How to use a token to make a Windows domain safer? Part 1

Some of you have probably heard about the incident that was made public recently. The American semiconductor manufacturer Allegro MicroSystem LLC sued its former IT specialist for sabotage. Nimesh Patel, who has worked for the company for 14 years, destroyed important financial data in the first week of the new fiscal year.
How did this happen?
Two weeks after his dismissal, Patel went to the territory of the company's headquarters in Worcester (Massachusetts, USA) in order to catch a corporate Wi-Fi network. Using the credentials of a former colleague and a working laptop, Patel logged into the corporate network. Then he introduced the code into the Oracle module and programmed its implementation on April 1, 2016, the first week of the new fiscal year. The code was intended to copy certain headers or pointers into a separate database table and then remove them from the module. Exactly on April 1 data was deleted from the system. And since the attacker logged into the Allegro network legally, his actions were not immediately noticed.
The general public does not know the details, but most likely the incident was made possible largely due to the fact that the company used password authentication to access the network. Surely there were other security problems, but it is the password that can be stolen unnoticed by the user and the fact that the password is stolen will not be detected, at best, until the use of the stolen credentials is used.
The use of strong two-factor authentication and the ban on the use of passwords in combination with a sound security policy could help, if not avoid the described development of events, then greatly complicate the implementation of such a plan.
We will talk about how you can significantly improve the security of your company and protect yourself from such incidents. You will learn how to configure authentication and signature of important data using tokens and cryptography (both foreign and domestic).
In the first article, we will explain how to configure strong two-factor authentication using PKI when logging into a domain account in Windows.
In the following articles we will tell you how to set up Bitlocker, protect email and the simplest workflow. We will also set up secure access to corporate resources and secure remote access via VPN.
Two-factor authentication
Experienced system administrators and security services are well aware that users are extremely unconscious about compliance with security policies, they can write their credentials on a sticker and stick it next to the computer, pass passwords to their colleagues, and the like. Especially often this happens when the password is complex (containing more than 6 characters and consisting of letters of different register, numbers and special characters) and it is difficult to remember. But such policies are set by administrators for a reason. This is necessary to protect the user account from simply dictionary passwords. Also, administrators recommend changing passwords at least once every 6 months, simply from the consideration that during this time it is theoretically possible even to reset a complex password.
Let's remember what authentication is. In our case, this is the process of verifying the authenticity of a subject or object. User authentication is the process of authenticating a user.
And two-factor authentication is such an authentication, in which you need to use at least two different ways to confirm your identity.
The simplest example of two-factor authentication in real life is a safe with a lock and code combination. To open such a safe you need to know the code and own the key.
