Almost manifesto design thinking
Most people are willing to work hard to get rid of the need to think a little. Simple and useful tools for analyzing the system, finding new solutions and creating unique products lie under our feet - all that remains is to take and use them. In the program "Common Frontal System" we generate a huge number of ideas. Design thinking helps identify the most viable of them and successfully solve existing problems.
In this article, we will show the universal design process, tell you why you need to train design thinking, and go through the entire design chain using proven old-school methods.
When designing any device or service, we first need to think about how this device or service interacts with the user and fits into the overall infrastructure of an existing device and the daily life of a person.
')
Previously, all efforts were aimed only at making the product, now the look has changed. Now there is a client at the top, and it interacts with the services via touch points - touch points . When you use an iPhone or a social network, you interact not directly with the product, but indirectly through a service that performs various types of operations: in the case of a banking service, this is, for example, all sorts of transactions.
The service must have a policy and internal philosophy. It exists in the ecosystem, interacts with other services, it has a structure, people who serve it. Service rarely acts automatically, it creates a certain environment, forms a certain shell around itself. Even when we interact with a conventional device, the service becomes just a part of this infrastructure.
The design process now boils down to designing new user interaction scenarios. We can design an interesting form, an exciting interface that will be convenient to use, but at the same time, if the logic is not worked out, the chain of interactions and the most important thing is a humanly understandable form of interaction with those who work with this software, the system will not be in demand.
In the classical paradigm, this scheme is clear. We have a user, we identify his needs in a specific context - what he wants to do: for example, use banking services, grow cucumbers on a balcony, find a partner for dancing. We must be aware of the context and analyze these needs. Therefore, in the classical form, we ask the user what he wants, and on the basis of this, we identify various insights.
First of all, we need to identify the issues with which we will work. In the classic sense of project activity, this is a search for a problem. In design research - empathy.
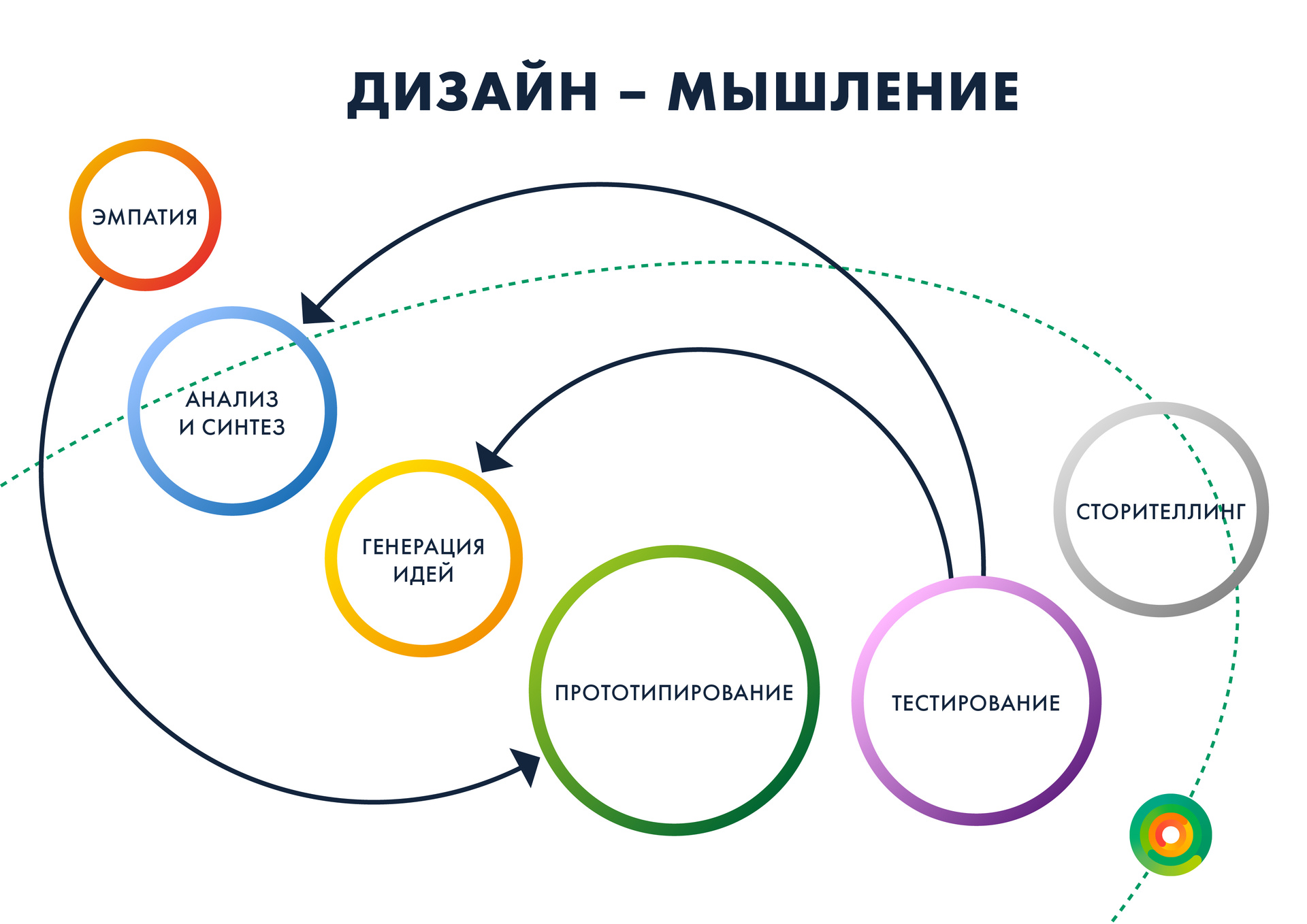
Empathy is an attempt to get into the client's skin and look at the problem with his eyes. The main tool that helps in this is observation.
When conducting empathy, in-depth interview methods are used: pains and needs of the client are identified, person – models are compiled - original avatars that combine the needs of a social group or a sample of certain clients, because this is a qualitative analysis. Of course, we are not able to interview millions and hundreds of thousands of customers, usually 6-8 people, representatives of some bright age or social target group.
