GitLab 9.2 released: Multiple task executors, pipelines on schedule, localization, disaster recovery alpha

GitLab is designed in such a way that each project participant can contribute, regardless of the size of the team and the location of its members.
Often, in the process of product development, several people work on one task: for example, front-end and back-end developers, interface designer, tester, and product manager. With the release of GitLab 9.2, all of them can be designated as executors of one task , which simplifies the process of joint development and allows you to visually display their common area of responsibility.
Also in version 9.2, the localization of GitLab was initiated: Cycle Analytics analytics is now available in Spanish and German . Localization of GitLab will be continued in subsequent releases so that everyone can contribute regardless of their native language.
In addition, developers have more control over the execution time of the CI / CD pipelines. Now you can schedule the execution of pipelines , which allows you to automate periodic tasks, such as nightly assembly, maintenance, or confirmation of external dependencies.

This month's MVP is Dosuken Shinya
Dosuken added additional search options to the pipeline interface . This innovation opens up many possibilities: for example, you can now easily create a request for the last pipeline of a specific branch. Dosuken also made a significant contribution to the last release - he laid the foundations for the implementation of pipelines on a schedule . Thank you, Dosuken!
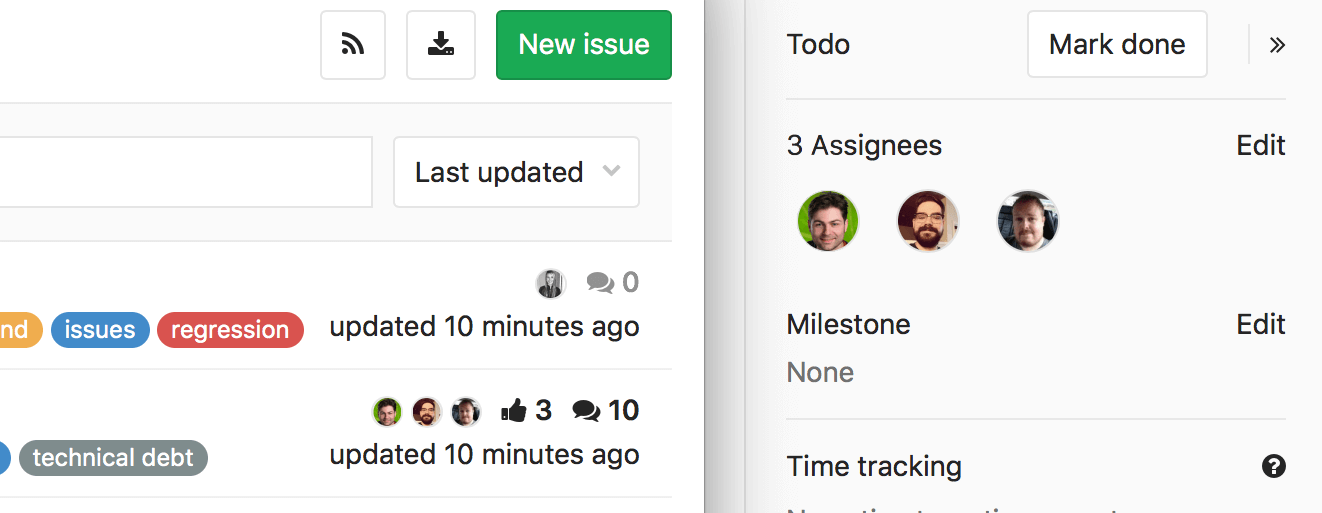
Several task executors (EES, EEP)
When working with GitLab, tasks often arise that require the joint efforts of several people at once. Earlier in such situations it was difficult to understand to whom the task was assigned; This was especially true for organizations in which performers do not contact each other daily. With the release of GitLab 9.2, it becomes possible to assign as many users as executors of a single task. All of them will have an equal level of responsibility and receive the same alerts as in previous versions. All performers are displayed in the task list and task boards, each of them can track their connection with the tasks on their control panel.
