Comparison of GPT and MBR partition structures
Have you ever thought about how a computer boots? Regardless of the hardware and operating system, all computers use either the traditional BIOS-MBR method or the more modern UEFI-GPT, implemented in the latest versions of the operating system.
In this article, we will compare the structure of the GPT and MBR sections; GPT stands for GUID Partition Table, and MBR stands for Master Boot Record. Let's start with the fact that we analyze the process of loading.
The following chapters highlight the differences between the styles of the GPT and MBR sections, including instructions on how to convert between the two styles, and tips on which one to choose.
When you press the power button on your PC, the process starts, which will eventually lead to the loading of the operating system into memory. The first command depends on the structure of the partitions on your hard disk.
')
If two kinds of partition structures: MBR and GPT. The partition structure on the disk defines three things:
Let's go back to the boot process. If your system uses the MBR partition structure, the first execution process will load the BIOS. The basic input / output system (Basic Input / Output System) includes the loader firmware. The bootloader firmware contains low-level functions, such as keyboard input, access to a video display, performing disk I / O operations, and code to load the initial stage of the bootloader. Before the BIOS can determine the boot device, it performs a sequence of system configuration functions, starting with the following:
Once the BIOS has detected a boot device, it reads the first disk sector of this device into memory. The first sector of the disk is the master boot record (MBR) of 512 bytes. Three objects fit into this size:
At this stage, the MBR scans the partition table and loads the boot sector, Volume Boot Record (VBR), into RAM.
VBR usually contains the Initial Program Loader (IPL), this code initiates the boot process. The initial program loader includes the second stage of the loader, which then loads the operating system. On Windows NT family systems, such as Windows XP, the bootloader first loads another program called NT Loader (abbreviated as NTLDR), which then loads the operating system.
For Linux kernel operating systems, the GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) is used. The boot process is similar to the one described above, the only difference is in the name of the boot loaders in the first and second stages.
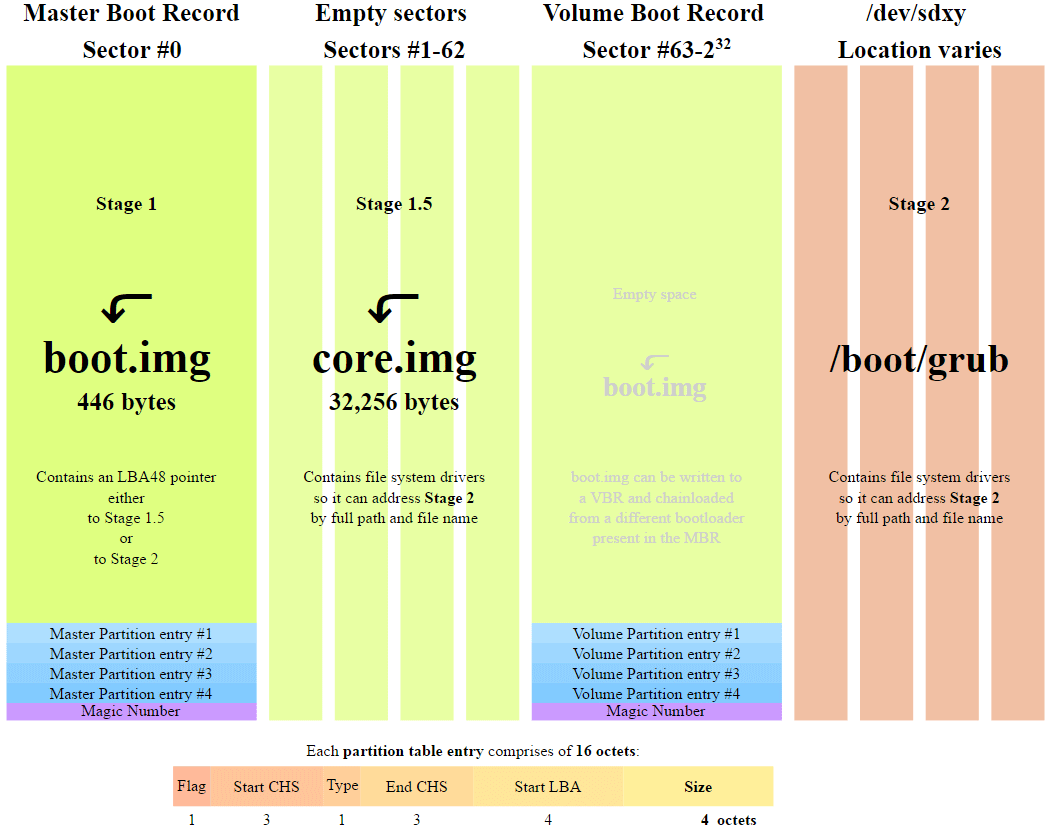
In GRUB, the first stage of the bootloader is called GRUB Stage 1. It loads the second stage, known as GRUB Stage 2. The second stage downloads it receives a list of operating systems on hard drives and provides the user with a list for choosing the OS to boot.