On the basis of surveys, portraits of users are compiled, which are carriers of aspirations, pain, and needs of a certain category of people - pensioners, students, businessmen. We identify the basic needs, then move on to analysis and synthesis. We have a bunch of different insights and needs. What to do with it?
The best way is to decompose these needs and project specific stories. It is necessary to try to get a certain scenario of the user's journey through the service, taking into account the needs that he comes in and the problems he has encountered. As a rule, already during the interview, you can go to complete logical pairs. Then they need to be shifted to the “user routes” (ustomer journey). This is like a kind of screenplay for the film.
A good movie has two main components: a good movie controls our emotions and does it with a certain rhythm. “User routes” is a clearly programmed “carrying” of a person through history, according to certain scenarios. A good director and screenwriter knows: to scare, you must first cheer. When we draw the user's route, we always take into account the “pre-service” (what happens before), the service itself and the post-service (what impressions a person is left when leaving the service).
We live in the age of social platforms, and that feedback that the client leaves about the service is very important. This emphasis is not accidental. As a rule, the developer and designer pay attention to the basic outline of the service, when a person communicates directly with the service representatives or with the device interface. But the impression you get about the film is very often formed at the end. Therefore, we prescribe an emotional map, make a kind of encephalogram: there are positive, negative and neutral reactions. We find out what reactions users demonstrate at the touch points with the service: “I waited a long time for the queue”, “the manager redirected me to the wrong rack”, draws an emotional map that allows you to align the client’s state to the ideal: from neutral to positive, from positive to neutral. Be sure to "push out" the client after providing the service.
The next step is the generation of ideas. Many participated in brainstorming, which resulted in a bunch of ideas. How to check and reflect them? And here come to the aid of methods of prototyping. The prototype is a quick way to understand the problem in its early stages, before it even had time to go into details. You can simply assemble a prototype of the service on your knee, make a game card and guide the user through it, generating various situations with the help of game bones. This method was actively used by Heinrich Altshuller in his methods.

After that we test and improve. Any process, be it research, design or design thinking, is an integration process. When we find a problem, we immediately go back to the stage and collect new prototypes, test and improve again. But there is one small problem - when we explore user experience, we get interesting sets with their needs, generate ideas and understand that services have become better to work, we have humanized them, questions arise. Where is the point of innovation? What have we done new? There is a silent pause, and people say: “I don't know.”
But to do something new is an instinctive process that is similar to evolution. If you do not do it - make your competitor.