Note that due to these changes, the assignee_id task API parameter is obsolete, assignee_ids should be used assignee_ids . Also, assignee should be used instead of the assignee JSON object.
More information in our documentation.
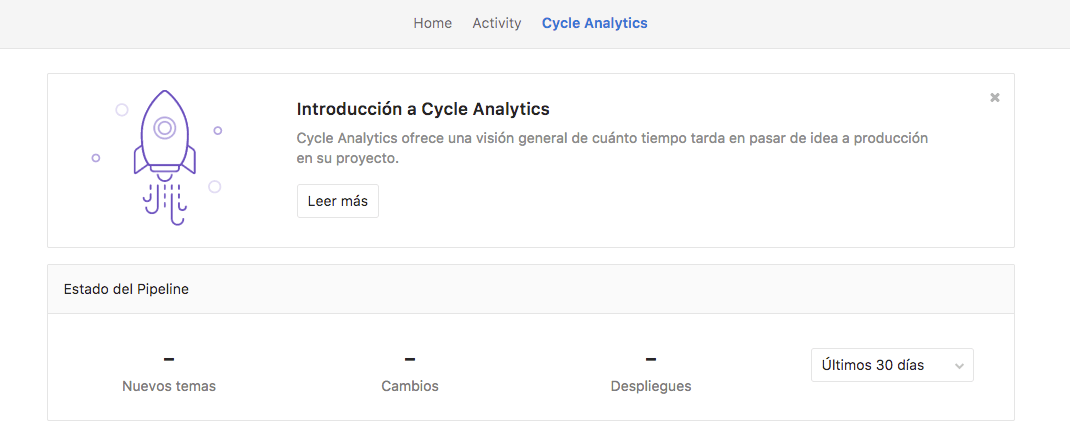
Localization of development cycle analytics (Cycle Analytics) (CE, EES, EEP)
Hola Mundo, Hallo Welt! We are pleased to announce that, starting with this release, we will begin work on the localization of GitLab. We welcome your support in this endeavor!
Version 9.2 adds tools and infrastructure for translating GitLab to any language in the world. So far, for testing purposes, we have translated only one page (Cycle Analytics) into Spanish and German. In the next versions we will translate new pages, as well as add other languages. If you want to help us with this - refer to the instructions .
To change the language of GitLab, click on its icon in the upper right corner of the screen and go to Settings.
More information about the analytics development cycle in our documentation.
Launch of pipelines on schedule (CE, EES, EEP)
In most projects, the CI / CD pipelines are launched for each new commit — thus, all changes in the code are built, tested and deployed. However, there are situations in which it is necessary to start the pipeline on a specific schedule.
With the release of GitLab 9.2, it becomes possible to customize the launch of pipelines when needed, and as often as needed . Daily and weekly launch of pipelines, verification of external dependencies, or just preventive launches - now all this can be easily customized.
This functionality completely replaces the alpha version of the interface for pipeline triggers on a schedule .
More information on pipeline launch planning in our documentation.

Installing GitLab on Kubernetes (CE, EES, EEP)
We want GitLab to be the best possible tool for native cloud development. For this, it is important that you can easily get started with Kubernetes . Therefore, we are happy to announce that the official Helm-charts of GitLab come out with version 9.2.
Helm is a package management tool that allows you to deploy, upgrade and configure applications in Kubernetes clusters. GitLab and Kubernetes interact perfectly with each other: all the ideas presented in our Idea to Production video, such as automating CI scaling and deployment to your clusters, are easily implemented with a minimum of additional configuration.
More information about installing GitLab using Helm-charts in our documentation.