Token and smart card
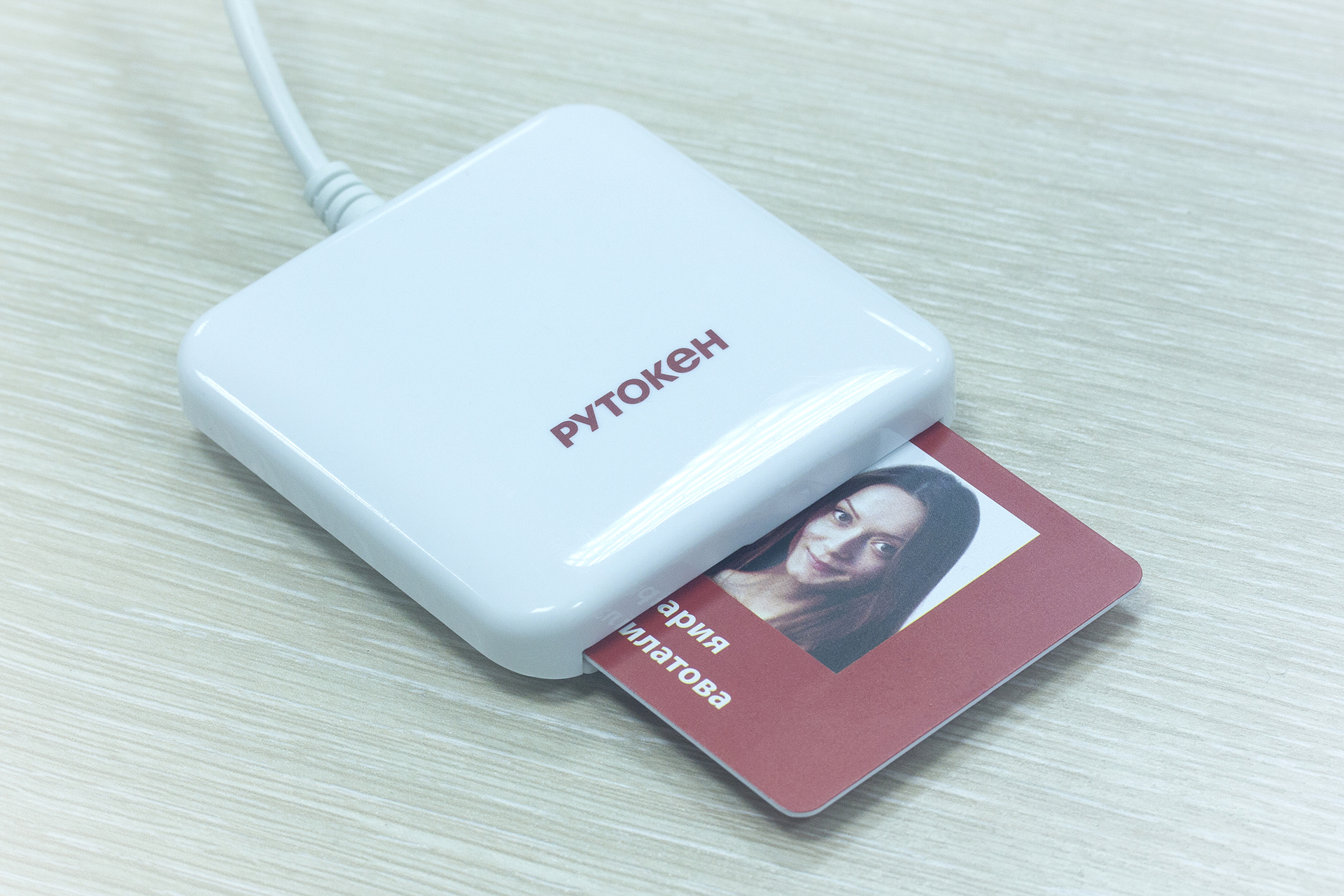
Probably the most reliable and easy to implement method of two-factor authentication is the use of a cryptographic token or a smart card. A token is a USB device that is both a reader and a smart card at the same time. The first factor in this case is the fact of possession of the device, and the second is the knowledge of its PIN-code.
Use a token or a smart card, then to someone, which is more convenient. But historically, it turned out that in Russia, tokens are more accustomed to using tokens, since they do not require the use of embedded or external smart card readers. Tokens have their drawbacks. For example, you can’t print a photo on it.
The photo shows a typical smart card and reader.

But back to corporate security.
And we start with the Windows domain, because in most companies in Russia, the corporate network is built around it.
As you know, Windows domain policies, user settings, group settings in Active Directory provide and differentiate access to a huge number of applications and network services.
By protecting an account in the domain, we can protect most, and in some cases, all internal information resources.
Why is two-factor domain-token authentication with a PIN code safer than a regular password scheme?
The PIN code is tied to a specific device, in our case to a token. Knowledge of the PIN-code in itself does not give anything.
For example, a PIN from a token can be dictated over the phone to others and it will not give anything to an attacker if you are careful enough about the token and do not leave it unattended.
With a password, the situation is completely different, if an attacker picked up, guessed, spied, or somehow took possession of a password from an account in the domain, then he will be able to freely enter both the domain itself and other services of the company that use this same account.
The token is a unique non-replicable physical object. It has a legitimate user. Two-factor authentication by token can be bypassed only when the administrator intentionally or due to an oversight left for this “loopholes” in the system.
Advantages of entering the domain by token
The PIN from the token is easier to remember, since it can be much easier than a password. Everyone probably saw at least once in their life how an “experienced” user could not painfully authenticate himself in the system with several attempts, remembering and entering his “secure” password.
The PIN code does not need to be constantly changed, since the tokens are more resistant to brute force PIN codes. After a number of unsuccessful input attempts, the token is blocked.
When using a token for a user, the login is as follows: after booting the computer, it simply connects the token to the USB port of the computer, enters 4-6 digits and presses the Enter button. The speed of entering numbers for ordinary people is higher than the speed of entering letters. Therefore, the PIN is entered faster.

Tokens allow you to solve the problem of "abandoned workplace" - when a user leaves his workplace and forgets to log out of his account.
Domain policy can be configured so that the computer is automatically blocked when removing the token. Also, the token can be equipped with an RFID tag for the passage between company premises, therefore, without taking the token from his workplace, the employee simply cannot move around the territory.
Disadvantages, where do without them
Tokens or smart cards are not free (decided by the budget).
They need to be taken into account, administered and maintained (solved by token management systems and smart cards).
