option is the one that is most widely, probably, used today in the infrastructure of many customers. Some time ago, for example, the data center was built, that is, substantial funds were invested in the network infrastructure, in the computing infrastructure, and now such a customer comes to understand that the network is indeed the brake that prevents it from managing the infrastructure more flexibly and new applications and services. Accordingly, he understands that he needs SDN, he needs programmability, he needs centralized management, but he does not want to change the network, that is, funds have been invested in it, the network equipment is up and running, and why change it. Here, the only way out is to build an overlay network, that is, on top of that traditional data network, which is, an overlay data network is created and this superimposed network is created using software. That is, either with the help of virtual candles, which can be created in the hypervisor, or with the help of simply superimposed software that runs from inside the virtual machine. That is, we are on top of the traditional network that simply provides connectivity, we create a logical network that provides us with automatic configurations and automatic provisioning.
The second option, which is offered, is an option that Huawei and other network vendors actually offer. This solution consists in the fact that we also install hardware switches, which now support full programmability, that is, it is not necessary, as I said, to configure each piece of hardware separately. We put just a new generation of programmable switches that work with a centralized controller.
And the third option is such a hybrid version. We put and new switches that can support this programmability, while in existing data centers we put virtual switches that spin on the server in the same place, conditionally speaking, and thus we get such a complete solution.

Another big plus of SDN is that now we can more efficiently utilize data transfer channels.
Speaking about these active-active solutions, disaster recovery solutions, when all of our computing resources are not within the same data center, but we make such geographical separation, here the cost of links between data centers is also important, these links are very, very expensive. When we talked about traditional solutions, there it was difficult for us to evaluate, to get some kind of comprehensive assessment about how data channels are used, how loaded they are. When we come to the SDN model, we somehow have a controller that sees, that is, receives information on the workload of data transmission channels. This allows us to load and utilize them more effectively, allows us to do load balancing, that is, load balancing. And thus we can distribute it more evenly, the load on communication channels, and in some cases we understand that we can even give up such wide channels that we have today, and simply use more efficiently those channels that we previously had .
From the point of view of hardware resources, Huawei offers here a whole line of switches, about 120 modifications of switches today.

This line is called CloudEngine. Here the main trend that is observed is the trend of transition to 25-gigabit connections, that is, if you look at absolutely all manufacturers of server equipment on the roadmap, then they all say that 10 gigabits is not enough, 40 gigabits is very, very expensive, therefore 25 gigabit is the golden mean. In fact, it is. If you look at the cost of a 25-gigabit port, then today it is fully on par with the cost of a 10-gigabit interface. Therefore, today, a modern data center is access, that is, connecting servers of 25 gigabits and actually connecting top-of-rack switches to the network core of 100 gigabits, that is, 25 plus 100. This is the formula by which all modern data centers are built .

Speaking of the ecosystem. As I said, for Huawei, one of the key areas of the SDN strategy is to build an open infrastructure. When we offer a non-proprietary solution and tell the customer, buy only our equipment, throw away everything that you have, but in fact it’s really an open infrastructure.
Here here are our partners in different areas. If we talk about cloud platforms, virtualization platforms, here we are certified by vmware and microsoft, we are working perfectly with openstack, and there is our own hypervisor, the fusion sphere, with which our SDN controller also interacts perfectly.

There are some other open source solutions, for example, Puppet, which allows you to get complete freedom in terms of programmability, but it requires a higher qualification of your network engineers, in fact, they should be for the most part even programmers now. This decision is for quite a guru. For the average customer, the recommended solution is to use our controller with a clear graphical interface, in which you use icons to control your entire network infrastructure using templates. That is, you don’t even have to go into the console, to the command line of some network equipment, and set something up there.

Well, speaking about the prospects of SDN, today, as I said at the beginning, SDN has already become a really working solution from such a long-playing topic, which began almost 7-8 years ago. If you look at the forecasts that give IDC, then by 2020 about 95 percent of large commercial data centers will be built using SDN technology. Huawei feels very comfortable in this market, that is, we are growing year to year by almost 70 percent in the supply of network equipment for data centers. And there are shown examples in different countries, what could we do.
A little bit about Russia if we talk, here our largest implementation of SDN is Sberbank, in fact it is one of the data centers, which is used directly by developers. And there they just need on the fly to create some new virtual infrastructure as quickly as possible and test their new developments. The second SDN project that we have, which is implemented, is NSPK, the national payment card system. If you know, these are MIR payment cards, which are now distributed to all state employees. Actually, these are two data centers operating in active-active mode, that is, virtual machines can move seamlessly, seamlessly, between these data centers. Here, the entire infrastructure is also built on Huawei equipment using our CloudEngine lines.
Colleagues, on this I complete my excursion on the program-defined networks “What is happening today?” I finish.
ANSWERS ON QUESTIONS
Data Center MIR cards they are in our territory?
Sure, of course. This is completely our infrastructure. The Central Bank oversees this topic, that is, everything is with us, yes, in the Moscow region.
But in principle, virtualization services, cloud solutions are in China?
No, look, those solutions that Huawei offers, controllers, it’s all sold as a finished product, and it’s all put in the local data center. Huawei itself does not provide any cloud resources, we work with our partner RUVDS, in fact, all the services from a partner.
Is it possible to connect an SDN, agile controller, controller to something that will enrich the data of agents that supply switches?
Good question really. Today, agile controller, SDN is on the path of development, when it is centralized to control, firstly, equipment, on the other hand, it is automation, provisioning configurations and tighter integration with computing resources. The next step is really Big Data, this is when we can integrate with various external sources, for example, attacks, antiviruses and other things, and from there control everything. Today we are not in the framework of the agile controller, but we have our separate firewalls, Next Generation devices that integrate with the agile controller. This allows the bundle to provide such a hardware and software solution.
That is, the SDN controller pushes some rules to these firewalls, or can it receive data from there?
He is pushing rules there for now only. That is, for example, you want to say that virtual machine A should interact with virtual machine B, passing the DPI, a deep analysis from the point of view, what is behind the traffic is spinning, and the agile controller just spreads this policy to network security devices, and there is this analyst.
Thanks for attention!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/331334/
All Articles