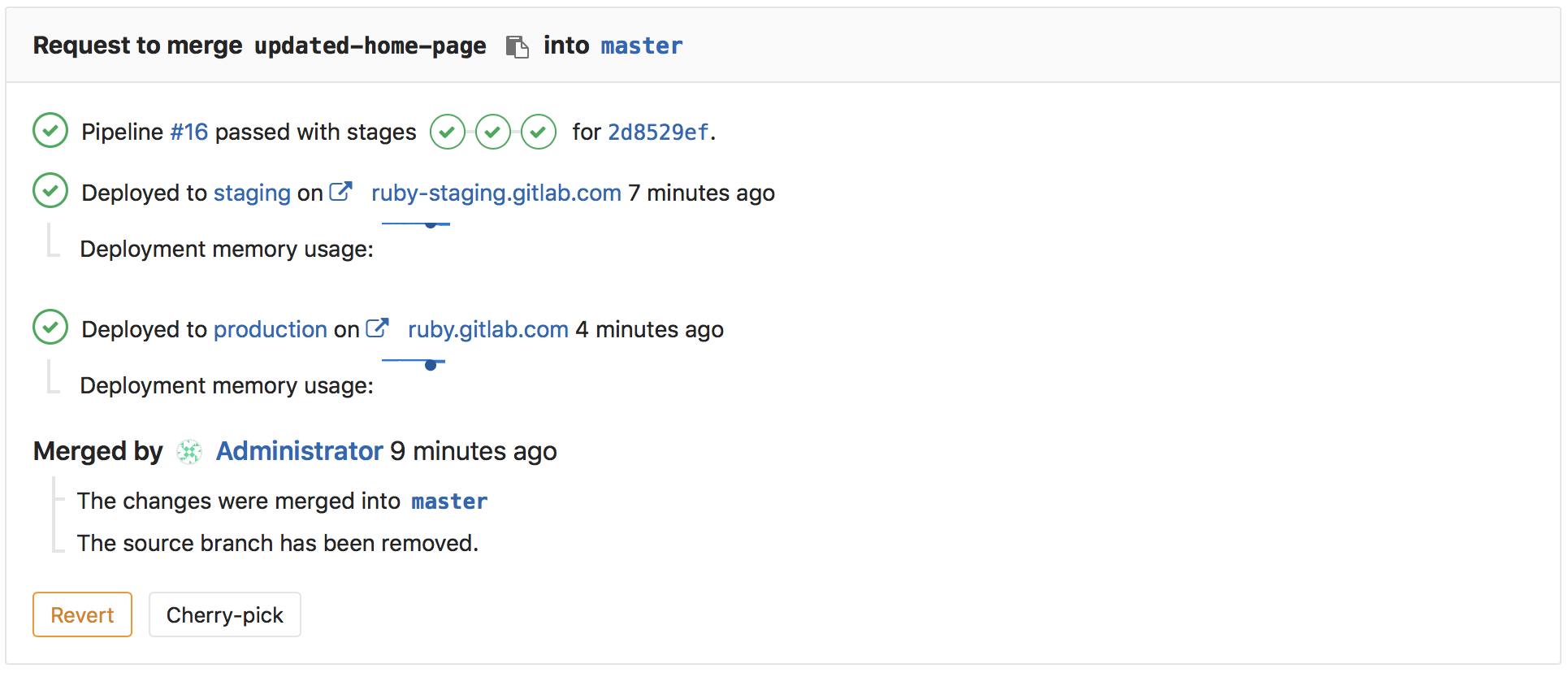
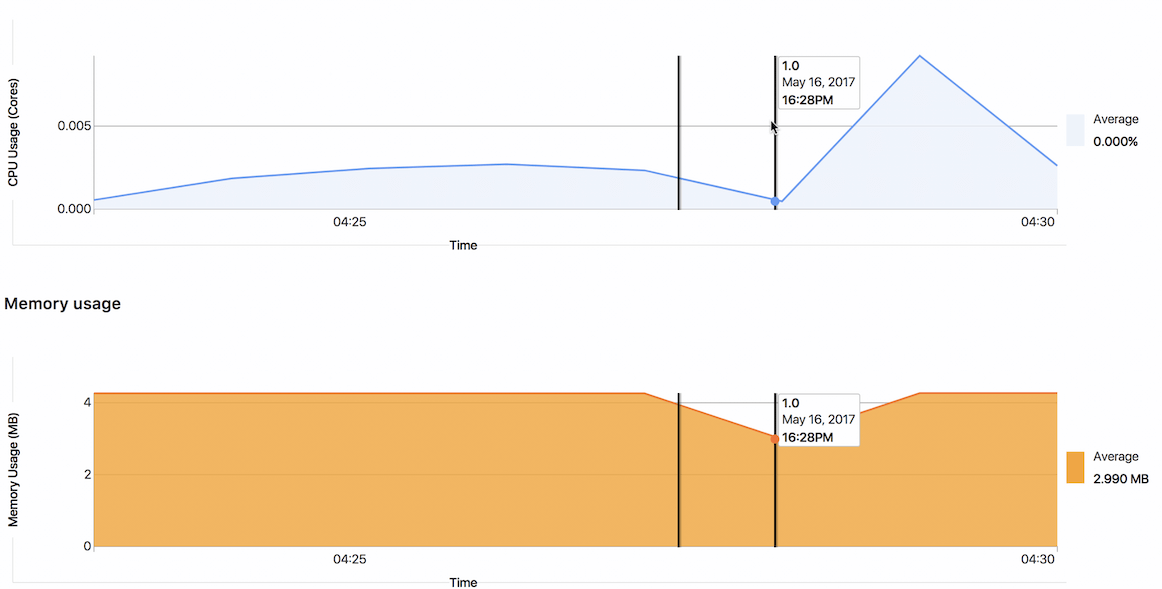
Data on the impact of Merger Requests on performance (CE, EES, EEP)
In most cases, it is not easy to track the effect of a certain merge on system performance. Often, a separate tool is responsible for performance data, to which the development team does not even have access. We want developers to be able to get this data for every change they make. Integration with Prometheus is a big step towards this goal.
Beginning with GitLab 9.2, changes in memory consumption after deployment are displayed directly in merge-quest. Now developers can track changes in