Some information systems may “out of the box” not support authentication by tokens (solved by systems like Single Sign-On — designed to enable the organization to use a single account to access any area resources).
Configuring two-factor authentication in the Windows domain
Theoretical part:
The Active Directory directory service supports authentication using a smart card and a token, starting with Windows 2000. It is embedded in the public key initialization (PKINIT) extension for the Kerberos RFC 4556 protocol.
The Kerberos protocol was specifically designed to provide strong user authentication. It can use centralized storage of authentication data and is the basis for building Single Sing-On mechanisms. The protocol is based on the key entity Ticket (ticket).
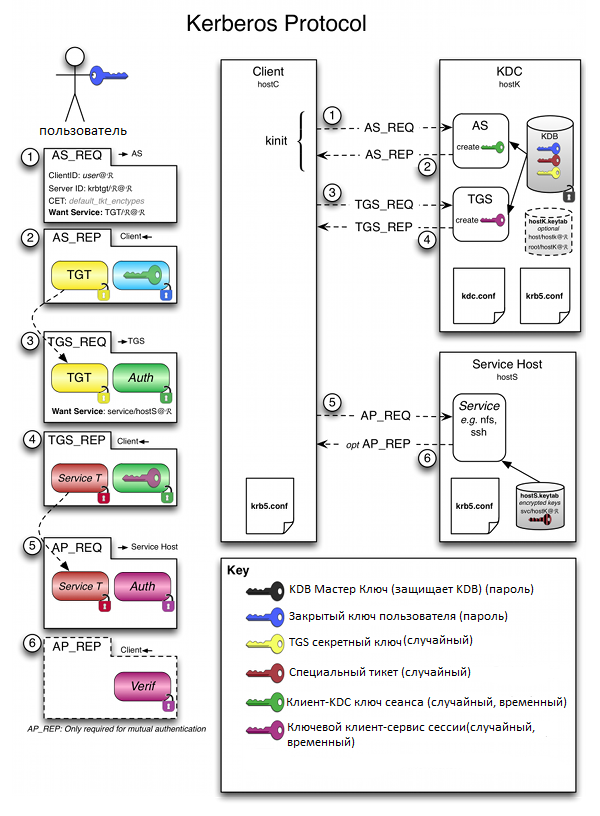
A ticket is an encrypted data packet that is issued by a trusted authentication center in terms of the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC).
When a user performs primary authentication after successfully verifying its authenticity, the KDC issues a primary user identity for accessing network resources — the Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT).
Later, when accessing individual network resources, the user submits the TGT, receives an identity from the KDC for access to a specific network resource - Ticket Granting Service (TGS).
One of the advantages of the Kerberos protocol, which provides a high level of security, is that, for any interactions, neither passwords nor password hash values are transmitted in the clear.
The PKINIT extension allows you to use two-factor authentication by tokens or smart cards during the Kerberos pre-authentication stage.
Logon can be provided by using both the domain’s directory service and the local directory service. A TGT is created based on an electronic signature that is calculated on a smart card or token.
All domain controllers must have the Domain Controller Authentication, or Kerberos Authentication certificate installed, as the client and server mutual authentication is implemented.
Practice:
We proceed to the setting.
We will make it so that you can enter the domain under your account only upon the presentation of the token and knowing the PIN code.
For the demonstration, we will use Rutoken EDS PKI manufactured by “Aktiv” company.
')
Stage 1 - Setting up the domain First, install the certification services.
Disclaimer
This article is not a tutorial on the implementation of corporate PKI. Issues of design, deployment and competent application of PKI are not considered here due to the immensity of this topic.
All domain controllers and all client computers within the forest where the implementation of such a solution is being implemented must necessarily trust the Root Certification Authority (Certificate Authority).
The task of the certification authority is to verify the authenticity of encryption keys using electronic signature certificates.
Technically, a certification authority is implemented as a component of a global directory service responsible for managing users' cryptographic keys. Public keys and other information about users are stored by certification authorities in the form of digital certificates.
A certificate authority issuing certificates for using smart cards or tokens must be placed in the NT Authority repository.
Go to Server Manager and select Add Roles and Components.
When adding server roles, select Active Directory Certificate Services (Microsoft strongly recommends not doing this on a domain controller, so as not to stumble on performance problems). In the window that opens, select "Add components" and select "Certification Authority".
On the page to confirm the installation of components, click "Install".
Stage 2 - Setting the entrance to the domain using a token
To log in, we need a certificate that contains the Smart Card Logon and Client Authentication identifiers.
