Scientists from ITMO University have proposed a new system for the transmission of energy over a distance
Scientists from ITMO University have developed a prototype device for wireless energy transfer, which is based on dielectric resonator disks. The efficiency of the technology reaches 90%, while it is consistent even if the relative position of the source and receiver changes.
 / Siez18 / Pixabay / PD
/ Siez18 / Pixabay / PD
In 2009, a group of scientists from MIT showed that it is possible to transfer energy over a distance of two meters with an efficiency of 45%. This was achieved by the interaction of two copper coils. One coil was connected to an alternating current source, which forms a magnetic field in it. The magnetic field, reaching the second coil (having the same resonant frequency), created an alternating current that ignited a 60-watt light bulb.
')
Based on this and several other papers, a team of scientists from the ITMO University began developing a new system of wireless energy transmission. Copper coils were replaced by dielectric ceramic resonators, in which a magnetic field is excited with less energy loss.
The first prototype of the system transmitted 1 W of power over a distance of 20–30 cm at a frequency of 2 GHz. In their new work, scientists have made some improvements. For example, samples of ceramics with a high dielectric constant were developed. For new samples, the value of this characteristic is 1 thousand, which is a hundred times higher than that of ordinary ceramics and ten times higher than that of the original prototype.
This material has allowed to increase the distance of energy transfer, as well as switch to operating frequencies of hundreds of megahertz. Earlier, the effectiveness of the Russian prototype dropped to 50% already at a distance of 2 cm, now it reaches 90% at a distance of up to 10 cm and decreases only at 16 cm. More details about the principles of the system can be read in a published study ( link ).
“We were able to five times increase the distance that energy can be transferred [compared to the first prototype], and made the system more resistant to displacement and rotation of the resonators relative to each other. In the future, this will give more freedom to the user, ” explains Polina Kapitanova, a researcher at the Department of Nanophotonics and Metamaterials at ITMO University. - The third global change has affected the design of the resonators. Now it is two disks. Unlike the spherical shape previously used by us, the flat configuration is practical and allows us to talk about the application of our technology in more compact devices. ”
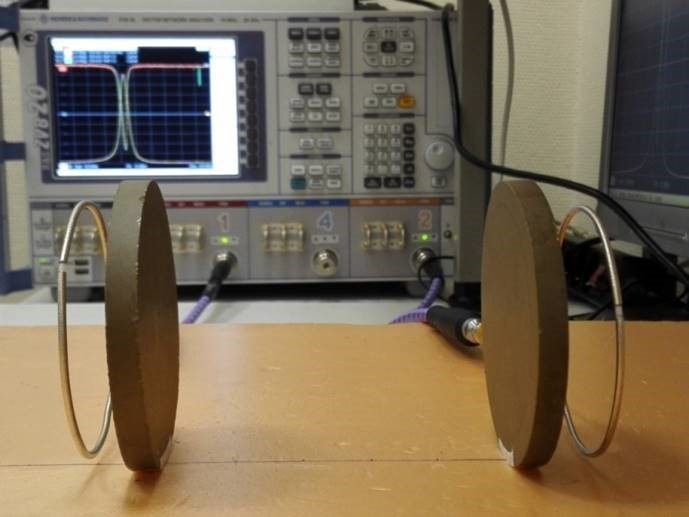 Wireless Power Transmission System / ITMO University
Wireless Power Transmission System / ITMO University
These recent improvements have allowed the development of the ITMO University to be equal in efficiency to their foreign counterpart, WiTricity. However, the Russian prototype is more resistant to changes in the mutual orientation of the receiver and the energy source. According to the statements of scientists, when the discs are moved a distance of 4–5 cm, the transfer of energy is not interrupted. The “signal” remains stable even when turning one disc at an angle of up to 60 degrees.