New create, to be the first and for some time to feel lonely. You get the attention of "business angels", a small temporary advantage to create a platform, make a name and start developing this platform. You break out of a circle of tough competition and make a small civilizational leap. New things are not made much: we are at the peak of creative activity, but there are very few really innovative products that change the scenarios of our life, open up new opportunities. 50th Instagram and Telegram , tuning versions of old applications do not count.
So how to make something new? Maybe take as a basis user insights or marketing research? Chat with users, identify preferences. So why it does not help to do new things? By and large, the client can not tell us anything about the future, of course, if it is not the Strugatsky brothers. Stumble upon a good futurologist among the survey participants is difficult. Marketing in general is sometimes amazing for innovations. For example, when marketers came to the creators of the system, which triggered the development of players, they said: "What kind of fool would walk down the street with headphones?"
Marketing is a great tool for analyzing existing reality, for positioning a product, but it doesn’t know how to invent something new.
In the 90s, the British Design Council conducted a study: interviewed users, made products that exactly met customer expectations, and as a result, 80% of new products were not successful in the market. If we rely on the user's “wishes”, then this is not very good. The main tool for creating a new one is data interpretation, on the basis of which the basic strategy of the development system is formed, that is, we analyze the market and create ideas of a real product. This method has certain disadvantages.
Can you imagine the Instagram creator who asked grandmothers how often they take pictures of food during the day? Hardly. Now they say that Steve Jobs connected the methods of design thinking in the development of their products, but this is absolutely not the case. Many cult products and services were created outside the marketing paradigm.
The first law for creating new products is the law of product evolution - the code of product evolution. We analyze users and show empathy, but we are looking for a vector of system development, a product evolution code, analyzing existing systems.
These methods are creative templates. In general, in creative patterns, patterned thinking is a bad thing. But we are not artists, the designer does not express himself by artistic methods and explores reality, is engaged in designing systems for solving the pressing problems of the user, humanity, the conscious improvement of life, the creation of new scenarios.
The first person to help us is Heinrich Altshuller. In the late 40s he was an officer of the Caspian fleet, an engineer who was arrested on a false denunciation, thrown into prison, was not allowed to sleep. They turned on the light in the camera, made noise, woke. On the third day, when he already knew that he would not stand up without questioning during interrogation, he invented such a fairy tale as if he had fallen into an enchanted kingdom, where the terrible witch said that if he closed his eyes, he would never get out of here. He found a contradiction in this, said to himself: I cannot close my eyes, but I want to sleep. What do you think, how did he decide it? He slept with his eyes closed, but he drew his eyes on his eyelids and asked his cellmate to talk to him. And only in the second week the female warden noticed it.
On the basis of this inference, he constructed a number of theories. He created the system of TRIZ - the theory of solving inventive problems. It is based on a number of paradigms, one of them is that systems develop as laws of physics, regardless of our desires. They just have a parallel development.
One of the rules for the development of the system is that the ideal system is one that does not exist, but its functions are performed. The system becomes invisible, turning into a subsystem. A good example is a laptop (typewriter, tape recorder, video camera - they are not there, but functions are performed).
When you communicate with clients, you will surely come across things that are not completely clear from the point of view of logic, with contradictions. They can be different, the main thing is to be able to formulate them. For example, recently we conducted empathy and heard that bank customers want to be informed, but without information noise. They want to receive information that comes in certain newsletters at certain times.
Altshuller paid great attention to controversy. He singled out administrative, technical and physical. Administrative contradictions are the most easily resolved, issues are resolved on a personal level through negotiations, for example.
Technical contradictions are eliminated by technical engineering methods. Physical contradictions - the new look, the most difficult, but they are solved. Altshuller believed that the quality of the solution of ideas depends on the level of compromise resolution of contradictions. The more compromises we make, the lower the quality of decisions.
The next person to talk about is Thomas Edison. He said: "A normal inventor needs a little talent and a landfill into which you can run your hands." Under the dump he meant the ideas of competitors. He was a very interesting person. Having started working as a conductor at the age of 12, he started a fire and was fired, became a telegraph operator, was dismissed because he almost made a disaster of two trains, threw his wives, was very jealous of the merits of his subordinates, never paid the bills. At the same time he was an absolutely brilliant man. His genius was in the following pattern - "Edison's gate" or a substitution pattern.
This is a classic story of invention. One day Edison was told by a friend: “Yes, you seem to have 1,200 patents, and the gate in the yard is barely open. You would at least smear it or come up with something. ” Edison said to him: "You know, yes, I just thought that this gate could serve as an excellent lever for the pump that pumps water into my pool." In other words, people entered his courtyard, opened the gate, which was tied to the pump and pumped water into the pool.