The certificate for smart cards or tokens must also contain the user's UPN (suffix for the member's name). By default, the user principal name suffix for the account is the DNS domain name that contains the user account.
The certificate and private key must be placed in the appropriate sections of the smart card or token, and the private key must be located in the protected memory area of the device.
The certificate must contain the path to the distribution point of the certificate revocation list (CRL distribution point). This file contains a list of certificates with the certificate’s serial number, revocation date and reason for revocation. It is used to transmit information about revoked certificates to users, computers, and applications trying to verify the authenticity of the certificate.
Configure the installed certification services. In the upper right corner, click on the yellow triangle with an exclamation mark and click "Configure Certificate Services ...".
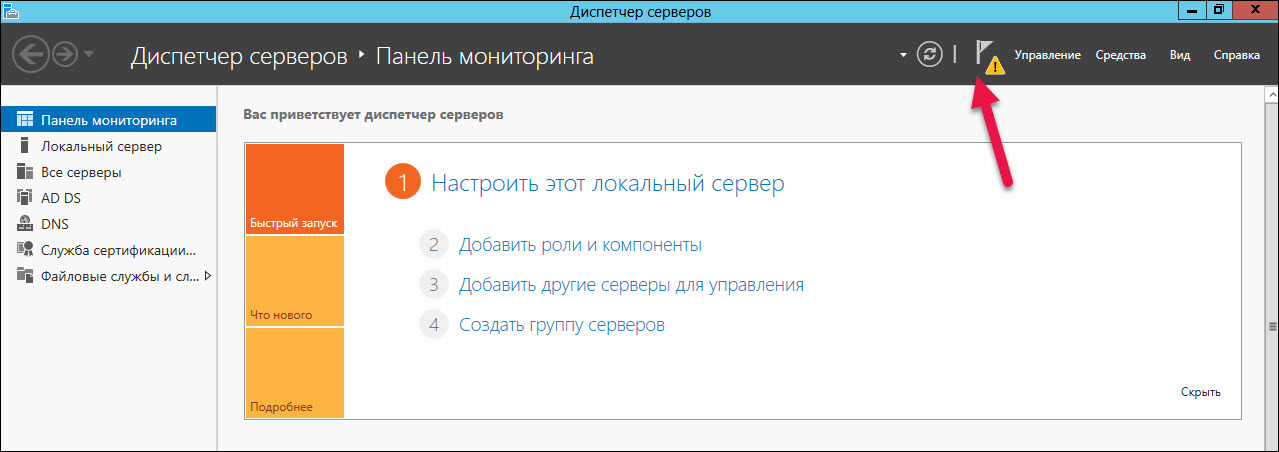
In the "Credentials" window, select the required user credentials to configure the role. Select "Certification Authority".
Select "Enterprise CA".
CA's enterprises are integrated with AD. They publish certificates and certificate revocation lists in AD.
Specify the type of "root CA".
In the next step, select “Create a new private key”.
Select the validity period of the certificate.
Stage 3 - Adding Certificate Templates
To add certificate templates, open the Control Panel, select “Administration” and open the Certificate Authority.
Click on the name of the folder "Certificate Templates", select "Management".
Click on the “Smart Card User” template name and select “Copy Template”. The following screenshots show which parameters in the “New Template Properties” window need to be changed.