performance without distracting from the usual process of work. In future releases, we plan to add other performance metrics .
More information on tracking the impact of merge requests on memory consumption in our documentation.
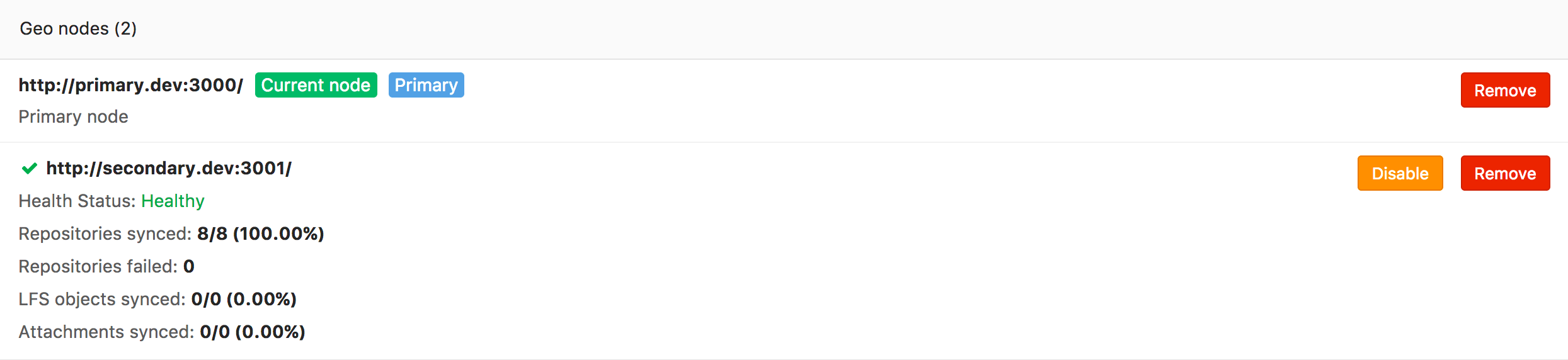
Improved alpha version of disaster recovery (EEP)
Starting with version 9.0, GitLab Geo includes the alpha version of disaster recovery. We strive to improve it with each new release, and GitLab 9.2 is no exception. In the new version, we have made disaster recovery more convenient: the sense of controls has become more obvious, and the replication process reports are more detailed.