At the same loading stage, the following happens in the GPT partition structure. GPT uses UEFI , in which there is no storage procedure in the boot sector of the first stage of the bootloader such as that of the MBR, followed by a call to the second stage of the bootloader. UEFI — the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface — is a more advanced interface than the BIOS. It can analyze the file system and even upload files by itself.
After turning on your computer, UEFI first performs the functions of the system configuration, as well as the BIOS. This energy management, installation of dates and other components of system management.
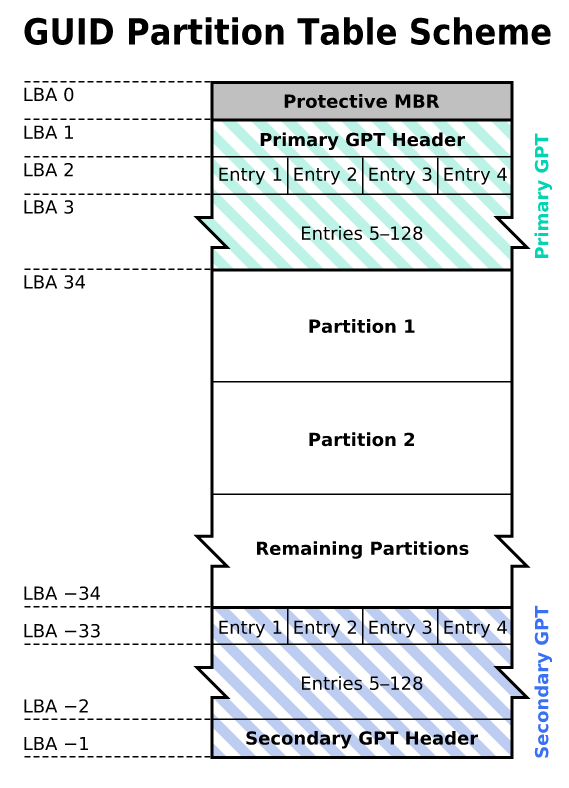
UEFI then reads the GPT partition table GUID. GUID stands for “globally unique identifier” (Globally Unique Identifier). GPT is located in the first sectors of the disk, immediately after sector 0, where the master boot record for the Legacy BIOS is still stored.
GPT defines a partition table on the disk where the EFI boot loader recognizes the EFI system partition. The system partition contains boot loaders for all operating systems installed on other partitions of the hard disk. The loader initializes the Windows boot manager, which then loads the operating system.
For operating systems on the Linux kernel, there is a version of GRUB with EFI support, which loads a file, such as grub.efi, or an EFI bootloader, which loads its file, such as elilo.efi.
You may notice that both the UEFI-GPT and the BIOS-MBR transfer control to the bootloader, but do not directly load the operating system. However, UEFI does not need to go through several stages of the bootloader, as in the BIOS. The boot process happens at a very early stage, depending on your hardware configuration.
If you have ever tried to install Windows 8 or 10 on a new computer, then you most likely saw the question: which partition structure to use, MBR or GPT.
If you want to learn more or you plan to install a new operating system on a computer, then read on. We have already considered the differences in the boot processes that are worth keeping in mind when breaking the disk or choosing the partition structure.
GPT is a newer and more advanced partition structure, and it has many advantages, which I will list below. MBR is used for a long time, it is stable and has maximum compatibility. Although GPT may eventually override the MBR, because it offers more advanced features, in some cases only the MBR can be used.
MBR is a traditional structure for managing disk partitions. Since it is compatible with most systems, it is still widely used. The master boot record is located in the first sector of the hard disk or, more simply, at the very beginning. It contains a partition table - information about the organization of logical partitions on the hard disk.
The MBR also contains executable code that scans partitions for an active OS and initializes the OS boot procedure.