This idea was based on an interesting principle. The product that we create is not one, but is surrounded by competing products and is constantly evolving in a specific environment. The environment is constantly changing, and we are evolving with it. In this case, evolution may occur, and mutation may occur. DNA is an evolutionary product code, it is the overthought that lies in the very idea of a product. And he, too, is constantly evolving; if he does not do this, then we will perish. And what is the external environment for our product? This is a cultural context, customers, political background, technology, information environment, economy.
It is useful to draw a diagram of the system, enter the environment into it, replace the internal component with the environment and make it part of the system. You can also make new services: look at the environment and enter it into the system. This is applicable in almost all situations.
Finally, we will analyze an important case with Domino's Pizza. This is a fairly old pizza provider, and it was no different from others, until it introduced the principle: “If we don’t deliver the pizza on time, the cost of delivery will be reduced by half.” Before that, everyone delivered delicious pizza, but no one changed the cost of delivery depending on the time. This is an approach of independent attributes: the price is not price and time - these are independent attributes of the system, they can be internal and external. And we organize the relationship between them. Price varies with delivery time.
By the way, another well-known example with the Lighthouse of Alexandria. The ruler of Alexandria ordered a lighthouse, the architect was Sostrat of Cnidus, they had a conflict. Sostrat said that he wanted to perpetuate his name at the lighthouse, the governor refused. Sostrat had a contradiction: if I become famous, I die, I want to become famous and I don’t want to die. And then he realized that he could become famous after death, fame through the ages is wonderful, it suited him. He used the external environment: salt, water, which could destroy the material, cut his name on the stone, covered it with plaster, after a while it fell off, everyone learned the name of the creator.
Another creative template is to find two independent attributes of the system, in banking it can be a loan rate and a characteristic feature of a bank customer, and if we are talking about food, the size of a hamburger and its shape. The independent attribute method is the developer’s ability to find system components and assign dynamic dependencies between them where they didn’t exist before. And due to this, the system acquires a new configuration and meaning.
Today we talked about the basic creative patterns that, most likely, you constantly apply in your work. We talked about the importance of contradictions, about the substitution system, about the attribute template. We will be able to discuss this with you in more detail on June 3 at a small workshop that will be held within the framework of the IT Promotion conference in Telegraph, we will be able to take a closer look at working with templates for functional analysis methods (this is a more in-depth method of designing system functions) and the possibilities design patterns (as simple methods) on a more detailed development method.

Books on the basis of which we form our knowledge base on systems that make us think a little about the things around us will help to delve into the topic:
Bruce Sterling "Shaping Things" - a well-known science fiction, owns a futurological laboratory in which they explore the future of things. The book examines aspects of the improvement of the system in such a paradigm that a person is not the creator of the system, but a tool for its improvement. The system has its own internal logic of life, and the creator-man loses his function and becomes such a tool for improving the system.
A classic, must read: Altshuller GS Algorithm of the invention. He created the TRIZ matrix, his methods formed the basis of many methods of modern design methods.
In the book “Creativity in product innovation,” aspects of the use of creative templates are considered in more detail, these are Altshuller students, they actively develop his theories.
Robert Persing “Zen and the Art of Motorcycle Maintenance” - we recommend that you read the obligatory cult book of the 70s about the philosophical aspect of world perception through the concept of lyrics and physics.
We also recommend watching Kubrick's film “Space Odyssey” 2001.
Try to look at the world through the eyes of an explorer, look at things around as a system, do not be afraid to analyze the logic of these systems, the interaction of its components, and then change and rebuild in such a way that you get new and wonderful products.
Do you use design thinking? Feel free to ask your questions, we will be happy to talk with you in the comments to the article.

In this article, we will show the universal design process, tell you why you need to train design thinking, and go through the entire design chain using proven old-school methods.
When designing any device or service, we first need to think about how this device or service interacts with the user and fits into the overall infrastructure of an existing device and the daily life of a person.
')
Product in the ecosystem
Previously, all efforts were aimed only at making the product, now the look has changed. Now there is a client at the top, and it interacts with the services via touch points - touch points . When you use an iPhone or a social network, you interact not directly with the product, but indirectly through a service that performs various types of operations: in the case of a banking service, this is, for example, all sorts of transactions.