The repository replication mechanism has also improved: now resynchronization for repositories damaged by synchronization errors occurs automatically. In addition, when updating the main database, it automatically synchronizes with the secondary databases.
More information about GItLab Geo in our documentation.
Automatic update of task names and descriptions (CE, EES, EEP)
Since the task page is the main collaboration point, its contents are constantly changing. Starting with GitLab 9.2, the title and description of the tasks are updated automatically, without refreshing the page. So now in order to constantly see the latest version of the task, you just need to keep its tab open. Even the tab name in the browser is updated automatically.
In addition, when editing a task description, a system note is added, so that you can view the complete history of changes to a task simply by scrolling through its comments. These changes are also affected by the comments - they are automatically updated in the same way when they are edited.
More information on the tasks in our documentation.

Remove filters in the search bar (CE, EES, EEP)
Now you can delete filters in the search bar of tasks and Merge-Requests with one click.
We also changed the style of the labels in the search bar: they now correspond in color to the rest of the labels throughout the application.
Details on finding tasks and merge requests
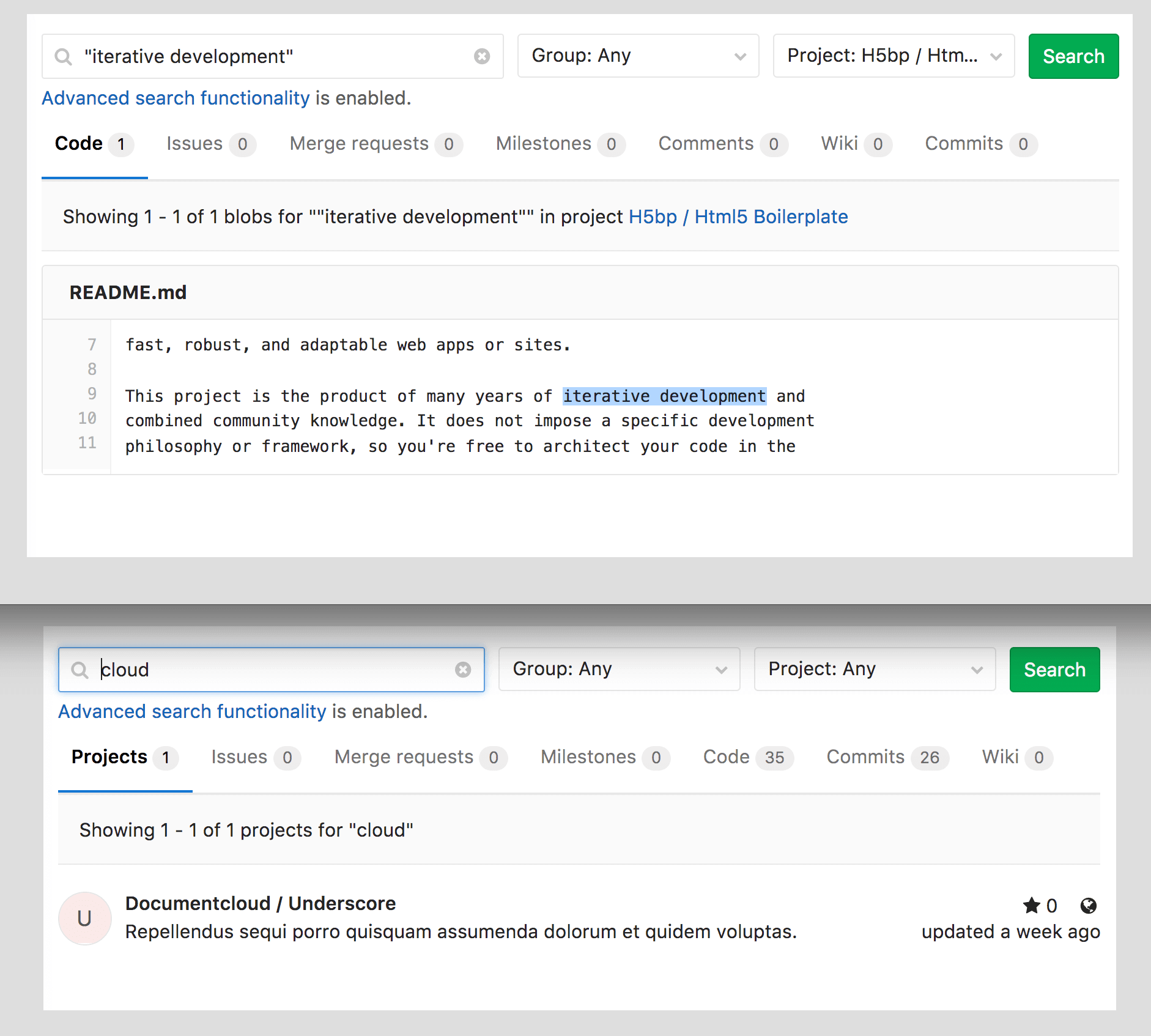
Improved search with Elasticsearch (EES, EEP)
We add more advanced search features by integrating with Elasticsearch. If you have configured Elasticsearch, you can search for exact phrases (in double quotes) or an unordered set of keywords, match part of the word, or use other search syntax options. (Note that this refers to the search bar in the upper right corner of any GitLab page, but not to the search in task lists and merge requests.)
Also thanks to Elasticsearch, a global search on all the wikis in your instance has become possible.
Learn more about advanced search with Elasticsearch
Other improvements in GitLab 9.2
Creation of a merge-request from a task (CE, EES, EEP)
