The best toys for future techies of our childhood (USSR and USA)
Hi, Habr! In this post we tried to collect toys, which, it seems to us, have influenced the development of the creative, engineering and technical skills of the generation of people born in the last century, to which we belong. Of course, the list is far from complete, and everyone will be able to add at least a few things from his childhood, which determined his choice of future profession.

Those who wish to plunge into pleasant memories are invited to go under the cat.
USA
The first science-based 100-in-one Science Fair in 1955 allowed children to create amplifiers, radios, lighting fixtures, and more without parental supervision and soldering irons.
')

the USSR
Since the beginning of 1982, the electronic designer Ekon-01 has been producing the Leningrad Experimental Plant at the SRI Electrostandard. The constructor is intended for technical creativity of school-age children and is a set of products that allows assembling simple existing electronic devices without the use of soldering, tools and installation wires. With the help of the designer, you can assemble various electronic devices according to 30 schemes and drawings given in the manual.

USA

Sold since 1964, the Creepy Crawlers Thing-Maker was a set that included metal forms with insects and other reptiles. These forms were filled with a colored substance called Plastigoop and placed in an open oven at a temperature of 200 degrees. The result was rubber replicas similar to real insects. Creepy Crawlers was one of the most dangerous and at the same time magnificent toys of that time. Production was discontinued due to safety issues.
the USSR
One of the popular hobbies of the Soviet era was the creation of paintings on the tree burner. This leisure could afford each. As a rule, the basics of burning were taught at school in labor classes or in special circles. The temperature of the heating element depends on the diameter of the wire. The thinnest wire heats up to 200 degrees, and the thickest (bone carving) up to 1000 degrees. The standard for wood is 250-300 degrees. Soviet burning devices, for example, "Pattern -1", "Vyaz", "Leisure" had a very simple design, but today they look unsafe. And, nevertheless, they were trusted by the children. With the help of Soviet burners, many works of folk art were created.
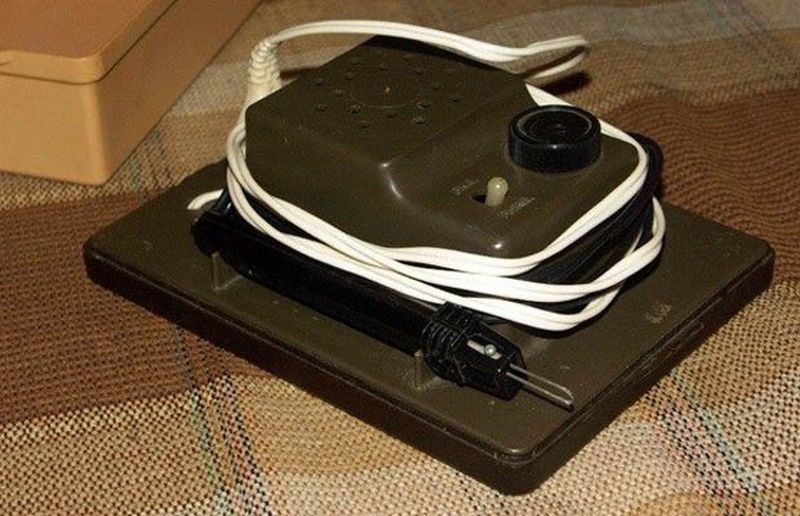