The service must have a policy and internal philosophy. It exists in the ecosystem, interacts with other services, it has a structure, people who serve it. Service rarely acts automatically, it creates a certain environment, forms a certain shell around itself. Even when we interact with a conventional device, the service becomes just a part of this infrastructure.
The design process now boils down to designing new user interaction scenarios. We can design an interesting form, an exciting interface that will be convenient to use, but at the same time, if the logic is not worked out, the chain of interactions and the most important thing is a humanly understandable form of interaction with those who work with this software, the system will not be in demand.
In the classical paradigm, this scheme is clear. We have a user, we identify his needs in a specific context - what he wants to do: for example, use banking services, grow cucumbers on a balcony, find a partner for dancing. We must be aware of the context and analyze these needs. Therefore, in the classical form, we ask the user what he wants, and on the basis of this, we identify various insights.
In search of insight
First of all, we need to identify the issues with which we will work. In the classic sense of project activity, this is a search for a problem. In design research - empathy.

Empathy is an attempt to get into the client's skin and look at the problem with his eyes. The main tool that helps in this is observation.
When conducting empathy, in-depth interview methods are used: pains and needs of the client are identified, person – models are compiled - original avatars that combine the needs of a social group or a sample of certain clients, because this is a qualitative analysis. Of course, we are not able to interview millions and hundreds of thousands of customers, usually 6-8 people, representatives of some bright age or social target group.
On the basis of surveys, portraits of users are compiled, which are carriers of aspirations, pain, and needs of a certain category of people - pensioners, students, businessmen. We identify the basic needs, then move on to analysis and synthesis. We have a bunch of different insights and needs. What to do with it?
The best way is to decompose these needs and project specific stories. It is necessary to try to get a certain scenario of the user's journey through the service, taking into account the needs that he comes in and the problems he has encountered. As a rule, already during the interview, you can go to complete logical pairs. Then they need to be shifted to the “user routes” (ustomer journey). This is like a kind of screenplay for the film.
A good movie has two main components: a good movie controls our emotions and does it with a certain rhythm. “User routes” is a clearly programmed “carrying” of a person through history, according to certain scenarios. A good director and screenwriter knows: to scare, you must first cheer. When we draw the user's route, we always take into account the “pre-service” (what happens before), the service itself and the post-service (what impressions a person is left when leaving the service).
We live in the age of social platforms, and that feedback that the client leaves about the service is very important. This emphasis is not accidental. As a rule, the developer and designer pay attention to the basic outline of the service, when a person communicates directly with the service representatives or with the device interface. But the impression you get about the film is very often formed at the end. Therefore, we prescribe an emotional map, make a kind of encephalogram: there are positive, negative and neutral reactions. We find out what reactions users demonstrate at the touch points with the service: “I waited a long time for the queue”, “the manager redirected me to the wrong rack”, draws an emotional map that allows you to align the client’s state to the ideal: from neutral to positive, from positive to neutral. Be sure to "push out" the client after providing the service.
The next step is the generation of ideas. Many participated in brainstorming, which resulted in a bunch of ideas. How to check and reflect them? And here come to the aid of methods of prototyping. The prototype is a quick way to understand the problem in its early stages, before it even had time to go into details. You can simply assemble a prototype of the service on your knee, make a game card and guide the user through it, generating various situations with the help of game bones. This method was actively used by Heinrich Altshuller in his methods.

After that we test and improve. Any process, be it research, design or design thinking, is an integration process. When we find a problem, we immediately go back to the stage and collect new prototypes, test and improve again. But there is one small problem - when we explore user experience, we get interesting sets with their needs, generate ideas and understand that services have become better to work, we have humanized them, questions arise. Where is the point of innovation? What have we done new? There is a silent pause, and people say: “I don't know.”
But to do something new is an instinctive process that is similar to evolution. If you do not do it - make your competitor.
New create, to be the first and for some time to feel lonely. You get the attention of "business angels", a small temporary advantage to create a platform, make a name and start developing this platform. You break out of a circle of tough competition and make a small civilizational leap. New things are not made much: we are at the peak of creative activity, but there are very few really innovative products that change the scenarios of our life, open up new opportunities. 50th Instagram and Telegram , tuning versions of old applications do not count.
So go on about the users or not?