The MBR disk allows only four main sections. If you need more, you can assign one of the partitions to the extended partition, and you can create more subsections or logical drives on it.
The MBR uses 32 bits to record the partition length expressed in sectors, so each partition is limited to a maximum size of 2 TB.
Benefits
disadvantages
GPT is a newer standard for defining partition structure on disk. To determine the structure, globally unique identifiers (GUIDs) are used.
This is part of the UEFI standard, that is, a UEFI-based system can only be installed on a disk using GPT, for example, this is the requirement of the Windows 8 Secure Boot feature.
GPT allows the creation of an unlimited number of partitions, although some operating systems may limit their number to 128 partitions. Also in GPT there is almost no limit on the size of the partition.
Benefits
disadvantages
The first sector (sector 0) on the GPT disk contains a protective MBR record, in which it is recorded that there is one partition on the disk, which applies to all media. In the case of using old tools that read only MBR disks, you will see one large partition the size of an entire disk. The security record was made so that the old tool did not mistakenly perceive the disk as empty and did not overwrite the GPT data with the new master boot record.
MBR protects GPT data from being overwritten.
Apple MacBooks use GPT by default, so you can't install Mac OS X on an MBR system. Even though Mac OS X can work on the MBR disk, it cannot be installed on it. I tried to do it, but without success.
Most operating systems on the Linux kernel are compatible with GPT. When installing Linux on a disk, GRUB 2 will be installed as a boot loader.
For Windows operating systems, downloading from GPT is possible only on computers with UEFI running under 64-bit versions of Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 and the corresponding server versions. If you bought a laptop with a 64-bit version of Windows 8, then there is likely GPT.
Windows 7 and earlier systems are usually installed on disks with MBR, but you can still convert partitions to GPT, as will be explained below.
All versions of Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 can read and use data from GPT partitions - but they cannot boot from such disks without UEFI.
You can feel comfortable with the MBR, and c GPT. But given the advantages of GPT, mentioned earlier, and the fact of the gradual transition of modern computers to this technology, you may prefer GPT. If the goal is to support old hardware or you need to use a traditional BIOS, then you are stuck on the MBR.
On each hard disk under Windows, you can check the type of partitions using Disk Management (Disk Management). To run Disk Management, do the following:
Press the "hotkeys" of Windows + R, a window opens to launch programs.
Type
Windows will scan the hard drives and soon show them. To check the partition type of any hard disk, right-click on the disk plate at the bottom of the interface. You need to click on "Disk 0", "Disk 1" and so on, and not on sections.
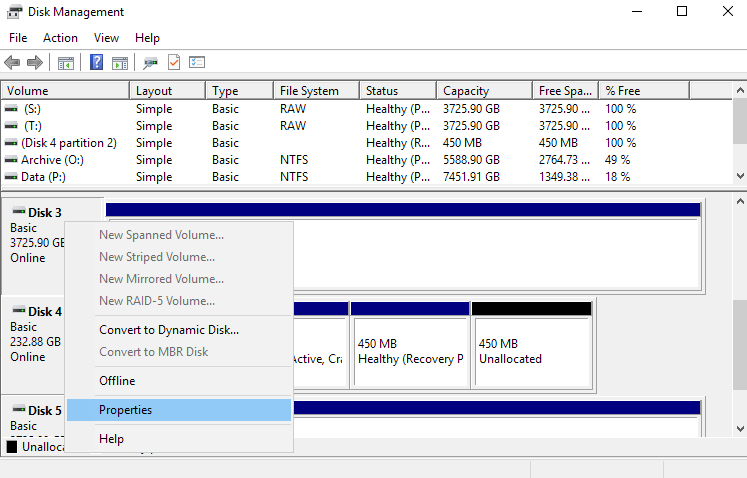
In the context menu that appears, select "Properties". A window opens with the properties of the selected disk.
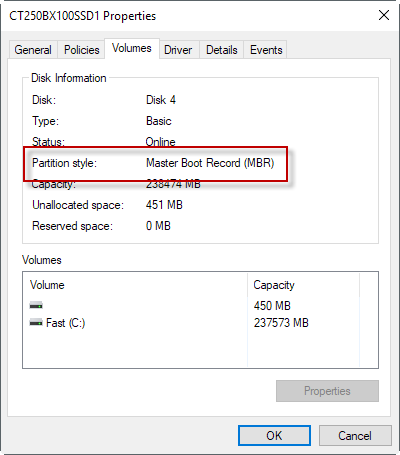
Go to the “Tom” tab and look at the “Section Style” value.