In each iteration of GitLab, we try to make the path from idea to production faster and easier.
This new little feature will allow you to create a merge request directly from the task page, and the GitLab branch will create the necessary branch automatically. This is especially useful when you need to make a small commit directly from the GitLab interface.
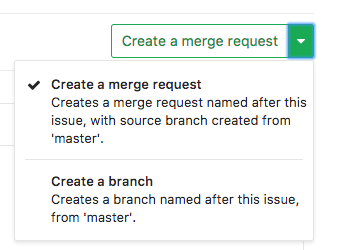
How to create a merge request from a task
Comments for personal snippets (CE, EES, EEP)
In snippets (even in personal ones), collaboration often occurs. In this update, comment threads will appear for each personal snippet - just like for project snippets.
You can read more about snippets in our documentation.
Preview of a rendered code (CE, EES, EEP)
When viewing GitLab files, many files, such as SVG & Markdown, are displayed in a rendered form. On the file viewing page, a convenient little switch appeared between the source code and the rendered file viewing modes.

Terraform support for GitLab Runner on Google Compute Engine (CE, EES, EEP)
In GitLab 9.1, we launched support for installing GitLab on GCE through Hashicorp 's Terraform . In version 9.2, we also add the ability to deploy GitLab Runner, adding to this the principle “from idea to production”.
Terraform configuration repository for GitLab
Preview of job artifacts in the user interface (CE, EES, EEP)
An artifact can be any file; You can access this file by searching the archive directly in the user interface. GitLab 9.2 has expanded the capabilities of this search: now PDF files, images, videos and other formats will have a preview right in the search for job artifacts - they no longer need to be downloaded.
More information about finding job artifacts in our documentation.
Handling ambiguous routes in dynamic paths (CE, EES, EEP)
In GitLab there are several ways to specific features. After the introduction of nested groups, these features could become unavailable for those projects or groups whose names conflict with these paths. For example, for a project called 'badges', badges of the statuses of the assembly or coverage became unavailable.