So how to make something new? Maybe take as a basis user insights or marketing research? Chat with users, identify preferences. So why it does not help to do new things? By and large, the client can not tell us anything about the future, of course, if it is not the Strugatsky brothers. Stumble upon a good futurologist among the survey participants is difficult. Marketing in general is sometimes amazing for innovations. For example, when marketers came to the creators of the system, which triggered the development of players, they said: "What kind of fool would walk down the street with headphones?"
Marketing is a great tool for analyzing existing reality, for positioning a product, but it doesn’t know how to invent something new.
In the 90s, the British Design Council conducted a study: interviewed users, made products that exactly met customer expectations, and as a result, 80% of new products were not successful in the market. If we rely on the user's “wishes”, then this is not very good. The main tool for creating a new one is data interpretation, on the basis of which the basic strategy of the development system is formed, that is, we analyze the market and create ideas of a real product. This method has certain disadvantages.
Can you imagine the Instagram creator who asked grandmothers how often they take pictures of food during the day? Hardly. Now they say that Steve Jobs connected the methods of design thinking in the development of their products, but this is absolutely not the case. Many cult products and services were created outside the marketing paradigm.
The first law for creating new products is the law of product evolution - the code of product evolution. We analyze users and show empathy, but we are looking for a vector of system development, a product evolution code, analyzing existing systems.
These methods are creative templates. In general, in creative patterns, patterned thinking is a bad thing. But we are not artists, the designer does not express himself by artistic methods and explores reality, is engaged in designing systems for solving the pressing problems of the user, humanity, the conscious improvement of life, the creation of new scenarios.
Do not cut, and invent: creative templates
The first person to help us is Heinrich Altshuller. In the late 40s he was an officer of the Caspian fleet, an engineer who was arrested on a false denunciation, thrown into prison, was not allowed to sleep. They turned on the light in the camera, made noise, woke. On the third day, when he already knew that he would not stand up without questioning during interrogation, he invented such a fairy tale as if he had fallen into an enchanted kingdom, where the terrible witch said that if he closed his eyes, he would never get out of here. He found a contradiction in this, said to himself: I cannot close my eyes, but I want to sleep. What do you think, how did he decide it? He slept with his eyes closed, but he drew his eyes on his eyelids and asked his cellmate to talk to him. And only in the second week the female warden noticed it.
On the basis of this inference, he constructed a number of theories. He created the system of TRIZ - the theory of solving inventive problems. It is based on a number of paradigms, one of them is that systems develop as laws of physics, regardless of our desires. They just have a parallel development.
One of the rules for the development of the system is that the ideal system is one that does not exist, but its functions are performed. The system becomes invisible, turning into a subsystem. A good example is a laptop (typewriter, tape recorder, video camera - they are not there, but functions are performed).
When you communicate with clients, you will surely come across things that are not completely clear from the point of view of logic, with contradictions. They can be different, the main thing is to be able to formulate them. For example, recently we conducted empathy and heard that bank customers want to be informed, but without information noise. They want to receive information that comes in certain newsletters at certain times.
Altshuller paid great attention to controversy. He singled out administrative, technical and physical. Administrative contradictions are the most easily resolved, issues are resolved on a personal level through negotiations, for example.
Technical contradictions are eliminated by technical engineering methods. Physical contradictions - the new look, the most difficult, but they are solved. Altshuller believed that the quality of the solution of ideas depends on the level of compromise resolution of contradictions. The more compromises we make, the lower the quality of decisions.
The next person to talk about is Thomas Edison. He said: "A normal inventor needs a little talent and a landfill into which you can run your hands." Under the dump he meant the ideas of competitors. He was a very interesting person. Having started working as a conductor at the age of 12, he started a fire and was fired, became a telegraph operator, was dismissed because he almost made a disaster of two trains, threw his wives, was very jealous of the merits of his subordinates, never paid the bills. At the same time he was an absolutely brilliant man. His genius was in the following pattern - "Edison's gate" or a substitution pattern.
This is a classic story of invention. One day Edison was told by a friend: “Yes, you seem to have 1,200 patents, and the gate in the yard is barely open. You would at least smear it or come up with something. ” Edison said to him: "You know, yes, I just thought that this gate could serve as an excellent lever for the pump that pumps water into my pool." In other words, people entered his courtyard, opened the gate, which was tied to the pump and pumped water into the pool.