If you prefer the command line, you can choose another option. Its advantages are that it is slightly faster, since it immediately displays disks and partition styles.
All drives are listed. The Gpt column indicates the partition style for each disk. If you see a star in the column, then this is GPT, if it is not there, this is the MBR.
There are two typical error messages that may occur when installing Windows on a hard disk:
When one of these two errors appears, you may not be able to select a partition to install. But this does not mean that something is wrong with the computer.
As you already know, MBR and GPT are two completely different structures of hard disk partitions. MBR is the traditional partition structure, and GPT is the newer one.
Error number 1 occurs when you try to install Windows on a computer with UEFI, and the hard disk partition is not configured for UEFI mode or Legacy BIOS compatibility. Microsoft TechNet offers two solutions to the problem.
Of course, there are third-party utilities for converting disks to GPT with data preservation, but it is still safer to make a backup in case the utility cannot complete the conversion.
Using Windows Setup
Manual conversion
Sometimes it is necessary to convert a disk to the MBR partition structure. For example, if during the installation of Windows you receive the following error message:
“Windows cannot be installed on this disk. The selected disk has GPT partition style. ”
Downloading from GPT is supported only on 64-bit versions of Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 and corresponding server versions on UEFI systems. This error message means that your computer does not support UEFI, and therefore you can only use BIOS, which works with the MBR partition structure.
Microsoft TechNet offers two solutions to the problem.
If you chose the second option, then follow the step-by-step instructions:
Using Windows Setup
Manual conversion
What are disk partitions?
Differences between BIOS and UEFI
MBR and GPT partition tables
The following sources contain additional information about the styles of the MBR or GPT sections:
In this article, we will compare the structure of the GPT and MBR sections; GPT stands for GUID Partition Table, and MBR stands for Master Boot Record. Let's start with the fact that we analyze the process of loading.
The following chapters highlight the differences between the styles of the GPT and MBR sections, including instructions on how to convert between the two styles, and tips on which one to choose.
Understanding the boot process
When you press the power button on your PC, the process starts, which will eventually lead to the loading of the operating system into memory. The first command depends on the structure of the partitions on your hard disk.
')
If two kinds of partition structures: MBR and GPT. The partition structure on the disk defines three things:
- The data structure on the disk.
- The code that is used when booting, if the partition is bootable.
- Where the section begins and ends.
MBR boot process
Let's go back to the boot process. If your system uses the MBR partition structure, the first execution process will load the BIOS. The basic input / output system (Basic Input / Output System) includes the loader firmware. The bootloader firmware contains low-level functions, such as keyboard input, access to a video display, performing disk I / O operations, and code to load the initial stage of the bootloader. Before the BIOS can determine the boot device, it performs a sequence of system configuration functions, starting with the following:
- Power on self test.
- Detection and initialization of the video card.
- Displays the BIOS start screen.
- Perform a quick memory check (RAM).
- Device configuration plug and play.
- Definition of the boot device.
Once the BIOS has detected a boot device, it reads the first disk sector of this device into memory. The first sector of the disk is the master boot record (MBR) of 512 bytes. Three objects fit into this size:
- The first stage of the loader (446 bytes).
- Disk partition table (16 bytes per partition × 4 partitions) - MBR supports only four partitions, more on this below.
- Signature (2 bytes).
At this stage, the MBR scans the partition table and loads the boot sector, Volume Boot Record (VBR), into RAM.
VBR usually contains the Initial Program Loader (IPL), this code initiates the boot process. The initial program loader includes the second stage of the loader, which then loads the operating system. On Windows NT family systems, such as Windows XP, the bootloader first loads another program called NT Loader (abbreviated as NTLDR), which then loads the operating system.
For Linux kernel operating systems, the GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) is used. The boot process is similar to the one described above, the only difference is in the name of the boot loaders in the first and second stages.

In GRUB, the first stage of the bootloader is called GRUB Stage 1. It loads the second stage, known as GRUB Stage 2. The second stage downloads it receives a list of operating systems on hard drives and provides the user with a list for choosing the OS to boot.