USA
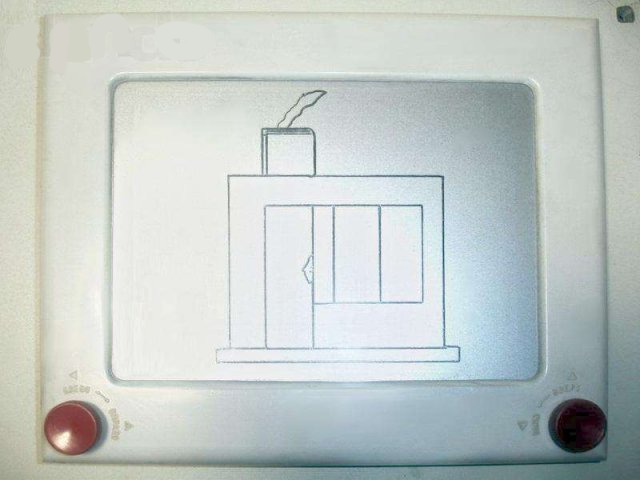
First introduced in 1986, the Etch-A-Sketch Animator was far from the animation apps for the iPad used by children today, but this toy was digital and already had a dot matrix, a few kilobytes of memory and speakers that played a shuffled static sound when turning the knobs or playing an animation.
The ancestor of the game came up with Andre Cassagne in the middle of the XX century (he called her Fr.L'Ecran Magique, Magic Screen). The magic screen is a sealed box, covered with glass on top. Inside the box there is an aluminum powder and a metal cursor on two axes, pressing against the glass with the sharp part. The cursor is controlled through two handles that move the cursor vertically and horizontally. When you move the cursor on the screen, covered with adhered aluminum powder, the image appears in the form of dark lines on a silver background. The game is “reset” by shaking (or turning over) the screen, after which the aluminum powder completely covers the previous image.
Subsequently, the rights to the game were sold to Ohio Art, which called it Etch-A-Sketch. In 1960, the game was launched into mass production. The game was especially popular in the USA. Under the name "Magic Screen" in the USSR, the game appeared in the 1970s. Production was carried out without licensing from the copyright holder.
USA
Designers have been around for more than 100 years, according to reports, the first was released in 1913. All these years, juvenile engineers have combined small design elements, sometimes creating cool cars, cars and tiny cranes.
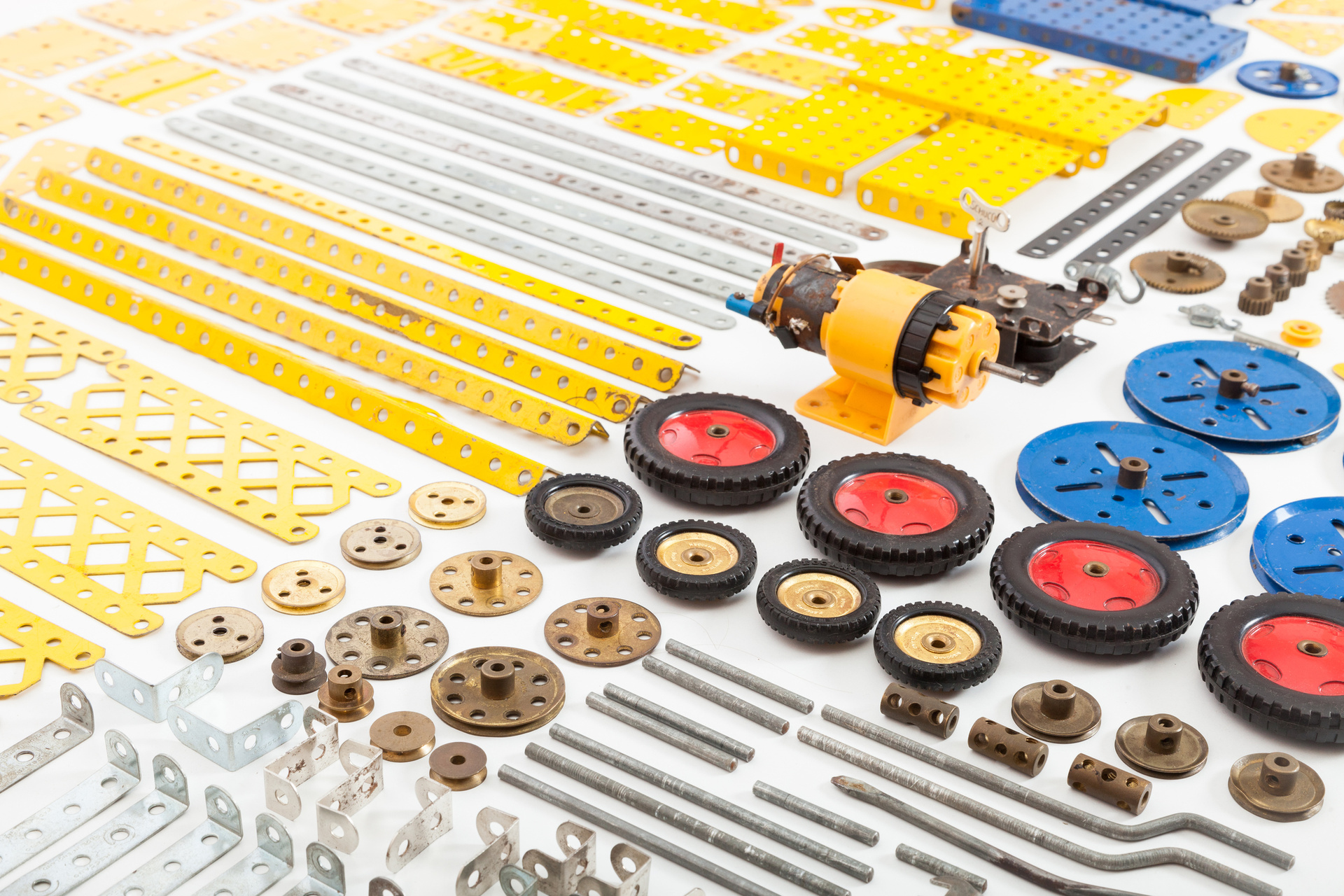