The market of wireless power transmission is one of the most actively developing. It is expected that in 2020 its value will reach $ 11 billion with an average annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23%. Now researchers are working on various options for the application of technology, in parallel working on reducing the size of the resonators. Their diameter of 8.5 cm makes it difficult to use the experience in mobile devices, so for now, scientists suggest using technology in electric vehicles.
“Such wireless systems can be useful for recharging cars,” says Polina Kapitanova. “Microwave ceramics are capable of working at higher powers than if they were made from metals that, by their nature, heat up quickly.”
Another application of technology that developers are considering is the creation of combined systems. One part of the system (ceramic disk) will be built into the work surface, for example, a kitchen table, and the other into electrical appliances, say, an electric kettle. This will allow you to create multifunctional surfaces that can simplify the handling of equipment. In the future, scientists also plan to create resonators, the work of which is not affected by their mutual arrangement.
PS What else do we write in our blog:
 / Siez18 / Pixabay / PD
/ Siez18 / Pixabay / PDIn 2009, a group of scientists from MIT showed that it is possible to transfer energy over a distance of two meters with an efficiency of 45%. This was achieved by the interaction of two copper coils. One coil was connected to an alternating current source, which forms a magnetic field in it. The magnetic field, reaching the second coil (having the same resonant frequency), created an alternating current that ignited a 60-watt light bulb.
')
Based on this and several other papers, a team of scientists from the ITMO University began developing a new system of wireless energy transmission. Copper coils were replaced by dielectric ceramic resonators, in which a magnetic field is excited with less energy loss.
The first prototype of the system transmitted 1 W of power over a distance of 20–30 cm at a frequency of 2 GHz. In their new work, scientists have made some improvements. For example, samples of ceramics with a high dielectric constant were developed. For new samples, the value of this characteristic is 1 thousand, which is a hundred times higher than that of ordinary ceramics and ten times higher than that of the original prototype.
This material has allowed to increase the distance of energy transfer, as well as switch to operating frequencies of hundreds of megahertz. Earlier, the effectiveness of the Russian prototype dropped to 50% already at a distance of 2 cm, now it reaches 90% at a distance of up to 10 cm and decreases only at 16 cm. More details about the principles of the system can be read in a published study ( link ).
“We were able to five times increase the distance that energy can be transferred [compared to the first prototype], and made the system more resistant to displacement and rotation of the resonators relative to each other. In the future, this will give more freedom to the user, ” explains Polina Kapitanova, a researcher at the Department of Nanophotonics and Metamaterials at ITMO University. - The third global change has affected the design of the resonators. Now it is two disks. Unlike the spherical shape previously used by us, the flat configuration is practical and allows us to talk about the application of our technology in more compact devices. ”

These recent improvements have allowed the development of the ITMO University to be equal in efficiency to their foreign counterpart, WiTricity. However, the Russian prototype is more resistant to changes in the mutual orientation of the receiver and the energy source. According to the statements of scientists, when the discs are moved a distance of 4–5 cm, the transfer of energy is not interrupted. The “signal” remains stable even when turning one disc at an angle of up to 60 degrees.
Future of the project
The market of wireless power transmission is one of the most actively developing. It is expected that in 2020 its value will reach $ 11 billion with an average annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23%. Now researchers are working on various options for the application of technology, in parallel working on reducing the size of the resonators. Their diameter of 8.5 cm makes it difficult to use the experience in mobile devices, so for now, scientists suggest using technology in electric vehicles.
“Such wireless systems can be useful for recharging cars,” says Polina Kapitanova. “Microwave ceramics are capable of working at higher powers than if they were made from metals that, by their nature, heat up quickly.”
Another application of technology that developers are considering is the creation of combined systems. One part of the system (ceramic disk) will be built into the work surface, for example, a kitchen table, and the other into electrical appliances, say, an electric kettle. This will allow you to create multifunctional surfaces that can simplify the handling of equipment. In the future, scientists also plan to create resonators, the work of which is not affected by their mutual arrangement.
PS What else do we write in our blog:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/326644/
All Articles