Hello, who is calling or determining the number in Asterisk
Given the specifics of telephone networks in Russia, problems with determining the number when setting up analog GTS lines on Asterisk occur quite often. The diversity of GATS and the quality of telephone lines mounted during the USSR times always present problems for integrators of IP PBXs.

An IP PBX Asterisk was installed, and successfully used. After some time, it became possible to connect the number identifier, since city lines were transferred to a digital GATS with CallerID support, before that the lines were connected to an analog GATS (yes, analog PBXs are still alive), but the identification did not work.
To begin with, let's look at some theoretical information about what standards there are for determining a phone number.
Number Theory
AON (also called Russian AON) - the work of the Soviet analog GATS, was distributed in the early 90s, but still occurs. Information about the caller's number is transmitted in the form of a code bearing the name "Without Interval Package." It is not a service as such, since it was not intended for subscribers. The phone number is transmitted in the form of 7 digits. A telephone device that supports caller ID when an incoming call "picks up the phone" and reads the service signals of the telephone exchange, while the call signal is simulated for the caller. At Asterisk, this type of number identifier cannot be made to earn.
')
CallerID (also known as Euro AON) is a service provided on digital GATS. Method for sending a request and receiving Caller ID information in the interval between calls. That is, in contrast to the caller ID here is not "lifting the tube." There are several standards in CallerID:
Bellcore-standard is used in the USA, Canada, Australia, China, Hong Kong, Singapore, Italy and some telephone companies in the UK.
DTMF-standard: the digits of the number are transmitted in the same way as the tone dialing - short dual-frequency parcels.
FSK-standard: The data stream is transmitted by frequency modulation before the first or before the second call on the line. Experience has shown that most digital GATS Rostelecom work on this standard.
Practice or why nothing works
To determine the number in DAHDI channels in most cases, adding the following lines in chan_dahdi.conf is enough:
chan_dahdi.conf
If the identification of the number did not work, I recommend to start by connecting a regular telephone with CallerID support and see if the definition works on it. In our case, the number on the TA was determined without problems, but on Asterisk did not want to. Moreover, when connecting the TA parallel to the asterisk, the definition ceased to work on the phone.
We proceed to further analysis. Let's write the audio channel of the line and analyze the recording in the audio editor. In it we will try to find the CallerID data.
The first dahdi channel is recorded by the following command:
We start the recording team and call our line. After this, we stop the execution of dahdi_monitor, as a result we will have the file streamrx.wav. Copy it to yourself and open it in an audio editor (for example Audacity).
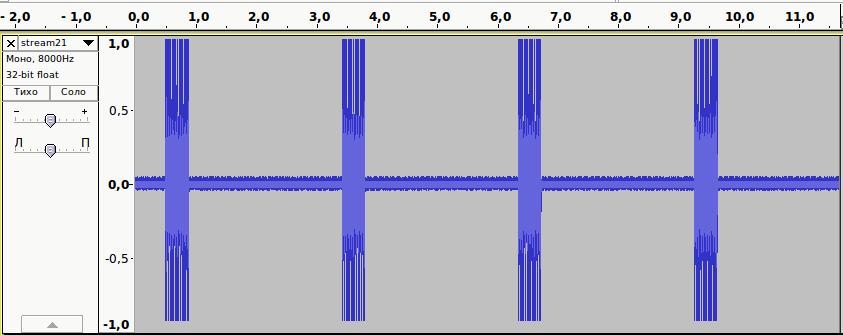
Apparently no data callerid does not come to us. Since the usual phone number determines, it can be assumed that there are problems with the equipment (board or FXO module).
We put the working FXO module into the board and check it again.
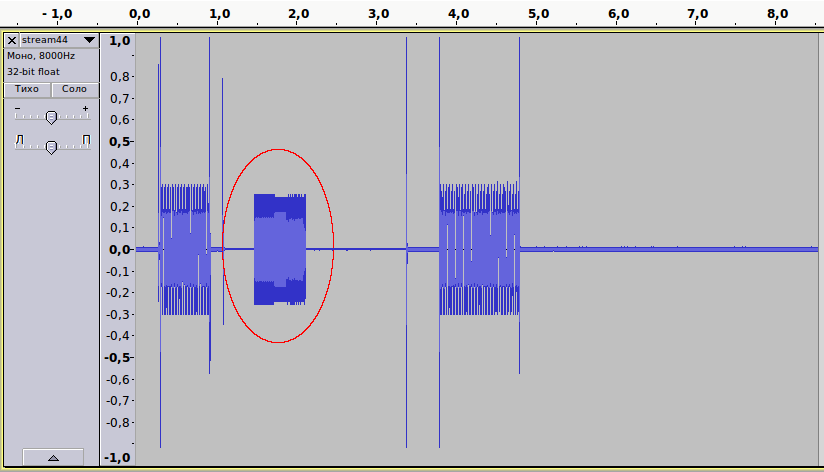
Now, the identification of the number works without problems, we see the CallerID data in the FSK standard on the record. As you can see, in this case there was a problem with the module.
Repair FXO Module
FXO modules of different manufacturers for analog cards are built almost according to the same scheme based on two microcircuits: SI3019 and SI3050.
An example of a circuit with a datasheet on the Si3050 Si3018 / 19:

In this scheme, the line is connected to the contacts RING and TIP. What elements should pay attention to when problems with the work of the module?
- Diode bridge D1 (can also be made in the form of two assemblies with 2 diodes each). Sometimes out of order on the lines of analog PBX and when exceeding the permissible voltage. In this case, the module itself can remain operational, but some of the diodes do not work. Checked after watering from the scheme.
- Dinistor RV1 (275 V, 100 A). In our case, it turned out to be workable.
- Resistors R30, R32 (15 M ?, 1/8 W, 5%), R31, R33 (5.1 M?, 1/8 W, 5%), R8, R7 (20 M?, 1/8 W). They also turned out to be all right.
The problem was in the Si3019 chip. The resistance at the connection point of the Ring1 pin was two times less than on the working module. After replacing the Si3019 chip, everything worked without problems.
Also in a thunderstorm period, in the absence of external protection, the Zener diode Z1 (43 V, 1/2 W) often fails. The symptoms are the following: the module does not see the incoming call, when trying to call through this channel, there is no action except silence. Solved by replacing the Zener diode.

An IP PBX Asterisk was installed, and successfully used. After some time, it became possible to connect the number identifier, since city lines were transferred to a digital GATS with CallerID support, before that the lines were connected to an analog GATS (yes, analog PBXs are still alive), but the identification did not work.
To begin with, let's look at some theoretical information about what standards there are for determining a phone number.
Number Theory
AON (also called Russian AON) - the work of the Soviet analog GATS, was distributed in the early 90s, but still occurs. Information about the caller's number is transmitted in the form of a code bearing the name "Without Interval Package." It is not a service as such, since it was not intended for subscribers. The phone number is transmitted in the form of 7 digits. A telephone device that supports caller ID when an incoming call "picks up the phone" and reads the service signals of the telephone exchange, while the call signal is simulated for the caller. At Asterisk, this type of number identifier cannot be made to earn.
')
CallerID (also known as Euro AON) is a service provided on digital GATS. Method for sending a request and receiving Caller ID information in the interval between calls. That is, in contrast to the caller ID here is not "lifting the tube." There are several standards in CallerID:
Bellcore-standard is used in the USA, Canada, Australia, China, Hong Kong, Singapore, Italy and some telephone companies in the UK.
DTMF-standard: the digits of the number are transmitted in the same way as the tone dialing - short dual-frequency parcels.
FSK-standard: The data stream is transmitted by frequency modulation before the first or before the second call on the line. Experience has shown that most digital GATS Rostelecom work on this standard.
Practice or why nothing works
To determine the number in DAHDI channels in most cases, adding the following lines in chan_dahdi.conf is enough:
chan_dahdi.conf
usecallerid=yes ; CallerID callerid=asreceived ; callerid If the identification of the number did not work, I recommend to start by connecting a regular telephone with CallerID support and see if the definition works on it. In our case, the number on the TA was determined without problems, but on Asterisk did not want to. Moreover, when connecting the TA parallel to the asterisk, the definition ceased to work on the phone.
We proceed to further analysis. Let's write the audio channel of the line and analyze the recording in the audio editor. In it we will try to find the CallerID data.
The first dahdi channel is recorded by the following command:
dahdi_monitor 1 -v -r streamrx.wav We start the recording team and call our line. After this, we stop the execution of dahdi_monitor, as a result we will have the file streamrx.wav. Copy it to yourself and open it in an audio editor (for example Audacity).

Apparently no data callerid does not come to us. Since the usual phone number determines, it can be assumed that there are problems with the equipment (board or FXO module).
We put the working FXO module into the board and check it again.

Now, the identification of the number works without problems, we see the CallerID data in the FSK standard on the record. As you can see, in this case there was a problem with the module.
Repair FXO Module
FXO modules of different manufacturers for analog cards are built almost according to the same scheme based on two microcircuits: SI3019 and SI3050.
An example of a circuit with a datasheet on the Si3050 Si3018 / 19:

In this scheme, the line is connected to the contacts RING and TIP. What elements should pay attention to when problems with the work of the module?
- Diode bridge D1 (can also be made in the form of two assemblies with 2 diodes each). Sometimes out of order on the lines of analog PBX and when exceeding the permissible voltage. In this case, the module itself can remain operational, but some of the diodes do not work. Checked after watering from the scheme.
- Dinistor RV1 (275 V, 100 A). In our case, it turned out to be workable.
- Resistors R30, R32 (15 M ?, 1/8 W, 5%), R31, R33 (5.1 M?, 1/8 W, 5%), R8, R7 (20 M?, 1/8 W). They also turned out to be all right.
The problem was in the Si3019 chip. The resistance at the connection point of the Ring1 pin was two times less than on the working module. After replacing the Si3019 chip, everything worked without problems.
Also in a thunderstorm period, in the absence of external protection, the Zener diode Z1 (43 V, 1/2 W) often fails. The symptoms are the following: the module does not see the incoming call, when trying to call through this channel, there is no action except silence. Solved by replacing the Zener diode.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/326600/
All Articles