the USSR
The most popular in the Soviet Union was a metal constructor, which developed not only fine motor skills while twisting numerous small nuts, but also engineering thinking. The technical potential of the designer allowed, having connected several sets, to assemble a marvelous machine, crane or helicopter.
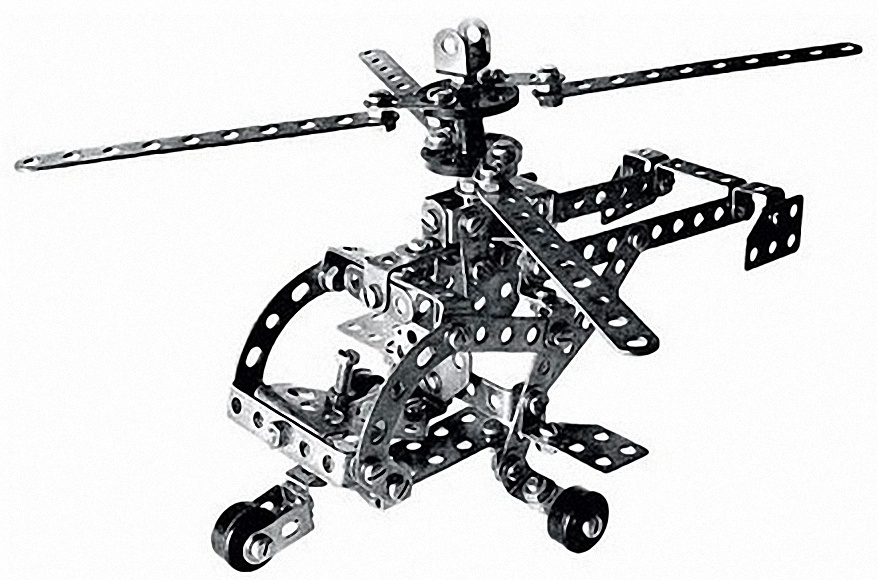

The Soviet designer turned out to be 100% compatible with the German Construction, which made it possible to significantly increase the number of possible mechanisms by adding gears.
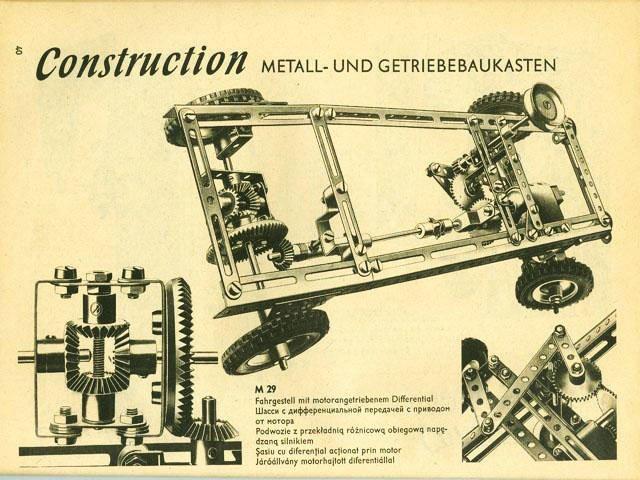
No less interesting was the version of the designer “Flight”, which gives the “flight of fantasy” the opportunity to materialize in almost anything.
USA
First introduced to the market in the 1950s, the Rock tumbler endured a security revolution in the children's toy industry. It is still on sale today. The rotating camera wets and polishes coarse stones to a state of smooth shiny pebbles.