To avoid such misunderstandings, we removed the ability to create projects or groups with names that might conflict with existing GitLab routes.
If you had projects or groups with the names of one of these paths, they will automatically be renamed when you update. A project called badges will be called badges0 .
Note that the git remote settings will need to be updated manually, for example, like this:
git remote set-url origin git@gitlab.com:the-updated-path/the-updated-name.git You can see the full list of reserved words in the dynamic_path_validator.rb . A list of existing projects and groups that were affected by automatic renaming in this release can be found in the migration that renamed them.
After accepting a merge-request, the branch is deleted by default (CE, EES, EEP)
Starting with GitLab 9.2, the original branches in merge-requests are deleted by default. If you want to keep the branch even after merge, you need to disable the option in the merge-request widget before accepting it.

Recovering artifacts after caching files in CI jobs (CE, EES, EEP)
It may happen that someone (accidentally or deliberately) uses the same path for cache (cache) and artifacts (artifacts) in .gitlab-ci.yml , which can cause a situation where a stale cache may accidentally overwrite artifacts that are used in the pipeline.
From this release, artifacts can be recovered after caching - to make sure that they are preserved and accessible even in a critical situation.
Omnibus Improvements (CE, EES, EEP)
GitLab Mattermost 3.9
GitLab 9.2 includes the Mattermost 3.9 , an open source alternative to Slack . In this release, we added a new catalog of integrations and Polish language support to it, supplemented desktop applications with a spelling checker and added many more useful things.
Version includes security updates . We recommend to upgrade.
GitLab Registry
The GitLab Container Registry (GitLab Container Registry) has been updated from version 2.4 to version 2.6.1.
Appointment of specific reviewers for Merge Requests (EES, EEP)
The Merge-Requests interface allows you to select individual reviewers who can accept (confirm) this request. The choice is offered only to the project participants, as well as the group to which the project (parent group) belongs, and the groups that are granted access to the project (project share). Therefore, you can easily find the right users.
Learn more about setting up Merge Requests viewers.
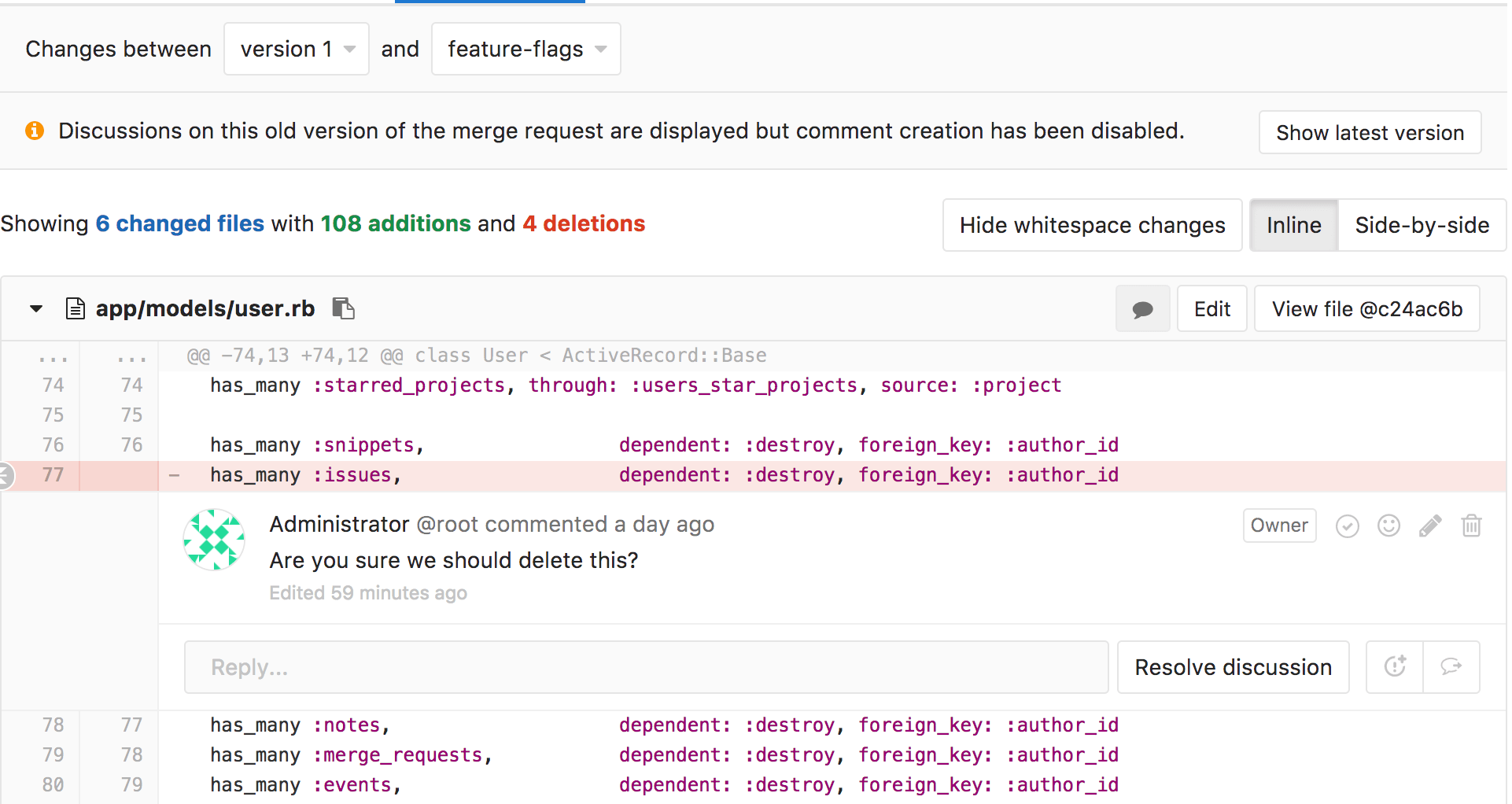
Commenting in legacy diffs (CE, EES, EEP)