This idea was based on an interesting principle. The product that we create is not one, but is surrounded by competing products and is constantly evolving in a specific environment. The environment is constantly changing, and we are evolving with it. In this case, evolution may occur, and mutation may occur. DNA is an evolutionary product code, it is the overthought that lies in the very idea of a product. And he, too, is constantly evolving; if he does not do this, then we will perish. And what is the external environment for our product? This is a cultural context, customers, political background, technology, information environment, economy.
It is useful to draw a diagram of the system, enter the environment into it, replace the internal component with the environment and make it part of the system. You can also make new services: look at the environment and enter it into the system. This is applicable in almost all situations.
Finally, we will analyze an important case with Domino's Pizza. This is a fairly old pizza provider, and it was no different from others, until it introduced the principle: “If we don’t deliver the pizza on time, the cost of delivery will be reduced by half.” Before that, everyone delivered delicious pizza, but no one changed the cost of delivery depending on the time. This is an approach of independent attributes: the price is not price and time - these are independent attributes of the system, they can be internal and external. And we organize the relationship between them. Price varies with delivery time.
By the way, another well-known example with the Lighthouse of Alexandria. The ruler of Alexandria ordered a lighthouse, the architect was Sostrat of Cnidus, they had a conflict. Sostrat said that he wanted to perpetuate his name at the lighthouse, the governor refused. Sostrat had a contradiction: if I become famous, I die, I want to become famous and I don’t want to die. And then he realized that he could become famous after death, fame through the ages is wonderful, it suited him. He used the external environment: salt, water, which could destroy the material, cut his name on the stone, covered it with plaster, after a while it fell off, everyone learned the name of the creator.
Another creative template is to find two independent attributes of the system, in banking it can be a loan rate and a characteristic feature of a bank customer, and if we are talking about food, the size of a hamburger and its shape. The independent attribute method is the developer’s ability to find system components and assign dynamic dependencies between them where they didn’t exist before. And due to this, the system acquires a new configuration and meaning.
Results and tips
Today we talked about the basic creative patterns that, most likely, you constantly apply in your work. We talked about the importance of contradictions, about the substitution system, about the attribute template. We will be able to discuss this with you in more detail on June 3 at a small workshop that will be held within the framework of the IT Promotion conference in Telegraph, we will be able to take a closer look at working with templates for functional analysis methods (this is a more in-depth method of designing system functions) and the possibilities design patterns (as simple methods) on a more detailed development method.

Day in the Telegraph
By the way, the day in the Telegraph promises to be rich and useful.
The finalists of the technological promotion "Promotion" will continue to fight for victory. In addition to the presentations of the teams, participants are expected to make speeches by leaders of the IT industry on current topics in the world of technology and master classes. The conference will be opened by speeches of representatives of the top management of Sberbank. For IT professionals, expert presentations on front-end and back-end topics will be organized. During the day, participants will undergo various demos in the field of artificial intelligence, virtual and augmented reality, and prototypes based on biometrics technology will be presented.
Students and applicants will be able to learn about internship opportunities and career development in Sberbank and SberTech, fill out questionnaires and have an interview to replace vacant positions.
Participation in the event is free, admission is pre-registration on the site , there is a map of the event.
Books for thinking and thinking
Books on the basis of which we form our knowledge base on systems that make us think a little about the things around us will help to delve into the topic:
Bruce Sterling "Shaping Things" - a well-known science fiction, owns a futurological laboratory in which they explore the future of things. The book examines aspects of the improvement of the system in such a paradigm that a person is not the creator of the system, but a tool for its improvement. The system has its own internal logic of life, and the creator-man loses his function and becomes such a tool for improving the system.
A classic, must read: Altshuller GS Algorithm of the invention. He created the TRIZ matrix, his methods formed the basis of many methods of modern design methods.
In the book “Creativity in product innovation,” aspects of the use of creative templates are considered in more detail, these are Altshuller students, they actively develop his theories.
Robert Persing “Zen and the Art of Motorcycle Maintenance” - we recommend that you read the obligatory cult book of the 70s about the philosophical aspect of world perception through the concept of lyrics and physics.
We also recommend watching Kubrick's film “Space Odyssey” 2001.
Try to look at the world through the eyes of an explorer, look at things around as a system, do not be afraid to analyze the logic of these systems, the interaction of its components, and then change and rebuild in such a way that you get new and wonderful products.
Do you use design thinking? Feel free to ask your questions, we will be happy to talk with you in the comments to the article.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/329560/
All Articles