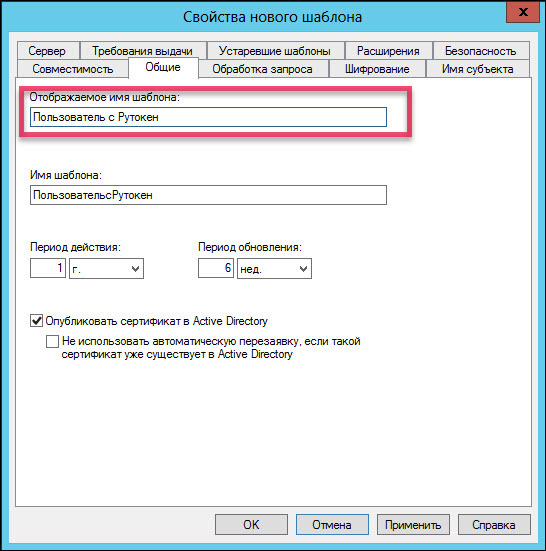
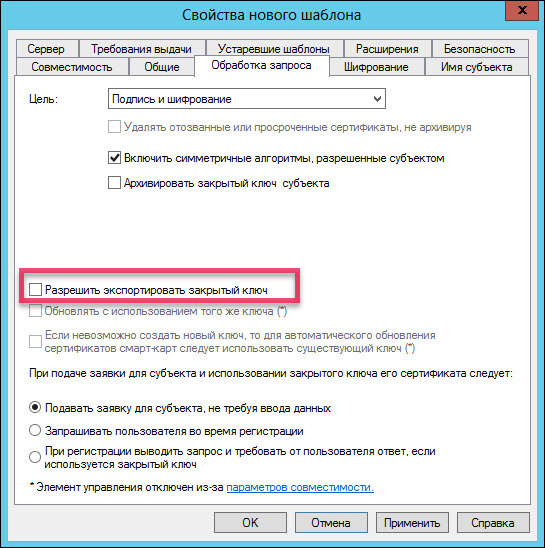
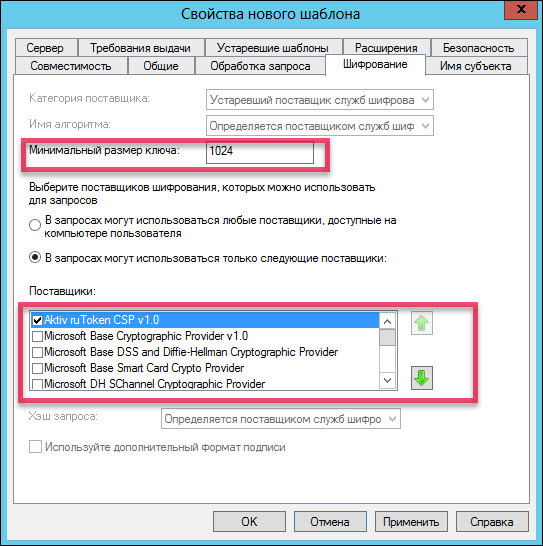
If there is no “Aktiv ruToken CSP v1.0” in the list of suppliers, then you need to install the “Rutoken for Windows drivers” kit.
Starting with Windows Server 2008 R2, instead of a special provider from the manufacturer, you can use the Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider.
For Rutoken devices, the mini-driver library, which supports the Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider, is distributed through Windows Update.
You can check whether the “minidriver” is installed on your server by connecting Rutoken to it and looking in the device manager.
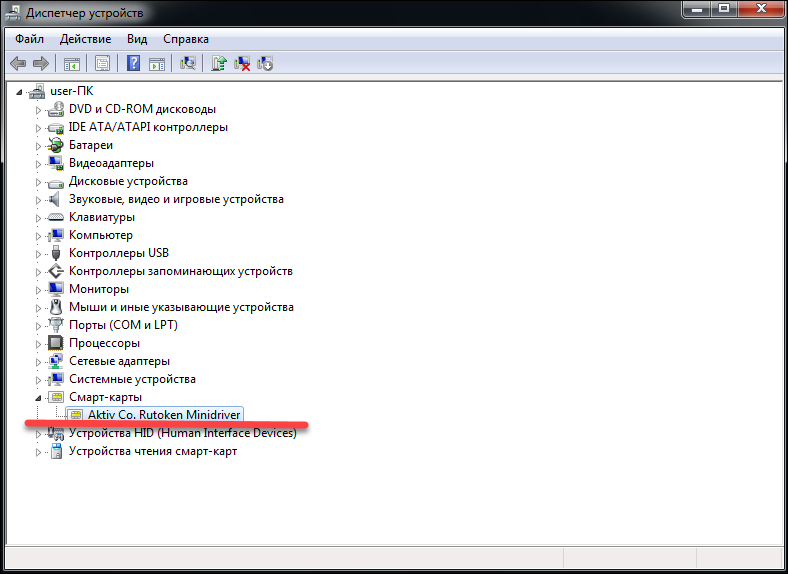
If for some reason there is no “mini driver”, you can install it forcibly by installing the “Rutoken drivers for Windows” kit, and then use the “Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider”.
The Rutoken Drivers for Windows kit is distributed free of charge from the Rutoken website.
