How Google Cloud protects its data centers from cybercriminals and internal errors
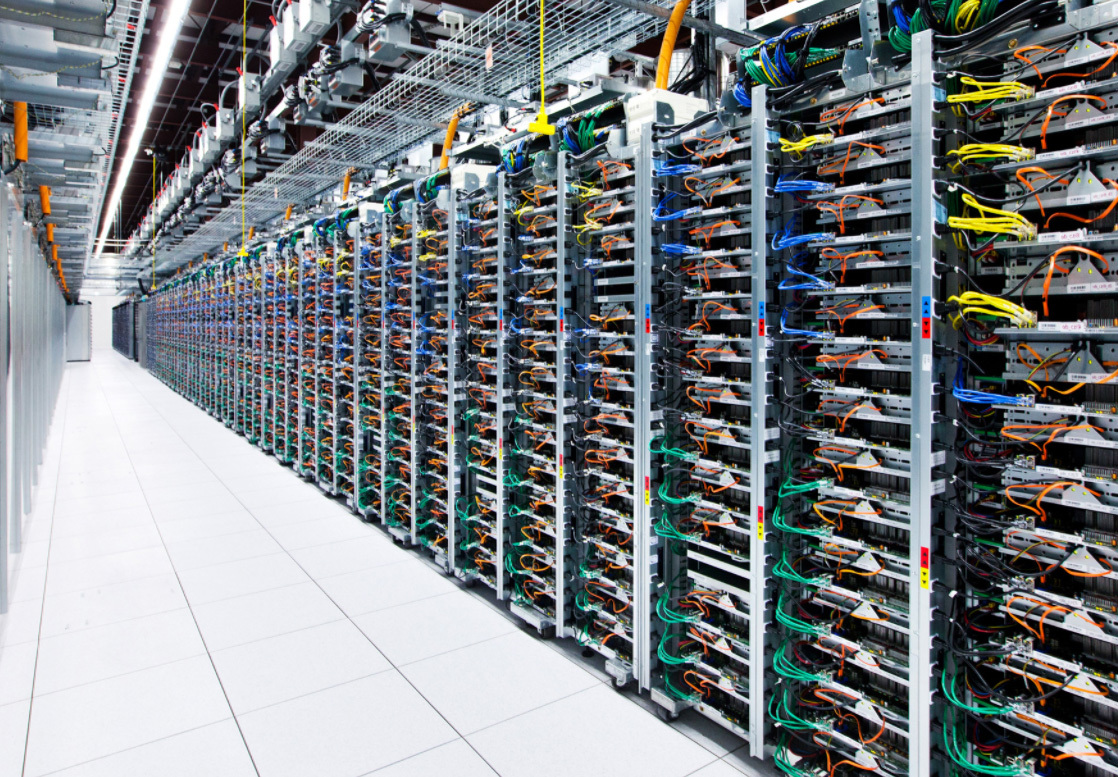

Google Inc. is a provider of services for billions of users. It is clear that the data of users that are stored on servers in Google data centers is a tidbit for cybercriminals. To protect data, the corporation uses several methods of multi-level protection. Now we are talking about the cloud platform Google Cloud, which is designed, for the most part, for business representatives.
The team that secures Google Cloud has about 700 engineers, including programmers, electronics engineers, and representatives of other specialties. Only authorized technical support representatives after a multi-level verification will get into the holy of holies of the company's data centers. Niels Provos, one of the security chiefs, revealed some of the details of his work.
 So, it all starts with a physical check, when an employee wants to go through the main gate in the outer fence of the company's data centers. Only a person whose name is on a special list can pass. Then you need to re-check already at the entrance to one of the buildings inside the perimeter of the fence. If everything is ok here, then the employee is required to pass the third stage of the check at the entrance to the main hall. This is a biometric test - usually we are talking about scanning the iris. Some of these security measures are shown in the video from 2014.
So, it all starts with a physical check, when an employee wants to go through the main gate in the outer fence of the company's data centers. Only a person whose name is on a special list can pass. Then you need to re-check already at the entrance to one of the buildings inside the perimeter of the fence. If everything is ok here, then the employee is required to pass the third stage of the check at the entrance to the main hall. This is a biometric test - usually we are talking about scanning the iris. Some of these security measures are shown in the video from 2014.')
As for the internal areas of the DC, here the whole space is divided into separate zones, each of which has a certain level of tolerance. Such rooms are equipped with additional protection, for example, thermal and laser sensors. In addition, various DC sectors are equipped with metal detectors and dynamic barriers for vehicles. Of course, there are still surveillance cameras that are connected to a “smart” platform that analyzes everything that happens. The platform, in particular, allows to identify the faces of people caught in the frame.
As for the "iron", there is a strict record of all drives. If the disk fails and needs to be replaced, it is initially checked by scanning the bar code and then deleted to erase the data or destroy it. The first stage is always deletion of data. If for some reason the data cannot be completely deleted, or it is very important, then the next stage begins - the physical destruction of the disks with the help of a mechanical system that literally grinds the media into dust. Demonstration of the process of destruction of disks - in the video below.
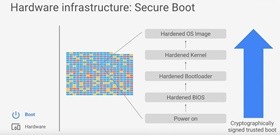
Strict controls also work with any other elements of the infrastructure to ensure that there are no unauthorized changes (randomly or intentionally). In particular, cryptographic signatures are used for this purpose. This infrastructure protection method works at all levels - from the BIOS, bootloaders, kernel, other OS elements used by the corporation. All this is created by the company and controlled by it.
In particular, we are talking about hardware methods, including specialized chips, which are embedded into routines developed by Google. One of these chips is Titan. His corporation <a
href = " blog.google/topics/google-cloud/bolstering-security-across-google-cloud "> presented last month without providing technical details of its work. It is only known that this is a custom security chip that is designed to prevent interference at the BIOS level, and also monitors and identifies the services and hardware that runs in Google data centers. This chip can monitor the connected equipment in order to ensure its safety. Now Titan is installed on servers.

In the Google ecosystem, all executable files are signed with a special cryptographic key, and the data is encrypted when written to disk. In addition to this, cryptographic keys are stored in RAM as much as they are needed. Remote connections and all other communication methods between data centers are encrypted by default.
Security is enhanced by special software. For example, all the services of a company interact with each other, “proving” that they are exactly what they are.
Fighting DDoS
The infrastructure of the company is designed to absorb weak DDoS attacks. In addition, the company has established intermediate layers of defense in order to make attacks of this type safe. For example, the Google Front End engine (GFE) was created specifically to absorb traditional types of attacks without harming infrastructure and services.
And in order to protect themselves in case a really dangerous attack comes, the company has its own communication channel - an underwater Internet backbone. True, it was the only one about 9 years ago, now the company operates independently or in partnership with someone else with several highways. This allows the company to withstand the attack of any power.
In addition, Google continues to increase the throughput of its DC. For example, in the latest generation of Jupiter infrastructure in the company's data centers, the width of the channels has been increased more than 100 times. One communication channel Jupiter can operate at a speed of 1 petabit per second. This channel is enough so that 100000 can be connected with themselves at any time and effectively repel DDoS attacks.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/327260/
All Articles