In this release, it became possible to refer to the outdated diff directly from the thread of discussion of a merge request. This allows you to quickly access the contents of old commits in the development process, collaboration and review. You can even leave comments in those outdated diffs.

Read more about Merge Requests
Deployments are displayed on a performance board (CE, EES, EEP)
If the performance of the product has changed, then the first question is whether the working environment has changed? GitLab 9.2 now quickly answers this question, displaying all deployments in the environment right on the monitoring board. This allows you to immediately see the relationship between changes in performance and the new version of the application (and all this without leaving GitLab).
Environmental Monitoring Documentation
Manual actions include protected branches (CE, EES, EEP)
Manual actions now require the same access rights as writing to the repository, which will allow controlling who can perform them. For example, you can now leave the right to manually start the task of deploying code from a stable branch to production only for users who have the right to commit to this branch.
This is a very important part in the list of security enhancements that we add to GitLab to protect deployments in your projects. Details can be found in this problem .
Failed Tasks tab summarizing all faults (CE, EES, EEP)
When you commit a new part of the code into a project with continuous integration (CI), you usually expect to see a mark that indicates that the pipeline has been completed successfully, and everything worked as it was intended. In the event that something went wrong, you need to find out the details as soon as possible. But the numerous transitions in each of the stages and tasks are not very inspiring, especially if the pipeline is difficult.
In GitLab 9.2, on the pipeline information page (in the Pipelines section, select a specific pipeline) the Failed Jobs tab appeared. On it you can see the logs of all failed tasks and evaluate the overall picture of the performance of the pipeline.

Detailed release notes and instructions for updating / installing can be found in the original English post: https://about.gitlab.com/2017/05/22/gitlab-9-2-released/
Translation from English is made by translational artel "Nadmozg and partners", http://nadmosq.ru . Worked on the translation nick_volynkin , rishavant and sgnl_05 .
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/330036/
All Articles