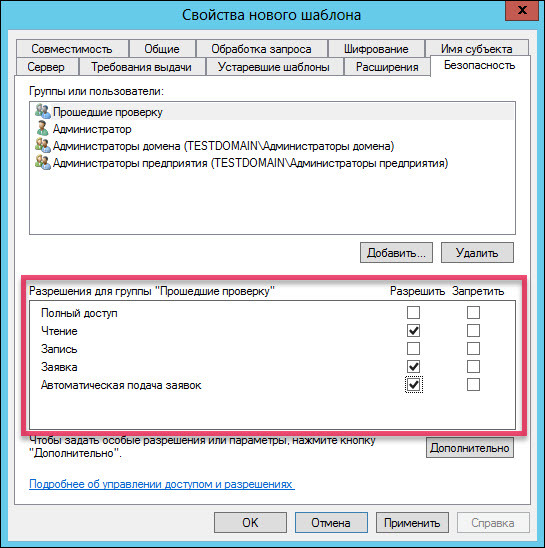
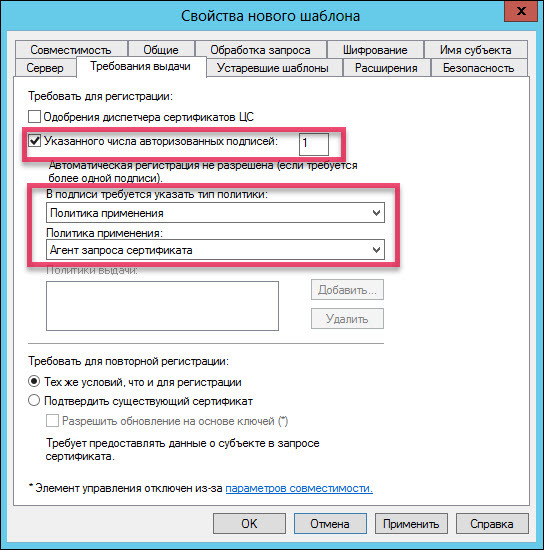
Add two new templates “Certification Agent” and “User with Rutoken”.
Next, we need to issue a certificate to the domain administrator. Open the Run service and specify the mmc command. Add the Certificates snap-in.
In the "Certificate Manager Snap-in" window, select "my user account". In the Add / Remove Snap-in window, confirm the addition of certificates.
Select the Certificates folder.
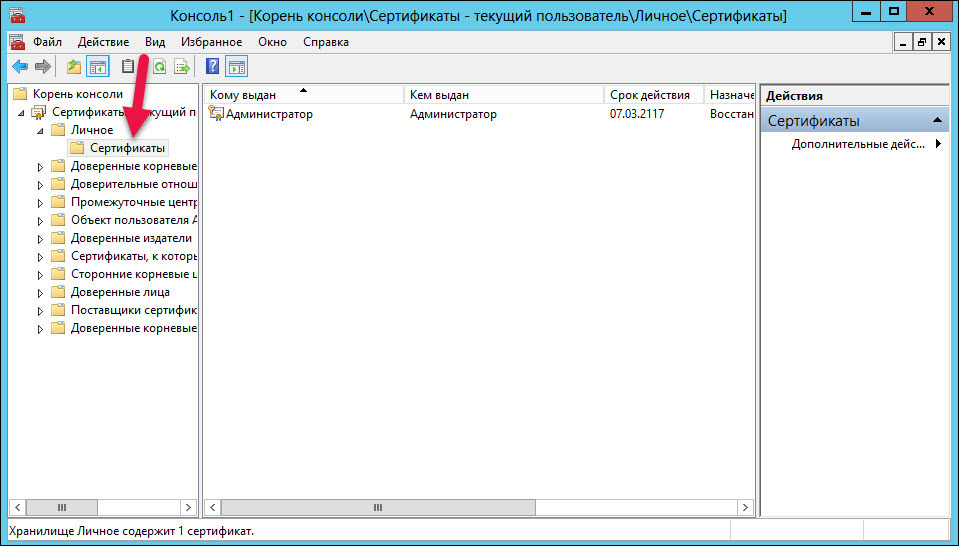
Request a new certificate. The page for registering the certificate will open. At the certificate request stage, select the “Administrator” registration policy and click “Application”.
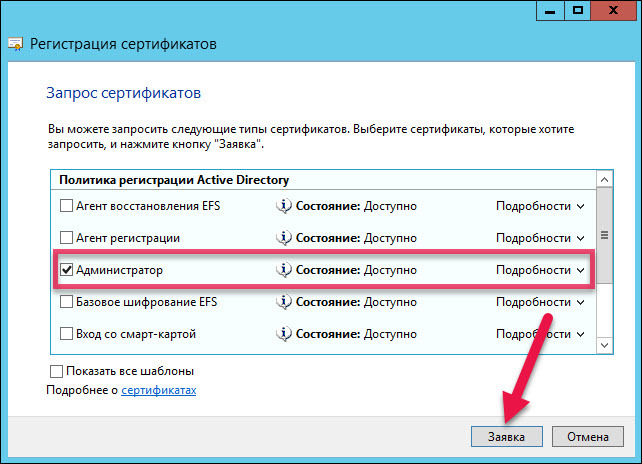
In the same way, request a certificate for the Registration Agent.