GPT boot process
At the same loading stage, the following happens in the GPT partition structure. GPT uses UEFI , in which there is no storage procedure in the boot sector of the first stage of the bootloader such as that of the MBR, followed by a call to the second stage of the bootloader. UEFI — the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface — is a more advanced interface than the BIOS. It can analyze the file system and even upload files by itself.

After turning on your computer, UEFI first performs the functions of the system configuration, as well as the BIOS. This energy management, installation of dates and other components of system management.
UEFI then reads the GPT partition table GUID. GUID stands for “globally unique identifier” (Globally Unique Identifier). GPT is located in the first sectors of the disk, immediately after sector 0, where the master boot record for the Legacy BIOS is still stored.
GPT defines a partition table on the disk where the EFI boot loader recognizes the EFI system partition. The system partition contains boot loaders for all operating systems installed on other partitions of the hard disk. The loader initializes the Windows boot manager, which then loads the operating system.
For operating systems on the Linux kernel, there is a version of GRUB with EFI support, which loads a file, such as grub.efi, or an EFI bootloader, which loads its file, such as elilo.efi.
You may notice that both the UEFI-GPT and the BIOS-MBR transfer control to the bootloader, but do not directly load the operating system. However, UEFI does not need to go through several stages of the bootloader, as in the BIOS. The boot process happens at a very early stage, depending on your hardware configuration.
Differences between GPT and MBR partition structures
If you have ever tried to install Windows 8 or 10 on a new computer, then you most likely saw the question: which partition structure to use, MBR or GPT.
If you want to learn more or you plan to install a new operating system on a computer, then read on. We have already considered the differences in the boot processes that are worth keeping in mind when breaking the disk or choosing the partition structure.
GPT is a newer and more advanced partition structure, and it has many advantages, which I will list below. MBR is used for a long time, it is stable and has maximum compatibility. Although GPT may eventually override the MBR, because it offers more advanced features, in some cases only the MBR can be used.
Master boot record
MBR is a traditional structure for managing disk partitions. Since it is compatible with most systems, it is still widely used. The master boot record is located in the first sector of the hard disk or, more simply, at the very beginning. It contains a partition table - information about the organization of logical partitions on the hard disk.
The MBR also contains executable code that scans partitions for an active OS and initializes the OS boot procedure.
The MBR disk allows only four main sections. If you need more, you can assign one of the partitions to the extended partition, and you can create more subsections or logical drives on it.
The MBR uses 32 bits to record the partition length expressed in sectors, so each partition is limited to a maximum size of 2 TB.
Benefits
- Compatible with most systems.
disadvantages
- Allows only four sections, with the possibility of creating additional subsections on one of the main sections.
- Limits the size of a partition to two terabytes.
- Information about the partition is stored only in one place - in the master boot record. If it is damaged, the entire disk becomes unreadable.
GUID Partition Table (GPT)
GPT is a newer standard for defining partition structure on disk. To determine the structure, globally unique identifiers (GUIDs) are used.
This is part of the UEFI standard, that is, a UEFI-based system can only be installed on a disk using GPT, for example, this is the requirement of the Windows 8 Secure Boot feature.
GPT allows the creation of an unlimited number of partitions, although some operating systems may limit their number to 128 partitions. Also in GPT there is almost no limit on the size of the partition.
Benefits
- Allows unlimited number of sections. The limit is set by the operating system, for example, Windows allows no more than 128 partitions.
Does not limit the size of the partition.It depends on the operating system. The limit on the maximum partition size is larger than the volume of any existing disks today. For disks with sectors of 512 bytes, the maximum size of 9.4 ZB is supported (one zettabyte equals 1,073,741,824 terabytes)- GPT stores a copy of the partition and boot data and can recover data in case of damage to the main GPT header.
- GPT stores checksum values using the Cyclic Redundancy Code (CRC) algorithm to verify the integrity of its data (used to verify the integrity of the GPT header data). In the event of damage, GPT may notice a problem and try to recover the damaged data from another place on the disk.
disadvantages
- May be incompatible with older systems.
GPT vs. MBR
- GPT allows for an unlimited number of primary partitions, while the MBR allows only four primary partitions and the rest is optional.
- GPT allows you to create partitions of any size, while the MBR has a limit of 2 TB.
- GPT stores a copy of the partition data, allowing you to restore it in case of damage to the main GPT header; The MBR stores only one copy of the partition data in the first sector of the hard disk, which can lead to the loss of all information in the event of partition information corruption.