the USSR
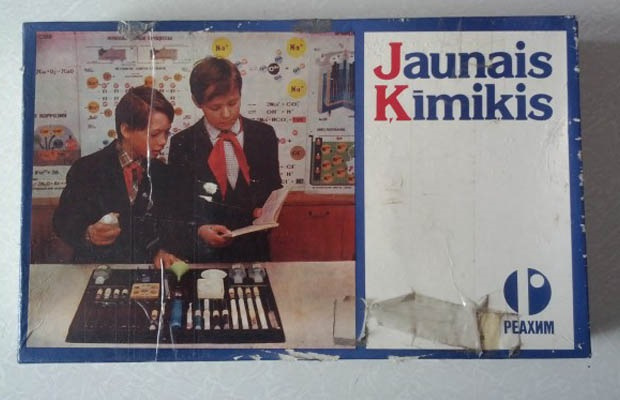
Sets for young chemists, of course, were sold not only in the USSR. Similar "toys" can be bought today in many stores. One of the first such sets in the USSR was created by a Latvian scientist and contained a heating device, test tubes, a couple of reagents, litmus papers, acid, magnesium, and a retort. This made it possible to conduct a lot of experiments and even make a small explosion.

USA
Verbot was first introduced in 1984. Tomy's voice robot could perform eight voice commands, but was not limited to using the built-in dictionary to launch them. Children could program any number of arbitrary voice commands to direct the movement of the robot left, right, back and forth.
the USSR
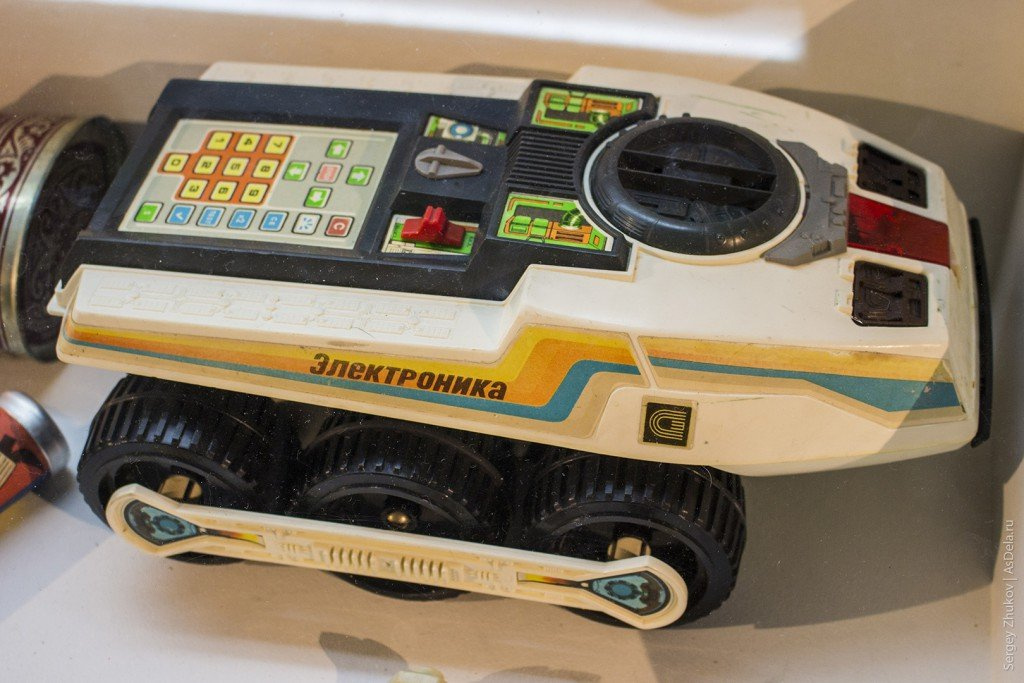
The Lunokhod "Electronics" was an all-terrain vehicle on batteries, controlled not by radio or by wire, but programmed with the help of an integrated remote control.
In one of the blogs we found some information about its functionality:

USA
Before the advent of the Game Boy by Nintendo in 1980, the legendary Game & Watch series was released. Many of the games in the series already contained buttons “A” and “B” corresponding to the levels of difficulty of the game.
the USSR
Pocket games of the Electronics series are a line of Soviet portable gaming devices with an LCD screen that have been produced by various manufacturers under the general trademark Electronics in 1984. Some of the games of this family were copies, analogues and variations of the Game & Watch electronic toys of the Wide Screen series, produced by Nintendo (EGG, Octopus, Mickey Mouse, Chef, and others).
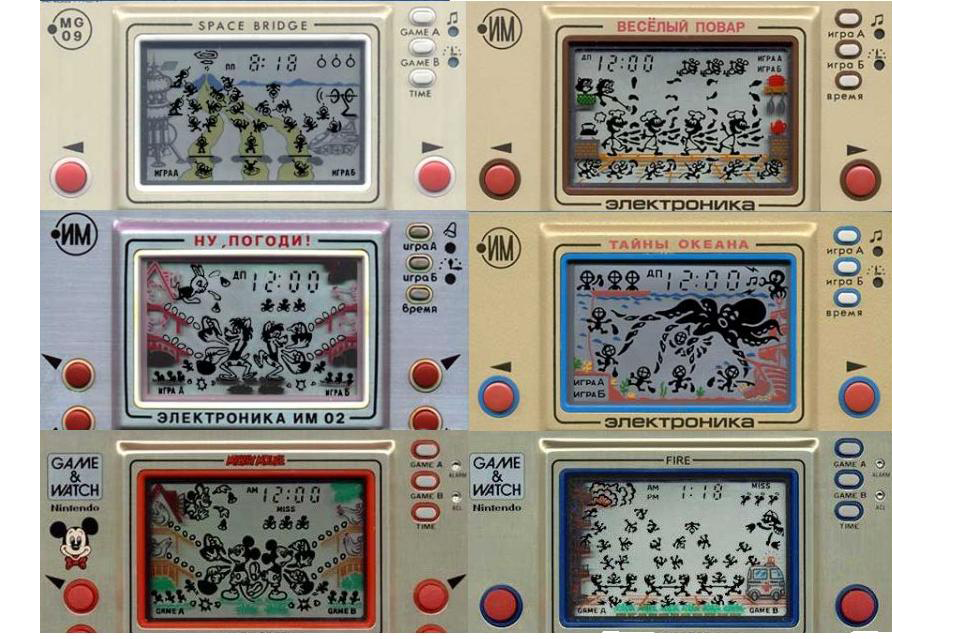

Wolf catches eggs - was the most popular. About such games there were legends about the existence of a certain cartoon that will be shown to you after 1000 points scored. The rumor about a non-existent (?) “Achivka” was a strong motivator and made the young players try to score the required number of points again and again. Repeat this with spoiled players in our time will not everyone.

Those who wish to plunge into pleasant memories are invited to go under the cat.
Electronic constructors
USA
The first science-based 100-in-one Science Fair in 1955 allowed children to create amplifiers, radios, lighting fixtures, and more without parental supervision and soldering irons.
')

the USSR
Since the beginning of 1982, the electronic designer Ekon-01 has been producing the Leningrad Experimental Plant at the SRI Electrostandard. The constructor is intended for technical creativity of school-age children and is a set of products that allows assembling simple existing electronic devices without the use of soldering, tools and installation wires. With the help of the designer, you can assemble various electronic devices according to 30 schemes and drawings given in the manual.

Toys that quickly learned safety
USA

Sold since 1964, the Creepy Crawlers Thing-Maker was a set that included metal forms with insects and other reptiles. These forms were filled with a colored substance called Plastigoop and placed in an open oven at a temperature of 200 degrees. The result was rubber replicas similar to real insects. Creepy Crawlers was one of the most dangerous and at the same time magnificent toys of that time. Production was discontinued due to safety issues.
the USSR
One of the popular hobbies of the Soviet era was the creation of paintings on the tree burner. This leisure could afford each. As a rule, the basics of burning were taught at school in labor classes or in special circles. The temperature of the heating element depends on the diameter of the wire. The thinnest wire heats up to 200 degrees, and the thickest (bone carving) up to 1000 degrees. The standard for wood is 250-300 degrees. Soviet burning devices, for example, "Pattern -1", "Vyaz", "Leisure" had a very simple design, but today they look unsafe. And, nevertheless, they were trusted by the children. With the help of Soviet burners, many works of folk art were created.