To request a certificate for a specific user, click "Certificates", select "Register as.".
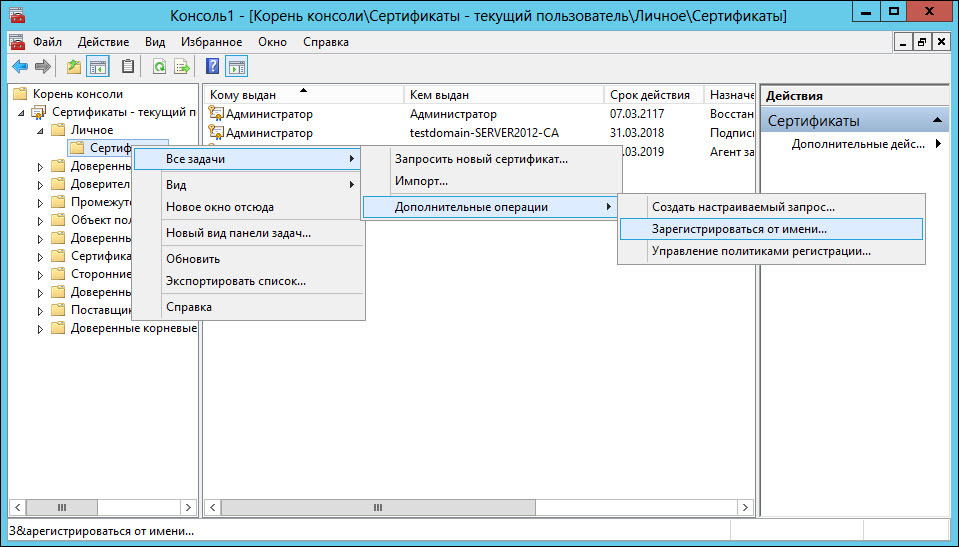
In the window for the certificate request, select the "User with Rutoken" checkbox.
Now you need to select a user.
In the field "Enter the names of the selected objects" enter the user name in the domain and click "Check Name".
In the window to select a user, click "Request".
In the drop-down list, select the name of the token and enter the PIN.
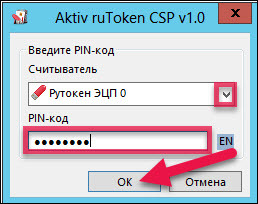
In the same way, select certificates for other users in the domain.
Stage 4 - Setting Up User Accounts
To set up accounts, open the list of users and AD computers.
Select the Users folder and the "Properties" item.
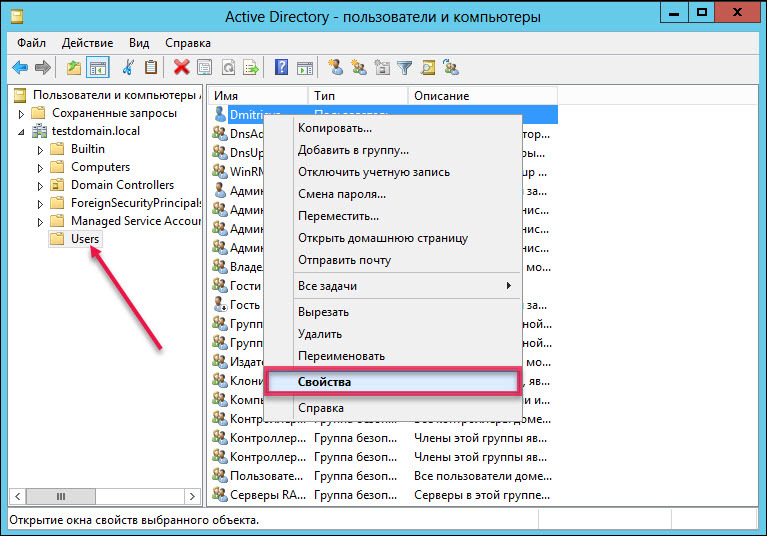
Go to the “Accounts” tab, check the box “You need a smart card for interactive logging into the network”.

Configure security policies. To do this, open the Control Panel and select "Administration". Open the menu to manage Group Policy.
In the left pane of the Group Policy Management window, click the Default Domain Policy and select Edit.

In the left part of the Group Policy Management Editor, select Security Settings.