- GPT stores checksum values to verify that the data is not damaged, and can perform the necessary recovery from other areas of the disk in case of damage; MBR has no way to find out about data corruption, you can only find out if the computer refuses to boot or the partition disappears.
Compatible with operating systems
The first sector (sector 0) on the GPT disk contains a protective MBR record, in which it is recorded that there is one partition on the disk, which applies to all media. In the case of using old tools that read only MBR disks, you will see one large partition the size of an entire disk. The security record was made so that the old tool did not mistakenly perceive the disk as empty and did not overwrite the GPT data with the new master boot record.
MBR protects GPT data from being overwritten.
Apple MacBooks use GPT by default, so you can't install Mac OS X on an MBR system. Even though Mac OS X can work on the MBR disk, it cannot be installed on it. I tried to do it, but without success.
Most operating systems on the Linux kernel are compatible with GPT. When installing Linux on a disk, GRUB 2 will be installed as a boot loader.
For Windows operating systems, downloading from GPT is possible only on computers with UEFI running under 64-bit versions of Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 and the corresponding server versions. If you bought a laptop with a 64-bit version of Windows 8, then there is likely GPT.
Windows 7 and earlier systems are usually installed on disks with MBR, but you can still convert partitions to GPT, as will be explained below.
All versions of Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 can read and use data from GPT partitions - but they cannot boot from such disks without UEFI.
So is GPT or MBR?
You can feel comfortable with the MBR, and c GPT. But given the advantages of GPT, mentioned earlier, and the fact of the gradual transition of modern computers to this technology, you may prefer GPT. If the goal is to support old hardware or you need to use a traditional BIOS, then you are stuck on the MBR.
Check hard disk partition type.
On each hard disk under Windows, you can check the type of partitions using Disk Management (Disk Management). To run Disk Management, do the following:
Press the "hotkeys" of Windows + R, a window opens to launch programs.
Type
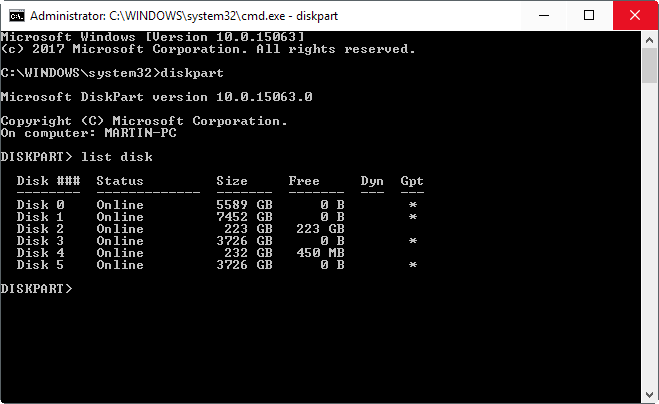
diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.Windows will scan the hard drives and soon show them. To check the partition type of any hard disk, right-click on the disk plate at the bottom of the interface. You need to click on "Disk 0", "Disk 1" and so on, and not on sections.

In the context menu that appears, select "Properties". A window opens with the properties of the selected disk.
Go to the “Tom” tab and look at the “Section Style” value.

If you prefer the command line, you can choose another option. Its advantages are that it is slightly faster, since it immediately displays disks and partition styles.
- Press the Windows key, type
cmd.exe, hold down Ctrl and Shift, press Enter. - Confirm the UAC system privilege escalation message.
- Type
diskpartand press Enter. - Type
list diskand press Enter again.

All drives are listed. The Gpt column indicates the partition style for each disk. If you see a star in the column, then this is GPT, if it is not there, this is the MBR.
Conversion between MBR and GPT during Windows Setup
There are two typical error messages that may occur when installing Windows on a hard disk:
- Error number 1: "Windows can not be installed on this disk. The selected disk does not have GPT partition style. ”
- Mistake number 2: “Windows cannot be installed on this disk. The selected disk has a GPT partition style. ”
When one of these two errors appears, you may not be able to select a partition to install. But this does not mean that something is wrong with the computer.
As you already know, MBR and GPT are two completely different structures of hard disk partitions. MBR is the traditional partition structure, and GPT is the newer one.
Error number 1 occurs when you try to install Windows on a computer with UEFI, and the hard disk partition is not configured for UEFI mode or Legacy BIOS compatibility. Microsoft TechNet offers two solutions to the problem.