Tablet computers of our childhood
USA
First introduced in 1986, the Etch-A-Sketch Animator was far from the animation apps for the iPad used by children today, but this toy was digital and already had a dot matrix, a few kilobytes of memory and speakers that played a shuffled static sound when turning the knobs or playing an animation.
The ancestor of the game came up with Andre Cassagne in the middle of the XX century (he called her Fr.L'Ecran Magique, Magic Screen). The magic screen is a sealed box, covered with glass on top. Inside the box there is an aluminum powder and a metal cursor on two axes, pressing against the glass with the sharp part. The cursor is controlled through two handles that move the cursor vertically and horizontally. When you move the cursor on the screen, covered with adhered aluminum powder, the image appears in the form of dark lines on a silver background. The game is “reset” by shaking (or turning over) the screen, after which the aluminum powder completely covers the previous image.
Subsequently, the rights to the game were sold to Ohio Art, which called it Etch-A-Sketch. In 1960, the game was launched into mass production. The game was especially popular in the USA. Under the name "Magic Screen" in the USSR, the game appeared in the 1970s. Production was carried out without licensing from the copyright holder.

Engineering flight
USA
Designers have been around for more than 100 years, according to reports, the first was released in 1913. All these years, juvenile engineers have combined small design elements, sometimes creating cool cars, cars and tiny cranes.

the USSR
The most popular in the Soviet Union was a metal constructor, which developed not only fine motor skills while twisting numerous small nuts, but also engineering thinking. The technical potential of the designer allowed, having connected several sets, to assemble a marvelous machine, crane or helicopter.

The Soviet designer turned out to be 100% compatible with the German Construction, which made it possible to significantly increase the number of possible mechanisms by adding gears.


No less interesting was the version of the designer “Flight”, which gives the “flight of fantasy” the opportunity to materialize in almost anything.
Toys for young physicists and chemists
USA
First introduced to the market in the 1950s, the Rock tumbler endured a security revolution in the children's toy industry. It is still on sale today. The rotating camera wets and polishes coarse stones to a state of smooth shiny pebbles.

the USSR
Sets for young chemists, of course, were sold not only in the USSR. Similar "toys" can be bought today in many stores. One of the first such sets in the USSR was created by a Latvian scientist and contained a heating device, test tubes, a couple of reagents, litmus papers, acid, magnesium, and a retort. This made it possible to conduct a lot of experiments and even make a small explosion.

Programmable toys
USA
Verbot was first introduced in 1984. Tomy's voice robot could perform eight voice commands, but was not limited to using the built-in dictionary to launch them. Children could program any number of arbitrary voice commands to direct the movement of the robot left, right, back and forth.
the USSR
The Lunokhod "Electronics" was an all-terrain vehicle on batteries, controlled not by radio or by wire, but programmed with the help of an integrated remote control.
In one of the blogs we found some information about its functionality:
Lunokhod could drive forward, backward, turn to a given angle, blink a light bulb with the sound of pi-piu and launch a spinning projectile in the form of a disk. In total, 16 actions were stored in memory. The toy was expensive and rare, it was played in crowds and organized all sorts of robot programming contests. Three types of competitions were held: passing from point A to point B in the shortest time, the same but with the shortest program (there is not much memory, save bytes!), And overcoming an obstacle course. In the latter case, the winner was declared the one whose moon rover was passing through it the greatest distance. There was a version without headlights, turn signals and a spinner (it was instead a compartment for the Krona battery), but with the presence of a front parking sensor. If the lunar rover rested against the muzzle in the obstacle, the program stopped without straining electric motors.

Electronic games: the beginning
USA
Before the advent of the Game Boy by Nintendo in 1980, the legendary Game & Watch series was released. Many of the games in the series already contained buttons “A” and “B” corresponding to the levels of difficulty of the game.
the USSR
Pocket games of the Electronics series are a line of Soviet portable gaming devices with an LCD screen that have been produced by various manufacturers under the general trademark Electronics in 1984. Some of the games of this family were copies, analogues and variations of the Game & Watch electronic toys of the Wide Screen series, produced by Nintendo (EGG, Octopus, Mickey Mouse, Chef, and others).

Wolf catches eggs - was the most popular. About such games there were legends about the existence of a certain cartoon that will be shown to you after 1000 points scored. The rumor about a non-existent (?) “Achivka” was a strong motivator and made the young players try to score the required number of points again and again. Repeat this with spoiled players in our time will not everyone.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/328870/
All Articles