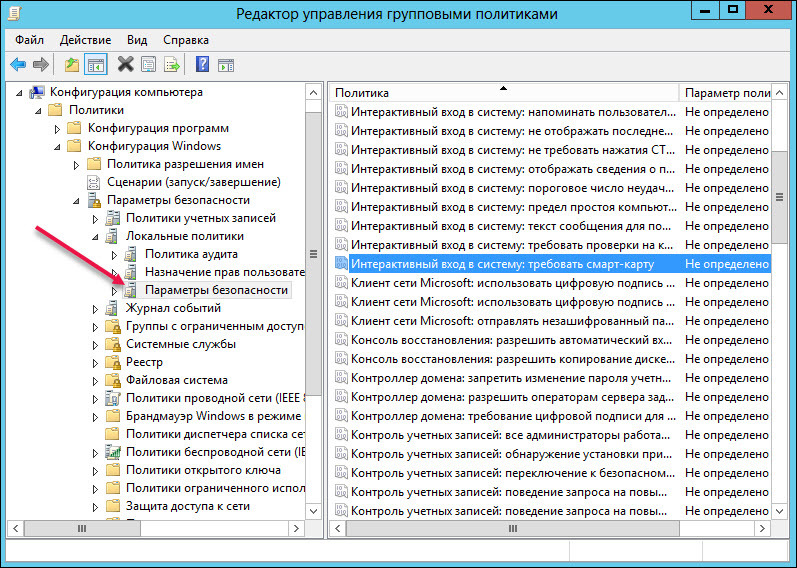
Open the Interactive Login: Require Smart Card policy.
On the Security Policy Settings tab, select the Define Next Policy Setting and Enabled checkboxes.
Open the Interactive Logon: Smart Card Removal Behavior policy.
On the "Security Policy Settings" tab, select the "Define the following policy setting" checkbox, from the drop-down list, select "Lock Workstation".
Reboot the computer. And the next time you try to authenticate to the domain, you can already use the token and its PIN.
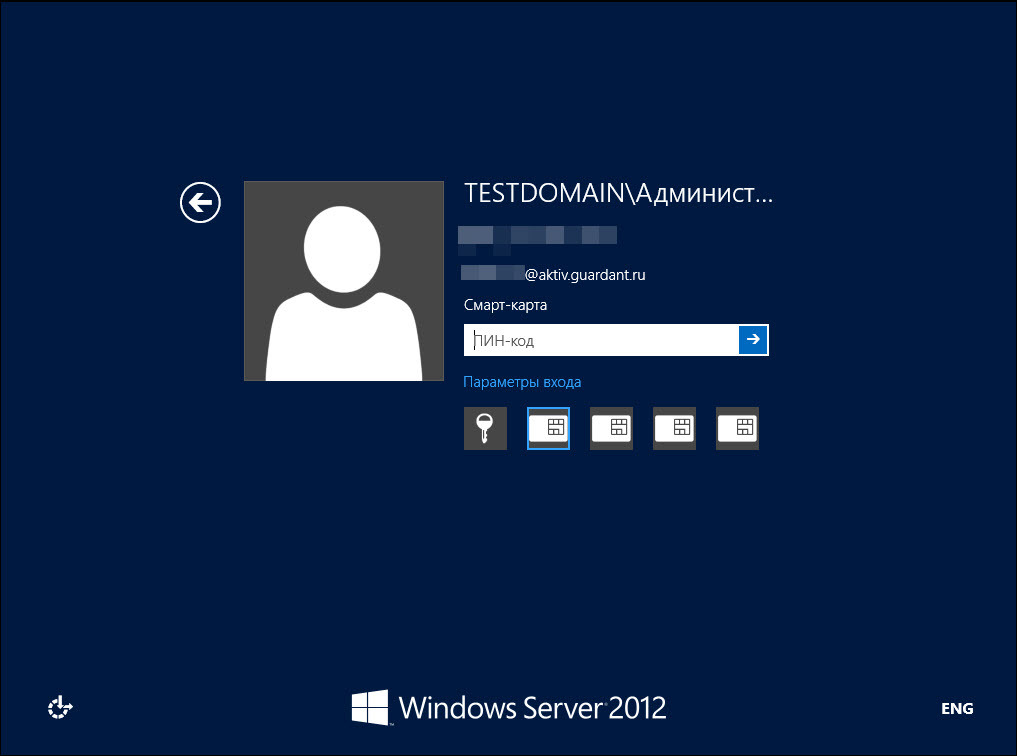
BINGO!
Two-factor authentication to log on to the domain is configured, which means that the level of security for logging on to the Windows domain is significantly improved without spending a hefty amount on additional protection. Now, no login is possible without a token, and users can breathe easy and not suffer with complex passwords.
The next step is secure mail, about this and setting up secure authentication in other systems, read our next articles.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/327232/
All Articles