- Restart the computer in Legacy BIOS compatibility mode. This option will keep the current section style.
- Reformat disk under UEFI using GPT partition style. This option will allow you to use the UEFI firmware features. Reformatting can be done independently by following the instructions below. Always back up your data before formatting.
Of course, there are third-party utilities for converting disks to GPT with data preservation, but it is still safer to make a backup in case the utility cannot complete the conversion.
Instructions to convert a hard disk from MBR to GPT

Using Windows Setup
- Shut down the computer and insert the Windows boot drive (USB or DVD).
- Boot from it in UEFI mode.
- Choose Custom in the installation type.
- A screen will appear with the message "Where do you want to install Windows?" Select all the partitions on the disk and click "Delete."
- After successful removal, the disk will be a single area of unallocated space.
- Select unallocated space and click Next. Windows will detect that the computer is booted in UEFI mode, and automatically reformat the disk using the GPT partition style. The installation process will start right after that.
Manual conversion
- Shut down the computer and insert the Windows boot drive (USB or DVD).
- Boot from it in UEFI mode.
- From the Windows installation, press Shift + F10 to open the console. After each next command, press Enter.
- Run the diskpart tool with the diskpart command.
- To select a disk for conversion, type
list disk. - Specify the number of the disk to convert:
select disk #. - Clean disk:
clean. - Conversion to GPT is done with the
convert gpt. - Type
exitto exit diskpart. - Close the console and return to the Windows installation.
- When choosing an installation type, select “Other”. The disk will be a single area of unallocated space.
- Select unallocated space and click Next. Windows will start the installation.
Instructions to convert a hard disk from GPT to MBR
Sometimes it is necessary to convert a disk to the MBR partition structure. For example, if during the installation of Windows you receive the following error message:
“Windows cannot be installed on this disk. The selected disk has GPT partition style. ”
Downloading from GPT is supported only on 64-bit versions of Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 and corresponding server versions on UEFI systems. This error message means that your computer does not support UEFI, and therefore you can only use BIOS, which works with the MBR partition structure.
Microsoft TechNet offers two solutions to the problem.
- Reboot the computer in BIOS compatibility mode. This option will keep the current section style.
- Reformat the disk using the MBR partition style. Always back up your data before formatting. Although there are third-party utilities for converting disks to GPT with saving data, it is still safer to make a backup in case the utility can not complete the conversion.
If you chose the second option, then follow the step-by-step instructions:
Using Windows Setup
- Shut down the computer and insert the Windows boot drive (USB or DVD).
- Boot from it in UEFI mode.
- Choose Custom in the installation type.
- A screen will appear with the message "Where do you want to install Windows?" Select all the partitions on the disk and click "Delete."
- After successful removal, the disk will be a single area of unallocated space.
- Select unallocated space and click Next. Windows will detect that the computer is booted in BIOS mode and automatically reformats the disk using the MBR partition style. The installation process will start right after that.
Manual conversion
- Shut down the computer and insert the Windows boot drive (USB or DVD).
- Boot from it in BIOS mode.
- From the Windows installation, press Shift + F10 to open the console. After each next command, press Enter.
- Run the diskpart tool with the diskpart command.
- To select a disk for conversion, type
list disk. - Specify the number of the disk to convert:
select disk #. - Clean disk:
clean. - Conversion to GPT is done with the
convert mbrcommand. - Type
exitto exit diskpart. - Close the console and return to the Windows installation.
- When choosing an installation type, select “Other”. The disk will be a single area of unallocated space.
- Select unallocated space and click Next. Windows will start the installation.
Training videos
What are disk partitions?
Differences between BIOS and UEFI
MBR and GPT partition tables
Sources
The following sources contain additional information about the styles of the MBR or GPT sections:
- Download in UEFI Mode or Legacy BIOS ( Microsoft Technet ) Rehimah
- Download from GPT ( Rod Smith )
- Convert MBR disk to GPT disk ( Microsoft Technet )
- Difference between GPT and MBR ( HowToGeek )
- GUID Partition Table ( Wikipedia )
- Problems using Legacy BIOS when using GPT ( Rod Smith )
- Master Boot Record ( Microsoft Technet )
- FAQ on Windows and GPT ( Microsoft Hardware Dev Center )
- Windows Setup: install using MBR or GPT ( Microsoft Technet ) partition styles
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/327572/
All Articles